健康與患根腐病三七根際和根內(nèi)微生物群落結(jié)構(gòu)與多樣性研究
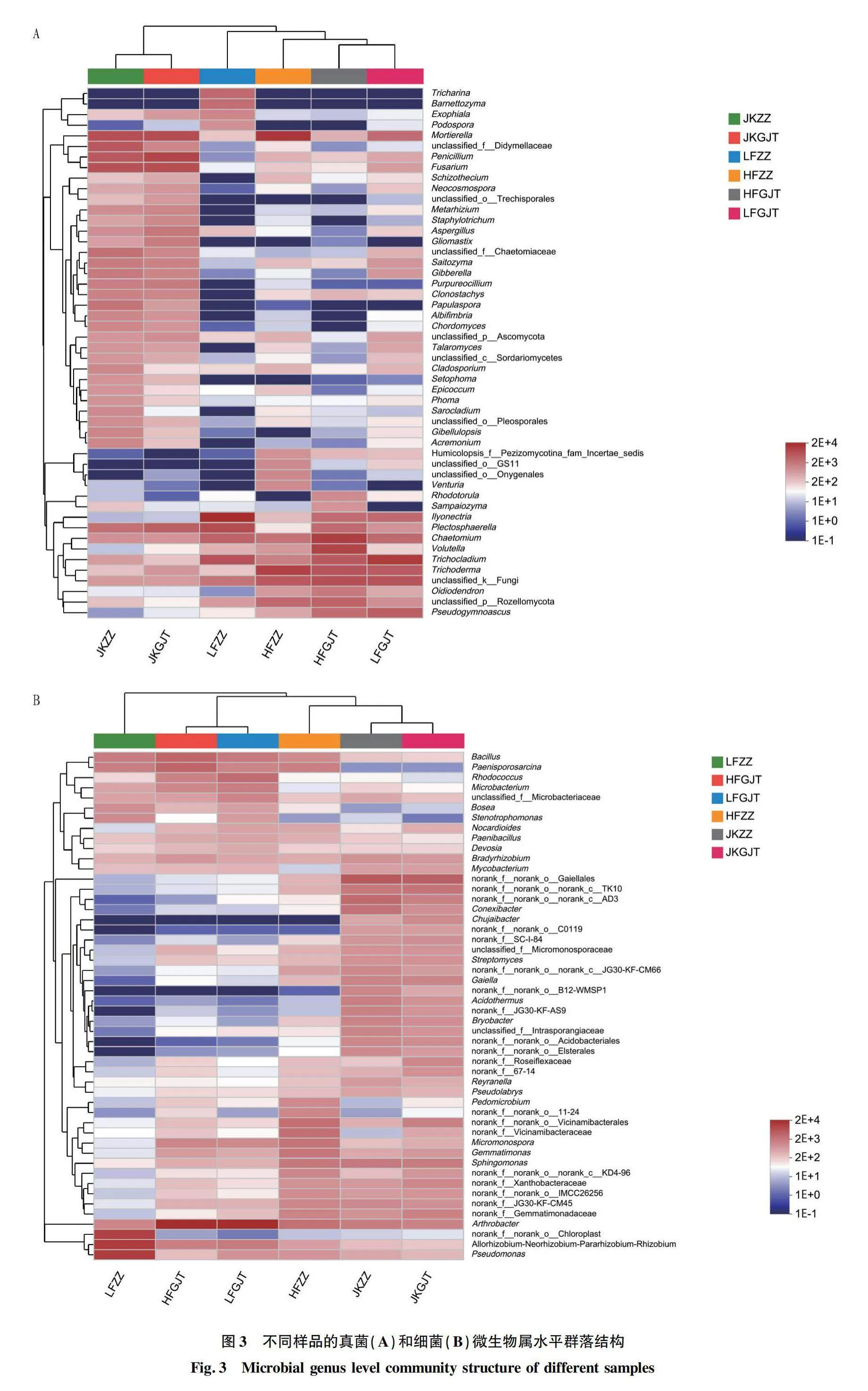
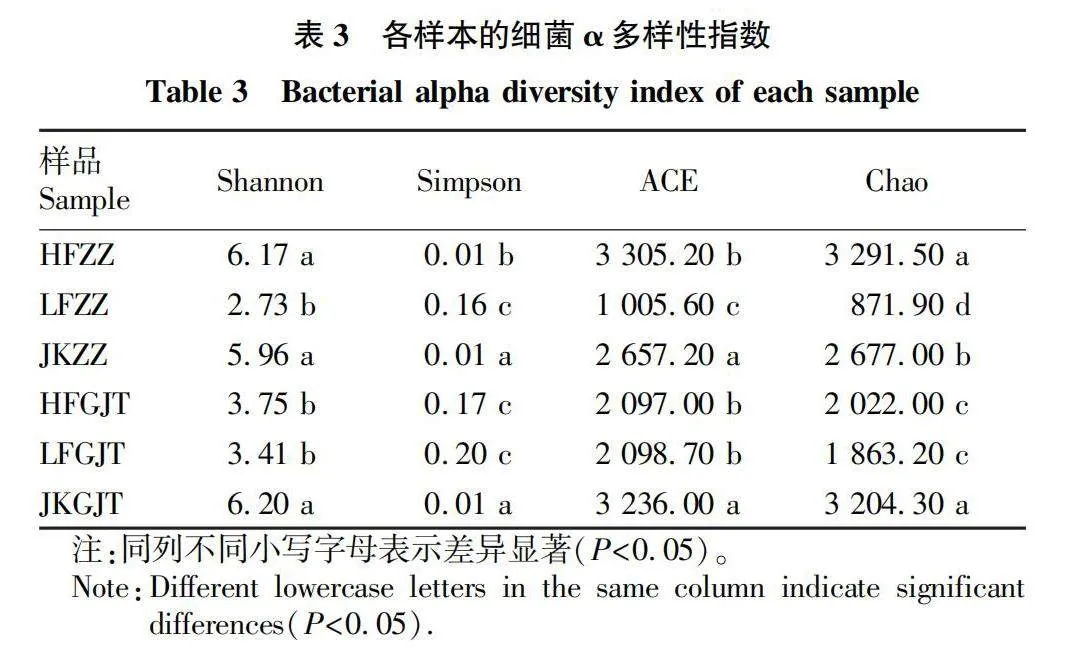
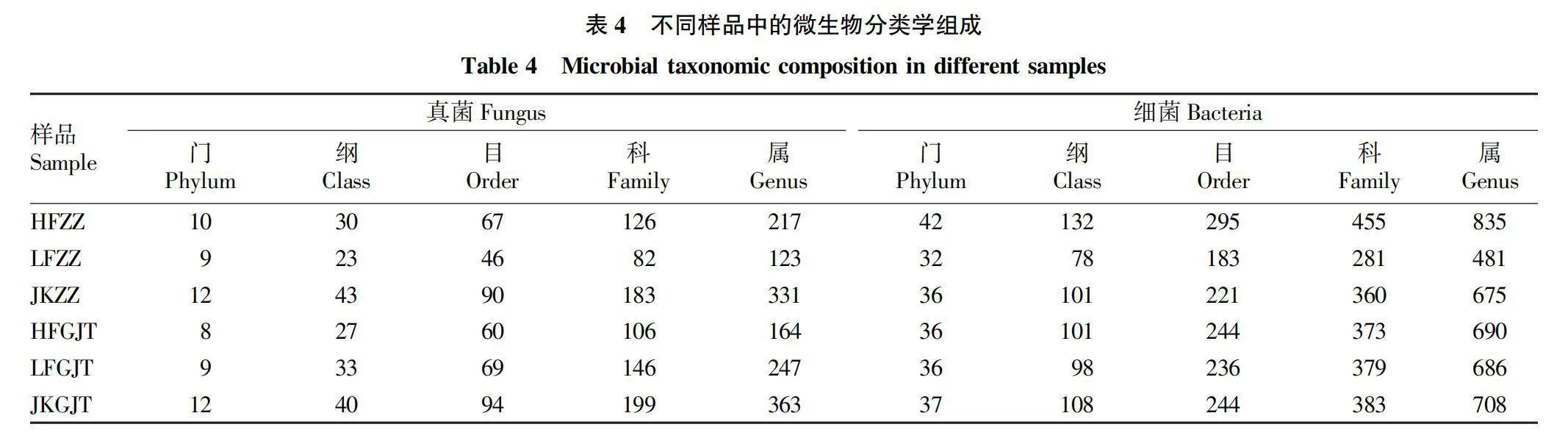
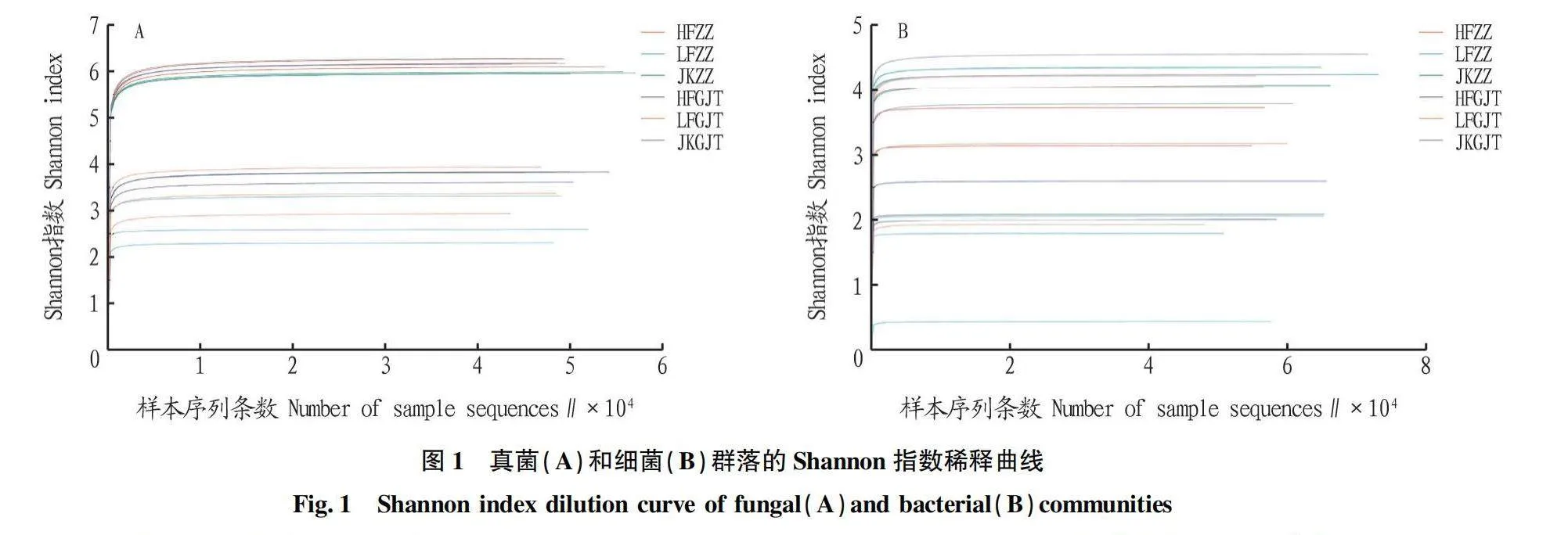
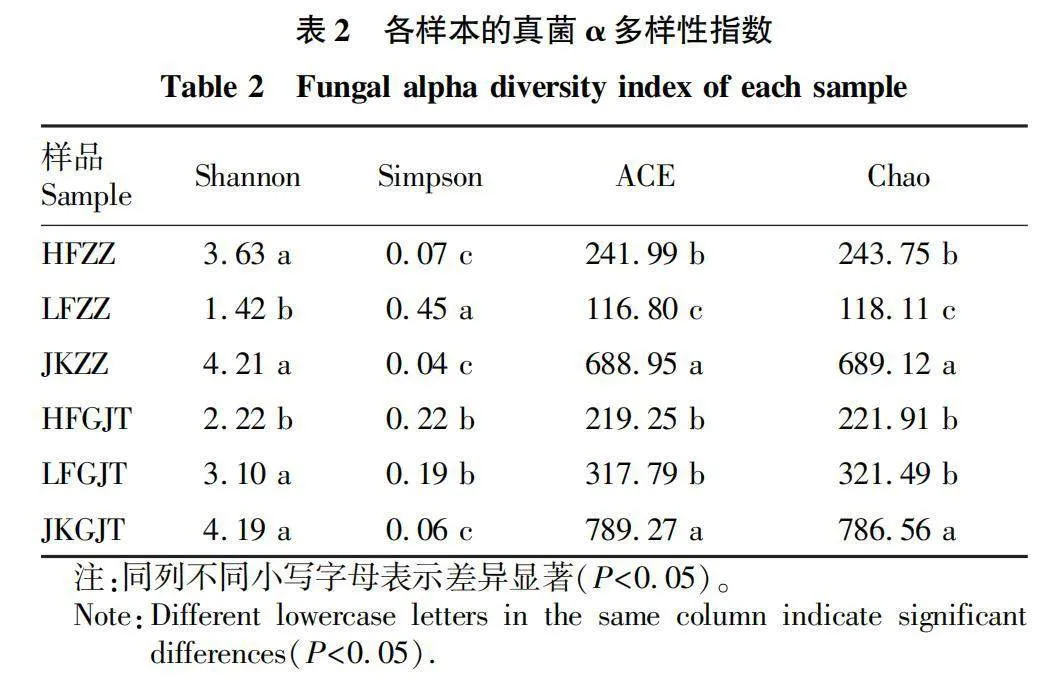
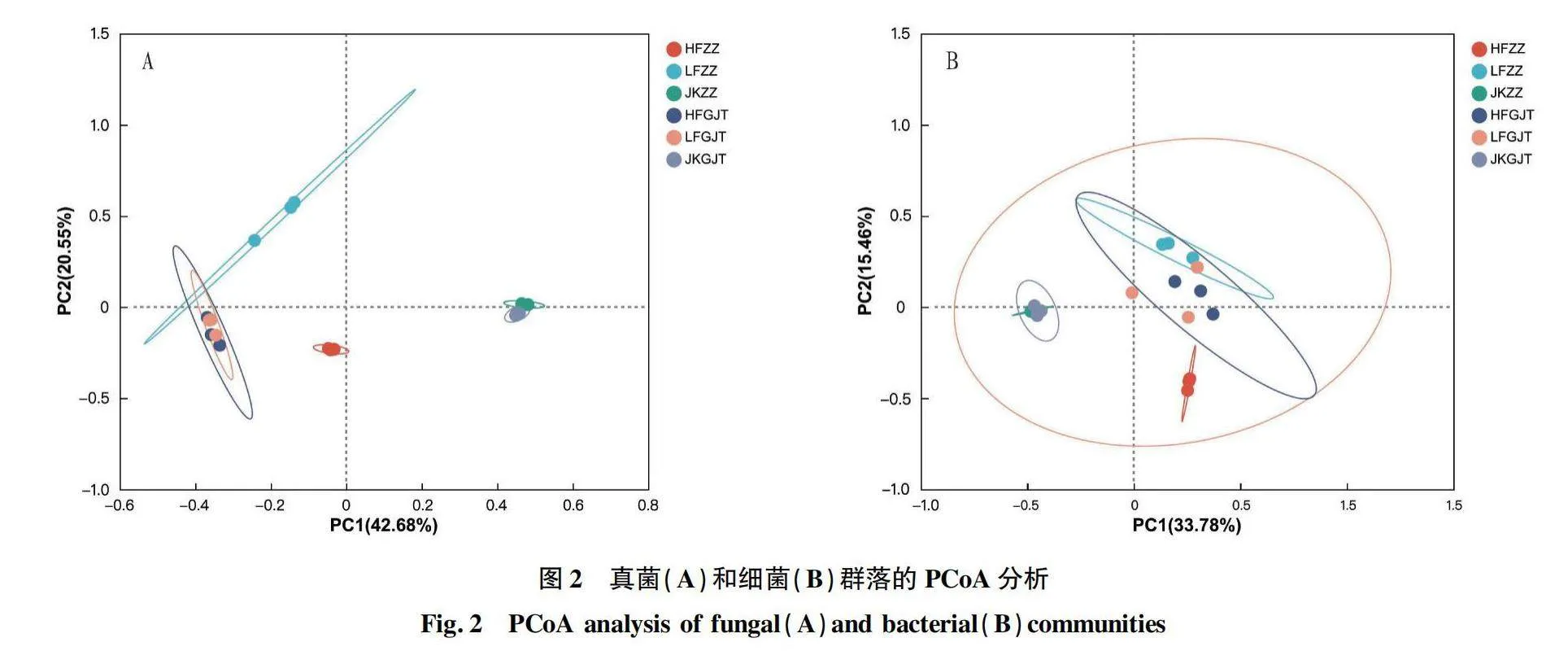
摘要 [目的]研究三七健康植株和根腐病植株根內(nèi)及根際土的微生物群落結(jié)構(gòu),探究其與三七根腐病發(fā)生的相關(guān)性。[方法]利用Illumina高通量測序技術(shù)對云南文山連作3年的健康植株根內(nèi)及其根際土壤、根腐病植株根內(nèi)及其根際土壤中的微生物群落結(jié)構(gòu)及多樣性進(jìn)行分析。[結(jié)果]健康植株及其根際土壤與根腐病植株及其根際土壤中微生物群落的豐富度存在顯著差異。黃腐植株根際土中的優(yōu)勢微生物為節(jié)桿菌屬(Arthrobacter)、毛殼菌屬(Chaetomium)和周刺座霉屬(Volutella),綠腐植株根際土中的優(yōu)勢微生物為節(jié)桿菌屬(Arthrobacter)和短梗蠕孢屬(Trichocladium)。黃腐植株根內(nèi)優(yōu)勢微生物為被孢霉屬(Mortierella)和木霉屬(Trichoderma),綠腐植株根內(nèi)優(yōu)勢微生物為假單胞菌屬(Pseudomonas)、土赤殼菌屬(Ilyonectria)和小不整球殼屬(Plectosphaerella)。[結(jié)論]三七根腐病的發(fā)生與植株根際及根內(nèi)微生物多樣性和群落結(jié)構(gòu)密切相關(guān)。
關(guān)鍵詞 三七;根腐病;根際微生物;高通量測序;群落結(jié)構(gòu);微生物多樣性
中圖分類號(hào) X172 文獻(xiàn)標(biāo)識(shí)碼 A 文章編號(hào) 0517-6611(2024)19-0151-07
doi:10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2024.19.033
開放科學(xué)(資源服務(wù))標(biāo)識(shí)碼(OSID):
Microbial Community Structure and Diversity in Rhizosphere and Roots of Healthy and Root Rot Panax notoginseng
DING Zi-yuan1,2, ZHAO Xue-qiang3, LI Ning4 et al
(1. Nutrition & Health Research Institute, COFCO Corporation, Beijing 102209; 2. Beijing Key Laboratory of Nutrition, Health and Food Safety, Beijing 102209; 3. North China Pharmaceutical Group Aino Co., Ltd., Shijiazhuang,Hebei 052165; 4. New Drug Research & Development Company of NCPC, Shijiazhuang,Hebei 050000)
Abstract [Objective]To study the microbial community structure in the root and rhizosphere soil of healthy and root rot infected plants of Panax notoginseng, and explore the correlation between microbial diversity with root rot of P. notoginseng.[Method]The microbial community composition and diversity of the roots and rhizosphere soil of healthy and root rot plants in Wenshan, Yunnan Province, which had been continuously cultivated for 3 years were analyzed by using Illumina high-throughput sequencing system.[Result]The richness of microbial communities in healthy plants roots and rhizosphere soil was significantly different from that in root rot plants roots and rhizosphere soil. The dominant microorganisms in the rhizosphere soil of yellow rot plants were Arthrobacter, Chaetomium and Volutella, and that of the rhizosphere soil of green rot plant were Arthrobacter and Trichocladium. The dominant microorganisms in roots of yellow rot plants were Mortierella and Trichoderma, while the dominant microorganisms in roots of green rot plants were Pseudomonas, Ilyoectria and Plectosphaerella.[Conclusion]The occurrence of root rot in Panax notoginseng is closely related to the diversity and community structure of microorganisms in the rhizosphere and roots of plants.
Key words Panax notoginseng;Root rot;Rhizosphere microbe;High-throughput sequencing;Community structure;Microbial diversity
基金項(xiàng)目 河北省重大科技成果轉(zhuǎn)化專項(xiàng)(20282901Z)。
作者簡介 丁子元(1984—),男,安徽安慶人,高級工程師,博士,從事環(huán)境微生物研究。
*通信作者,高級工程師,碩士,從事環(huán)境微生物研究。
收稿日期 2023-08-02
三七又名田七、金不換,屬于五加科人參屬多年生草本植物,是我國名貴的藥食同源中藥材,兼具營養(yǎng)和藥用雙重價(jià)值,具有良好的抗凝血、抗血栓、緩解疼痛等作用,對預(yù)防和治療心腦血管疾病具有顯著療效[1],被廣泛應(yīng)用于食品和醫(yī)藥領(lǐng)域。……

