耳穴壓豆聯合穴位按摩治療對胃癌術后胃腸功能恢復及腦腸肽分泌的影響
周芳燕 宋彩芳 周申康
[摘要] 目的 探討耳穴壓豆聯合穴位按摩治療對胃癌術后胃腸功能恢復及腦腸肽分泌的影響。 方法 選取2016年7月~2018年12月我院胃腸外科行胃癌根治術患者80例,采用拋銀幣法分為干預組與對照組各40例。兩組予全麻下腹腔鏡胃癌根治術,術后予圍手術期常規干預,對照組在此基礎上予穴位按摩,干預組在此基礎上予耳穴壓豆聯合穴位按摩治療,兩組均連用5 d。觀察兩組患者術前2 d與術后2 d血清腦腸肽(胃動素和P物質)指標變化,并比較胃腸功能恢復指標和住院時間。 結果 術后2 d,兩組血清胃動素和P物質指標均較術前2 d顯著下降(P<0.05或P<0.01),且干預組胃動素和P物質水平下降值少于對照組(P<0.05);干預組患者術后腸蠕動恢復時間、首次排氣時間、首次排便時間和住院時間較對照組更短(P<0.05)。 結論 耳穴壓豆聯合穴位按摩治療用于胃癌術后可減少術后胃動素和P物質水平下降幅度,促進胃腸道蠕動,有利于胃腸功能恢復。
[關鍵詞] 胃癌;耳穴壓豆;穴位按摩;胃腸功能;腦腸肽
[中圖分類號] R735.2? ? ? ? ? [文獻標識碼] B? ? ? ? ? [文章編號] 1673-9701(2020)11-0159-04
Effect of auricular acupoint pressing combined with acupoint massage in the treatment of recovery of gastrointestinal function and secretion of brain gut peptide after gastric cancer surgery
ZHOU Fangyan SONG Caifang ZHOU Shenkang
Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Taizhou Enze Medical Center(Group) Taizhou Hospital, Linhai? 317000, China
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the effect of auricular acupoint pressing combined with acupoint massage on the recovery of gastrointestinal function and secretion of brain gut peptide after gastric cancer surgery. Methods From July 2016 to December 2018, 80 patients with radical gastrectomy in the department of gastrointestinal surgery in our hospital were selected. The method of flipping silver coins was used to divide the patients into the intervention group and control group, with 40 patients in each group. Laparoscopic radical gastrectomy was performed in both groups under general anesthesia. Perioperative routine intervention was performed after surgery. The control group was given acupoint massage on this basis. On the basis of this, the intervention group was given auricular acupoint pressing combined with acupoint massage. The treatment was given for 5 days in both groups. The changes of serum brain gut peptide (motilin and substance P) levels were observed 2 days before and 2 days after surgery in both groups, and the gastrointestinal function recovery indicators and length of stay were compared. Results At 2 days after surgery, serum motilin and substance P levels in the two groups were significantly lower than those 2 days before surgery(P<0.05 or P<0.01). The descending value of motilin and substance P in the intervention group were lower than those in the control group(P<0.05); the postoperative bowel movement recovery time, first exhaust time, first defecation time and length of stay were significantly shorter in the intervention group than in the control group(P<0.05). Conclusion Auricular acupoint pressing combined with acupoint massage for postoperative gastric cancer can reduce the decrease of postoperative motilin and substance P and promote gastrointestinal motility, which is beneficial to the recovery of gastrointestinal function.
[Key words] Gastric cancer; Auricular acupoint pressing; Acupoint massage; Gastrointestinal function; Brain gut peptide
胃癌根治術是目前治療胃癌最常用的手術方式,術后可出現胃腸功能抑制、胃腸功能紊亂現象,增加術后并發癥的發生率,使得患者術后恢復緩慢。因此,如何有效促進胃癌術后患者胃腸功能的恢復至關重要[1-3]。目前研究已證實腦腸肽的分泌與釋放與術后胃腸功能的恢復密切相關[4,5]。耳穴壓豆與穴位按摩均為傳統的中醫外治手段,對術后胃腸功能的恢復均有促進作用,但兩者的聯合作用及對血清腦腸肽水平的影響國內外鮮有報道[6,7]。本研究觀察了耳穴壓豆聯合穴位按摩用于治療對胃癌術后胃腸功能恢復和腦腸肽分泌情況的影響,現報道如下。
1 資料與方法
1.1 一般資料
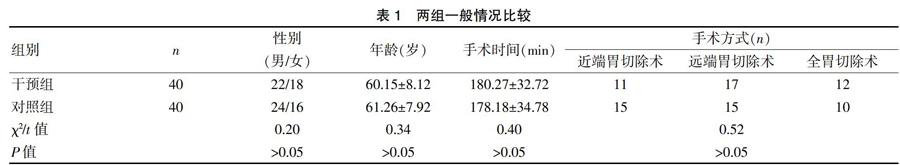
選擇2016年7月~2018年12月我科擬行胃癌根治術患者80例。納入標準[8]:(1)術前均經胃鏡檢查及病理確診;(2)年齡18~80歲。排除標準[9]:(1)有明顯遠處轉移者;(2)以往有胃腸道肝膽系統疾病或胃腸道手術史者;(3)嚴重心肺、肝腎功能不全者。采用拋銀幣法分為兩組各40例。兩組性別、年齡、手術時間和手術方式等情況比較差異無統計學意義(P>0.05),具有可比性。見表1。
1.2 治療方法
兩組均予全麻下腹腔鏡胃癌根治術,術后予胃腸減壓、禁食禁飲、抗生素治療、靜脈補液及營養支持等圍手術期常規干預,對照組在此基礎上予以穴位按摩。干預組在此基礎上予以耳穴壓豆聯合穴位按摩治療,兩組均連用5 d。穴位按摩:術后6 h開始,取足三里穴、合谷穴和上巨虛穴,采用點、揉、按方式按摩,3次/d,1 min/次;耳穴壓豆:術后6 h開始,取胃穴、皮質下、大腸、小腸、神門、交感和阿是穴,將貼粘有王不留行籽的耳貼分別貼于以上穴位,患者自行局部按壓,使患者感覺酸麻和脹痛為宜,按壓3~5 min/次,按壓5次/d,雙耳交替進行。觀察兩組患者術前2 d與術后2 d血清腦腸肽(胃動素和P物質)水平變化,并評估胃腸功能恢復相關指標及住院時間。
1.3 觀察指標
1.3.1 血清胃動素和P物質水平? 取患者晨8AM空腹時肘靜脈血約5 mL,將其置于干燥抗凝試管中,低溫離心后分離出上層血清,存于-20°C低溫冰箱,采用放射免疫法測定。
1.3.2 胃腸功能恢復相關指標評估? 采用術后腸蠕動恢復時間、首次排氣時間和首次排便時間進行評估。
1.4 統計學處理
選擇SPSS22.0軟件進行統計,計量資料用均數±標準差(x±s)表示,采用t檢驗;計數資料用[n(%)]表示,采用χ2檢驗。以P<0.05為差異有統計學意義。
2 結果
2.1 兩組血清胃動素和P物質指標比較
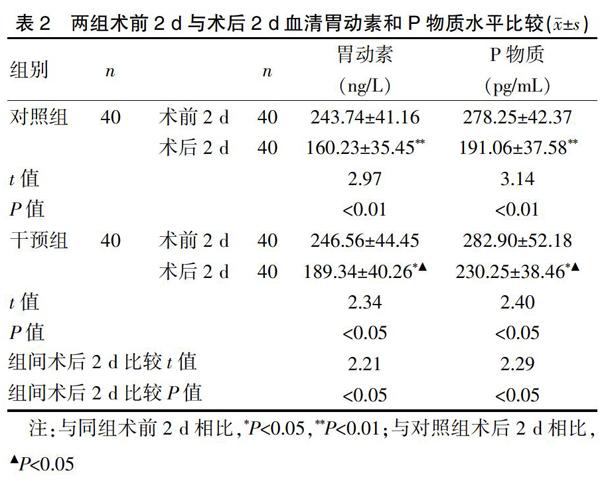
術前2 d兩組血清胃動素和P物質指標相接近(P>0.05)。術后2 d,兩組血清胃動素和P物質指標均較術前2 d顯著下降(P<0.05或P<0.01),且干預組下降值少于對照組(P<0.05)。見表2。
2.2 兩組術后胃腸功能恢復指標和住院時間比較
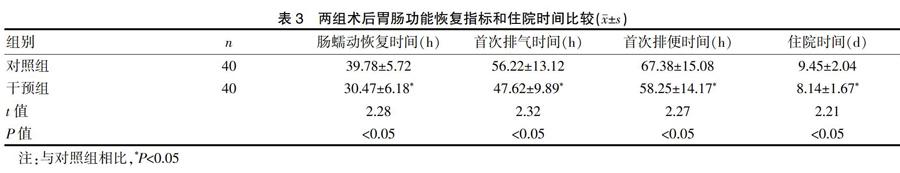
干預組術后腸蠕動恢復時間、首次排氣時間、首次排便時間和住院時間較對照組更短(P<0.05)。見表3。
3 討論
胃癌是常見的胃腸道惡性腫瘤之一,近年來隨著社會的快速發展、人均壽命的延長和生活習慣方式的改變,胃癌的發病率和死亡率不斷升高,且年齡也有年輕化趨勢[10-11]。腹腔鏡胃癌根治術作為胃癌常見的術式,因術中麻醉干擾、手術操作、解剖關系改變引起部分神經支配受抑制,腦腸肽調節功能障礙,加上術前進行腸道準備,術后易發生水電解質酸堿平衡失調,術后患者胃腸道蠕動能力受到一定程度的抑制,會發生短期的胃腸道蠕動能力麻痹狀態[12-14]。目前臨床上多采用胃腸減壓、禁食、抗感染、靜脈補液及營養支持等方法促進胃腸蠕動能力的恢復,但總體來說效果不甚理想,部分頑固的患者治療頗棘手[15]。近年研究已證實術后胃腸功能紊亂狀況與腦腸肽的釋放分泌異常密切相關,其中關系較密切的主要有胃動素與P物質,兩者均為參與胃腸道蠕動與消化道分泌的主要腦腸肽[16,17]。胃動素主要由十二指腸和近端的空腸黏膜分泌釋放,主要激活腸黏膜神經系統中的胃動素相關神經元,觸發小腸非消化期周期性移行性復合運動,增強胃腸動力和加快胃腸道的排空。P物質也是一種體內主要的腦腸肽,可促進胃腸道平滑肌和括約肌收縮和胃腸蠕動。因此,調節腦腸肽,尤其是胃動素與P物質的分泌釋放是治療胃腸道手術后胃腸功能抑制的新方向。
耳穴壓豆和穴位按摩均為常用的治療胃腸道術后胃腸功能抑制的中醫外治方法。耳穴壓豆將王不留行籽貼于患者相應的穴位后,通過按壓刺激耳穴,加快氣血循環起到治療疾病的作用[18]。本研究選擇的神門、皮質下能激活人體大腦的皮層組織,興奮中樞神經系統起到安神、鎮靜作用;按壓交感和阿是穴能進一步調節自主神經功能,加快胃腸道平滑肌的收縮,大腸、小腸和胃穴可激活胃腸道蠕動能力,以上各穴聯用刺激胃腸道蠕動,調節消化道功能,具有溫通氣血、調整陰陽,改善患者術后胃腸功能紊亂作用[19-23]。穴位按摩選擇足三里、合谷、上巨虛穴,均便于暴露,對切口不造成影響,其中足三里穴調理脾胃,扶正祛邪,有助于促進消化;合谷穴和胃通腑,增強胃腸蠕動;上巨虛穴專司六腑之通,刺激該穴可促進胃腸動力,按摩以上諸穴可有調理臟腑、舒筋通絡作用[24]。本研究發現術后2 d,干預組血清胃動素和P物質指標較術前2 d顯著下降,且其下降值少于對照組,提示耳穴壓豆聯合穴位按摩治療用于胃癌術后可減少術后胃動素和P物質水平下降幅度;同時研究還發現干預組患者術后腸蠕動恢復時間、首次排氣時間、首次排便時間和住院時間較對照組更短,提示耳穴壓豆聯合穴位按摩治療用于胃癌術后可促進胃腸道蠕動,有利于胃腸功能恢復。我們推測耳穴壓豆聯合穴位按摩用于胃癌術后患者促進胃腸蠕動功能恢復可能是通過促進胃動素和P物質等腦腸肽的分泌釋放,減少術后胃動素和P物質水平下降幅度,減少手術對腦腸肽分泌的抑制作用,加快胃腸道蠕動,有利于胃腸道功能的恢復[25]。
總之,耳穴壓豆聯合穴位按摩治療用于胃癌術后可減少術后胃動素和P物質水平下降幅度,促進胃腸道蠕動,有利于胃腸功能恢復。
[參考文獻]
[1] 陳萬青,張思維,曾紅梅,等. 中國2010年惡性腫瘤發病與死亡[J]. 中國腫瘤,2014,23(1):1-10.
[2] Hiranyakas A,Bashankaev B,Seo CJ,et al.Epidemiologypashophysiology and medical management of postoperative ileus in the elderly[J]. Drug Aging,2011,28(2):107-108.
[3] Tseng YT,Cherng R,Harroun SG,et al. Photoassisted photoluminescence fine-tuning of gold nanodots through free radical-mediated ligand-assembly[J]. Nanoscale,2016, 8:9771-9779.
[4] Ozaki K,Yogo K,Sudo H,et al. Effects of mitemeinal(GM-611),an acid-resistant nonpeptide motilin receptor agonist oil the gastrointestinal contractile activity in conscious dogs[J]. Pharmacology,2007,79(4):223-235.
[5] 王歡,黃永坤,劉梅. 胃腸激素與胃腸道功能及疾病的關系[J]. 醫學綜述,2013,19(15):2735-2738.
[6] 盧蔚起,吳健瑜,郝蕾. 中西醫結合快速康復技術在胃癌根治術圍手術期的應用[J]. 臨床心身疾病雜志,2015, 21(5):31-32.
[7] 裴哲,周博,金燦輝,等. 快速康復外科理念應用于老年進展期胃癌患者圍術期的回顧性對照研究[J]. 醫學研究雜志,2017,46(2):129-133.
[8] 孟成,于洋,王智浩,等. 加速康復外科在胃癌根治術中臨床價值的前瞻性研究[J]. 中華消化外科雜志,2015, 14(1):52-56.
[9] Al Quait A,Doherty P,Gutacker N,et al. In the modern era of percutaneous coronary intervention:Is cardiac rehabilitation engagement purely a patient or a service level decision?[J]. Eur J Prev Cardiol,2017,24(2):1351-1357.
[10] 王鵬文,田小名,趙群. 腹腔鏡與開腹行急性膽囊切除術對體液免疫功能及機體能量代謝的影響[J]. 中國普通外科雜志,2014,23(8):1101-1105.
[11] 丁海濤,韓智君,曹杰,等. 胃十二指腸三角吻合術在遠端胃癌根治術后消化道重建中的安全性及療效觀察[J]. 中國現代手術學雜志,2017,21(3):182-186.
[12] Shao AM,Fei JP,Hu FY,et al.The influence of gastrointestinal function after operation of patients with laparoscopic gallbladder excision by auricular application pressure[J].Journal of Chinese Medicine,2016,31(12):2029-2032.
[13] Qian SQ,Gao L,Wei Q,et al. Vacuum therapy in penile rehabilitation after radical prostatectomy:Review of hemodynamic and antihypoxic evidence[J]. Asian J Andrology,2016,18(2):446-451.
[14] Dong H,Wei Y,Xie C,et al. Structural and functional analysis of two novel somatostatin receptors identified from topmouth culter(Erythroculter ilishaeformis)[J]. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol,2018,210(1):18-29.
[15] Camilleri M. The stomach in diabetes:from villain to ally[J].Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol,2009,7(3):285-287.
[16] 鄒永平,李龍鶴,袁巍,等. 腹腔鏡胃癌根治術和開腹手術對胃癌患者胃腸激素水平的影響[J]. 臨床與實驗醫學雜志,2018,17(4):384-387.
[17] 劉曉,韓朝陽,王銀中,等. 腹腔鏡與開腹胃癌根治術的療效和對微轉移及胃腸激素水平的影響[J]. 中國普通外科雜志,2017,26(12):1637-1641.
[18] Li H,Wang YP. Effect of auricular acupuncture on gastrointestinal motility and its relationship with vagal activity[J]. Acupuncture in Medicine Journal of the British Medical Acupuncture Society,2013,31(1):57-60.
[19] Kim Y,Kim CW,Kim KS. Clinical observation on post-operative vomiting treated by auricular acupuncture[J]. Am J Chin Med,2003,31(3):475-476.
[20] Yeh CH,Chien LC,Chiang YC,et al. Reduction in nausea and vomiting in children undergoing cancer chemotherapy by either appropriate or sham auricular acupuncture points with standard care[J]. J Altern Complement Med,2012,18(4):334-336.
[21] 張小翠,魏海梁,張永梅,等. 胃癌手術前后不同時間點耳穴貼壓對胃腸功能恢復的影響[J]. 陜西中醫藥大學學報,2017,40(3):37-42.
[22] 孫龍,段培蓓,黃為君,等. 耳穴貼壓促進胃癌術后胃腸功能恢復的研究[J]. 中國中西醫結合消化雜志,2014, 22(5):239-241.
[23] 郭書娟,陳文競,李琴娜. 胃癌手術前后不同時間點耳穴貼壓對胃腸功能恢復的影響效果[J]. 數理醫藥學雜志,2018,31(10):1485-1486.
[24] 鄧文闊. 循經穴位按摩促進直腸癌術后胃腸功能恢復的研究[J]. 光明中醫,2015,30(11):2365-2366.
[25] 黃福霞. 耳穴埋籽聯合穴位貼敷對消化道腫瘤患者術后排氣的影響[J]. 中國繼續醫學教育,2018,10(4):146-147.
(收稿日期:2019-04-28)

