基于GIS的海南島森林生態(tài)系統(tǒng)服務(wù)功能價(jià)值評(píng)估
周亞?wèn)|
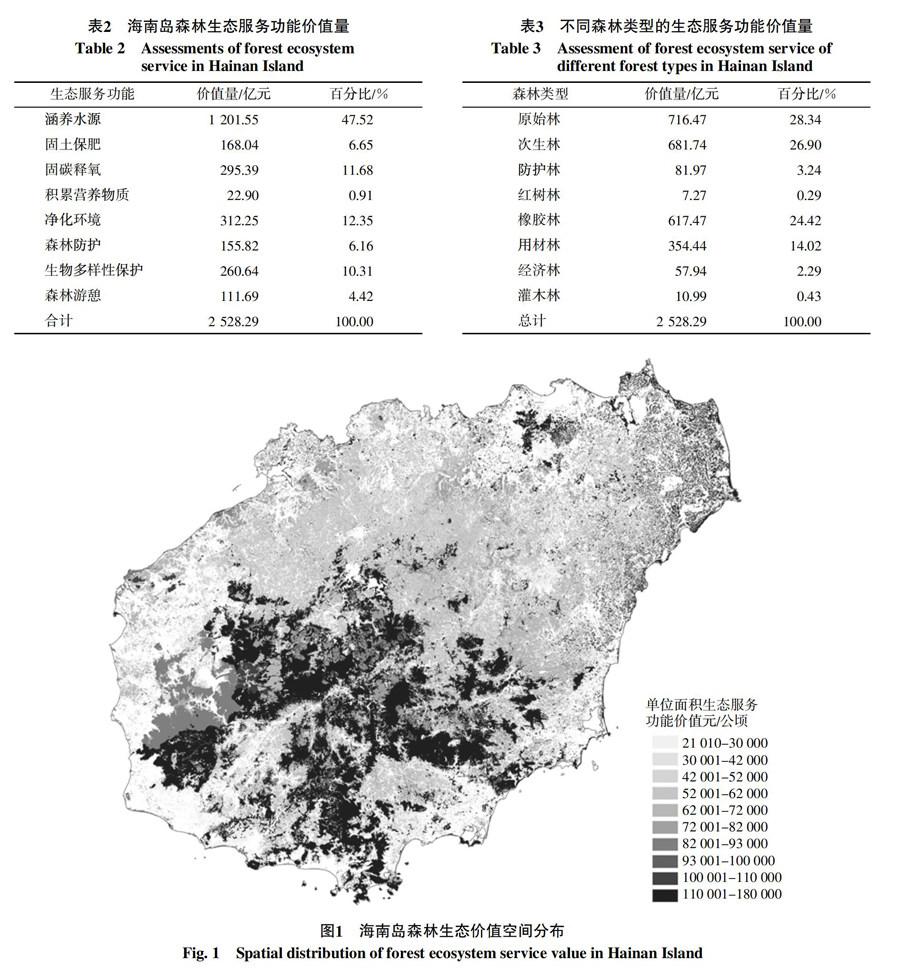
摘 要 對(duì)海南島森林涵養(yǎng)水源、保育土壤、固碳釋氧、積累營(yíng)養(yǎng)物質(zhì)、凈化大氣環(huán)境、生物多樣性保護(hù)、森林防護(hù)和森林游憩8個(gè)方面14個(gè)指標(biāo)進(jìn)行生態(tài)系統(tǒng)服務(wù)功能價(jià)值評(píng)估。結(jié)果表明:海南島8項(xiàng)生態(tài)服務(wù)功能總價(jià)值量2 528.29億元/年,功能價(jià)值貢獻(xiàn)大小依次為:涵養(yǎng)水源(47.52%)>凈化環(huán)境(12.35%)>固碳釋氧(11.68%)>生物多樣性保護(hù)(10.31%)>固土保肥(6.65%)>森林防護(hù)(6.16%)>森林游憩(4.42%)>積累營(yíng)養(yǎng)物質(zhì)(0.91%),根據(jù)不同森林類(lèi)型的生態(tài)服務(wù)功能價(jià)值量分析,原始林(28.34%)>次生林(26.96%)>橡膠林(24.42%)>用材林(14.02%)>防護(hù)林(3.24%)>經(jīng)濟(jì)林(2.29%)>灌木林(0.43%)>紅樹(shù)林(0.29%)。
關(guān)鍵詞 森林;生態(tài)服務(wù)功能;價(jià)值評(píng)估;海南島
中圖分類(lèi)號(hào) S718.5 文獻(xiàn)標(biāo)識(shí)碼 A
Abstract The forest ecosystem service in Hainan island are assessed as water conservation, soil conservation, carbon fixation & oxygen release, nutrient accumulation, atmosphere environmental purification, action of forest against natural calamities, species conservation and forest recreation 8 services and 14 indicators. Based on assessment result, water conservation has the highest ecosystem service value with 47.52% of total value, the rest are atmosphere environmental purification(12.35%), carbon fixation & oxygen release(11.68%), species conservation(10.31%), soil conservation(6.65%), action of forest against natural calamities(6.16%), forest recreation(4.42%), nutrient accumulation(0.91%). By forest type, primary forest has the highest ecosystem service value of 28.34% of total value, followed by secondary forest with 26.96%, rubber plantation with 24.42%, timber plantation 14.02%,shelter forest with 3.24%, economic forest of 2.29%, shrub of 0.43% and mangroves of 0.29%.
Key words Forest; Ecosystem Service; Assessment; Hainan Island
doi 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2015.03.030
生態(tài)系統(tǒng)服務(wù)功能又稱(chēng)生態(tài)服務(wù),是建立在生態(tài)系統(tǒng)功能基礎(chǔ)上,人類(lèi)能夠從中獲益的生態(tài)系統(tǒng)功能,是生態(tài)系統(tǒng)結(jié)構(gòu)的外在表現(xiàn)和生態(tài)系統(tǒng)所固有的本質(zhì)屬性[1]。森林是陸地生態(tài)系統(tǒng)的主體,森林生態(tài)服務(wù)功能既是人類(lèi)生存的基本條件,又是實(shí)現(xiàn)生態(tài)文明的基礎(chǔ),森林的興衰直接影響生態(tài)環(huán)境,關(guān)系著經(jīng)濟(jì)和社會(huì)的可持續(xù)發(fā)展[2]。近年來(lái),對(duì)森林生態(tài)系統(tǒng)服務(wù)功能價(jià)值進(jìn)行評(píng)估已成為生態(tài)學(xué)研究的熱點(diǎn)之一。在國(guó)際上,生態(tài)系統(tǒng)服務(wù)功能始于20世紀(jì)50年代,但直到Constanza等[3]創(chuàng)立了較為成熟的生態(tài)系統(tǒng)服務(wù)功能價(jià)值評(píng)估體系,對(duì)全球生物圈生態(tài)系統(tǒng)服務(wù)功能價(jià)值進(jìn)行估算,才掀開(kāi)了生態(tài)系統(tǒng)服務(wù)功能研究的熱潮[4-5]。國(guó)內(nèi)生態(tài)系統(tǒng)服務(wù)功能研究開(kāi)展得比較晚,侯元兆[6]首先對(duì)森林涵養(yǎng)水源,防風(fēng)固沙和凈化空氣的生態(tài)價(jià)值進(jìn)行了評(píng)估,得出生態(tài)價(jià)值高于林木價(jià)值的結(jié)論。近年來(lái),中國(guó)學(xué)者在自然保護(hù)區(qū)……

