血培養陽性報警時間對臨床病原菌鑒別的意義
蘇俊梅
【摘要】 目的:研究與分析血培養陽性報警時間對臨床病原菌鑒別的意義。方法:選取2016年
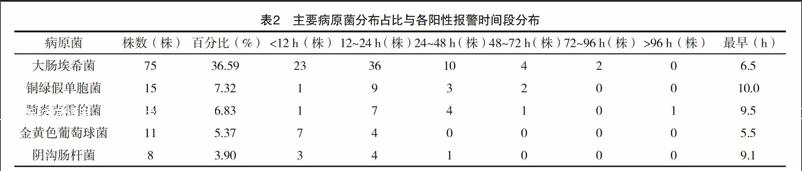
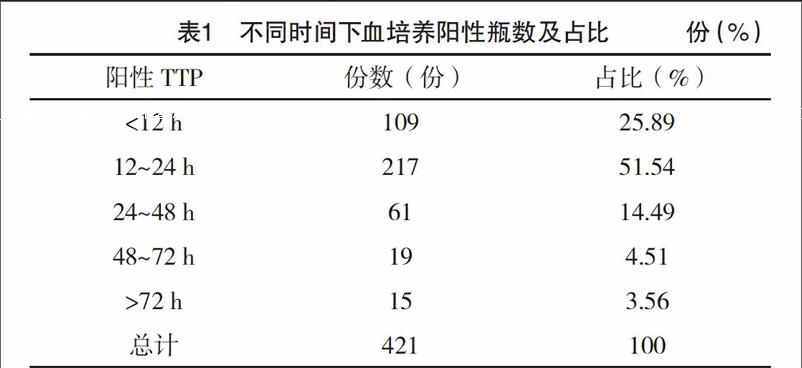
2月-2017年2月本院發熱患者送檢病原微生物室的血培養標本為研究對象,分析其血培養陽性報警時間對鑒別臨床病原菌的應用。結果:7226份血培養標本檢測陽性率為5.83%(421/7226),在421份血培養陽性瓶中,同時為陽性標本的厭氧瓶與需氧瓶共377份(89.55%),僅報陽性的厭氧瓶為21份(4.99%),僅報陽性的需氧瓶為23份(5.46%)。421份報陽性瓶中,共檢出菌株205株,病原菌主要以大腸埃希菌、銅綠假單胞菌、肺炎克雷伯菌、金黃色葡萄球菌及陰溝腸桿菌為主;陽性報警時間平均為(24.53±2.47)h。而需氧瓶與厭氧瓶的平均陽性報警時間分別為(18.60±1.29)、(17.30±1.31)h,兩者比較差異無統計學意義(P>0.05),各病原菌以及污染菌的平均陽性報警時間比較,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。結論:血培養陽性報警時間有助于初步鑒別臨床病原菌及污染菌,為臨床明確診斷提早使用抗生素提供實驗室依據。
【關鍵詞】 血培養; 陽性報警時間; 病原菌鑒別; 臨床意義
Significance of Time to Positivity of Blood Culture for Clinical Pathogenic Bacteria Identification/SU Jun-mei.//Medical Innovation of China,2017,14(30):121-124
【Abstract】 Objective:To study and analyze the significance of time to positivity of blood culture for clinical pathogenic bacteria identification.Method:The blood culture specimens of pathogenic microorganisms from fever patients in our hospital from February 2016 to February 2017 were selected as the research objects,the time to positivity of blood culture and its application in clinical pathogenic bacteria identification were analyzed.Result:The positive rate of 7226 blood culture specimens was 5.83%(421/7226),there were 377 bottles(89.55%) of anaerobic and aerobic bottles positive samples in 421 blood culture positive bottles,only 21(4.99%) of positive anaerobic bottles were reported,only 23(5.46%) of positive aerobic bottles were reported.205 strains were detected in 421 positive bottles.The main pathogenic bacteria were escherichia coli,pseudomonas aeruginosa,klebsiella pneumoniae,staphylococcus aureus and enterobacter cloacae,the average time to positivity was(24.53±2.47)h.the average time to positivity of aerobic bottles and anaerobic bottles was(18.60±1.29) and(17.30±1.31)h respectively,the difference was not statistically significant(P>0.05).The average time to positivity of pathogenic bacteria and contaminated bacteria were compared,the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05).Conclusion:The blood culture time to positivity is helpful for the clinical pathogenic bacteria identification.It would provided evidence of laboratory for the diagnosis and early use of antibiotics for patients.
【Key words】 Blood culture; Time to positivity; Pathogenic bacteria identification; Clinical significance
First-authors address:Yunfu Peoples Hospital,Yunfu 527300,China
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-4985.2017.30.036
目前在對血流感染進行臨床診斷以及確診的過程中,血培養是最主要的手段,然而臨床工作中血培養標本存在一定的污染率,對判定血流感染存在一定的困難,容易誤導臨床。然而菌血癥的病情復雜嚴重,早診斷有利于臨床合理使用抗生素。因此,判斷血培養陽性菌株是病原菌或污染菌顯得尤其重要。血培養菌株的陽性報警時間(Time-to-positivity,TTP)是較具臨床價值和意義的指標,同時也是血流感染診斷的參考標準,因此也逐漸成為了病情監測以及血流感染診斷的關鍵手段[1-3]。研究表明,根據全自動血培養儀的報警機制、不同病原菌的生長特點以及觀察其TTP值可對臨床病原菌的種類進行鑒別[4-5]。因此……

