一類具有領導者的群集運動分析
王慶亮,孔祥智,吳晨
?
一類具有領導者的群集運動分析
王慶亮,孔祥智,吳晨
江南大學理學院, 江蘇 無錫 214122
本文主要研究了多智能體系統中具有領導者的群集運動。利用李雅普洛夫穩定性和比較定理,證明了跟隨者與領導者之間的耦合系數足夠大,系統能在任意給定的初始條件下達到群集運動。
群集運動; 領導者; 李雅普洛夫
智能體是指能感受到周圍信息并能對自身做出相應調整的個體。例如每只鳥,每條魚,每個人都是智能體。近年來,越來越多的文獻開始涉及多智能體系統[1-5]。自然界中有很多生動有趣的群集現象,例如大雁成群結隊的南飛,魚類的群游和蟻群的聚集等等,我們將此類現象統稱為群集運動。在這些群集運動中,各個智能體之間如何互相合作完成任務這一問題吸引了來自生物學,數學,人工智能學和計算機科學等領域學者的興趣[6-8]。1986年,Reynolds[9]提出了群集運動的三條規則。這三條規則分別是:(1)速度匹配;(2)聚合規則;(3)分離規則。這對以后群集運動的研究具有深遠的指導意義。它通常定義為當系統滿足:(1)當時間趨于無窮時,智能體之間的速度差趨于0;(2)智能體之間的位移差趨于一個常數。我們就說智能體達到群集運動。
Cucker和Smale考慮的是無領導者的情形,但在現實生活中,會有領導者和跟隨者的情形。例如在2017年8月13日,深圳地鐵1號線上一名乘客因為上班遲到突然跑動,帶動整節車廂的乘客全部跑動。這其實可以看成一個領導跟隨者的群集運動。根據這種情形,本文建立數學模型并給出了達到群集運動的充分條件。
1 模型描述
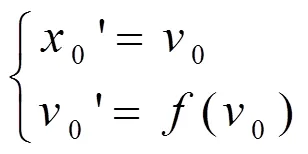
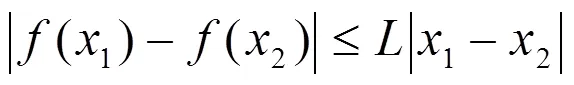
其中為利普西茨常數。
,=1,2,…,
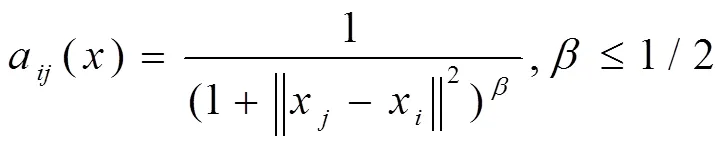
其中,是耦合強度。
定義2.1[10]對于1≤≤,若系統(3)中的狀態x,v滿足:
2 帶有領導者的群集運動
定理3.1:若系統(3)中的耦合強度大于函數的利普西茨常數,則系統(3)可以達到群集運動。
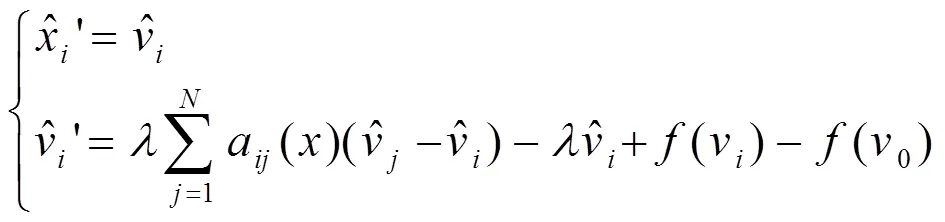
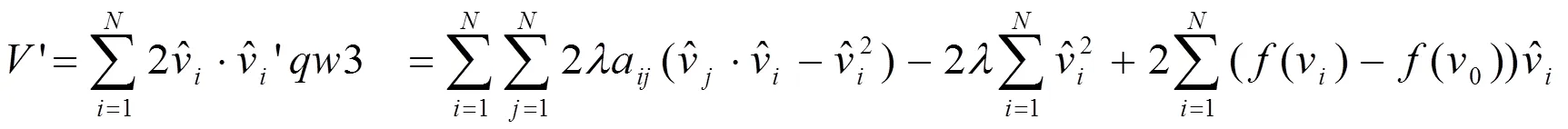
根據數列求和的性質,我們有:
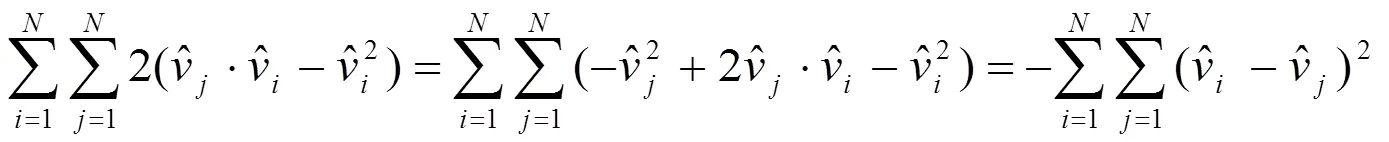
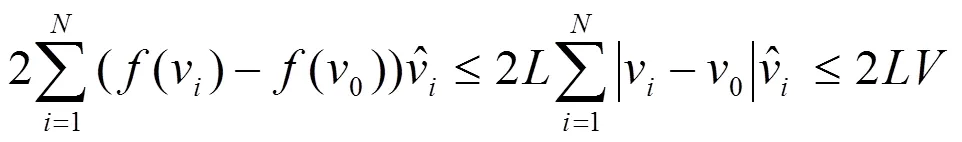

其中是一個常數。
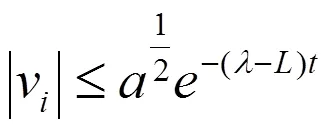
根據(10)和(11)可知系統(4)達到群集運動。
證畢。
3 數值仿真
本節利用MATLAB四階龍格庫塔方法進行仿真,舉出具體的例子來驗證結論的正確性。本節選取八個跟隨著的多智能系統進行分析。其中(0,0)=(80,12),(1,1)=(24,19),(2,2)=(45,16),(3,3)=(46,15),(4,4)=(78,7),(5,5)=(98,8),(6,6)=(88,14),(7,7)=(68,10),(8,8)=(39,9),其中()=sin,則利普西茨常數=1。我們取=0.3。
定義兩個新的函數來描述系統中速度和位移的動態過程:
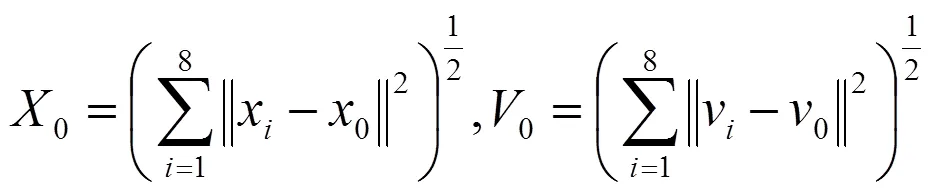
考慮在時間20 s內,當0≤0.01時,我們就認為速度達到一致。
例1當耦合系數=0.5時,對該系統進行仿真所得速度與位置誤差數據如下(圖1)。
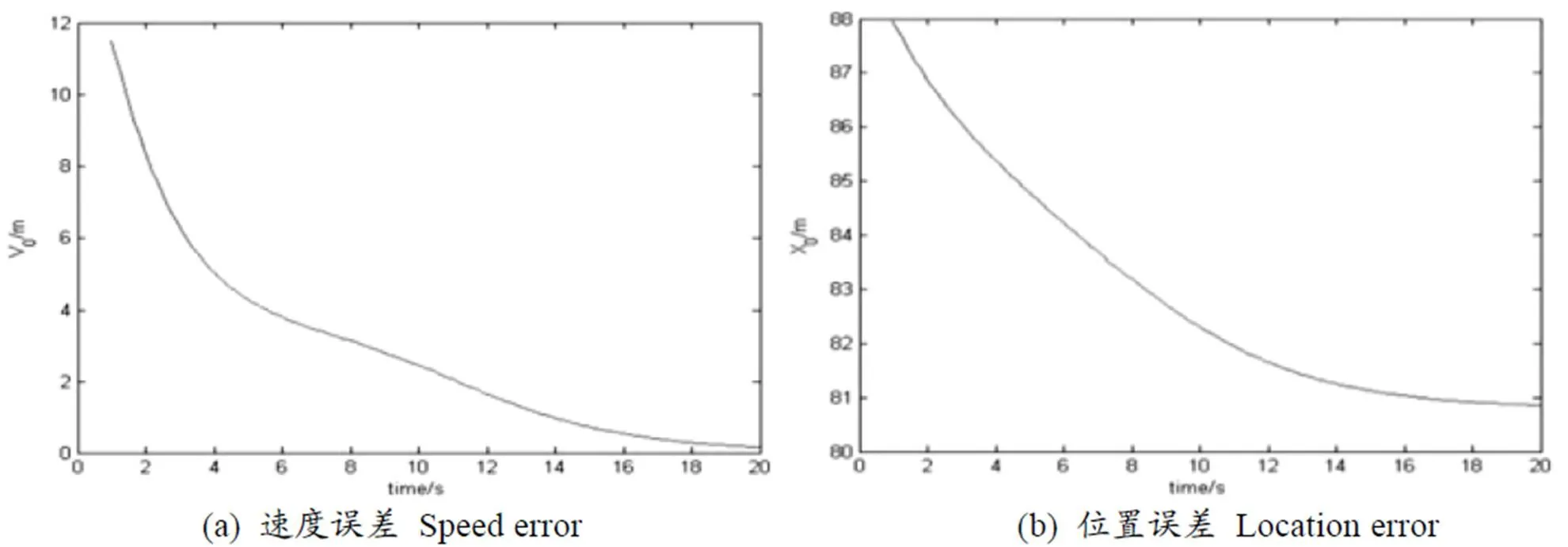
圖 1 誤差數據
函數的利普西茨常數是1,當=0.5,也就是<,沒有滿足我們定理中的條件。從MATLAB仿真中(圖1 (a))可以看出,速度誤差在20 s內沒有趨于0,即沒有達到群集運動。
例2耦合系數=1時,對該系統進行仿真所得速度與位置誤差數據如下(圖2)
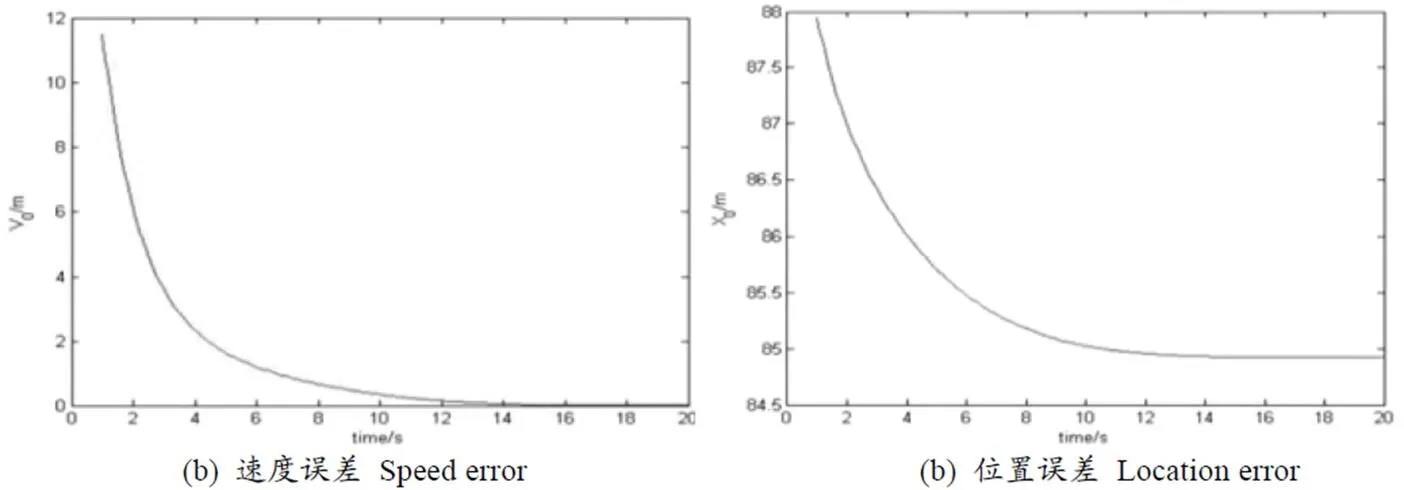
圖2 誤差數據
當=1時,即=時,由圖2(a)可以看出,系統最終速度差趨于0,圖2(b)位移差趨于一個常數,即系統達到群集運動。并求出速度達到一致的時間為0=15.9162。
例3耦合系數=2時,對該系統進行仿真所得速度與位置誤差數據如下(圖3)
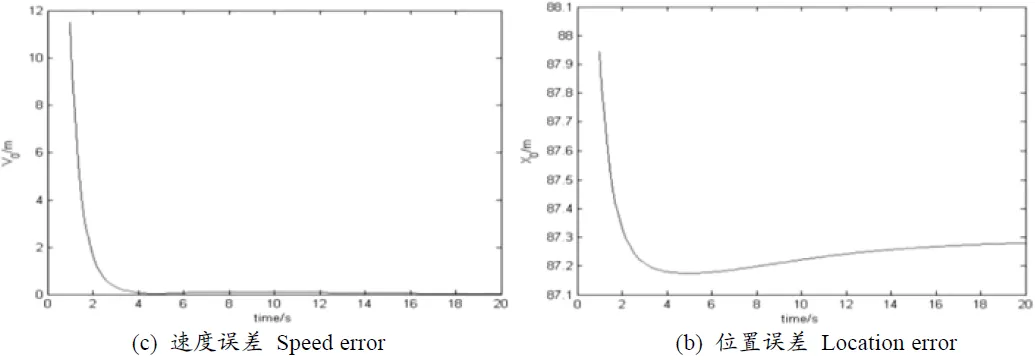
圖3 誤差數據
當=2時,即>時,由圖3(a)可以看出,系統最終速度差趨于0,(b)位移差趨于一個常數,即系統達到群集運動。并求出速度達到一致的時間為0=3.0366。
由例1,例2和例3的比較看出,當耦合系數比較小,小于函數的利普西茨常數時,系統達不到群集運動。當耦合系數大于等于利普西茨常數時,群集運動會出現,并且由上述的仿真結果可以得到,耦合系數越大,速度達到一致的時間越短。
[1] Tian Y, Liu C. Consensus of multi-agent systems with diverse input and communication delays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2008,53(9):2122-2128
[2] Liu C, Liu F. Stationary consensus of heterogeneous multi-agent systems with bounded communication delays[J]. Automatica, 2011,47(9):2130-2133
[3] Lin P, Jia Y. Average-consensus in networks of multi-agents with both switching topology and coupling time-delay[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2008,387(1):303-313
[4] Olfati-Saber R. Flocking for multi-agent with a virtual leader[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2006,51:401-420
[5] Tian Y, Liu C. Robust consensus of multi-agen systems with diverse input delays and asymmetric interconnection perturbations[J]. Automatic, 2009,45(5):1437-1353
[6] Xiao F, Wang L. Consensus protocols for discrete-time multi-agent systems with time-varying delays[J]. Automatica, 2009,45(5):1347-1353
[7] Ben-Jacob E, Cohen I, Czirók A,. Chemomodulation of cellular movement, collective formation of vortices by swarming bacteria, and colonial development[J]. Physical A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 1997,238(1-4):181-197
[8] Reif J, Wang H. Social potential ?elds: A distributed behavioral control for autonoomous robots[J]. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 1999,27:171-194
[9] Vicsek T, Czirók A, Farkas IJ,Application of statistical mechanics to collective motion in biology[J]. Physical A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2015,274(1-2):182-189
[10] Fax JA, Murray RM. Information flow and cooperative control of vehicle formations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2004,49(9):1465-1476
Analysis on a Class of Flocking Motion with a Leader
WANG Qing-liang, KONG Xiang-zhi, WU Chen
214122,
This paper mainly studied the flocking motion with a leader in multi-agent system. By using Lyapunov stability and comparison theorem, the article proved that the coupling coefficient between followers and leaders was large enough and the system could achieve the flocking motion under any given initial conditions.
Flocking motion; leader; Lyapunov
TP273
A
1000-2324(2018)03-0547-04
2017-03-10
2017-04-02
王慶亮(1991-),男,碩士研究生,研究領域為模糊代數. E-mail:wangqingliang91@163.com

