心力衰竭患者B型鈉尿肽、可溶性ST2和白介素33水平變化及其臨床診斷價值
楊 威 韓紅彥 潘云紅 賈海珍 趙智慧 馬 麗 劉 敏
hhy2009218@163.com
?
心力衰竭患者B型鈉尿肽、可溶性ST2和白介素33水平變化及其臨床診斷價值
楊威韓紅彥*潘云紅賈海珍趙智慧馬麗劉敏
hhy2009218@163.com
【摘要】目的:分析心力衰竭(HF)不同心功能分級患者B型鈉尿肽(BNP) 和可溶性人基質裂解素(sST2)、白細胞介素-33(IL-33)的血清水平變化及其與HF的關系,以及對HF的臨床診斷價值。方法:211例HF患者(HF組)分別測定血清BNP、sST2、IL-33水平,并參照紐約心臟病協會(NYHA) 心功能分級標準,將HF患者分為Ⅰ級(n=57)、Ⅱ級(n=96)、Ⅲ級(n=45)和Ⅳ級(n=13),另選同期體檢健康者共75例作為對照組。統計分析HF組與對照組、HF患者不同心功能分級間BNP、sST2 和IL-33的水平差異;logistic回歸分析HF危險因素;ROC曲線分析BNP、sST2對HF的診斷價值。結果:與對照組相比,HF組BNP和sST2水平明顯升高(P<0.01),IL-33水平明顯降低(P<0.01)。隨著NYHA分級增加,HF患者血清中sST2和BNP水平也增加(P<0.05)。單因素回歸分析顯示上述三指標與HF相關性有統計學意義(P均<0.01);而多因素回歸分析顯示只有BNP為HF的獨立危險因素(P<0.01)。ROC結果表明,sST2診斷HF的ROC曲線下面積明顯高于BNP,分別為0.920 Vs 0.890(P<0.05),診斷價值優于BNP。 結論:正確選擇應用有關生化標志物對篩選HF影響因素和診斷HF有重要臨床實踐意義。
【關鍵詞】心力衰竭;B型鈉尿肽;可溶性人基質裂解素;白細胞介素33
心力衰竭(簡稱心衰,HF)是由多種病因導致的一種復雜的心功能不全臨床綜合征。雖然HF的治療已經取得很大進步,但HF患者5年病死率仍可高達50%[1]。臨床上HF的癥狀和體征特異性較差,超聲心動圖、X 線及有創血流動力學檢查有其局限性,相關生化標志物的檢測已被臨床廣泛接受,并據此采取積極治療方案,如B型鈉尿肽(BNP)業已廣泛應用于HF的鑒別診斷、風險評估、預后判斷和危險分層;可溶性人基質裂解素(sST2,IL-1受體家族成員之一,一種新的心血管炎癥標志物)及其配體白細胞介素-33(IL-33),已被國外研究證實與心肌重構和HF診斷密切相關,表現為sST2水平升高、IL-33水平降低[2,3,11,13-16],但國內對這一對標志物的研究較少。因此,本文檢測分析國人HF患者血清BNP、sST2和IL-33水平變化及其與HF心功能分級的關系,以及該3個指標診斷HF的臨床價值。
1資料與方法
1.1研究對象和分組
選取2013-07-2015-07在本院確診為HF且住院患者211例(HF組),并依據紐約心臟病協會(NYHA)心功能分級標準[4]將患者分為Ⅰ級(n=57)、Ⅱ級(n=96)、Ⅲ級(n=45)、Ⅳ級(n=13),另選取同期健康體檢者作為對照組(n=75),兩組年齡、性別和BMI分布差異無統計學意義(P>0.05,表1)。HF患者納入標準:(1)參照2012年歐洲心臟病學會(ESC)《急慢性心力衰竭臨床治療指南》[5],并結合患者癥狀、體征、超聲心動圖及胸片明確診斷者;(2)性別不限,年齡>18歲,HF病因包括冠心病、高血壓性心臟病、心肌病及瓣膜性心臟病者。排除入院時確診為急性冠狀動脈綜合征、腫瘤及肺動脈栓塞者(多次住院患者以第一次入院診斷為準)。所有入選患者均簽署知情同意書,其伴隨病癥、臨床治療情況以及入院48h內超聲心動圖檢查結果如表1。
1.2檢測指標及方法
1.2.1超聲心動圖檢查
使用德國西門子SON05500型彩色超聲心動圖儀,采用美國超聲心動圖協會推薦的測量方法,取左室長軸面的超聲圖像測定心臟各項指標,即左心室射血分數(LVEF)、左房內徑(LAD)、左室內徑(LVDD)、右房內徑(RAD)、右室內徑(RVDD)、升主動脈內徑(AO)、肺主動脈內徑(PA)、室間隔厚度 (IVST)、 左室后壁厚度(LVPWT)等。所有測量都在不同掃查中重復3次。

表1 HF患者一般資料
1.2.2生化標志物檢測
所有對象均于入院當天采肘部靜脈血3-5ml,置入無抗凝管中,所有標本均無明顯脂血、溶血和黃疸。以3 000r/min離心10min,取血清分裝于凍存管中,-80℃冰箱中保存待批檢。從冰箱中取出標本,室溫解凍。采用化學發光免疫法測定BNP濃度,試劑盒由美國Beckman公司提供,測量范圍2.0-5 000pg/ml,批內變異系數<6.5%,批間變異系數<9.5%;酶聯免疫吸附法測定sST2濃度,試劑盒由上海blue gene公司提供,測量范圍0-10ng/L,批間及批內變異系數均<10%;酶聯免疫吸附法測定IL-33濃度,試劑盒由美國ebioscience公司提供,測量范圍0-500pg/L。所有血標本平均儲藏時間≤8個月。
1.3統計學處理
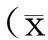
2結果
2.1HF患者血清BNP、sST2、IL-33水平
與對照組相比,HF組BNP和sST2水平明顯升高(u=6.315,P<0.01;t=3.016,P<0.01),IL-33水平明顯降低(t=4.257,P<0.01)。見表2。

表2 HF患者BNP、sST2和IL-33血清水平
注:與對照組比較,1)P<0.01
2.2血清BNP、sST2和IL-33水平及與NYHA分級的線性回歸分析
方差分析顯示,NYHA分級HF患者血清BNP和sST2水平差異有統計學意義(P均<0.01)。而IL-33水平差異無統計學意義(P>0.05)。見表3。
單因素回歸分析顯示,BNP (OR 0.936)、sST2(OR 0.519)、IL-33(OR 1.191)與HF分級相關性均有統計學意義(P<0.01)。經校正可能影響HF混雜因素后的多因素回歸分析結果表明,影響HF的獨立危險因素只有BNP(OR 0.953,P<0.01);sST2(OR 0.504)、IL-33(OR 0.002)為非獨立因素(P>0.05)。見表4。

表3 不同心功能分級HF患者BNP、sST2、IL-33水平
注:與Ⅰ級比較,1)P<0.01,與Ⅱ級比較,2)P<0.01,與Ⅲ級比較,3)P<0.01

表4 單因素和多因素logistic回歸分析結果
2.3血清sST2和BNP對HF的診斷價值
血清sST2和BNP診斷HF的ROC曲線下面積分別為0.920(95%CI:0.890-0.951)和0.890(95%CI:0.853-0.927),sST2略優于BNP(P<0.05)。血清BNP診斷心衰的最佳Cut-off值為435 pg/ml時,對應的靈敏度和特異度分別為0.822和0.765;血清sST2診斷心衰的最佳Cut-off值為4.76ng/ml時,對應的診斷靈敏度和特異度分別為0.773和0.881,前者靈敏度較高,后者特異度較高。見圖1。
3討論
已有研究顯示,多種生化標志物聯合檢測可以提高心血管疾病死亡危險分層的準確性[6]。BNP、sST2和IL-33同屬于反映心肌負荷狀況的生化標志物,能夠明確診斷HF、提示危險分層和預后信息,也是潛在的治療靶標[7]。

圖1 sST2和BNP診斷心力衰竭的ROC曲線
BNP具有排鈉、利尿和舒張血管作用,其水平增加是心功能不全時機體的代償機制之一,有助于診斷HF;同時也是HF患者預后不良的獨立預測因子[8]。美國心臟學會(AHA)/美國心臟病學會(ACC)[9]、歐洲心臟病學會(ESC)[5]和中國HF診斷治療指南[10]均肯定了其對HF診斷的價值。ST2是IL-1R家族成員,分為可溶性ST2(sST2)和跨膜形式的ST2(ST2L)。sST2作為一種新的心臟標記物,與心肌成纖維細胞的激活及心肌重塑有關。2013年美國心臟病學基金會學會(ACCF)/美國心臟學會(AHA)心衰指南[11]明確指出,sST2水平不僅可以預測HF患者的住院率和死亡率,并且與BNP和半乳凝集素(Galectin-33)一并對評估患者預后有重要價值。sST2的優勢是診斷HF的準確性不受腎功能、肥胖指數、年齡等因素影響[12]。IL-33是sST2的功能配體,由拉伸的成纖維細胞分泌,具有抗心肌細胞肥大作用,在血管炎癥和動脈粥樣硬化等心血管疾病的病理生理過程中發揮重要作用[13,14];IL-33被sST2競爭性結合后,與ST2L結合減少,無法進入心臟保護信號轉導通路,防止心肌細胞死亡、心肌組織纖維化和HF的進展[15,16]。
本文結果表明,與對照組相比,HF組BNP、sST2水平升高,IL-33水平降低。隨著NYHA心功能分級增加,HF患者血清BNP和sST2水平升高,而IL-33水平變化無統計學差異。單因素回歸分析顯示,BNP、sST2、IL-33與HF具有相關性,但校正可能影響HF的混雜因素后,BNP成為HF的獨立危險因素,但從診斷價值而言,sST2比BNP更有優勢。因此sST2作為新的診斷HF特異性較高的標志物,不僅可與血清BNP和IL-33一同用于診斷HF嚴重程度,還可為HF預后提供更多信息,或將成為進一步研究的重要方向。
?
楊威(1988-),男,漢族,碩士研究生,主要從事心血管疾病的臨床診療
參考文獻
1Eugene B. The war against heart failure: the Lancet lecture[J]. Lancet,2015,385(9970):812-824.
2Zhang RC,Zhang YH,Zhang J,et al. The prognostic value of plasma soluble ST2 in hospitalized Chinese patients with heart failure[J]. Plos one, 2014, 9(10):1-9.
3Karolina W, Tadeusz P, Agata S, et al. Soluble ST2 protein in chronic heart failure is independent of traditional factors[J]. Arch Med Sci, 2013,9(1): 21-26.
4Yancy CW , Jessup M , Bozkurt B,et al.2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure[J].J Am Coll Cardiol,2013,62 (16):147-239.
5McMurray JJ , Adamopoulos S , Anker SD, et al. ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2012[J]. Eur J Heart Fail,2012,14 (8): 803-69.
6Zethelius B, Berglund L, Sundstrtim J, et al.Use of multiple biomarkers to improve the prediction of death from cardiovascular causes[J]. N Engl J Med,2008,358(20):2 107-2 116.
7Braunwald E.Biomarkers in heart failure[J].N Engl J Med,2008,358(20):2 148-2 159.
8Januzzi JL, Trough T. Are serial BNP measurements useful in heart failure management serial natriuretic peptide measurements are useful in heart failure management[J] .Circulation,2013,127 (4): 500 -507.
9Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, et al. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the manage-ment of heart failure: a report of the American college of cardiology foundation/american heart association task force on practice guidelines[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol,2013,62(16):147-239.
10中華醫學會心血管病學分會,中華心血管病雜志編輯委員會.慢性心力衰竭診斷治療指南[J].中華心血管病雜志,2007(12):1 076-1 095.
11Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, et al. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure[J]. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 2013, 62(16):e147-239.
12Bartunek J,Delrue L,Van Durme F,et al.Nonmyocardial production of ST2 protein in human hypertrophy and failure is related to diastolic load[J].J Am Coll Cardiol,2008,52( 25):2166-2174.
13Foks AC, Lichtman AH, Kuiper J. Treating atherosclerosis with regulatory T cells[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2015,35(2):280-287.
14Miller AM,Liew FY.The IL-33/ST2 pathway-a new therapeutic target in cardiovascular disease[J].Pharmacology & Therapeutics,2011,131 (2) :179-186.
15Villarreal DO, Weiner DB. Interleukin 33: a switch-hitting cytokine[J]. Curr Opin Immunol, 2014,28:102-106.
16Bartunek J, Delrue L, Van Durme F, et al. Nonmyocardial production of ST2 protein in human hypertrophy and failure is related to diastolic load[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2008,52(25): 2166-74.
Clinical Research about B-brain Natriuretic Peptide,Soluble ST2 and Interleukin 33 in Patients with Heart Failure
YANG Wei, HAN Hong-yan*,PAN Yun-hong,JIA Hai-zhen,ZHAO Zhi-hui,MA Li,LIU Min
Department of Cardiology,Tianyou Hospital Affiliated to Wuhan University of Science and Technology,Wuhan 430060,China;*Corresponding author
【Abstract】Objective: To analyze heart failure (HF) patients with different heart function classification B-brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) and soluble matrix cracking element (sST2), interleukin 33(IL-33),analysis of the three myocardial cell stress biomarkers with the relationship between HF and the clinical diagnostic value.Method: 211 patients with HF group (HF) were determined serum BNP, sST2, IL-33 level, and with reference to the New York heart association (NYHA) cardiac function grading HF patients divided into Ⅰ level (n=57), Ⅱ level (n=96), Ⅲ level (n=45), Ⅳ level (n=13), the other to choose the healthy physical examination, a total of 75 cases for the same period as the control group.Statistical analysis of HF group and control group, patients with HF BNP, sST2 between different cardiac function classification and the levels of IL-33 difference;Logistic regression analysis of risk factors for HF, ROC curve analysis the BNP, sST2 value to the diagnosis of HF.Results: Compared with control group, the BNP and the sST2 level HF group in were increased significantly (P<0.01), IL-33 level significantly decreased (P<0.01).With the increase of NYHA classification, Serum sST2 and BNP level in HF patients were increased (P<0.05).Single factor regression analysis showed that the above three indicators and HF correlation was statistically significant (P<0.01), and multiple factors regression analysis showed that only the BNP as independent risk factors for HF (P<0.01).ROC results show that sST2 diagnosis of HF area under the ROC curve was slightly higher than that of the BNP, 0.920 Vs. 0.890 respectively (P<0.05), and superior value to diagnosis the BNP.Conclusion: Proper application on biochemical markers for screening of HF influence factors and diagnosis of HF has important clinical significance.
【Key words】Heart failure;B-brain natriuretic peptide;Soluble ST2;Interleukins 33
作者簡介:本文第一
[中圖分類號]R541
[文獻標識碼]A
[文章編號]1005-1740(2016)01-0045-05
本文2015-10-28收到,2015-12-15修回

