水分梯度對麥冬種植土壤碳氮磷生態化學計量的影響
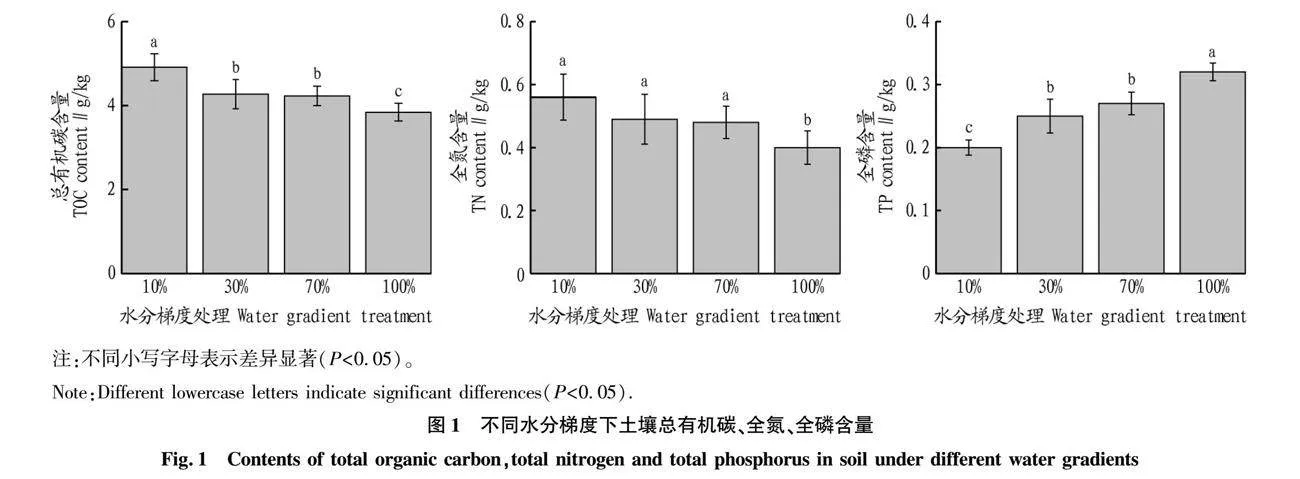
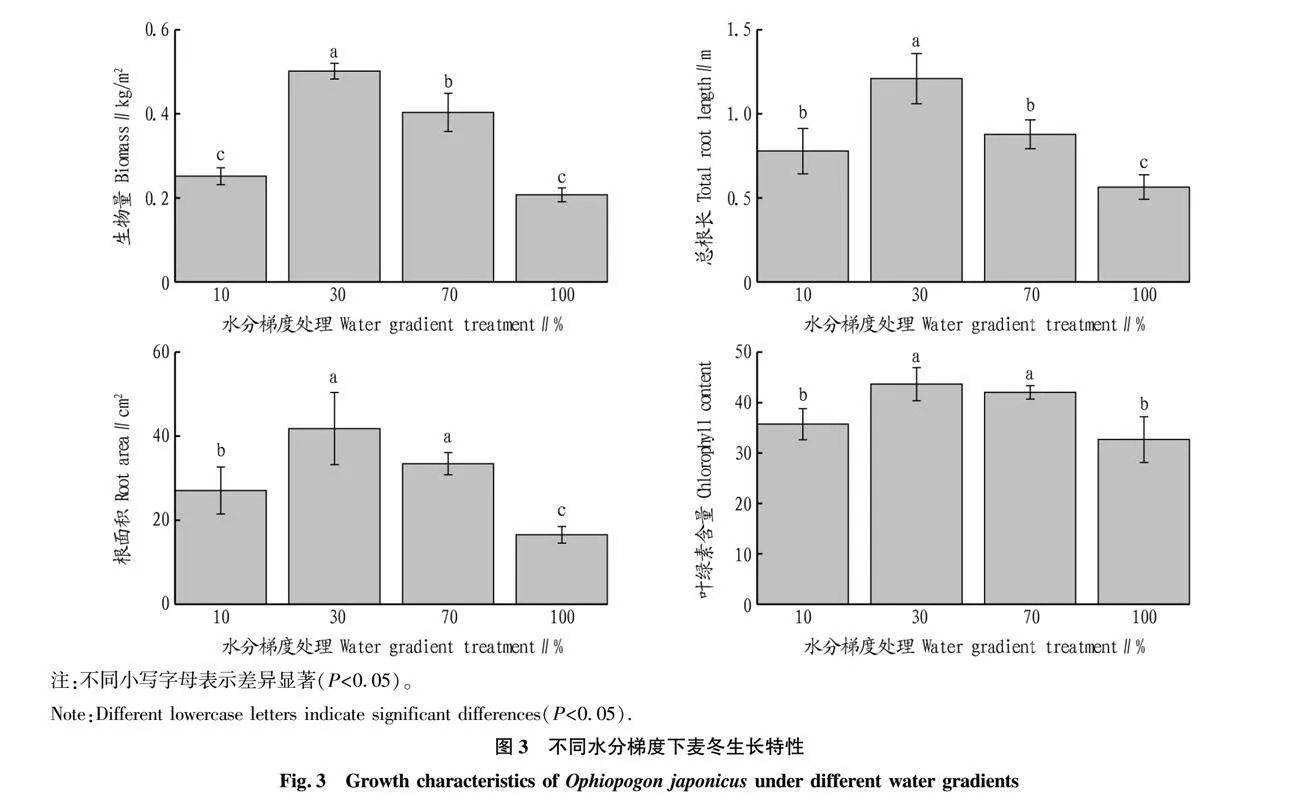
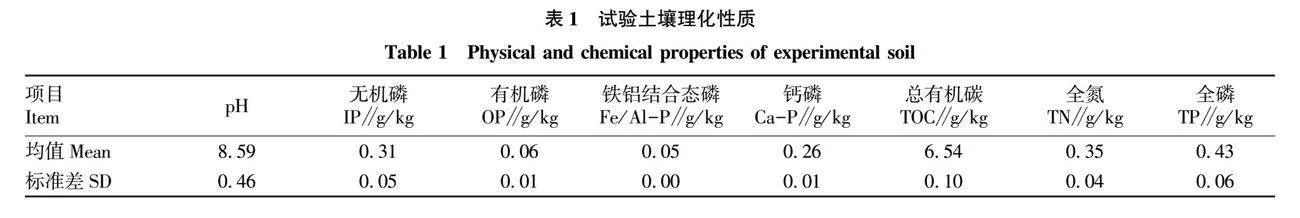
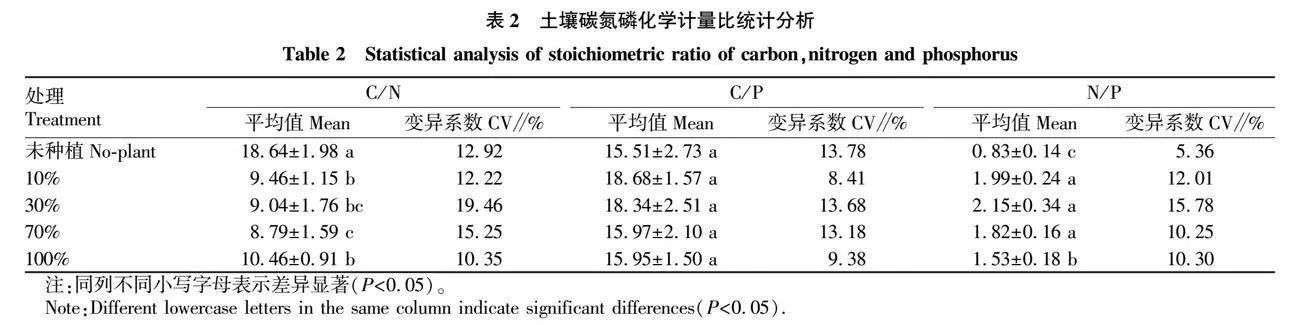
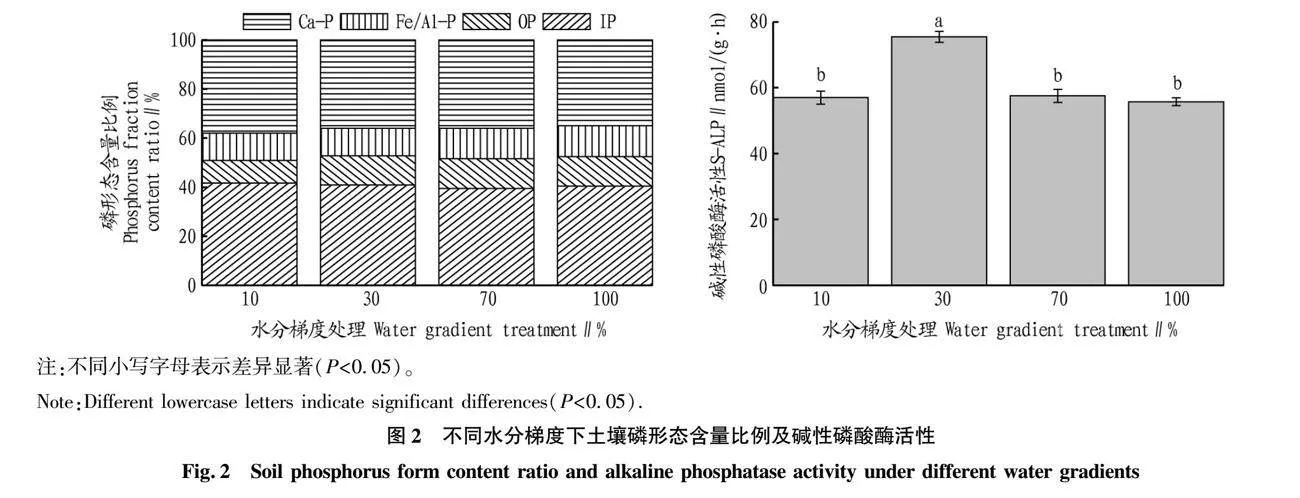
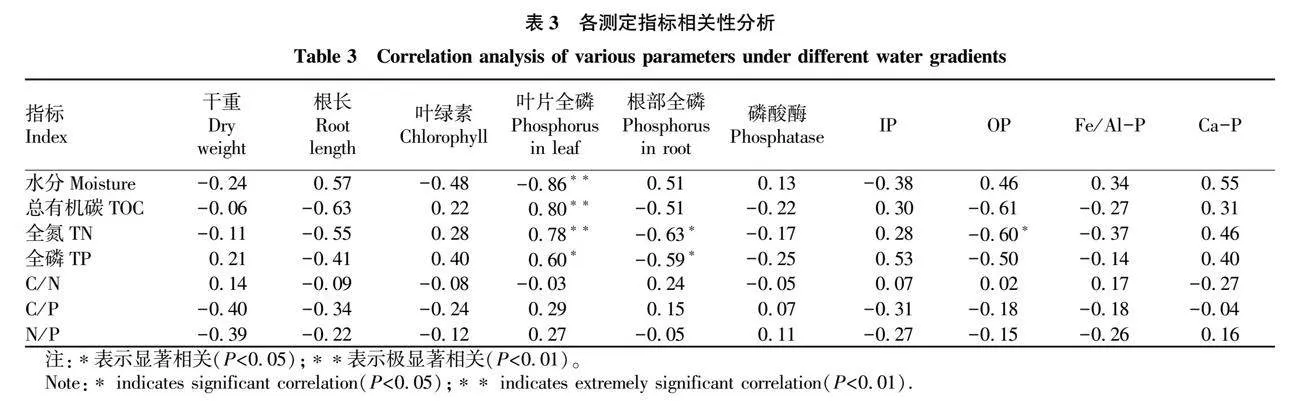
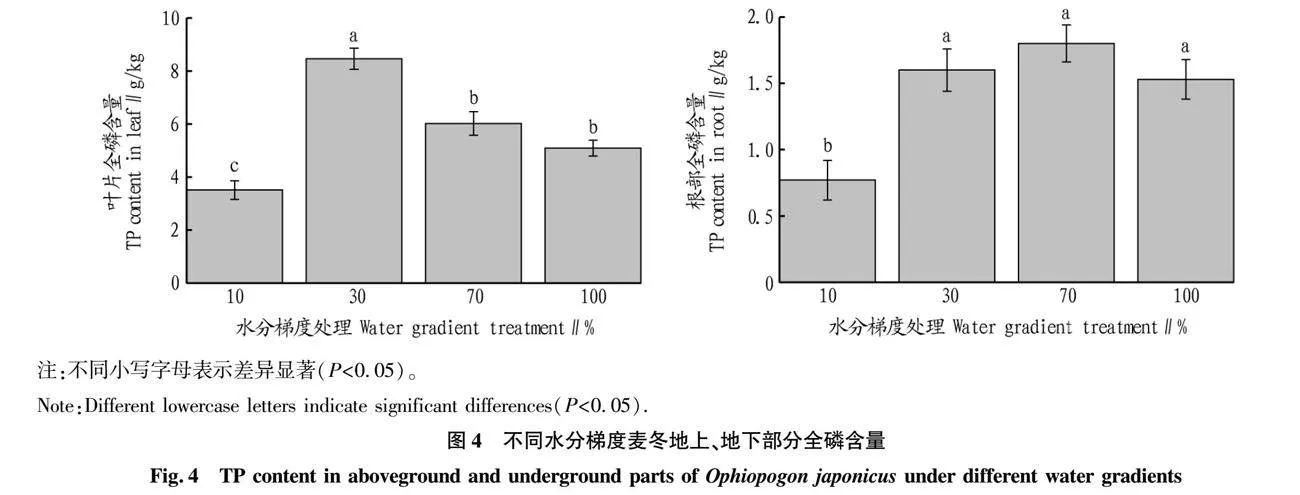
摘要 通過麥冬盆栽試驗,控制土壤水分(10%、30%、70%、100%,W/W),對麥冬生長特性、土壤碳氮磷生態化學計量特征、磷素形態以及磷酸酶活性等進行測定,并分析各測定參數之間的相關性。結果表明,隨著水分含量的增加麥冬種植土壤總有機碳、全氮呈降低趨勢,但是全磷含量呈上升趨勢,土壤磷素各形態占比對水分梯度響應差異性不明顯;土壤C/N、C/P、N/P分別為8.79~10.46、15.95~18.68和1.53~2.15,對水分梯度響應特性不同,均屬于弱變異;30%水分處理土壤堿性磷酸酶活性顯著高于其他3種水分處理(P<0.05),可以直接利用磷比例為52.76%,略高于其他水分組;在30%水分組中,麥冬生物量、總根長、葉片全磷含量顯著高于其他處理組(P<0.05),根面積、葉綠素含量略高于70%水分組(P>0.05)且顯著高于10%和100%水分組(P<0.05),100%水分組麥冬生長被顯著抑制。30%水分梯度利于麥冬改善土壤質量,提高麥冬對土壤碳氮磷的利用,增加土壤對氮素的累積,利于其生長。
關鍵詞 水分梯度;土壤碳氮磷;生態化學計量;麥冬
中圖分類號 X173 文獻標識碼 A 文章編號 0517-6611(2024)17-0061-05
doi:10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2024.17.013
Effect of Water Gradient on the Ecological Stoichiometry of Soil Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Ophiopogon japonicus Plant
SHUI Jun-hua1,2, SHAO Zhe-wen1, XIANG Ke-xin1 et al
(1.Engineering Research Center of Eco-enviroU+GxtUqjIhWT0nSuX+ij/wgnd0OdxiLCgoOps9jZ46s=nment in Three Gorges Reservoir Region, Ministry of Education, China Three Gorges University, Yichang, Hubei 443002;2.Environmental Monitoring Station of Zigui, Yichang,Hubei 443699)
Abstract The experimental water gradient (10%, 30%, 70%, 100%,W/W) was controlled by the potted plant test, and the growth characteristics of Ophiopogon japonicus, and the soil carbon (C), nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) ecological stoichiometry,phosphorus forms and phosphatase activity were measured, and the correlation relationships between different measurement parameters were analyzed.The results showed that with the soil moisture content increasing, the total organic carbon and total nitrogen decreased in the soil, while total phosphorus increased, and the phosphorus forms had no significant correlation with the soil moisture content. The C/N, C/P, N/P were 8.79-10.46, 15.95-18.68 and 1.53-2.15, respectively, and their response characteristics to water gradient, belong to weak variants, were variant.The soil alkaline phosphatase activity under 30% water treatment was significantly higher than that under other groups (P<0.05), and the proportion of directly available phosphorus was 52.76%, which was higher than other water groups. The biomass, total root length and total phosphorus in the leaf of Ophiopogon japonicus under 30% water treatment were significantly higher than other treatment groups (P<0.05). The root area and chlorophyll content were slightly higher than those in the 70% water group (P>0.05) and significantly higher than those in the 10% and 100% water group (P<0.05),and the growth of Ophiopogon japonicus was inhibited under 100% water gradient.30% water gradient was conductive to improving soil quality and the utilization of soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus, increasing soil nitrogen accumulation and conductive to Ophiopogon japonicus growth.
Key words Water gradient;Soil carbon,nitrogen and phosphorus;Ecostoichiometry;Ophiopogon japonicus
基金項目 宜昌市森林資源監測站項目(SDHZ2020313);高等學校學科創新引智計劃項目(D20015);三峽大學高等教育研究項目(GJ2223)。
作者簡介 稅軍華(1972—),男,湖北宜昌人,工程師,從事水環境保護與治理研究。
通信作者,講師,博士,從事土壤安全利用研究。
收稿日期 2023-10-22;修回日期 2023-11-28
土壤生態化學計量學主要是研究土壤碳(C)、氮(N)、磷(P)元素動態收支平衡關系,它們的含量及比值能夠影響土壤生態系統過程[1-3],其研究可以明確土壤養分豐度、植物養分有效性,能夠判斷群落生產力過程的限制性因素[4],對于探討植物-土壤養分循環的調控機制具有重要意義[5-6]。……

