SIRT1基因的rs2273773和rs7895833突變與漢族人群冠狀動脈疾病風險相關性分析
韓巧君,韓海榮,鄒大進,連士杰,吳 惠,徐洪濤
·基因組學·
SIRT1基因的rs2273773和rs7895833突變與漢族人群冠狀動脈疾病風險相關性分析
韓巧君,韓海榮,鄒大進,連士杰,吳 惠,徐洪濤
目的 旨在調查漢族人群冠狀動脈疾病患者SIRT1基因rs2273773和rs7895833的單核苷酸多態性。方法 共納入77例冠狀動脈疾病患者和80例對照者。所有冠狀動脈疾病患者通過血管造影術確診。通過巢式聚合酶鏈反應測定SIRT1基因rs2273773和rs7895833多態性的基因分型。結果 發現在中國漢族人群中,冠狀動脈疾病患者和對照組SIRT1基因rs2273773和rs7895833的基因型頻率差異無統計學意義(P>0.05)。本研究人群具有相比于發表的荷蘭人群rs7895833的顯著不同的等位基因頻率。結論 SIRT1基因遺傳變異體rs2273773和rs7895833與中國漢族人群冠狀動脈疾病無關。
冠狀動脈疾病;巢式聚合酶鏈式反應;單核苷酸多態性;SIRT1基因
心臟病如冠狀動脈疾病(coronary artery disease,CAD)的患病率隨年齡增加而增加[1]。在老年動物的心肌中經常觀察到凋亡和壞死的增加、肌細胞核的增殖、肌細胞體積的增加和結締組織的積累[2]。Sir2蛋白近年來引起了很多關注,因為它在釀酒酵母中與熱量限制下的壽命延長有關[3]。哺乳動物中,在Sir2蛋白家族中有7個成員,稱為sirtuins(SIRT)。其中,SIRT1蛋白是酵母Sir2蛋白最接近的同源物[4]。SIRT1蛋白是一種能促進細胞調節的蛋白質脫乙酰酶。SIRT1蛋白具有許多生物學功能,包括轉錄調節、細胞分化抑制、細胞周期調節和抗細胞凋亡。SIRT1蛋白還具有保護心臟作用。Alcendor等[5]研究顯示,SIRT1蛋白是無血清培養基培養心肌細胞中細胞存活的重要因子,抑制凋亡、減少氧化應激[6]。此外,Kao等[7]發現SIRT1蛋白表達在老化和動脈粥樣硬化血管中減少,并且在內皮細胞中顯著減少。用SIRT1基因的激活劑白藜蘆醇可以有效地阻止H2O2處理過的人類臍靜脈內皮細胞的衰老過程。白藜蘆醇的抗氧化應激和抗衰老作用可以在H2O2處理過的人臍靜脈內皮細胞中通過SIRT1基因抑制逆轉。
鮮見關于SIRT1基因rs2273773和rs7895833多態性的分布或這些基因多態性與CAD發展風險的關聯文獻。因此,作者調查在中國漢族人群的冠狀動脈疾病中這2種常見的SIRT1基因變異體。
1 資料與方法
1.1 研究對象 選取2010年在第二軍醫大學長海醫院住院的77例CAD患者為研究組,通過血管造影證實其中至少一個主要冠狀動脈顯示>50%的狹窄。對照受試者包括145例常規體檢人員,將具有心肌梗死和腦血管疾病史的受試者排除,通過結構式問卷和心電圖排除亞臨床CAD的可能性,最后選取80例作為對照組。所有受試者在納入研究之前均知情同意。采用標準問卷從所有受試者收集關于種族、病史、有無糖尿病以及血脂異常和當前用藥情況。所有研究對象都是中國漢族公民。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 實驗室檢查 通過標準實驗室程序測量臨床和生物化學指標。在不同時間間隔測量收縮壓>140 mmHg和(或)舒張壓>90 mmHg,目前服用抗高血壓藥物的受試者被認為有高血壓。使用標準酶法測量總膽固醇、低密度脂蛋白膽固醇、高密度脂蛋白膽固醇和三酰甘油水平。受試者中糖尿病定義為空腹血糖水平>7 mmol/L,或者有使用抗糖尿病藥物史的患者;如果總膽固醇濃度>6.2 mmol/L和(或)其三酰甘油濃度>2.3 mmol/L,則將定義為血脂異常。2組相關資料見表1。

表1 研究人群相關資料
1.2.2 遺傳分析 使用DNA提取試劑盒[SK1261,(上海)Sangon公司]從外周血中提取基因組DNA。
通過使用正向引物(5′-TGTAGGTGTGTGTCGCA TCC-3′)和反向引物(5′-TAATGCTTTATCTCCACTTC TCG-3′)的巢式聚合酶鏈反應(nested polymerase chain reaction,nPCR)擴增含有主要單核苷酸多態性rs2273773的部分DNA序列(95℃5 min;然后95℃30 s、66℃30 s、72℃1 min,20個循環;再95℃30 s、58℃30 s、72℃1 min,20個循環;最后在72℃進行最終延伸步驟6 min;保持在4℃)。然后正向引物(5′-GCGGT CCCAAAAGGGTCAGTCCCAGGGTTCAACAAATCTATG-3′)和反向引物(5′-GCGGTCCCAAAAGGGTCAGTGC TTCCTAATCTCCATTACGTCGA-3′(95℃5 min;然后95℃25 s、66℃25 s、72℃40 s,20個循環;再95℃30 s、68℃1 min,20個循環;最后在72℃進行最終延伸步驟6 min;保持在4℃)。15 μL PCR混合物含有終濃度為50 pmol/μL的引物、25 mmol/L MgCl2、2.5 mmol/L的4種堿基脫氧核糖核苷三磷酸和5 U/ μL Taq聚合酶。將模板DNA(0.5 μL)引入外部反應混合物中。將0.1 μL外部PCR產物引入15 μL內部擴增混合物中。PCR產物在37℃下通過MboⅠ限制性內切核酸酶消化過夜,得到144 C等位基因的44、140 bp片段,以及144 T等位基因的非消化184 bp片段。通過在4%高分辨率瓊脂糖凝膠上使用1×Tris-硼酸緩沖液在150 V電泳分離DNA片段。最后在每個基因型的2個樣本中對基因型進行測序,以確認基因分型。
rs7895833使用初始擴增的正向引物(5′-TACC TCCCACTATACACACTCCA-3′)和反向引物(5′-TGA CTAGACAGGGCAGGATAAC-3′)、內部正向引物(5′-GCGGTCCCAAAAGGGTCAGTCCCAGGGTTCAACAAA TCTATG-3′)和反向引物5′-GCGGTCCCAAAAGGGT CAGTGCTTCCTAATCTCCATTACGTCGA-3′),用于在63℃的退火溫度下進行第2輪擴增。
1.3 統計學處理 應用SPSS 16.0軟件,分類數據比較采用χ2檢驗,數值組間比較采用Student’s t檢驗,通過Hardy-Weinberg平衡測試基因型的分布,P<0.05為差異有統計學意義。
2 結果
2.1 rs2273773和rs7895833多態性 研究組與對照組SIRT1基因的rs2273773和rs7895833多態性差異無統計學意義(P>0.05,表2),rs2273773和rs7895833多態性的分布和等位基因頻率見表2。2組基因型的分布與Hardy-Weinberg平衡相一致(P>0.05,表3)。

表2 2組rs2273773和rs7895833多態性
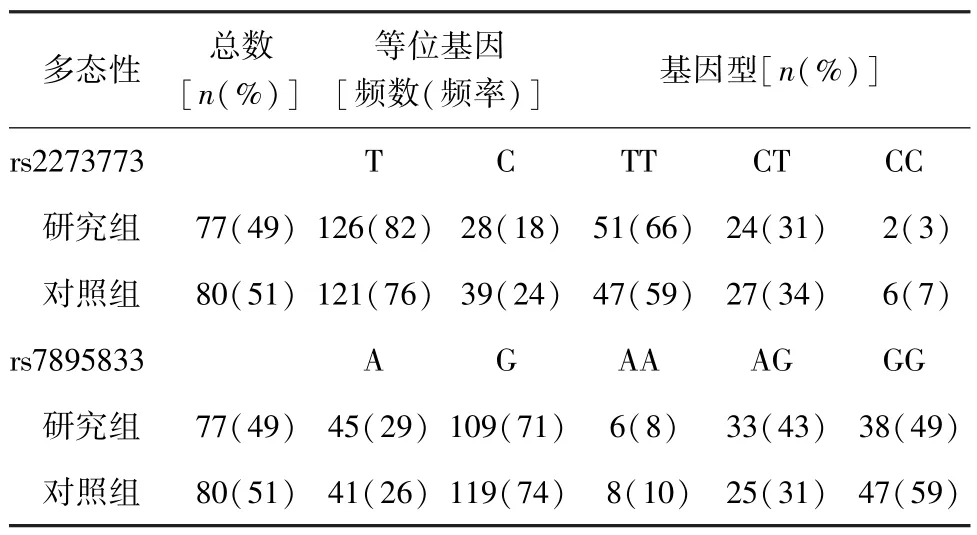
表3 2組等位基因和基因型頻率平衡定律檢驗
2.2 rs2273773和rs7895833多態性樣本電泳rs2273773和rs7895833多態性樣本的瓊脂糖凝膠電泳結果見圖1。rs2273773多態性樣本經nPCR擴增示TT、TC、CC基因型(圖1A)。rs7895833多態性樣本經nPCR擴增示AA、AG和GG基因型(圖1B)。nPCR與測序數據一致。

圖1 SIRT1基因rs2273773和rs7895833多態性樣本瓊脂糖凝膠電泳
3 討論
盡管以前的研究證明,SIRT1蛋白在心臟和動脈粥樣硬化血管中發揮作用[6-8]。本研究表明,SIRT1基因遺傳變異(rs2273773和rs7895833)與漢族人群中的CAD不相關,但本組小樣本量可能是一個原因,不能排除存在真正的關聯。SIRT1蛋白屬于煙酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸依賴性組蛋白脫乙酰酶的SIRT蛋白家族。在低等生物體如酵母、蒼蠅、蠕蟲中,沉默信息調節劑Sir2蛋白與長壽相關[9-10],在熱量限制后延長壽命[11-13]。SIRT1蛋白位于細胞核和細胞質中[14],與Sir2蛋白共享催化結構域[15]。研究表明,具有SIRT1的心臟特異性過表達轉基因小鼠表現出延遲衰老和對抗心臟氧化應激的保護[6]。在具有SIRT1的心臟特異性過表達轉基因小鼠中,SIRT1的低(2.5倍)至中度(7.5倍)過表達減少了年齡依賴性增長的心臟肥大、心肌細胞凋亡/纖維化[8]。在少量的人體研究中,單核細胞SIRT1蛋白表達在穩定的CAD和急性冠狀動脈綜合征患者中減少[16]。有研究觀察到SIRT1基因的遺傳變異與體重指數、肥胖風險、代謝反應、身體脂肪和血壓有關[17-20]。rs7895833的次要等位基因與6 251例老年受試者的低體重指數相關[17]。對1 279例日本人的研究顯示,攜帶rs7895833的A等位基因和rs2273773的T等位基因是男性肥胖的高危因素,而女性攜帶rs7895833的A等位基因、男性攜帶rs2273773的C等位基因是其高血壓的高危因素,此外攜帶rs2273773的T等位基因是男性高血糖的高危因素[20]。另一104例研究中,SIRT1基因rs1467568和rs7895833在南非印第安人與早期發病的冠狀動脈疾病相關[21]。
已知rs2273773(T/C,次要等位基因頻率=0.311,中國北京漢族人)及rs7895833(G/A,次要等位基因頻率=0.267,中國北京漢族人)(http:// www.hapmap.org),rs2273773是同義單核苷酸多態性(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/snp)。本研究顯示與上述相似的次要等位基因頻率結果。然而,荷蘭人群中rs7895833的“主要”等位基因是中國漢族人群的“次要”等位基因;根據6 251例老年荷蘭人群研究,rs7895833的G等位基因頻率為0.20[17]。本研究中,rs7895833的G等位基因頻率為0.71(表3),與文獻報道一致[20]。
目前不清楚SIRT1基因激活是否能作用于人體,由于潛在的多效性和組織依賴性生理功能,有人擔心廣義SIRT1基因活化也可能造成早衰或不利于健康。
總之,SIRT1基因遺傳變異體rs2273773和rs7895833與中國漢族人群的CAD無關。rs7895833的次要等位基因頻率不同于荷蘭人群。本研究結論應該通過大樣本重復研究來證實。
[1]Rosamond W,Flegal K,Friday G,et al.Heart disease and stroke statistics--2007 update:a report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee[J].Circulation,2007,115(5):e69-e171.
[2]Kajstura J,Cheng W,Sarangarajan R,et al.Necrotic and apoptotic myocyte cell death in the aging heart of Fischer 344 rats[J].Am J Physiol,1996,271(3 Pt 2):H1215-H1228.
[3]Kaeberlein M,Mcvey M,Guarente L.The SIR2/3/4 complex and SIR2 alone promote longevity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by two different mechanisms[J].Genes Dev,1999,13(19):2570-2580.
[4]Frye RA.Characterization of five human cDNAs with homology to the yeast SIR2 gene:Sir2-like proteins(sirtuins)metabolize NAD and may have protein ADP-ribosyltransferase activity[J].Biochem Biophys Res Commun,1999,260(1):273-279.
[5]Alcendor RR,Kirshenbaum LA,Imai S,et al.Silent information regulator 2alpha,a longevity factor and classⅢhistone deacetylase,is an essential endogenous apoptosis inhibitor in cardiac myocytes[J].Circ Res,2004,95(10): 971-980.
[6]Hsu CP,Odewale I,Alcendor RR,et al.Sirt1 protects the heart from aging and stress[J].Biol Chem,2008,389(3): 221-231.
[7]Kao CL,Chen LK,Chang YL,et al.Resveratrol protects human endothelium from H(2)O(2)-induced oxidative stress and senescence via SirT1 activation[J].J Atheroscler Thromb,2010,17(9):970-979.
[8]Alcendor RR,Gao S,Zhai P,et al.Sirt1 regulates aging and resistance to oxidative stress in the heart[J].Circ Res,2007,100(10):1512-1521.
[9]Sinclair DA,Guarente L.Extrachromosomal rDNA circles--a cause of aging in yeast[J].Cell,1997,91(7):1033-1042. [10]Blander G,Guarente L.The Sir2 family of protein deacetylases[J].Annu Rev Biochem,2004,73:417-435.
[11]Lin SJ,Defossez PA,Guarente L.Requirement of NAD and SIR2 for life-span extension by calorie restriction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae[J].Science,2000,289(5487): 2126-2128.
[12]Rogina B,Helfand SL.Sir2 mediates longevity in the fly through a pathway related to calorie restriction[J].Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2004,101(45):15998-16003.
[13]Wang Y,Tissenbaum HA.Overlapping and distinct functions for a Caenorhabditis elegans SIR2 and DAF-16/FOXO [J].Mech Ageing Dev,2006,127(1):48-56.
[14]Tanno M,Sakamoto J,Miura T,et al.Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of the NAD+-dependent histone deacetylase SIRT1 [J].J Biol Chem,2007,282(9):6823-6832.
[15]Sherman JM,Stone EM,Freeman-Cook LL,et al.The conserved core of a human SIR2 homologue functions in yeast silencing[J].Mol Biol Cell,1999,10(9):3045-3059.
[16]Breitenstein A,Wyss CA,Spescha RD,et al.Peripheral blood monocyte Sirt1 expression is reduced in patients with coronary artery disease[J].PLoS One,2013,8(1): e53106.
[17]Zillikens MC,van Meurs JB,Rivadeneira F,et al.SIRT1 genetic variation is related to BMI and risk of obesity[J]. Diabetes,2009,58(12):2828-2834.
[18]Peeters AV,Beckers S,Verrijken A,et al.Association of SIRT1 gene variation with visceral obesity[J].Hum Genet,2008,124(4):431-436.
[19]Weyrich P,Machicao F,Reinhardt J,et al.SIRT1 genetic variants associate with the metabolic response of Caucasians to a controlled lifestyle intervention--the TULIP study [J].BMC Med Genet,2008,9:100.
[20]Shimoyama Y,Suzuki K,Hamajima N,et al.Sirtuin 1 gene polymorphisms are associated with body fat and blood pressure in Japanese[J].Transl Res,2011,157(6):339-347.
[21]Ramkaran P,Phulukdaree A,Khan S,et al.Sirtuin 1 rs1467568 and rs7895833 in South African Indians with early-onset coronary artery disease[J].Cardiovasc J Afr,2016,27(4):213-217.
The relationship between the rs2273773 and rs7895833 mutations of SIRT1 gene and the risk of coronary artery disease among Han Chinese
HAN Qiaojun1,HAN Hairong2,ZOU Dajin3,LIAN Shijie1,WU Hui1,XU Hongtao1
(1.Department of Cadre Health Care,Navy General Hospital,Beijing 100048,China;2.Department of Clinical Laboratory,Guanghua Chinese and Western Medicine Hospital,Shanghai 200052,China;3.Department of Endocrine,Changhai Hospital,Second Military Medical University,Shanghai 200433,China)
Objective To investigate the single-nucleotide polymorphisms rs2273773 and rs7895833 of SIRT1 gene in patients with coronary artery disease in the Han Chinese population. Methods Seventy-seven coronary artery disease patients and 80 controls were studied in the present study.All coronary artery disease patients were confirmed by angiography.The genotyping of polymorphisms rs2273773 and rs7895833 in SIRT1 gene was determined by nested polymerase chain reaction.Results However,there was no significant difference in genotype frequencies between coronary artery disease patients and controls in the Chinese Han population.In addition,our study cohort has considerably differing allele frequencies of rs7895833 compared to the Dutch population. Conclusion The rs2273773 and rs7895833 mutations of SIRT1 gene are not associated with the risk of coronary artery disease among Han Chinese.
Coronary artery disease(CAD);Nested polymerase chain reaction(nPCR);Single-nucleotide polymorphism(SNP);SIRT1 gene
R543.3
B
2095-3097(2017)03-0147-04
10.3969/j.issn.2095-3097.2017.03.005
2017-02-25 本文編輯:徐海琴)
海軍后勤部科研課題(CHJ12L024)
100048北京,海軍總醫院干部保健科(韓巧君,連士杰,吳 惠,徐洪濤);200052上海,光華中西醫結合醫院(韓海榮);200433上海,第二軍醫大學長海醫院內分泌科(鄒大進)
徐洪濤,E-mail:xuhongtao11@tom.com
[注 明]韓巧君,韓海榮:并列第一作者

