4R危機管理理論視閾下農村突發公共衛生事件治理能力阻滯及優化
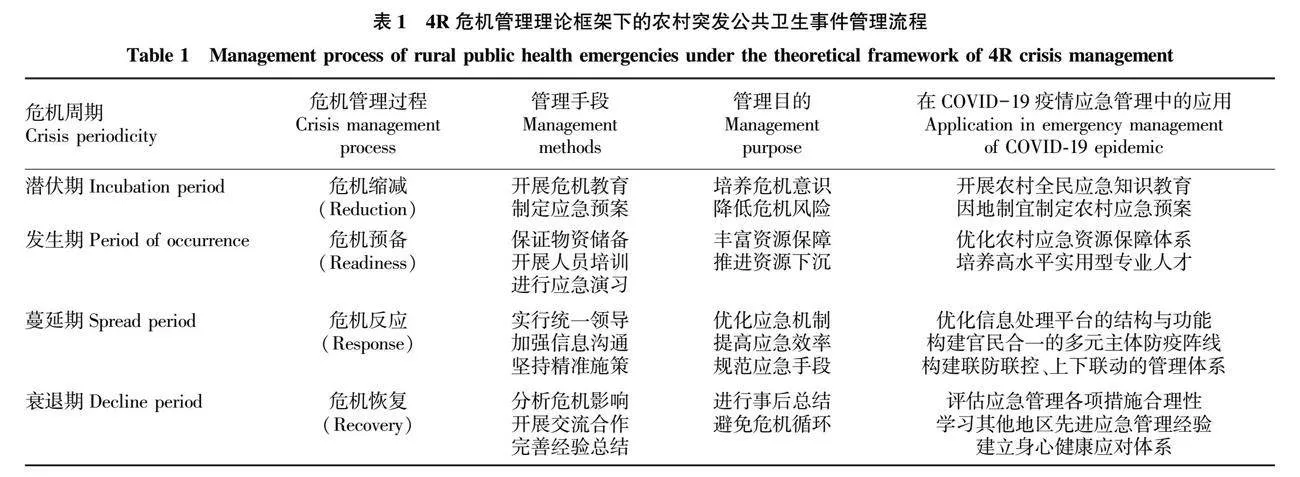
摘要 突發公共衛生事件應急情境下,以4R危機管理為動態治理流程視角,結合鄉村實地調研與訪談素材,分析了直面農村基層政府衛生應急治理能力的阻滯因素:危機縮減能力疲軟,風險意識淡薄,應急預案偏離實際;危機預備能力有限,應急人力、物力供需失衡,應急物資分配效率低下;危機反應能力局促,應急部門反應遲滯,應急管理精細化程度不足;危機恢復能力輕視,事后恢復大局觀不足,缺乏系統總結與經驗溝通。提出了農村基層政府突發公共衛生事件治理能力的優化建議:更新理念,強化基層官民風險意識和危機學習能力;下沉資源,完善農村應對突發公共衛生事件資源保障體系;優化體制,構建多元主體共同參與的公共危機治理格局;革新機制,完善“上下聯動,橫向協同”的應急處置機制。
關鍵詞 突發公共衛生事件;應急管理能力;4R危機管理理論;基層治理
中圖分類號 D669 文獻標識碼 A 文章編號 0517-6611(2024)17-0251-04
doi:10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2024.17.058
Obstruction and Optimization of Governance Capability for Rural Public Health Emergencies from the Perspective of 4R Crisis Management Theory
BAI Hua1,LI Xin-yue2
(1.College of Public Administration and Law, Hunan Agricultural University,Changsha, Hunan 410128;2.School of International Business, Shanghai University of International Business and Economics,Shanghai 201620)
Abstract Under the governance of public health emergencies, taking 4R crisis management as the perspective of dynamic governance process,combined with rural field research and interviews, we directly face the shortcomings exposed in the grass-roots health emergency governance practice:weak crisis reduction capacity, weak risk awareness, and deviation of emergency plans from the actual situation;limited crisis preparedness, imbalance between supply and demand of emergency manpower and materials, and inefficient distribution of emergency materials;limited crisis response capacity, delayed response of the emergency department, and insufficient refinement of emergency management;Crisis recovery capacity is belittling, insufficient big-picture view of recovery after the incident, and lack of systematic summarisation and communication of experience.Proposed optimization suggestions for the governance capacity of rural grassroots governments in sudden public health emergencies: update the concept, strengthen the risk awareness and crisis learning ability of grass-roots officials and citizens;sink resources, optimise the resource guarantee system for rural areas to cope with public health emergencies;optimise the system, build a public crisis management pattern in which diversified main bodies participate together;innovate the mechanism, and improve the emergency disposal mechanism of “up and down linkage, horizontal synergy” emergency response mechanism.
Key words Public health emergency;Emergency management capacity;4R Crisis Management Theory;Grass-roots governance
基金項目 湖南省教育廳開放基金項目(20K067);湖南農業大學青年科學基金項目(19QN52)。
作者簡介 柏花(1991—),女,湖南長沙人,講師,在讀博士,從事農村應急管理、衛生管理與政策研究。
收稿日期 2023-10-19
2019年末以來,COVID-19疫情的暴發、蔓延、防控、反復、平穩等進程對社會經濟生活的方方面面形成巨大沖擊。與SARS相比,COVID-19具有傳播速度快、傳播范圍廣、存續時間長、防控難度大等顯著特點。除了病毒傳染性、危害性的變化,更為顯著的是,隨著治理理念、治理工具、輿論環境的變遷,政府衛生應急決策的復雜性已不可同日而語。……

