全麻剖宮產患者術前泵注右美托咪定對其應激反應和血流波動的影響
,海霞,,
(1.濟南軍區總醫院,山東 濟南 250031;2.山東省濰坊市臨朐縣九山中心衛生院,山東 濰坊 262608)
全麻剖宮產患者術前泵注右美托咪定對其應激反應和血流波動的影響
宋強1,宋海霞2,邊洪春1,高成杰1
(1.濟南軍區總醫院,山東濟南250031;2.山東省濰坊市臨朐縣九山中心衛生院,山東濰坊262608)
目的觀察全麻剖宮產患者術前泵注右美托咪定對其應激反應和血流動力學的影響。方法選取于2014年8月至2016年7月來濟南軍區總醫院就診的全麻剖宮產患者60例,按照隨機數表法將所有患者分為實驗組和對照組,每組30例患者。實驗組患者在全麻誘導前20min靜脈泵入右美托咪定0.8μg·kg-1·h-1,對照組患者在全麻誘導前20min靜脈泵入生理鹽水0.8μg·kg-1·h-1。記錄泵藥前、泵藥后20min、氣管插管時、切皮、胎兒娩出時和拔管后10min時患者的心率和平均動脈壓;胎兒娩出后,記錄新生兒出生后1min和5min時的Apgar評分,抽取臍靜脈血進行血氣分析。結果實驗組和對照組患者的年齡、身高、體重、胎兒剖出時間、出生體重、孕周、麻醉時間的比較差異無統計學意義(均P>0.05)。實驗組和對照組兩組患者泵藥前心率和平均動脈壓比較,差異無統計學意義(t值分別為0.000、0.701,均P>0.05)。泵藥后20min及之后的時間點實驗組的心率明顯低于對照組,差異有統計學意義(t值分別為-9.874、-9.548、-7.789、-8.886、-12.241,均P<0.05),泵藥后20min及之后時間點實驗組患者的平均動脈壓明顯低于對照組,差異有統計學意義(t值分別為-4.747、-6.111、-6.393、-5.720、-4.562,均P<0.05)。實驗組患者新生兒臍帶血血氣分析中的pH、PaCO2、PaO2、SaO2與對照組的比較差異無統計學意義(t值分別為1.711、-1.603、-1.019、-0.771,均P>0.05)。兩組患者新生兒出生后1min和5min時的Apgar評分比較差異無統計學意義(t=0.000,P>0.05)。結論全麻剖宮產患者術前泵注右美托咪定有利于穩定母體的血流動力學,減弱患者的應激反應,同時對新生兒無不良影響。
全身麻醉;剖宮產;右美托咪定;應激反應
多數剖宮產患者術前麻醉均選擇椎管內阻滯的方式,當患者由于病情或恐懼手術而不能進行椎管內阻滯時,也會采用全身麻醉的方式對剖宮產患者進行術前麻醉。右美托咪定是一種新型α2腎上腺素能受體激動劑,具有鎮靜、抑制交感神經、抗焦慮的作用,單次注射或持續泵注均能引起血流動力學波動和應激反應[1]。右美托咪定有利于維持術中血流動力學的穩定,持續泵注右美托咪定可有效減少低血壓和心動過緩的發生率,本研究通過探討分析全麻剖宮產患者術前泵注右美托咪定對其應激反應和血流動力學的影響,為臨床右美托咪定的使用提供理論依據,現將結果報道如下。
1資料和方法
1.1一般資料
選取于2014年8月至2016年7月來濟南軍區總醫院就診的全麻剖宮產患者60例,按照隨機數表法將所有患者分為實驗組和對照組,每組30例患者。所有患者均符合病例納入標準和病例排除標準。病例納入標準:①懷孕36周以上的患者;②單胎;③患者年齡為21~35歲;④美國麻醉醫師學會(American Society of Anesthesiologists,ASA)分級Ⅰ級或Ⅱ級的患者。病例排除標準:①心臟傳導阻滯的患者;②伴有肝腎功能明顯異常的患者;③對右美托咪定過敏的患者;④濫用藥物或酒精的患者;⑤懷疑胎兒宮內缺氧的患者;⑥伴有糖尿病、妊娠期高血壓疾病的患者。所有患者及家屬均知情同意,均簽署知情同意書。本研究經本院醫學倫理學委員會批準。
1.2麻醉方法
產婦均于術前6h開始禁食。患者進入手術室后,常規監測患者心電圖、心率、無創血壓、血氧飽和度等。實驗組患者在全麻誘導前20min靜脈泵入右美托咪定0.8μg·kg-1·h-1,對照組患者在全麻誘導前20min靜脈泵入生理鹽水0.8μg·kg-1·h-1。隨后對患者進行麻醉誘導,充分預氧5min后,靜脈注射羅庫溴胺0.6mg/kg,丙泊酚2.5mg/kg,壓迫環狀軟骨,1min后氣管插管。胎兒娩出后,改用瑞芬太尼0.15μg·kg-1·min-1,丙泊酚100~150μg·kg-1·min-1維持麻醉完成手術。所有手術均由一名經驗豐富的產科醫師完成。
1.3觀察指標
記錄泵藥前及泵藥后20min、氣管插管時、切皮、胎兒娩出時和拔管后10min時患者的心率和平均動脈壓,若患者血壓低于麻醉前30%給予麻黃堿5~10mg,若患者心率低于60次/分鐘給予阿托品0.2~0.3mg;胎兒娩出后,記錄新生兒出生后1min和5min Apgar評分,抽取臍靜脈血進行血氣分析。
1.4統計學方法
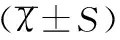
2結果
2.1一般資料比較
實驗組和對照組患者的年齡、身高、體重、胎兒剖出時間、出生體重、孕周、麻醉時間比較差異均無統計學意義(均P>0.05),見表1。
2.2平均動脈壓和心率比較
實驗組和對照組兩組患者泵藥前心率和平均動脈壓比較差異無統計學意義(t值分別為0.000、0.701,均P>0.05)。泵藥后20min及之后時間點實驗組患者的心率明顯低于對照組,差異有統計學意義(t值分別為-9.874、-9.548、-7.789、-8.886、-12.241,均P<0.05)。泵藥后20min及之后時間點實驗組患者的平均動脈壓明顯低于對照組,差異有統計學意義(t值分別為-4.747、-6.111、-6.393、-5.720、-4.562,均P<0.05),見表2、表3。
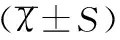


項目實驗組(n=30例)對照組(n=30例)tP年齡(歲)27.63±4.3227.48±5.09 0.1010.920身高(cm)160.22±7.91162.38±9.25-0.9720.335體重(kg)61.29±3.2661.05±3.20 0.2320.818孕周(周)31.21±5.0731.42±4.12-0.1400.889胎兒剖出時間(min)8.44±1.578.89±1.97-0.9780.332麻醉時間(min)57.32±13.2759.42±14.93-0.5760.567新生兒出生體重(kg)3.27±0.433.32±0.29-0.5280.599



項目實驗組(n=30)對照組(n=30)tP泵藥前94±1094±13 0.0001.000泵藥后20min67±893±12-9.874<0.001氣管插管時82±9114±16-9.548<0.001切皮87±11117±18-7.789<0.001胎兒娩出時85±9112±14-8.886<0.001拔管后10min84±6116±13-12.241<0.001



項目實驗組(n=30)對照組(n=30)tP泵藥前106±12104±10 0.7010.486泵藥后20min90±9103±12-4.747<0.001氣管插管時100±11119±13-6.111<0.001切皮99±12118±11-6.393<0.001胎兒娩出時97±11114±12-5.720<0.001拔管后10min99±12115±15-4.562<0.001
2.3新生兒臍帶血氣分析和Apgar評分比較
實驗組患者新生兒臍帶血血氣分析中的pH、PaCO2、PaO2、SaO2與對照組患者比較差異均無統計學意義(t值分別為1.711、-1.603、-1.019、-0.771,均P>0.05)。兩組患者新生兒出生后1min和5min Apgar評分比較差異均無統計學意義(均P>0.05),見表4。
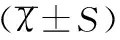

Table 4 Comparison of neonatal umbilical cord blood gas analysis and Apgar score(±S)
3討論
全身麻醉通過鎮痛、鎮靜和肌松作用抑制交感神經興奮性,同時配合呼吸機支持,能夠更好的改善患者氧氣供應,保證母體供氧。由于誘導麻醉迅速,麻醉效果確切,有利于對機體血容量的調控[2]。為了減少對胎兒的影響,全麻剖宮產時,常選用小劑量的麻醉藥,因而手術的應激性較強,術中血流動力學波動較大。應激反應過高會導致患者血壓升高、心率加快,降低胎盤血流灌注,導致新生兒剖出后Apgar評分降低。本次研究通過探討全麻剖宮產術前泵注右美托咪定對其應激反應和血流波動的影響,為臨床全麻剖宮產用藥提供理論依據。
3.1右美托咪定的藥理作用
右美托咪定是一種新型α2腎上腺能受體激動劑,具有鎮痛、鎮靜、降低應激反應、抗交感神經反射的作用,對呼吸無明顯抑制作用[3]。右美托咪定通過激動藍斑核內的突觸前膜α2受體,抑制去甲腎上腺素的釋放,降低突觸后膜的興奮性,有效抑制交感神經活性,從而有效抑制大腦皮質的覺醒反應[4]。右美托咪定可以穩定患者血流動力學水平,能夠有效減少鎮痛藥和麻醉藥的用量,減少患者的惡心嘔吐、寒戰、躁動。右美托咪定具有半衰期短的特點,鎮靜水平容易調節,已廣泛應用于ICU長時間的鎮靜,有著較高的安全性和可靠性。同時,患者處于類似正常睡眠的鎮靜狀態,被鎮靜同時可被喚醒,撤除喚醒的刺激患者很快可回到被鎮靜狀態[5]。
3.2本研究結果分析
本研究結果表明,實驗組和對照組兩組患者泵藥前心率和平均動脈壓無差異,泵藥后20min及以后時間點實驗組患者的心率和平均動脈壓都明顯低于對照組。提示右美托咪定能夠有效減少手術期間各種強烈刺激所引起的循環反應,這一研究結果與鄧超等人于2015年的研究結果一致。右美托咪定能夠有效維持患者術中循環的穩定,同時可減弱血流動力學反應。麻醉誘導前靜脈泵注右美托咪定對患兒出生后1min和5min Apgar評分無明顯影響,未見明顯嚴重不良反應。這一研究結果與右美托咪定的清醒鎮靜效應有關,被娩出后新生兒有著被刺激時自然喚醒的可能。實驗組患者新生兒臍帶血血氣分析中的pH、PaCO2、PaO2、SaO2與對照組患者比較差異無統計學意義,兩組患者的血氣分析相似,提示麻醉誘導前靜脈泵注右美托咪定不影響新生兒的胎盤血流,不影響胎兒氧供。這與研究結果中新生兒Apgar評分相同的結果一致。這一研究結果與韓傳寶等[6]的研究結果一致。本次研究結果表明,全麻剖宮產患者術前泵注右美托咪定對新生兒無不良影響。
3.3結論
綜上所述,全麻剖宮產患者術前泵注右美托咪定有利于穩定母體的血流動力學,減弱患者的應激反應,同時對新生兒無不良影響。
[1]張洋,潘道波.鹽酸右美托咪定的藥理作用及其在全身麻醉中的應用[J].醫學臨床研究,2011,28(3):535-538.
[2]Nguyen J,Nacpil N.A comparison between dexmedetomidine and propofol on extubation times in postoperative adult cardiac surgery patients: a systematic review protocol[J/OL].JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep,2016,14(11):63-71.
[3]Bajwa S J,Gupta S,Kaur J,etal.Reduction in the incidence of shivering with perioperative dexmedetomidine: a randomized prospective study[J].J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol, 2012,28(1):86-91.
[4]Li Z,Tian M,Zhang C Y,etal.A randomised controlled trial to evaluate the effectiveness of intrathecal bupivacaine combined with different adjuvants (fentanyl,clonidine and dexmedetomidine) in caesarean section[J].Drug Res(Stuttg),2015,65(11):581-586.
[5]徐鵬,冉菊紅,楊華東.右美托咪定應用對子癇前期剖宮產術麻醉效果及安全性[J].中國婦幼健康研究,2016,27(6):765-767.
[6]韓傳寶,蔣秀紅,于力,等.全麻剖宮產術中右美托咪定胎盤轉移及其對新生兒的影響[J].中華麻醉學雜志,2016,36(4):488-490.
[專業責任編輯:陳 寧]
Effects of preoperative infusion of dexmedetomidine on stress response and hemodynamics of patients undergoing cesarean section under general anesthesia
SONG Qiang1, SONG Hai-xia2, BIAN Hong-chun1, GAO Cheng-jie1
(1.GeneralHospitalofJinanMilitaryArea,ShandongJinan250031,China; 2.LinquCountyNineMountainCentralHospital,ShandongWeifang262608,China)
ObjectiveTo observe the effects of preoperative infusion of dexmedetomidine on stress response and hemodynamics of patients undergoing cesarean section under general anesthesia.MethodsA total of 60 cases undergoing cesarean section under general anesthesia from August 2014 to July 2016 in General Hospital of Jinan Military Area were selected, and they were divided into experimental group and control group according to random number table method with 30 patients in each group. Patients in the experimental group were intravenously pumped with 0.8μg/(kg·h) of dexmedetomidine at 20mins before induction of general anesthesia, and patients in the control group were intravenously pumped with 0.8μg/(kg·h)of normal saline at 20mins before induction of general anesthesia. Heart rate and mean arterial blood pressure before drug infusion, at 20mins after infusion, at tracheal intubation, skin incision, fetal disengagement, and 10min after extubation were recorded. After delivery of fetus, the Apgar score of newborns at 1min and 5mins were recorded, and umbilical vein blood was extracted for blood gas analysis.ResultsThere was no significant difference in age, height and weight of patients, fetal dissection time, birth weight, gestational age and anesthesia time between two groups (allP>0.05). There was no significant difference in heart rate and mean arterial blood pressure before drug infusion between two groups (tvalue was 0.000 and 0.701, respectively, bothP>0.05). Heart rate of patients in the experimental group was significantly lower than that in the control group at 20min and later time points after drug administration, and differences were statistically significant (tvalue was -9.874, -9.548, -7.789, -8.886 and -12.241, respectively, allP<0.05). Mean arterial pressure in the experimental group was significantly lower than that in the control group at 20min and later time points after pumping of drug, and differences had statistical significance (tvalue was -4.747, -6.111, -6.393, -5.720 and -4.562, respectively, allP<0.05). Differences in PH, PaCO2, PaO2and SaO2in neonatal umbilical cord blood gas analysis were not significant between two groups (t value was 1.711, -1.603, -1.019 and -0.771, respectively, allP>0.05). There was no significant difference in the Apgar scores of newborns at 1min and 5mins after birth between two groups (t=0.000,P>0.05).ConclusionPump infusion of dexmedetomidine before operation is beneficial for maternal hemodynamics in patients undergoing cesarean section under general anesthesia. It can reduce patient’s stress response, and no adverse effects is made on newborns.
general anesthesia; cesarean section; dexmedetomidine; stress response
2017-01-06
宋 強(1982—),男,住院醫師,主要從事臨床麻醉工作。
高成杰,主任醫師。
10.3969/j.issn.1673-5293.2017.09.038
R719.8
A
1673-5293(2017)09-1154-03

