聚馬來酸酐對(duì)設(shè)施土壤微生物生物量碳、氮及土壤呼吸速率的影響
喬潔+張春丹+韓曉光
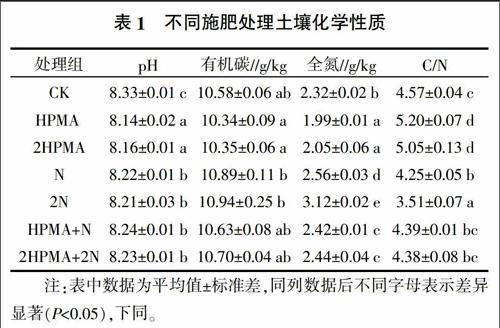
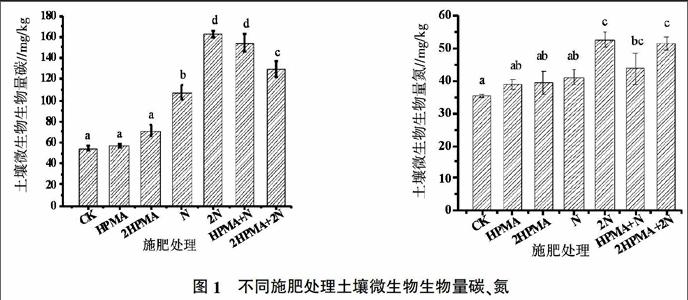
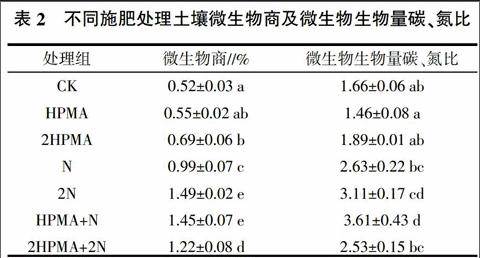
摘要:研究聚馬來酸酐對(duì)設(shè)施土壤有機(jī)碳、 全氮、土壤微生物生物量碳、生物量氮及土壤呼吸速率的影響。結(jié)果表明,單施氮肥、聚馬來酸酐氮肥配施均顯著提高了土壤微生物生物量碳、氮含量與土壤呼吸速率強(qiáng)度。單施聚馬來酸酐顯著提高土壤C/N,對(duì)土壤微生物生物量碳、氮與土壤呼吸速率無顯著影響。土壤微生物生物量碳、氮及土壤呼吸速率與土壤有機(jī)碳、全氮呈極顯著(P<0.01)或顯著相關(guān)關(guān)系(P<0.05)。與聚馬來酸酐氮肥配施處理相比,單施氮肥對(duì)土壤微生物生物量碳、氮以及土壤呼吸速率無顯著影響。氮肥配施適量的聚馬來酸酐對(duì)提高設(shè)施土壤肥力、改善設(shè)施土壤質(zhì)量效果最好。土壤微生物生物碳、氮及土壤呼吸速率可反映土壤質(zhì)量的變化,作為評(píng)價(jià)設(shè)施土壤肥力的指標(biāo)。
關(guān)鍵詞:聚馬來酸酐;設(shè)施土壤;土壤微生物生物量碳;土壤微生物生物量氮;土壤呼吸速率
中圖分類號(hào):S154.3 ? ? ? ?文獻(xiàn)標(biāo)識(shí)碼:A ? ? ? ?文章編號(hào):0439-8114(2015)23-5877-04
DOI:10.14088/j.cnki.issn0439-8114.2015.23.020
Effects of PMA on Soil Microbial Biomass Carbon, Soil Microbial Biomass Nitrogen and Soil Respiration Rate in Greenhouse Soil
QIAO Jie1,2, ZHANG Chun-dan1, HAN Xiao-guang1
( 1. College of Life Science, Langfang Teachers College, Langfang 065000, Hebei, China;
2. Edible and Medicinal Fungi Research and Development Center of Hebei Universities, Langfang 065000, Hebei, China)
Abstract: Effect of poly maleic anhydride (PMA) on soil organic carbon, total nitrogen, microbial biomass carbon, microbial biomass nitrogen and soil respiration rate were studied in green house. The results showed that the application of nitrogen fertilizers and the mixture of PMA and nitrogen fertilizers could enhance the quantity of microbial biomass carbon, microbial biomass nitrogen and the intensity of soil respiration rate. The application of PMA increased the quantity of soil C/N, but had no significant effect on microbial biomass carbon, microbial biomass nitrogen and soil respiration rate. The correlation between soil organic carbon, total nitrogen and microbial biomass carbon, microbial biomass nitrogen and soil respiration rate were significantly (P<0.05) or highly significant (P<0.01).Compared with the application of the mixture of PMA and nitrogen fertilizers, the application of nitrogen fertilizers had no significant effect on microbial biomass carbon, microbial biomass nitrogen and soil respiration rate. So the application of the mixture of nitrogen fertilizers with an appropriate amount of PMA could improve the greenhouse soil fertility and quality. Microbial biomass carbon, microbial biomass nitrogen and soil respiration rate could reflect the change of greenhouse soil fertility and value greenhouse soil quality.
Key words: Poly maleic anhydride; greenhouse soil; soil microbial biomass carbon; soil microbial biomass nitrogen; soil respiration rate
土壤微生物量是植物營養(yǎng)物質(zhì)的源和庫,代表土壤養(yǎng)分的活性部分,作為評(píng)價(jià)土壤質(zhì)量的生物學(xué)指標(biāo),對(duì)土壤培肥、作物栽培等實(shí)踐有重要的參考價(jià)值。土壤呼吸速率和微生物代謝商是土壤微生物量的大小和活性指標(biāo),可較好的反映土壤環(huán)境質(zhì)量變化。Doran等[1]認(rèn)為微生物量碳、微生物量氮、礦化氮、土壤呼吸速率、微生物商等是反映土壤質(zhì)量的基本指標(biāo)。有研究表明,設(shè)施農(nóng)業(yè)雖然提高了作物產(chǎn)量,但是容易導(dǎo)致土壤表層發(fā)生次生鹽漬化,致使土壤質(zhì)量惡化,最終影響作物的產(chǎn)量和品質(zhì)[2]。設(shè)施土壤性質(zhì)的改變會(huì)導(dǎo)致有益微生物減少,破壞土壤生物平衡,影響土壤養(yǎng)分利用和植物吸收。近年來有關(guān)高聚物作為土壤改良劑的研究引起了國際上的廣泛關(guān)注。向鹽堿地中施入高聚物土壤改良劑能夠改善土壤結(jié)構(gòu),加快土壤排鹽效果,提高鹽堿地的生產(chǎn)能力[3],高聚物土壤改良劑對(duì)土壤質(zhì)量、作物生長有一定的影響[4,5]。……

