孕前正常BMI孕婦孕早期體成分與妊娠期糖尿病關系的研究
徐麗麗 鄭薇 袁仙仙 馬愷文 張浦楊 李光輝

基金項目:國家自然科學基金資助項目(82301916,82171671);北京市衛生健康委員會高層次公共衛生技術人才建設項目培養計劃(領軍人才-02-02)
引用本文:徐麗麗,鄭薇,袁仙仙,等. 孕前正常BMI孕婦孕早期體成分與妊娠期糖尿病關系的研究[J]. 中國全科醫學,2024,27(29):3602-3607,3615. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2024.0023. [www.chinagp.net]
XU L L,ZHENG W,YUAN X X,et al. The relationship between body composition in early pregnancy and gestational diabetes mellitus in a population of normal BMI pregnant women[J]. Chinese General Practice,2024,27(29):3602-3607,3615.
? Editorial Office of Chinese General Practice. This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 license.
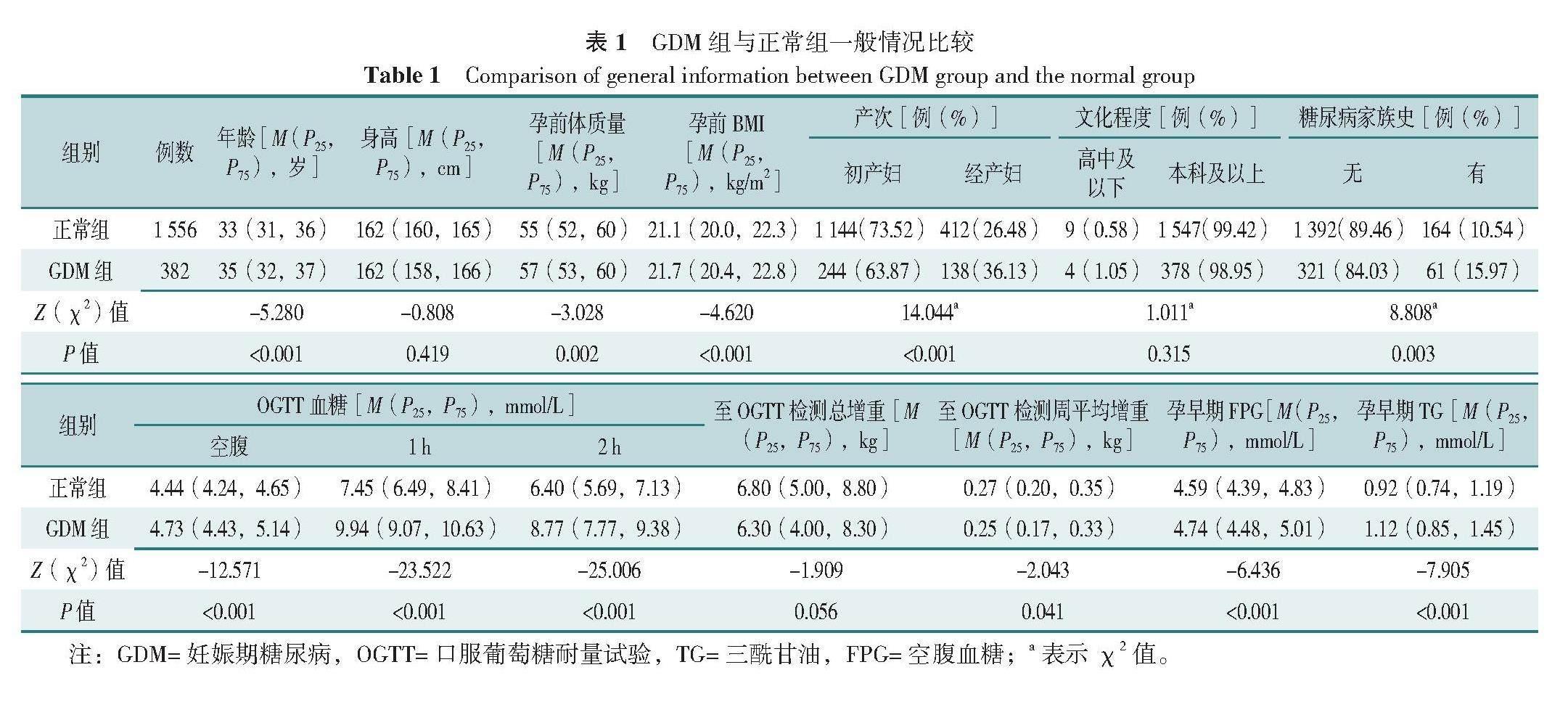
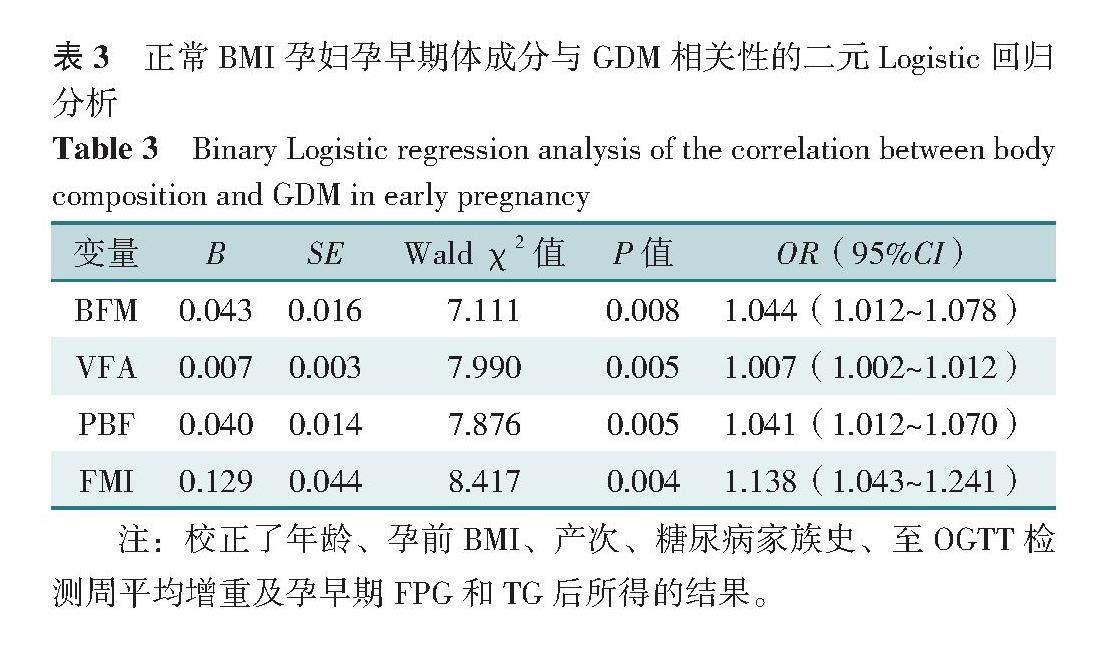
【摘要】 背景 妊娠期糖尿病(GDM)對母兒的近遠期健康造成影響。孕前BMI與GDM密切相關,但BMI無法評估脂肪與脂肪分布情況,因此僅用其評估肥胖存在一定缺陷。隱性肥胖人群[BMI正常但體脂百分比(PBF)>30%]及正常體質量伴中心性肥胖人群[BMI正常但內臟脂肪面積(VFA)≥80 cm2]存在著不同程度的代謝異常,然而在臨床中此部分人群常被忽視,關于其與GDM關系的研究相對缺乏。目的 分析孕前正常BMI孕婦孕早期體成分與GDM的相關性并探討脂肪分布情況與GDM的關系。方法 本研究納入2018年10月—2022年10月于首都醫科大學附屬北京婦產醫院產科門診建檔,孕早期自愿接受營養評價并定期產前檢查至妊娠24~28周的單胎孕婦1 938例。研究對象于孕早期(6~16周)進行人體成分檢測、妊娠24~28周行口服葡萄糖耐量試驗(OGTT)。根據OGTT結果,將研究對象分為GDM組(n=382)和正常組(n=1 556)。采用二元Logistic回歸分析探究孕早期體成分及體脂分布與GDM的關系。結果 GDM組孕婦體脂量(BFM)、VFA、PBF、脂肪質量指數(FMI)均高于正常組(P<0.05)。二元Logistic回歸分析結果顯示,孕早期BFM、VFA、PBF、FMI升高(OR=1.044,95%CI=1.012~1.078;OR=1.007,95%CI=1.002~1.012;OR=1.041,95%CI=1.012~1.070;OR=1.138,95%CI=1.043~1.241)(P<0.05)和中心性肥胖即VFA≥80 cm2(OR=1.396,95%CI=1.101~1.770,P<0.05)是GDM發生的危險因素。Spearman秩相關分析顯示,BFM、VFA、PBF、FMI與OGTT各時點血糖呈正相關(P<0.05)。結論 在孕前正常BMI孕婦中,孕早期BFM、VFA、PBF、FMI是GDM發生的危險因素,中心性肥胖即VFA≥80 cm2可以獨立預測GDM的發生。產檢時需要關注孕婦的脂肪分布,對于中心性肥胖人群加強孕期管理。
【關鍵詞】 妊娠期糖尿病;妊娠初期;體成分;體脂百分比;內臟脂肪面積;中心性肥胖;影響因素分析
【中圖分類號】 R 714.256 【文獻標識碼】 A DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2024.0023
The Relationship between Body Composition in Early Pregnancy and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in a Population of Normal BMI Pregnant Women
XU Lili,ZHENG Wei,YUAN Xianxian,MA Kaiwen,ZHANG Puyang,LI Guanghui*
Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism,Department of Obstetrics,Beijing Obstetrics and Gynecology Hospital,Capital Medical University,Beijing 100026,China
*Corresponding author:LI Guanghui,Chief physician/Professor;E-mail:liguanghui@ccmu.edu.cn
【Abstract】 Background Gestational diabetes mellitus(GDM) is closely related to the short-term and long-term health outcomes of the mothers and offspring. Pre-pregnancy BMI is strongly associated with GDM,nevertheless,it does not distinguish between body fat content and fat distribution. Only using it to assess obesity is flawed. Normal weight obesity(normal BMI but body fat percentage above 30%) and normal weight with central obesity(normal BMI but visceral fat area above 80 cm2)
show different degree of metabolic dysregulation. However,those population are usually overlooked in clinical practice and there is a paucity of research on those population and GDM. Objective To explore the correlation between body composition in early pregnancy and GDM in a population of normal pre-pregnancy BMI,and to investigate the relationship between fat distribution and GDM. Methods We performed a study that included 1 938 singleton pregnant women registered in the obstetric out-patient clinic of Beijing Obstetrics and Gynecology Hospital,Capital Medical University from October 2018 to October 2022. They voluntarily underwent nutritional assessment in early pregnancy and had regular pregnancy check-ups until 24-28 weeks of gestation,who underwent body composition testing in early pregnancy(6-16 weeks)and oral glucose tolerance test(OGTT) at 24-28 weeks. According to the OGTT results,the study population were divided into the GDM group(n=382) and the normal group(n=1 556). We estimated the relationship between body composition and fat distribution with GDM in early pregnancy with binary Logistic regression. Results Body fat mass(BFM),visceral fat area(VFA),percentage body fat(PBF),and fat mass index(FMI)in the GDM group were higher than in the normal group(P<0.05). BFM,VFA,PBF,FMI(OR=1.044,95%CI=1.012-1.078;OR=1.007,95%CI=1.002-1.012;OR=1.041,95%CI=1.012-1.070;OR=1.138,95%CI=1.043-1.241)(P<0.05) and central obesity(VFA≥80 cm2)(OR=1.396,95%CI=1.101-1.770,P<0.05) associated with a significant increased risk for GDM with binary Logistic regression analysis. Spearman rank correlation analysis showed that BFM,VFA,PBF,FMI and blood glucose of the OGTT test were positively correlated(P<0.05). Conclusion Among normal pre-pregnancy BMI women,BFM,VFA,PBF,and FMI in early pregnancy were the risk factors of GDM. Central obesity(VFA≥
80 cm2) could independently predict the development of GDM. It is necessary to pay attention to fat distribution during pregnancy check-ups and to strengthen the pregnancy management for central obesity women.
【Key words】 Gestational diabetes mellitus;Pregnancy trimester,first;Body composition;Percentage of body fat;Visceral fat area;Central obesity;Root cause analysis
妊娠期糖尿病(gestational diabetes mellitus,GDM)是妊娠期特有的代謝障礙性疾病,全球GDM發生率約為14%,不同國家之間發生率存在較大差異[1],我國GDM患病率達14.8%~19.7%[2],且呈逐年上升趨勢。G……

