煙葉多肽的提取工藝優(yōu)化及其抗氧化活性研究
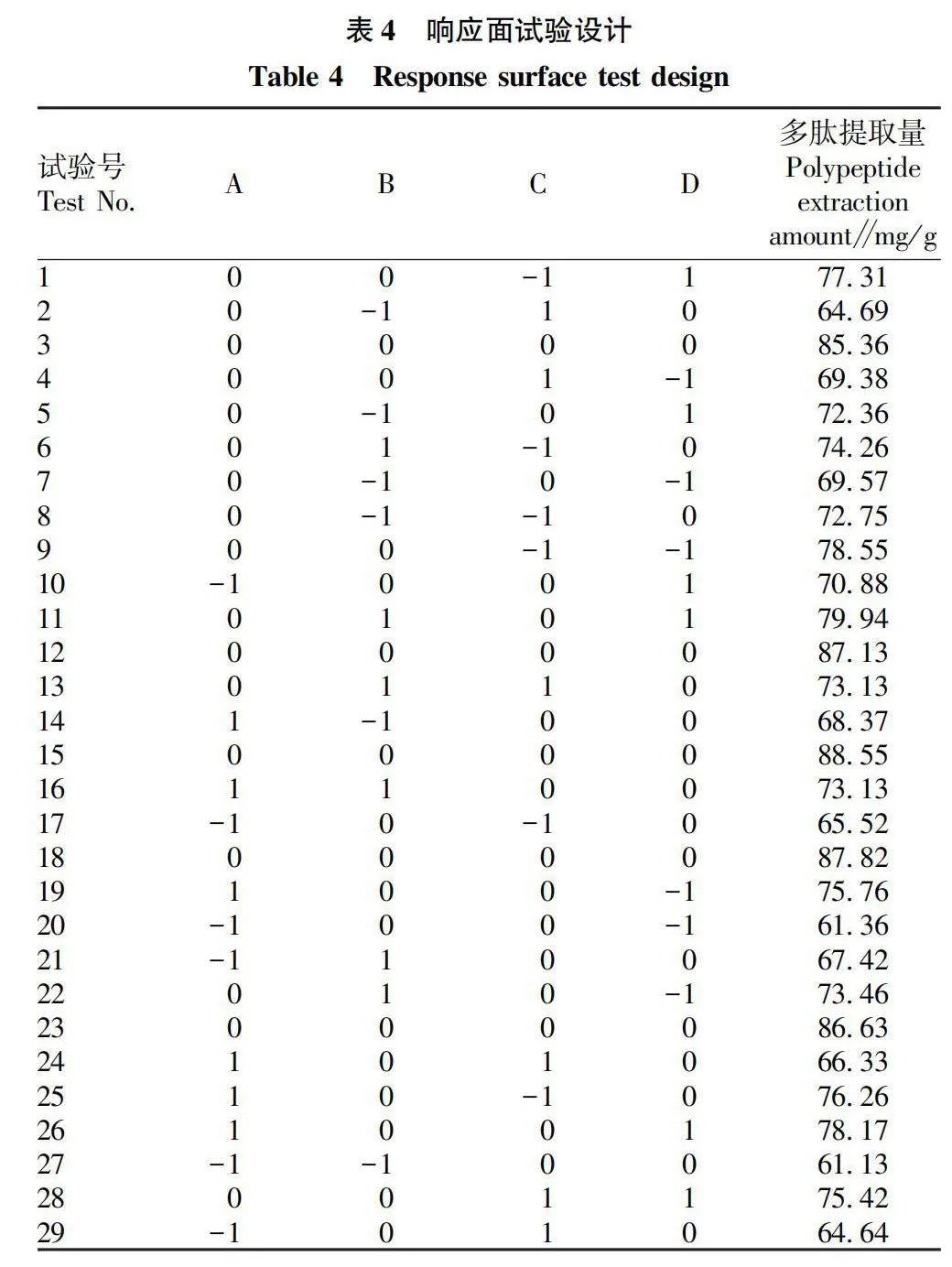
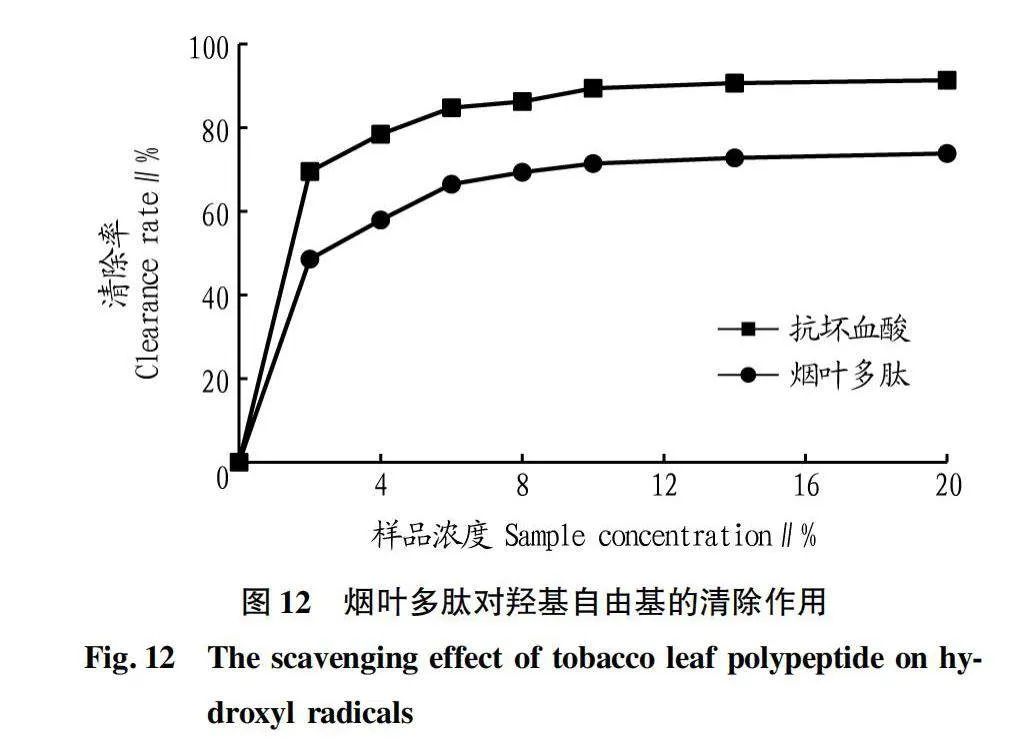
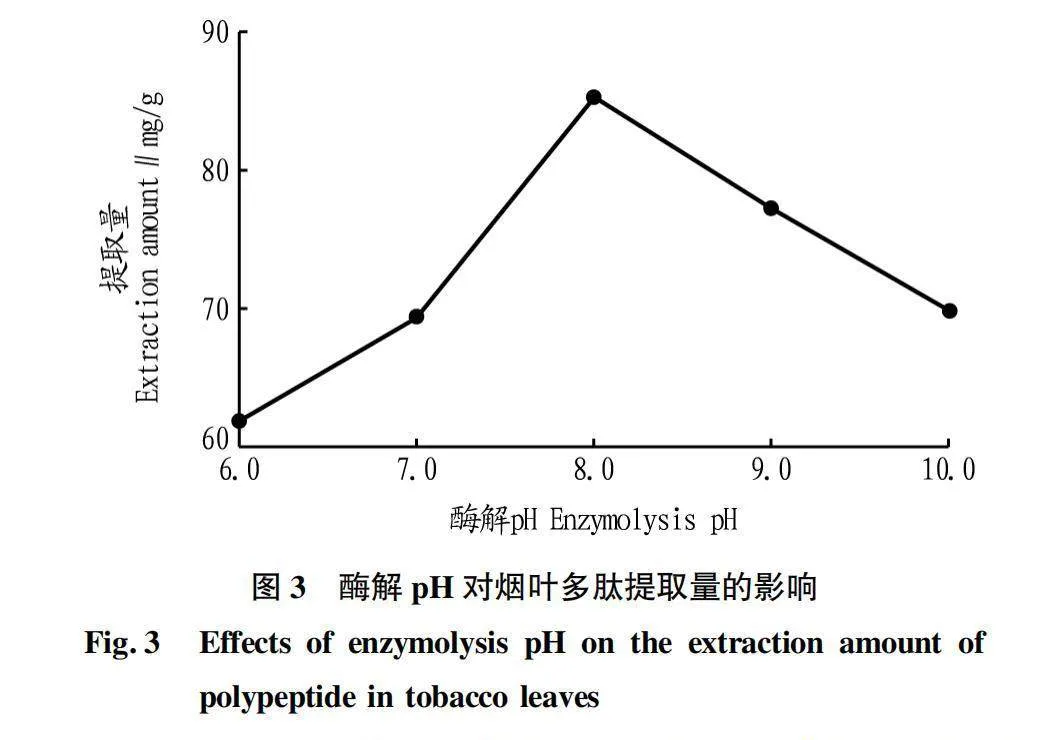
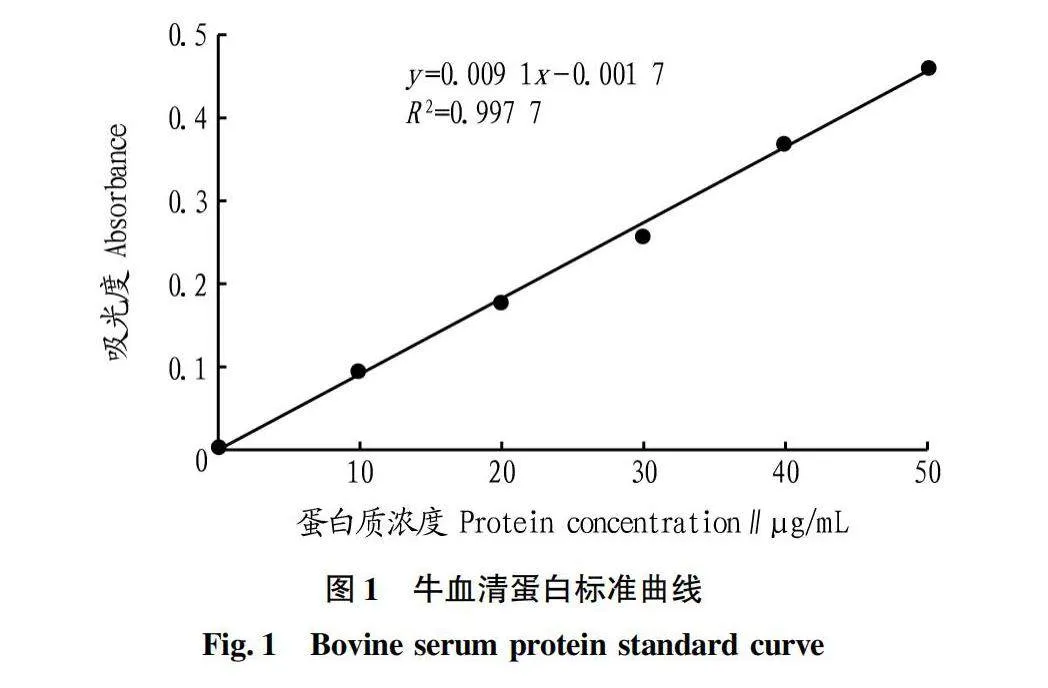

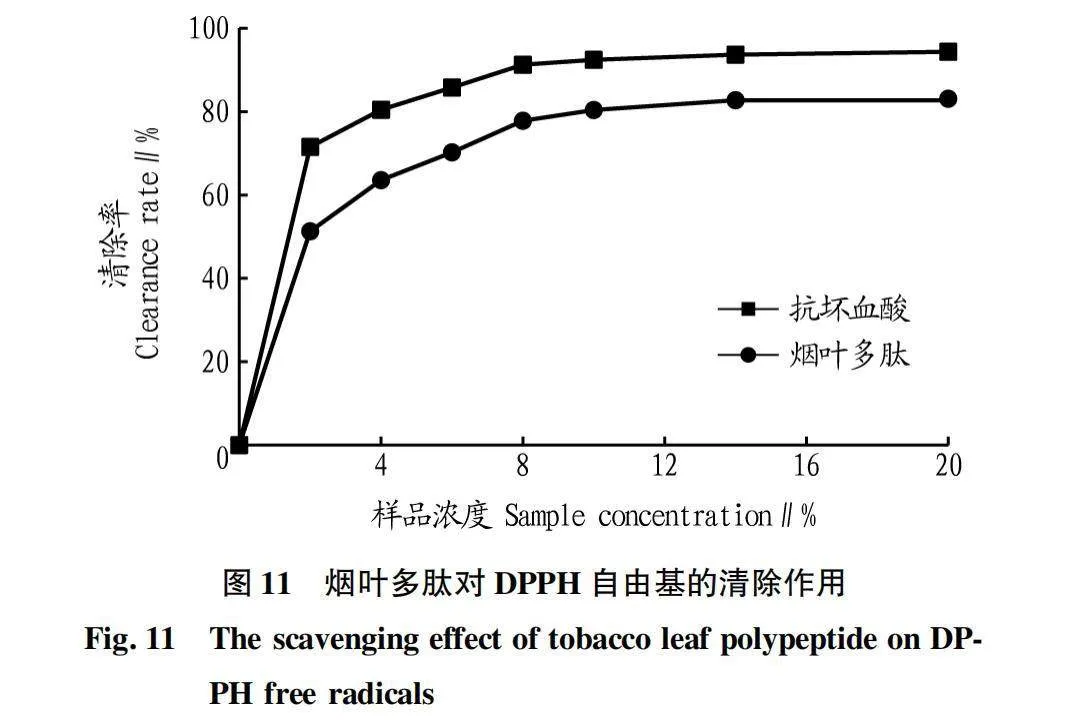
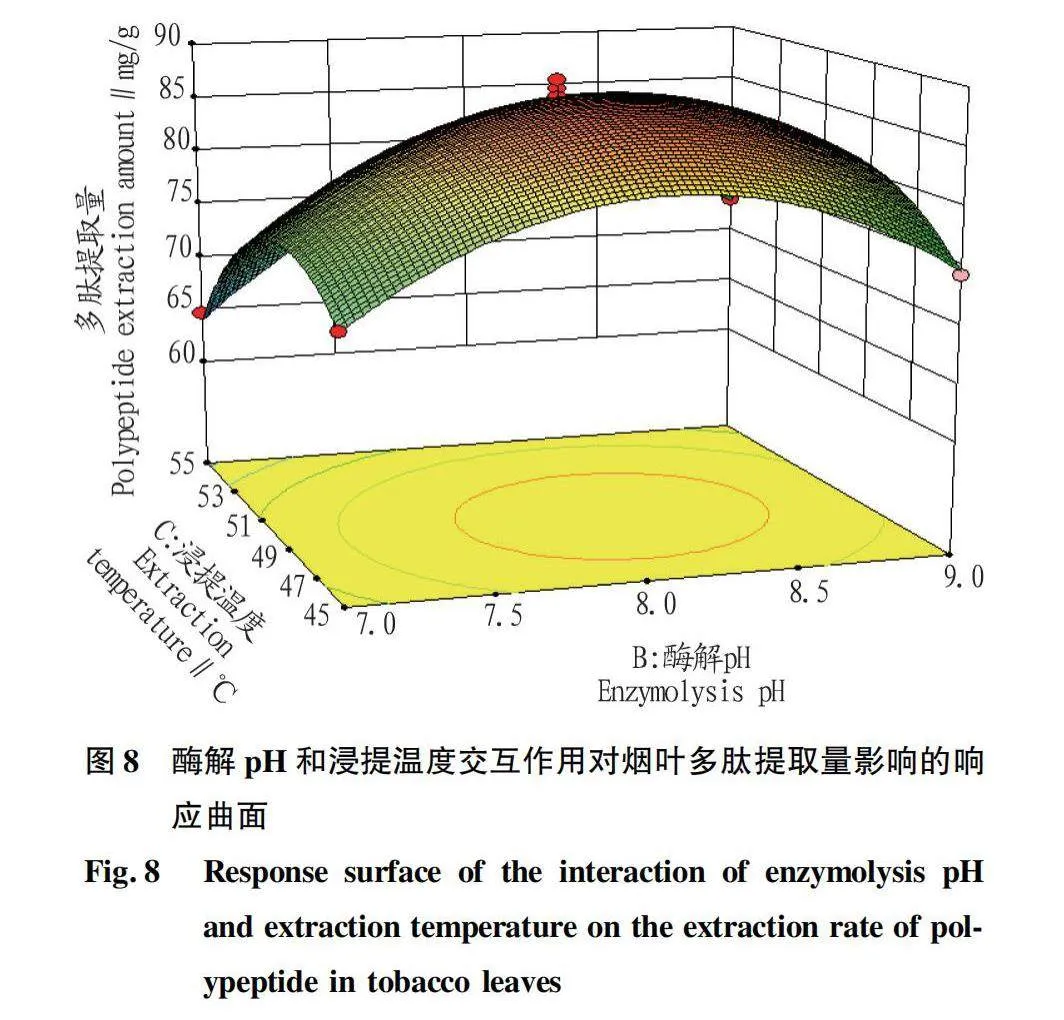
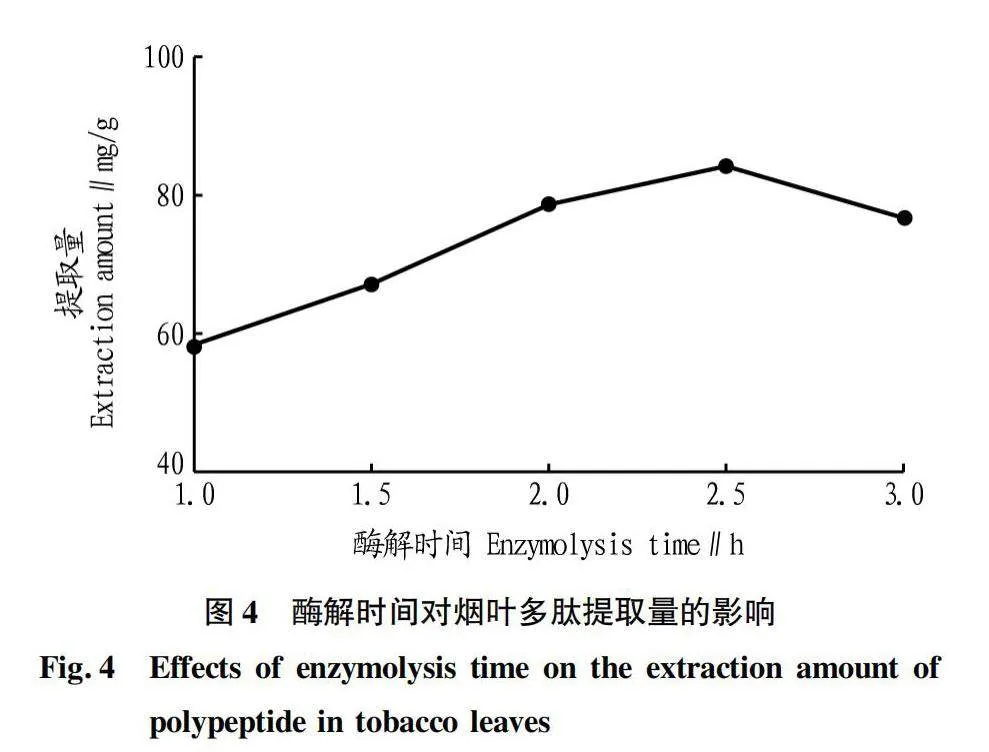
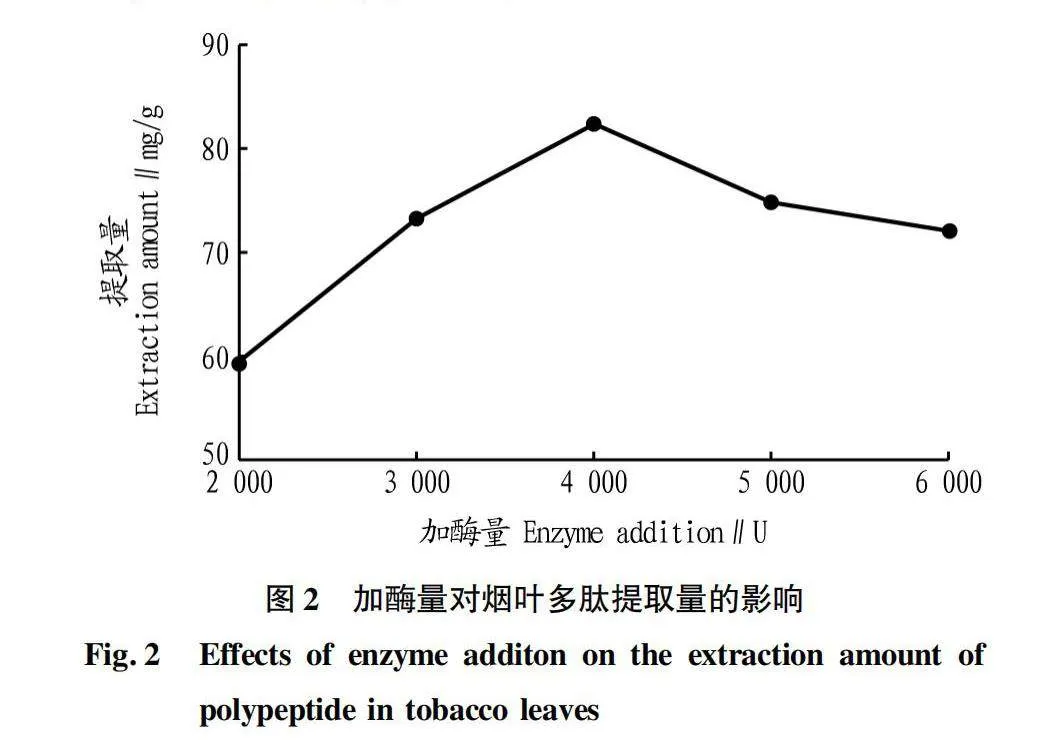
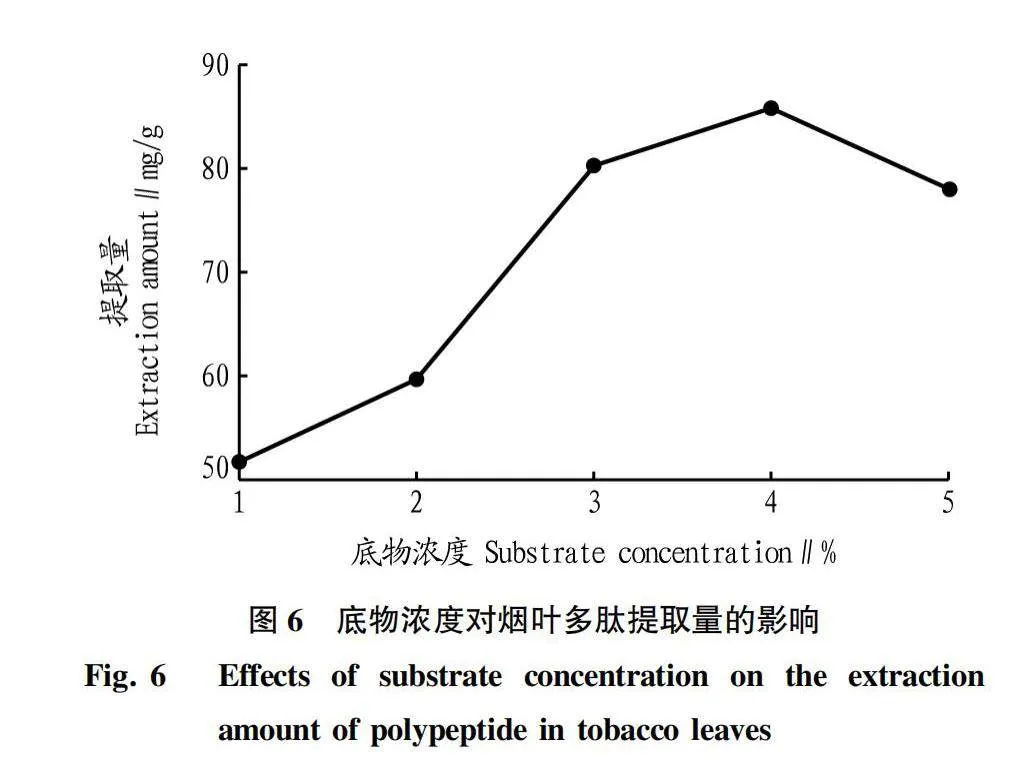
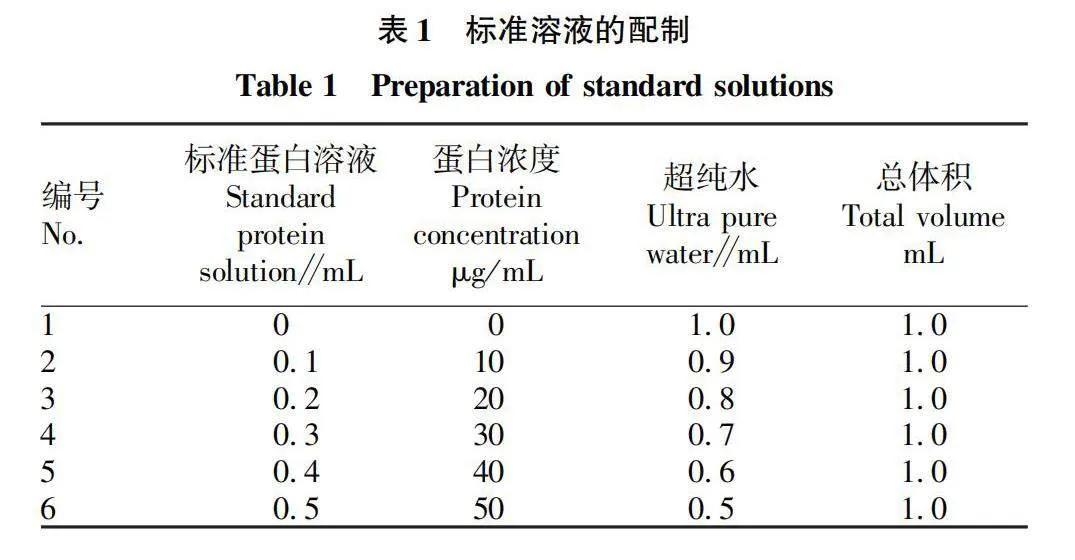
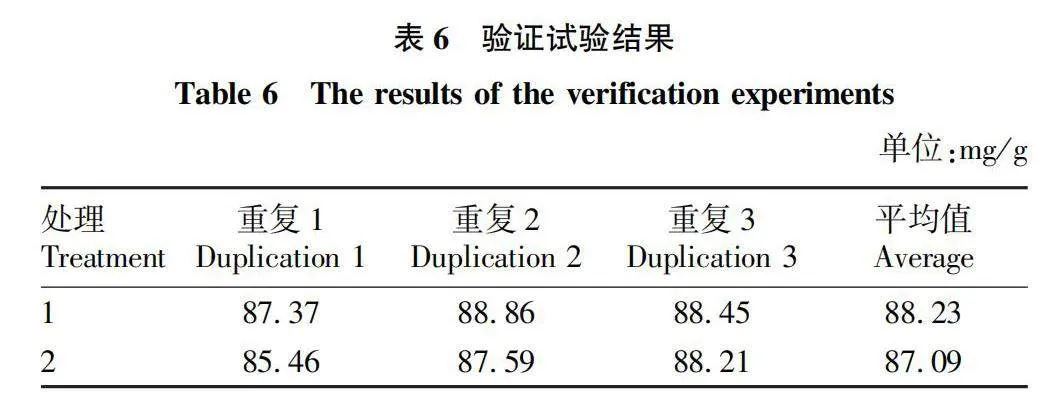
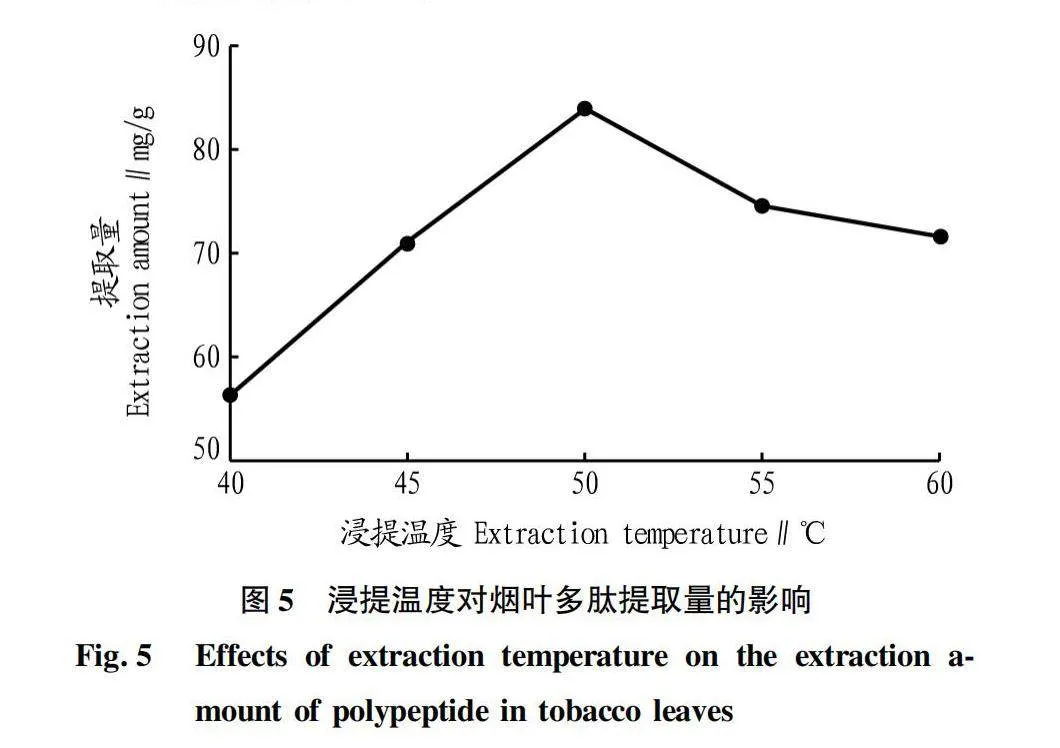
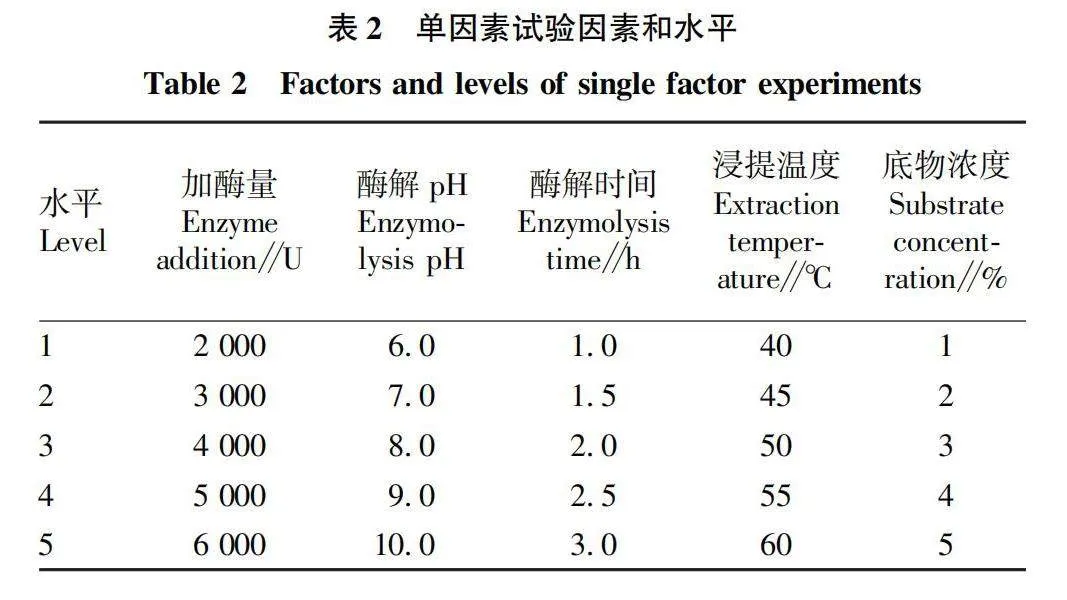
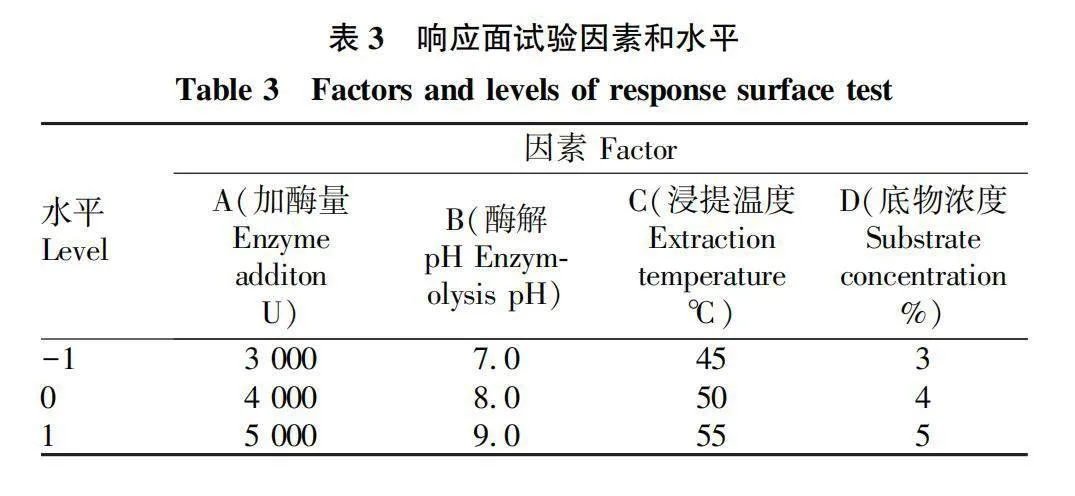
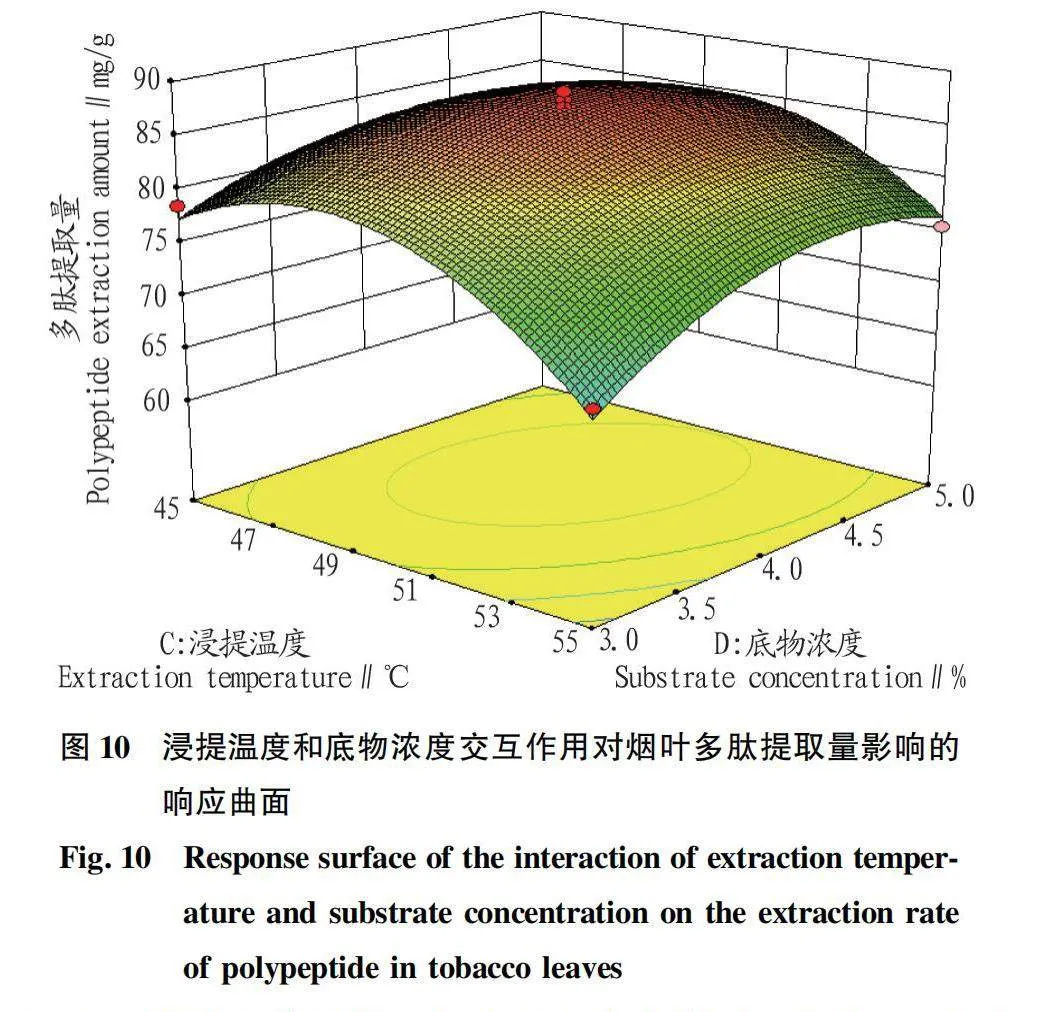
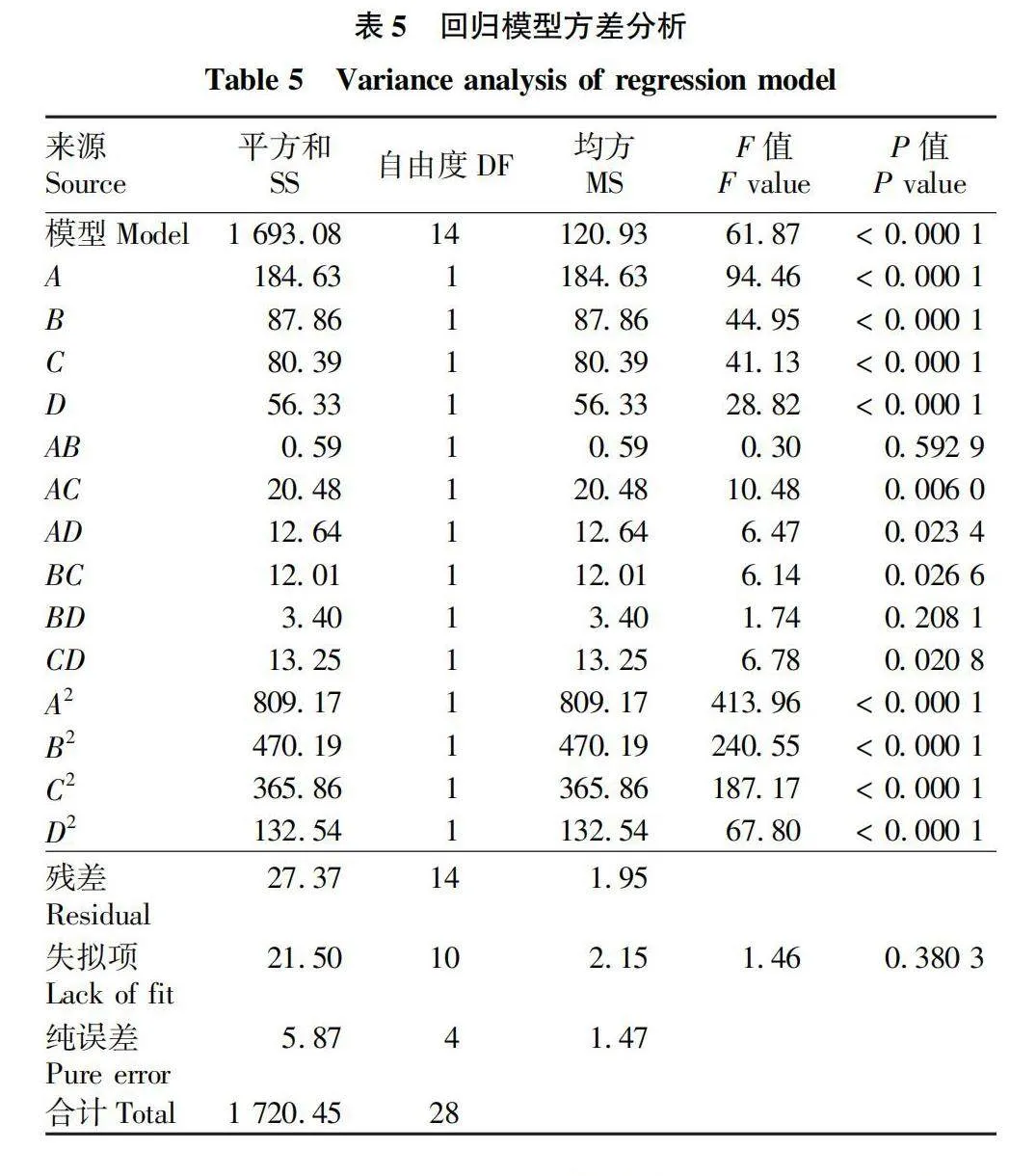
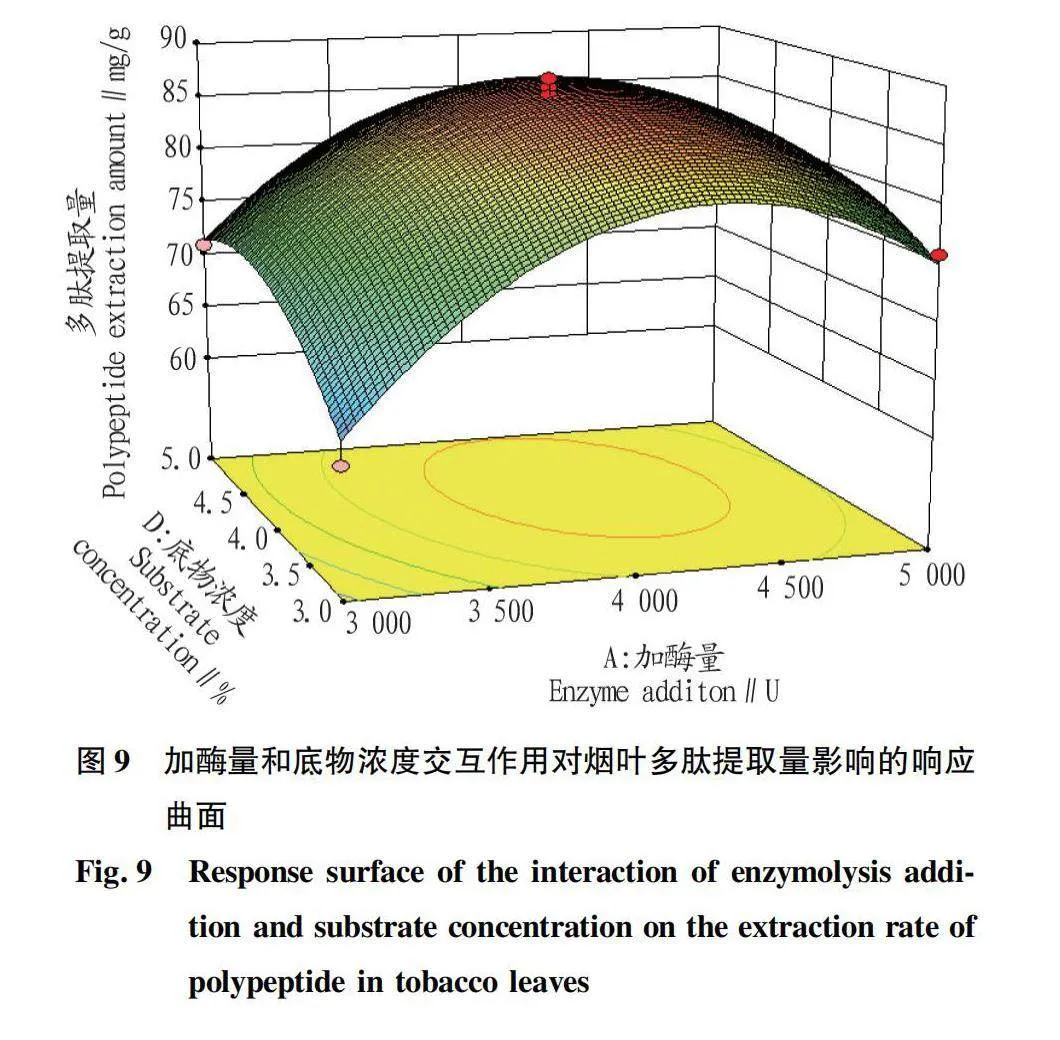
摘要 [目的]以煙葉為原料,進(jìn)行煙葉多肽的提取及其抗氧化活性研究。[方法]采用酶法輔助水提醇沉法提取煙葉多肽,應(yīng)用單因素試驗(yàn)考察加酶量、酶解pH、酶解時(shí)間、浸提溫度、底物濃度5個(gè)單因素對(duì)煙葉多肽提取量的影響,采用響應(yīng)面法確定煙葉多肽的最佳提取工藝,并分析煙葉多肽對(duì)DPPH自由基和羥基自由基的清除作用,研究煙葉多肽的抗氧化活性。[結(jié)果]以處理樣品質(zhì)量1 g為基準(zhǔn),煙葉多肽的最佳提取工藝為加酶量4 200 U、酶解pH 8.2、酶解時(shí)間2.5 h、浸提溫度49 ℃、底物濃度4.2%,煙葉多肽提取量為88.23 mg/g。按照該條件所提取的煙葉多肽對(duì)DPPH自由基和羥基自由基的清除率分別為83.09%和73.84%,表明煙葉多肽具有一定的抗氧化能力。[結(jié)論]該研究為煙葉的藥用價(jià)值和煙葉多肽的藥物開發(fā)提供一定的理論基礎(chǔ)和技術(shù)指導(dǎo)。
關(guān)鍵詞 煙葉;多肽;酶解;提取工藝優(yōu)化;響應(yīng)面法;抗氧化活性
中圖分類號(hào) R284 文獻(xiàn)標(biāo)識(shí)碼 A 文章編號(hào) 0517-6611(2024)19-0158-06
doi:10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2024.19.034
開放科學(xué)(資源服務(wù))標(biāo)識(shí)碼(OSID):
Study on the Optimization of Extraction Process of Tobacco Polypeptide and Its Antioxidant Activity
CHEN Yue-xing1,2,SHI Ye-lin1,DU Xue-ting1 et al
(1.School of Biomedical and Food Engineering,Shangluo University,Shangluo,Shaanxi 726000;2.Shaanxi Qinling Characteristic Biological Resources Industry Technology Research Institute,Shangluo,Shaanxi 726000)
Abstract [Objective]Taking tobacco as experiment material,extraction process of tobacco polypeptide and its antioxidant activity was studied in this research.[Method]Tobacco polypeptide was extracted by enzyme-assisted water extraction and alcohol precipitation.Single factor test was used to investigate the effects of enzyme addition,enzymolysis pH,enzymolysis time,extraction temperature and substrate concentration on the extraction rate of tobacco polypeptide.The optimal extraction process of tobacco polypeptide was determined by response surface method.The scavenging activity of tobacco polypeptide on DPPH and hydroxyl radicals was detected.[Result]The optimal extraction process for tobacco polypeptide was as follows (based on 1 g tobacco sample):enzyme addition 4 200 U,enzymolysis pH 8.2,enzymolysis time 2.5 h,extraction temperature 49 ℃ and the substrate concentration 4.2%.Under the optimized extraction process,the extraction rate of tobacco polypeptide was 88.23 mg/g.The scavenging rates of DPPH and hydroxyl radicals of the tobacco polypeptide were 83.09% and 73.84%,respectively.Tobacco polypeptide was of a certain antioxidant capacity.[Conclusion]This study provides a certain theoretical basis and technical guidance for the medicinal value of tobacco leaves and the drug development of tobacco peptides.
Key words Tobacco;Polypeptide;Enzymolysis;Extraction process optimization;Response surface method;Antioxidant activity
基金項(xiàng)目 陜西省大學(xué)生創(chuàng)新訓(xùn)練計(jì)劃項(xiàng)目(202411396005);陜西省科技廳自然科學(xué)基礎(chǔ)研究面上項(xiàng)目(2024JC-YBMS-187)。
作者簡(jiǎn)介 陳月星(1984—),女,河北衡水人,講師,博士,從事農(nóng)林生物專業(yè)相關(guān)教學(xué)與科研工作。
收稿日期 2024-03-21
煙草(Nicotiana tabacum L.)為一年生或有限多年生草本[1]。煙葉中含有多種化學(xué)成分,包括糖類物質(zhì)、有機(jī)酸和脂質(zhì)等[2]。煙葉的含氮化合物主要有蛋白質(zhì)和生物堿等,其中蛋白質(zhì)經(jīng)酶分解轉(zhuǎn)化為多肽,具有一定生物活性的化合物分子,穩(wěn)定性較高,具有易消化吸收、促進(jìn)免疫、降血……

