低溫脅迫對(duì)俄羅斯大果沙棘抗寒生理指標(biāo)的影響
吳飛 朱生秀 向江湖 李萬(wàn)棟
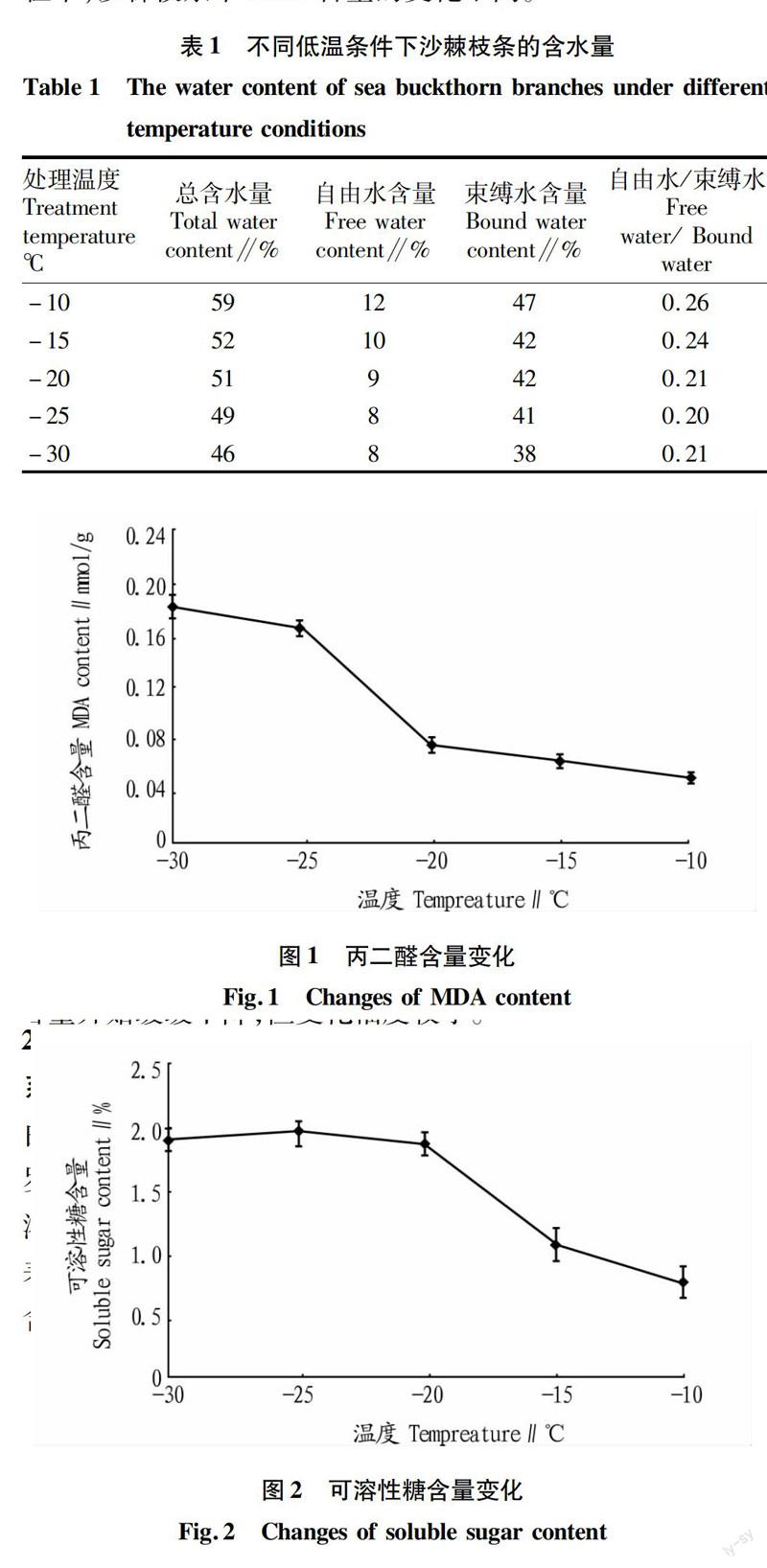

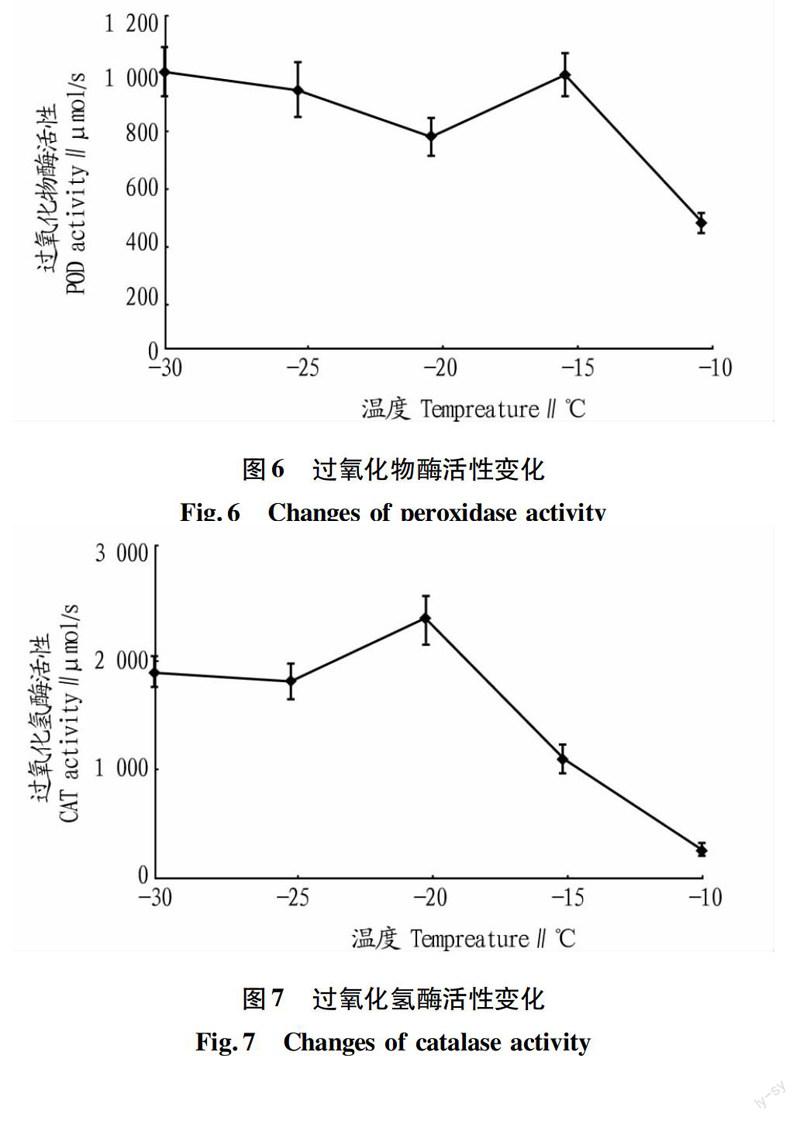
摘要[目的]探討不同低溫條件下,沙棘抗寒生理指標(biāo)變化及與抗寒性的關(guān)系。[方法]以俄羅斯大果沙棘1年生枝條為試驗(yàn)材料,通過(guò)-30~-10 ℃低溫脅迫處理,測(cè)定其含水量、滲透調(diào)節(jié)物質(zhì)、保護(hù)酶活性指標(biāo)與抗寒性的關(guān)系。[結(jié)果]沙棘在低溫條件下,枝條中自由水/束縛水比值較小,丙二醛含量隨溫度的變化而呈規(guī)律性變化;可溶性糖、可溶性蛋白含量隨溫度呈相反的變化趨勢(shì);隨著溫度的降低,沙棘枝條中保護(hù)酶活性增強(qiáng)。[結(jié)論]沙棘應(yīng)對(duì)低溫能力較強(qiáng),通過(guò)各生理指標(biāo)調(diào)節(jié)系統(tǒng)穩(wěn)定,具有較強(qiáng)的滲透調(diào)節(jié)能力。
關(guān)鍵詞沙棘;低溫脅迫;抗寒指標(biāo);滲透調(diào)節(jié)物質(zhì);保護(hù)酶活性
中圖分類(lèi)號(hào)S793.6;Q945.18文獻(xiàn)標(biāo)識(shí)碼A文章編號(hào)0517-6611(2017)10-0013-03
Effects of Low Temperature Stress on Physiological Indexes of Hippophae rhamnoides Hrm.Variety from Russia
WU Fei,ZHU Shengxiu,XIANG Jianghu et al
(Xinjiang Oasis in the Western Ecological Development Co., Ltd., Karamay, Xinjiang 834000)
Abstract[Objective] To investigate the physiological indexes of Hippophae rhamnoides and its relationship with cold resistance under the different low temperature.[Method] Oneyear old Russian Hippophae rhamnoides branches was used as experimental materials,and through -30--10 ℃ low temperature stress treatment, measured water content, osmotic adjustment, the relationship protected activity index and cold resistance.[Result] After low temperature treatment, shoots free water / bound water ratio was small, and MDA content changed with temperature regularly; Soluble sugar, soluble protein content with temperature showed the opposite trend; With decreasing temperature, the protection activity of Hippophae rhamnoides increased. [Conclusion] Hippophae rhamnoides has strong cold resistance, regulating system stability through physiological indices, with strong osmotic adjustment ability.
Key wordsHippophae rhamnoides;Low temperature stress;Cold resistance index;Osmotic adjustment;Protective enzyme activity
俄羅斯大果沙棘(Hippophae rhamnoides Linn.variety from Russia)是胡頹子科沙棘屬的多年生落葉灌木,是從俄羅斯引進(jìn)的優(yōu)良品種[1]。由于其具有廣泛的適應(yīng)性,加之移栽成活率高,生長(zhǎng)較快,抗寒性強(qiáng),耐干旱,耐瘠薄,是防治水土流失、防風(fēng)固沙、改善生態(tài)環(huán)境的“生態(tài)先鋒樹(shù)種”[2-3]。
沙棘品種較多,目前國(guó)內(nèi)研究、應(yīng)用較多的是中國(guó)沙棘[3],但由于中國(guó)沙棘普通存在枝條刺多、果實(shí)小、采摘困難等瓶頸問(wèn)題,導(dǎo)致沙棘經(jīng)濟(jì)效益低,制約了沙棘產(chǎn)業(yè)的良性發(fā)展。針對(duì)以上問(wèn)題,國(guó)內(nèi)許多科研單位、企業(yè)嘗試從國(guó)外引進(jìn)果大、口感好的沙棘品種,但由于缺乏對(duì)引進(jìn)品種適應(yīng)的研究,導(dǎo)致引進(jìn)的品種栽植成活率低,區(qū)域適應(yīng)性差,品種在國(guó)內(nèi)栽培范圍小,沒(méi)有形成規(guī)模。新疆區(qū)域遼闊,區(qū)域氣候差異較大,因此,對(duì)于引進(jìn)品種的適應(yīng)性尤其是對(duì)新疆冬季低溫的適應(yīng)性研究顯得極其重要。……

