慢性乙肝患者長期口服NAs后的腎功能變化及影響因素
葛孝定 項波 劉斐 田洪飛
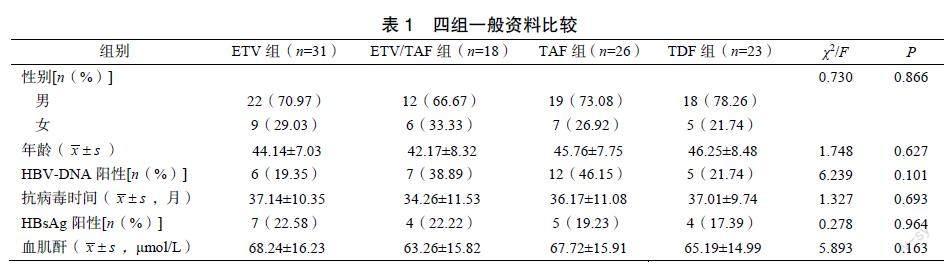
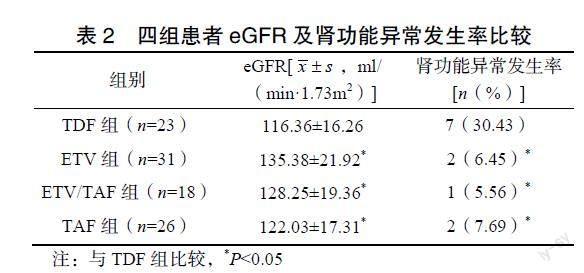

[摘要]?目的?探討慢性乙型肝炎患者長期口服核苷酸類抗病毒藥物(nucleoside?antiviral?drugs,NAs)治療后腎功能指標異常發(fā)生狀況及其影響因素。方法?回顧性分析2020年6月至2021年5月于杭州市西溪醫(yī)院就診的慢性乙型肝炎患者98例的臨床資料,按照服用藥物不同分為恩替卡韋組(ETV組,n=31)、恩替卡韋與富馬酸丙酚替諾福韋組(ETV/TAF組,n=18)、富馬酸丙酚替諾福韋組(TAF組,n=26)、富馬酸替諾福韋二吡呋酯組(TDF組,n=23)。治療結(jié)束后選擇簡化腎臟病飲食調(diào)整工作組方程對所有患者的腎小球濾過率估算值(estimated?glomerular?filtration?rate,eGFR)進行估算,計算各組腎功能異常率,并選擇單因素、多因素Logistic回歸分析其影響因素。結(jié)果?ETV組、ETV/TAF組、TAF組患者的eGFR水平顯著高于TDF組(P<0.05),且腎功能異常發(fā)生率顯著低于TDF組(P<0.05);單因素Logistic回歸分析顯示,年齡、使用TDF治療、伴有糖尿病是導(dǎo)致慢性乙型肝炎患者腎功能異常的影響因素,差異有統(tǒng)計學意義(P<0.05);多因素Logistic回歸分析顯示,年齡、使用TDF治療、伴有糖尿病是導(dǎo)致慢性乙型肝炎患者腎功能異常的獨立危險因素。結(jié)論?長期口服NAs治療慢性乙型肝炎,腎功能指標異常發(fā)生率最高的是采用TDF治療的患者,年齡、使用TDF治療、伴有糖尿病為患者腎功能異常的獨立危險因素。
[關(guān)鍵詞]?慢性乙型肝炎;腎功能;核苷酸類抗病毒藥物;影響因素
[中圖分類號]?R512.62??????[文獻標識碼]?A??????[DOI]?10.3969/j.issn.1673-9701.2023.17.019
Incidence?and?influencing?factors?of?abnormal?renal?function?indexes?in?chronic?hepatitis?B?patients?after?long-term?oral?NAs?therapy
GE?Xiaoding,?XIANG?Bo,?LIU?Fei,?TIAN?Hongfei
Department?of?Liver?Diseases,?Hangzhou?Xixi?Hospital,?Hangzhou?310023,?Zhejiang,?China
[Abstract]?Objective?To?investigate?the?occurrence?and?influencing?factors?of?abnormal?renal?function?indexes?after?long-term?oral?nucleotide?antiviral?drugs?(NAs)?treatment?for?chronic?hepatitis?B.?Methods?To?retrospectively?analyze?the?clinical?data?of?98?patients?with?chronic?hepatitis?B?who?attended?Hangzhou?Xixi?Hospital?from?June?2020?to?May?2021,?and?divided?into?entecavir?group?(ETV?group,?n=31),?entecavir?and?tenofovir?alafenamide?fumarate?group?(ETV/TAF?group,?n=18),?tenofovir?alafenamide?fumarate?group?(TAF?group,?n=26)?and?tenofovir?disoproxil?fumarate?group?(TDF?group,?n=23)?according?to?different?medications.?After?the?treatment,?the?estimated?glomerular?filtration?rate?(eGFR)?values?of?all?patients?were?estimated?by?selecting?the?simplified?kidney?disease?diet?adjustment?working?group?equation,?and?calculate?the?rate?of?renal?dysfunction,?and?the?influencing?factors?were?analyzed?by?univariate?and?multi-factor?Logistic?regression?analysis.?Results?Significantly?higher?eGFR?levels?in?the?ETV,?ETV/TAF?and?TAF?groups?than?that?in?the?TDF?group?(P<0.05),?and?a?significantly?lower?incidence?of?renal?function?abnormalities?than?that?in?the?TDF?group?(P<0.05).?Univariate?Logistic?regression?analysis?showed?that?age,?use?of?TDF?treatment,?and?concomitant?diabetes?were?the?influential?factors?leading?to?abnormal?renal?function?in?patients?with?chronic?hepatitis?B,?the?difference?was?statistically?significant?(P<0.05).?Multi-factor?Logistic?regression?analysis?showed?that?age,?use?of?TDF?treatment,?and?concomitant?diabetes?were?independent?risk?factors?leading?to?abnormal?renal?function?in?patients?with?chronic?hepatitis?B.?Conclusions?Long-term?oral?NAs?for?chronic?hepatitis?B?has?the?highest?incidence?of?abnormal?renal?function?indicators?in?patients?treated?with?TDF.?Age,?treatment?with?TDF,?and?concomitant?diabetes?are?independent?risk?factors?for?abnormal?renal?function?in?patients.
[Key?words]?Chronic?hepatitis?B;?Renal?function;?Nucleotide?antiviral?drugs;?Influencing?factors
![]()
慢性乙型肝炎在全球范圍內(nèi)屬于一個公共健康問題,相關(guān)數(shù)據(jù)顯示約有2.4億人感染乙型肝炎病毒(hepatitis?B?virus,HBV)[1]。國內(nèi)調(diào)查顯示,1~59歲人群中攜帶乙型肝炎表面抗原(hepatitis?B?surface?antigen,HBsAg)的概率為7.18%,感染HBV的人數(shù)約為9300萬,其中慢性乙型肝炎人數(shù)為2000萬[2]。有文獻顯示,慢性乙型肝炎初治病患發(fā)生腎臟病的概率顯著高于非慢性乙型肝炎人群[3]。核苷酸類抗病毒藥物(nucleoside?antiviral?drugs,NAs)治療慢性乙型肝炎,能夠快速抑制HBV復(fù)制,但治療后出現(xiàn)腎臟不良反應(yīng)的相關(guān)報道不斷增加[4-5]。腎臟不良反應(yīng)相關(guān)實驗室指標包括血尿、蛋白尿、鈣磷代謝失調(diào)、血肌酐值提升等[6]。有研究顯示,在使用NAs對慢性乙型肝炎人群進行治療時,需定時監(jiān)測腎功能,有助于盡早發(fā)現(xiàn)腎功能不全[7-8]。……

