基于VSMB模型的灌溉水損耗模擬研究
周鴻文+翟祿新+呂文星+劉東旭
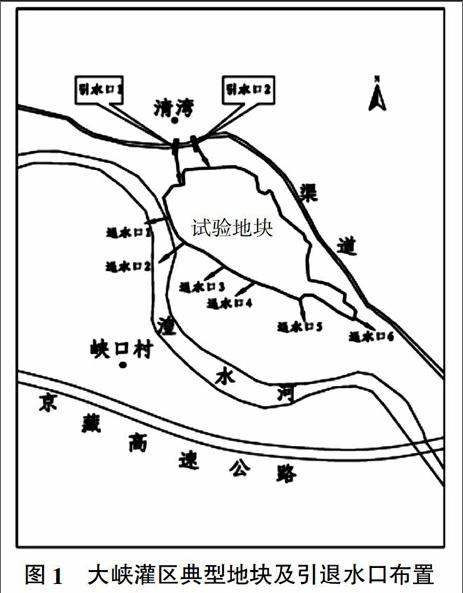

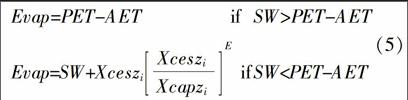
摘要:在青海省大峽灌區典型地塊內挖掘5眼地下水觀測井,開展農田灌溉水下滲及對地下水動態的影響研究,同時在大峽灌區典型地塊布置2個土壤含水量監測點,采用TDR300土壤水分速測儀分別對10、30、50、70 cm 4種深度土壤含水量進行監測。在此基礎上,運用VSMB模型對青海省黃河谷地大峽灌區灌溉用水損耗進行模擬,其中包括土壤含水量、實際蒸散、下滲、徑流、地下水埋深等。結果表明,大峽灌區典型地塊2013年3月1日至4月30日和8月1日至9月30日2個時段通過土壤蒸發和作物蒸騰消耗水量分別占灌溉與降水總量之和的46.4%和24.1%,滲漏量分別占灌溉與降水總量之和的30.3%和60.6%。大峽灌區2個時段地下水埋深的模擬結果的均方根誤差分別為92.3 mm和27.7 mm。說明模擬結果具有一定的可信度。
關鍵詞:VSMB模型;灌溉水損耗;土壤水分平衡;灌區;青海省
中圖分類號:TV138 ? ? ? ?文獻標識碼:A ? ? ? ?文章編號:0439-8114(2015)23-5866-06
DOI:10.14088/j.cnki.issn0439-8114.2015.23.018
Simulation Study on the Irrigation Water Loss Based on the VSMB Model
ZHOU Hong-wen1,ZHAI Lu-xin2,L?譈 Wen-xing1,LIU Dong-xu1
(1. Yellow River Institute of Hydrology and Water Resources, Zhengzhou 450004, China;
2.College of Environment and Resources, Guangxi Normal University, Guilin 541004, Guangxi, China)
Abstract: The farmland irrigation water infiltration and its effects on the groundwater dynamic were studied through setting up and supervising 5 groundwater wells in Daxia irrigation area of Qinghai province, moreover 2 soil moisture monitoring sites were set up in two typical plots, and the soil moisture at four kinds of depth(10 cm,30 cm,50 cm and 70 cm) was monitored by TDR300. On this basis,the VSMB model was used to study the irrigation water loss in the irrigation area of Yellow River valley of Qinghai province, including soil moisture content,the actual evapotranspiration, infiltration, runoff, groundwater buried depth and so on. The results showed that the water consumption caused by soil evaporation and crop transpiration accounted for 46.4% and 24.1% of the total precipitation plus irrigation, respectively, and the leakage occupied 30.3% and 60.6% of it separately, during two periods March 1st to April 30th, and August 1st to September 30th in 2013. The root-mean-square error of the simulation results of the groundwater depth in Daxia irrigation area during the two periods were 92.3 mm and 27.7 mm respectively. It indicated that the simulation results have certain credibility.
Key words: VSMB model; irrigation water loss; soil water balance; irrigation area; Qinghai province
青海省水資源豐富,多年平均水資源總量為629.3億m3,但區域降水稀少,時空分配不均,黃河一級支流湟水流域水資源總量只占全省的3.5%,卻集中了全省52.3%的耕地面積,每667 m2水資源量平均為483 m3,水資源開發利用程度較低和水資源供需矛盾突出成為湟水流域農業發展最主要的制約因素[1]。因此在灌溉過程中水分消耗的多寡在一定程度上影響著黃河流域的水量分配,故有必要進行深入研究。
通用土壤水分平衡模型(VSMB)由加拿大的Baier等[2]于1966年首次提出,作為土壤水分預測的概念模型,其特點是將土壤分為多層,且只需要日常氣象數據和簡單的土壤參數即可模擬土壤各層的水分動態分布,特別適宜于灌溉入滲過程中土壤水分的剖面分布模擬和地下水位模擬。……

