最佳養(yǎng)分管理下我國花生磷需求特征
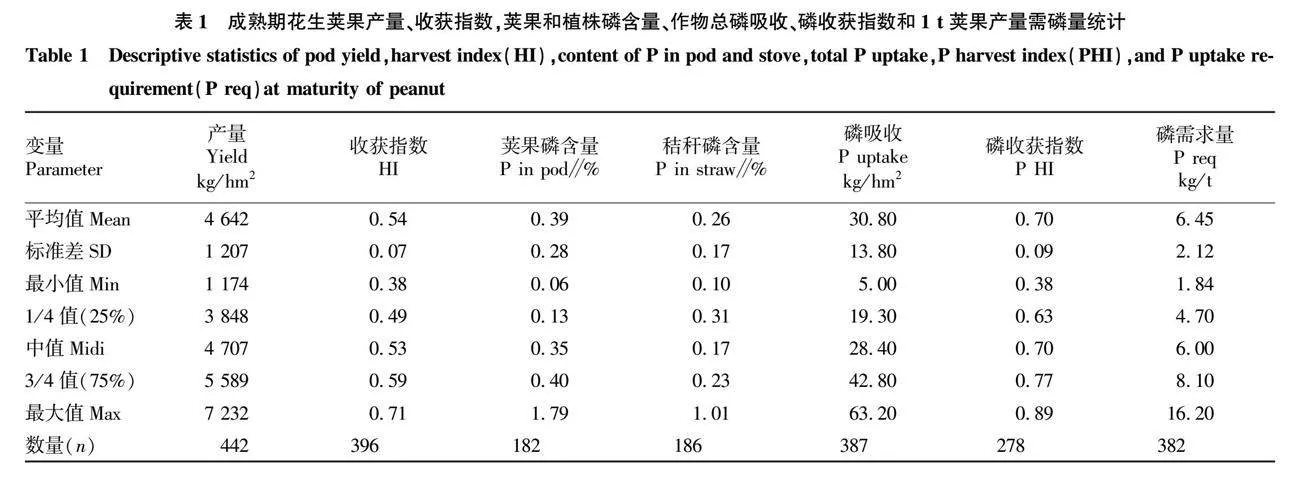
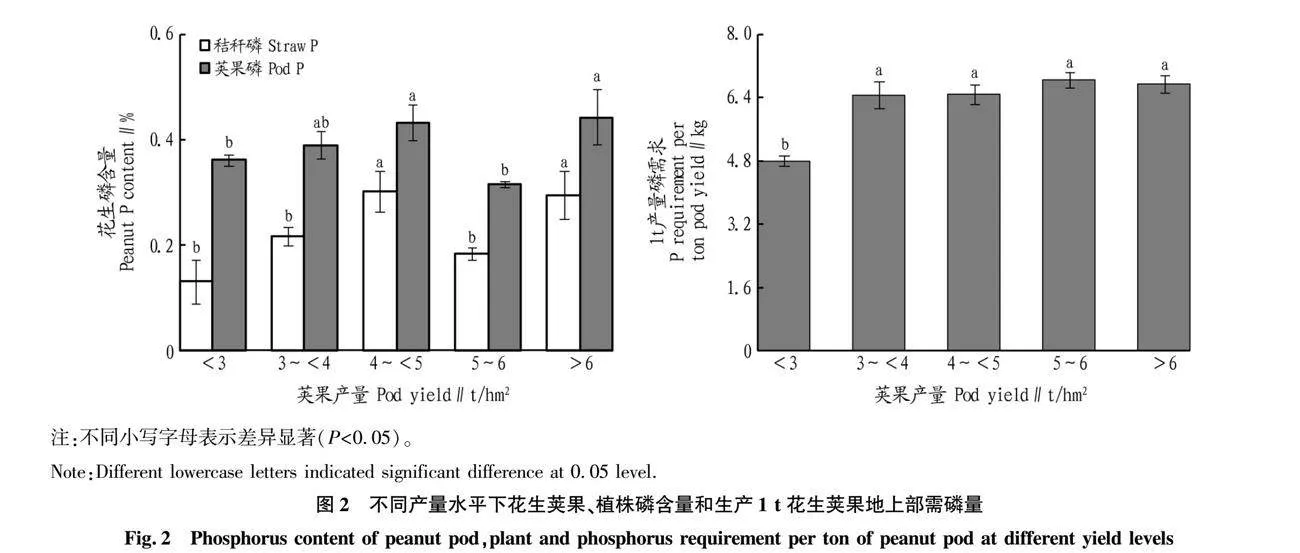
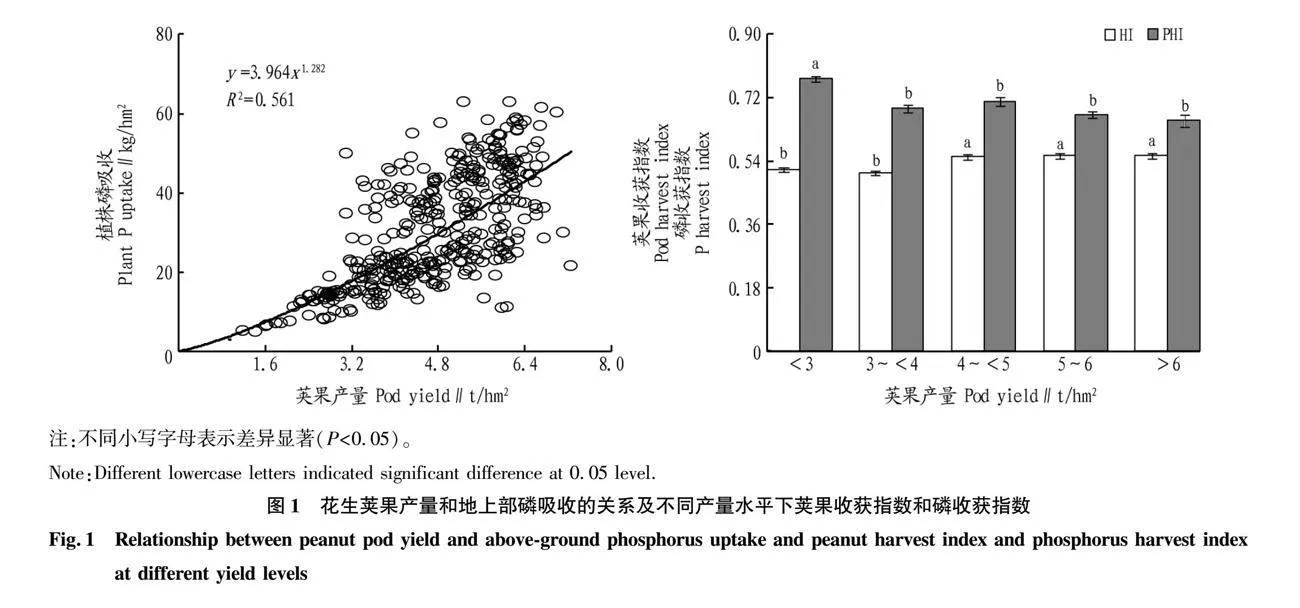
摘要 評價花生莢果產(chǎn)量和植株磷素需求,為高產(chǎn)花生的施肥管理提供理論指導(dǎo)。收集1990—2021年我國主要花生種植區(qū)的大量田間試驗數(shù)據(jù)集(n=265),以評估在最佳施肥管理下花生的磷吸收特征。結(jié)果表明,在整個數(shù)據(jù)集中,平均花生莢果產(chǎn)量和收獲指數(shù)(HI)分別為4 642 kg/hm2 和0.54。花生莢果對磷(P)的平均需求量為6.45 kg/t。在<3、3~<4、4~<5、5~6和>6 t/hm2 5個莢果產(chǎn)量范圍內(nèi),磷素吸收和HI均隨莢果產(chǎn)量的增加而增加。磷需求量隨著產(chǎn)量的增加而增加,這歸因于在莢果產(chǎn)量高的情況下,秸稈磷的過量吸收。
關(guān)鍵詞 花生;莢果產(chǎn)量;收獲指數(shù);磷素吸收;磷需求量
中圖分類號 S565.2 文獻標識碼 A 文章編號 0517-6611(2024)17-0167-04
doi:10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2024.17.039
Phosphorus Uptake Behavior of Peanut Under Optimum Fertilization Management in China
WANG Hong-mei1,L Ji-long2
(1.Dancheng County Institute of Agricultural Sciences, Zhoukou, Henan 477150;2.Henan Zhoukou National Agricultural Science and Technology Park Management Committee, Zhoukou, Henan 477150)
Abstract Assessing pod yield and plant phosphorus demand can provide theoretical guidance for fertilization management of high yielding peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Following this rationale, a large dataset was collected from field experiments (n = 265) across the main peanut planting regions of China for a period spanning from 1990 to 2021 to evaluate nutrient uptake behavior of peanut under current optimum fertilization management. Across the entire dataset, the results showed that average peanut pod yield and harvest index (HI) were 4 642 kg/hm2 and 0.54. The average peanut phosphorus (P) requirement was 6.45 kg/t. Across five ranges of pod yields (<3, 3-<4, 4-<5, 5-6, and >6 t/hm2), both nutrient uptake and HI increased with increasing pod yield. The P requirement increased with yield, attributed to an increase in straw P concentration as P luxury uptake occurs under high pod yield.
Key words Peanut;Pod yield;Harvest index(HI);Phosphorus uptake;Phosphorus requirement
作者簡介 王紅梅(1981—),女,河南鄲城人,副研究員,從事作物栽培研究。通信作者,研究實習員,碩士,從事作物養(yǎng)分資源管理研究。
收稿日期 2023-08-10;修回日期 2023-11-07
花生在我國種植歷史悠久,是優(yōu)質(zhì)植物蛋白質(zhì)和食用油的重要來源,也是我國重要的經(jīng)濟作物之一。研究表明花生中蛋白質(zhì)含量約為30%,脂肪含量高達50%[1]。以花生為基礎(chǔ)的食品、飲料等相繼被開發(fā)供人們食用,而榨油后的花生餅粕可用作動物飼料,花生作為油料作物除家庭用途外,還是潤滑劑、淬火劑等工業(yè)產(chǎn)品的原料[2]。
在我國花生種植面積約為460.8萬hm2,總產(chǎn)量為1 709.2萬t,平均產(chǎn)量為3 810 kg/hm2 [3]。雖然近年來我國花生產(chǎn)量穩(wěn)步增加,但仍不能滿足日益增長的人口的需求。影響花生高產(chǎn)的因素包括氣候條件、土壤特征、品種、養(yǎng)分管理和栽培措施等[4]。不同氣候條件(最低和最高溫度、有效積溫、日照時間和降雨等)影響作物的播種期、灌漿期和總生育期等,進而影響作物產(chǎn)量[5-6]。……

