達比加群酯在心房顫動伴左心耳血栓中的應用*
韋怡春,李菊香,俞建華,顏素娟,程曉曙
(南昌大學第二附屬醫院心內科 330006)
達比加群酯在心房顫動伴左心耳血栓中的應用*
韋怡春,李菊香△,俞建華,顏素娟,程曉曙
(南昌大學第二附屬醫院心內科 330006)
新型口服抗凝藥(NOAC)凝血酶抑制劑達比加群酯通過可逆性地與凝血酶結合而發揮抗凝作用[1-2]。臨床試驗證明,達比加群酯可有效降低房顫患者卒中風險,是一種有效且安全性較好的口服抗凝藥[3-5]。本文報道2例達比加群酯對心房顫動伴左心耳血栓的療效及安全性。
1 臨床資料
病例1:男,51歲,反復心悸發作2月余,再發4 d。患者于2個月前無明顯誘因出現心悸,心電圖提示心房顫動,食道超聲未見血栓,經胺碘酮治療后轉為竇性心律。以胺碘酮、華法林維持治療2周后自行停藥。有高血壓病史4年余,服用氨氯地平和依那普利血壓控制良好。超聲心動圖提示左心室肥厚,心電圖顯示左心室肥厚勞損。4 d前再次發作心悸,心電圖提示心房顫動,僅持續4~5 h心悸自行緩解。2 d后患者感到胸悶不適,行冠脈CT血管造影(CTA)檢查時,發現左房充盈缺損,進一步經食道超聲檢查證實為左心耳血栓,大小7 mm×8 mm(圖1)。給予達比加群酯110 mg(每天2次)治療1個月,復查食道超聲,左心耳血栓消失(圖2)。患者無明顯不適,未出現出血等并發癥,肝、腎功能無明顯變化,國際標準凝血時間1.03。
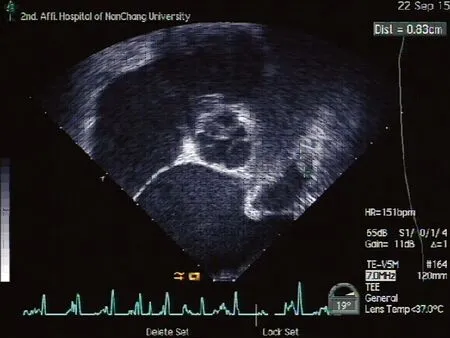
圖1 TEE 左心耳血栓(7 mm×8 mm)
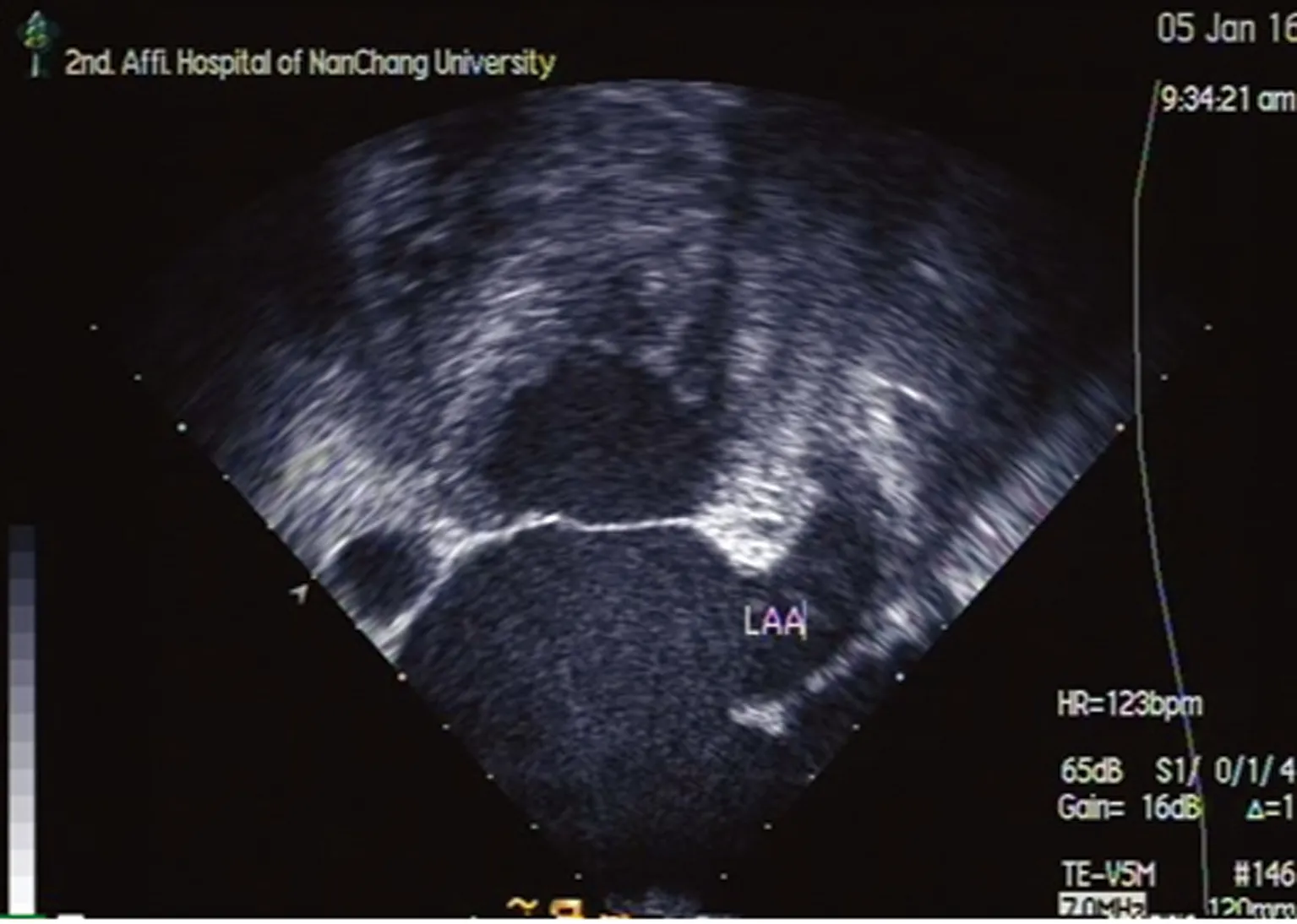
圖2 1個月后復查血栓消失
病例2:男,63歲,體檢發現心房顫動1年余,偶有胸悶、心悸等不適。高血壓病史2年余,服鹽酸貝那普利及氨氯地平治療,血壓控制良好。超聲心動圖提示左室舒張功能不全,左房40 mm,于外院行房顫射頻消融治療,術后服用索他洛爾、華法林治療。半年后房顫復發,患者不規律服用阿司匹林。3個月前,患者因胸悶在外院行胸部CTA檢查發現充盈缺損,經食道超聲檢查證實為左心耳血栓,大小14 mm×8 mm(圖3)。給予達比加群酯110 mg(每天2次)治療3個月,復查食道超聲,左心耳血栓消失(圖4)。患者無明顯不適,未出現出血等并發癥。復查肝功能、腎功能、血尿常規無明顯異常發現,國際標準凝血時間0.94。
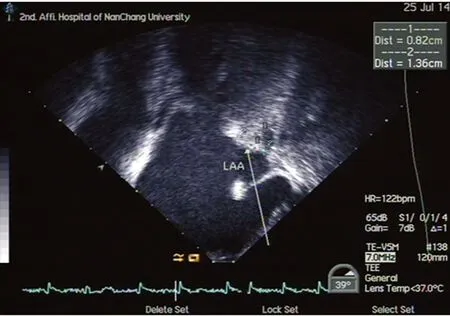
圖3 TEE 左心耳血栓(14 mm×8 mm)

圖4 3個月后復查血栓消失
2 討 論
凝血酶抑制劑達比加群酯通過可逆性地與凝血酶結合發揮抗凝作用,系列研究表明,達比加群具有良好的預防房顫、腦卒中的作用[6-8]。著名的RE-LY研究[9-11]表明,小劑量達比加群酯(110 mg)的作用與經典的口服抗凝藥物華法林相當,而大劑量的達比加群酯(150 mg)療效優于華法林,而出血尤其大出血的發生率明顯低于華法林,是目前認為療效好而不良反應相對較少的新型口服抗凝藥物。因此,達比加群酯降低非瓣膜房顫患者中風風險的安全性及有效性已得到公認,各大指南已將其列為房顫卒中預防的適應證,2014 AHA/ACC/HRS最新房顫指南首次將達比加群酯作為NVAF高危患者Ⅰ類推薦[12]。目前,FDA增加的達比加群酯新適應證包括深靜脈血栓(DVT)與肺動脈栓塞(PE)治療及復發風險的降低。然而,所有前期研究均針對房顫的卒中預防,對于心房已形成的血栓是否能夠溶解消除,尚不清楚。
本文報道2例房顫患者,并不是房顫卒中的高危患者,CHADS-VASC評分僅1分,依據指南可選擇抗凝或阿司匹林治療,而2例患者藥物依從性差,不愿服藥而自行停用華法淋抗凝治療導致左房血栓形成。在發現左心耳血栓后,給予達比加群酯110 mg(每天2次)治療,分別于1個月和3個月后血栓消失,表明達比加群酯對已形成的左心耳血栓可能有一定溶解作用。其作用機制可能是達比加群與凝血酶的活性位點結合[1,13-15],不僅可以特異并可逆性地抑制游離凝血酶的作用,而且可以抑制與血塊結合的凝血酶的作用,阻止纖維蛋白原裂解為纖維蛋白, 另外可以抑制凝血因子Ⅲ、 Ⅴ、 Ⅶ、 Ⅹ、 Ⅺ及凝血酶誘導的血小板聚集達到抗凝作用,阻止血栓進一步形成,同時人體會啟動纖維蛋白溶解系統使已形成的血栓破壞,從而使已形成的左心耳血栓消除,當然達比加群酯參與其中的具體機制還不是十分清楚。但本文2例患者,從病史推測發生血栓的時間不長,且血栓體積不是很大。對于時間較長和血栓體積較大的情況,能否達到同樣的效果需要更多的病例來證實。
[1]van Ryn J,Stangier J,Haertter S,et al.Dabigatran etexilate a novel,reversible,oral direct thrombin inhibitor:interpretation of coagulation assays and reversal of anticoagulant activity[J].Thromb Haemost,2010,103(6):1116-1127.
[2]Enriquez A,Lip GY,Baranchuk A.Anticoagulation reversal in the era of the non-vitamin K oral anticoagulants[J].Europace,2016,18(7):955-964.
[3]Hanley CM,Kowey PR.Are the novel anticoagulants better than warfarin for patients with atrial fibrillation?[J].J Thorac Dis,2015,7(2):165-171.
[4]Gomezoutes A,Terleirafernandez AI,Calvorojas G,et al.Dabigatran,rivaroxaban,or apixaban versus warfarin in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation:a systematic review and meta-analysis of subgroups[J].Thrombosis,2013:640723.
[5]Bancroft T,Lim J,Wang C,et al.Health care resource utilization,costs,and persistence in patients newly diagnosed as having nonvalvular atrial fibrillation and newly treated with dabigatran versus warfarin in the United States[J].Clin Ther,2016,38(3):545-556.
[6]O′Dell KM,Igawa D,Hsin J.New oral anticoagulants for atrial fibrillation:a review of clinical trials[J].Clin Ther,2012,34(4):894-901.
[7]Mohd HM,Shaharuddin S,Long CM,et al.Preliminary study of safety and efficacy of warfarin versus dabigatran in atrial fibrillation patients in a tertiary hospital in Malaysia[J].Value Health,2015,18(7):A378.
[8]Verdecchia P,Angeli F,Bartolini C,et al.Safety and efficacy of non-vitamin K oral anticoagulants in non-valvular atrial fibrillation:a Bayesian meta-analysis approach[J].Expert Opin Drug Saf,2015,14(1):7-20.
[9]Brambatti M,Darius H,Oldgren J,et al.Comparison of dabigatran versus warfarin in diabetic patients with atrial fibrillation:results from the RE-LY trial[J].Int J Cardiol,2015,196(2):127-131.
[10]Nagarakanti R,Wallentin L,Noack H,et al.Comparison of characteristics and outcomes of dabigatran versus warfarin in hypertensive patients with atrial fibrillation (from the RE-LY Trial)[J].Am J Cardiol,2015,116(8):1204-1209.
[11]Connolly SJ,Ezekowitz MD,Yusuf S,et al.Dabigatran versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation[J].N Engl J Med, 2009,361(12):1139-1151.
[12]January CT,Wann LS,Alpert JS,et al.2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation:a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society[J].J Am Coll Cardiol,2014,64(21):2071-2104.
[13]Stangier J.Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the oral direct thrombin inhibitor dabigatran etexilate[J].Clin Pharmacokinet, 2008,47(5):285-295.
[14]Stangier J,Rathgen K,Stahle H,et al.The pharmacokinetics,pharmacodynamics and tolerability of dabigatran etexilate,a new oral direct thrombin inhibitor,in healthy male subjects[J].Br J Clin Pharmacol, 2007,64(3):292-303.
[15]Stangier J,Clemens A.Pharmacology,pharmacokinetics,and pharmacodynamics of dabigatran etexilate,an oral direct thrombin inhibitor[J].Clin Appl Thromb Hemost, 2009,15 Suppl 1:9-16.
10.3969/j.issn.1671-8348.2017.27.048
R541
C
1671-8348(2017)27-3887-02
2016-11-06
2017-05-22)
國家十二五“重大新藥創制”科技重大專項(20142X09303305)。
韋怡春(1990-),碩士,住院醫師,主要從事心律失常的研究。△
,E-mail:ljx912@126.com。

