GEDI星載激光雷達數據估測森林冠層高度精度評估

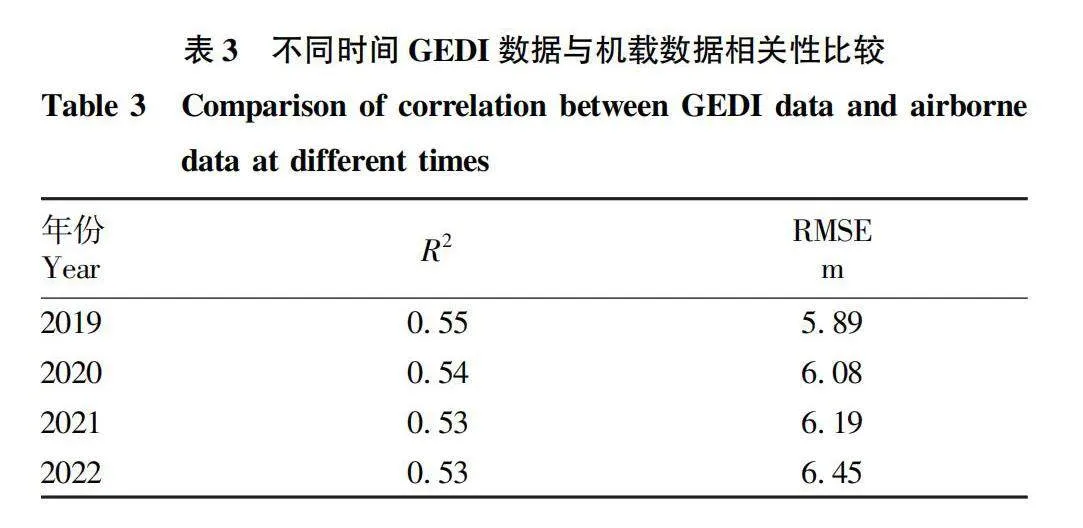
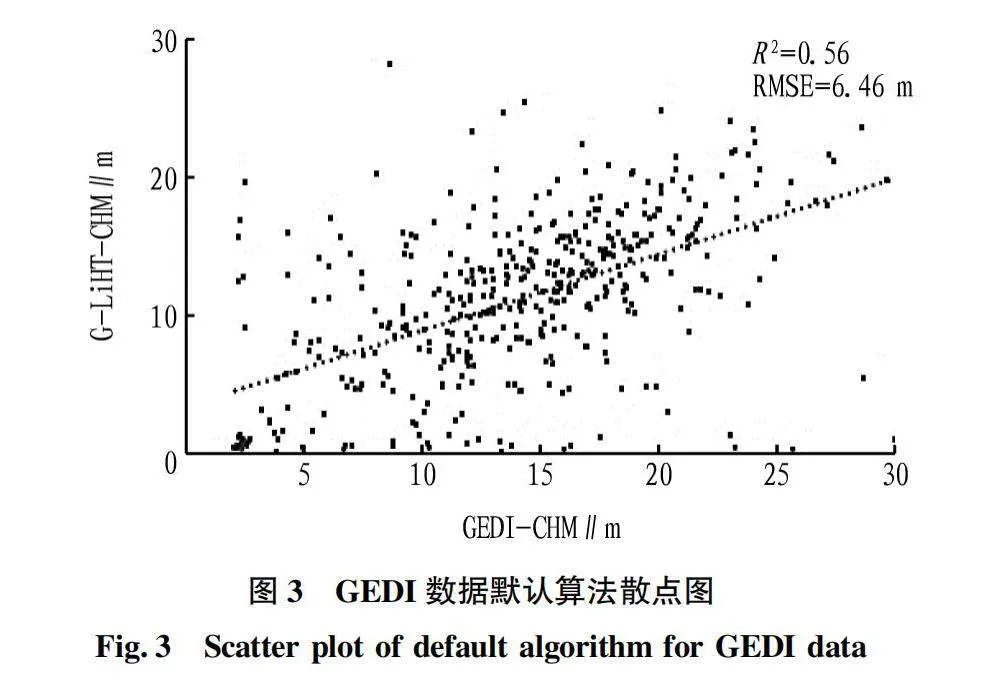
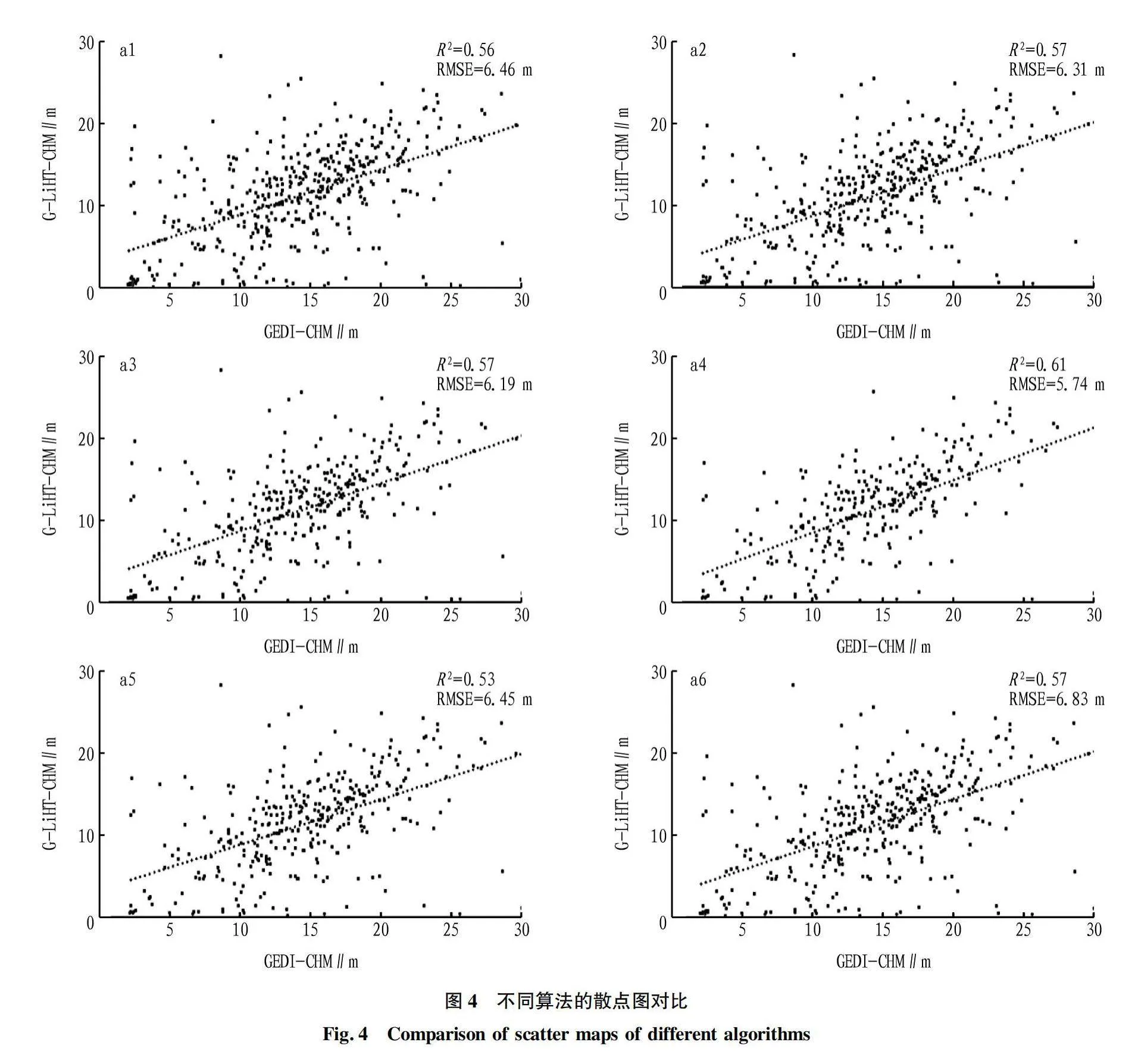
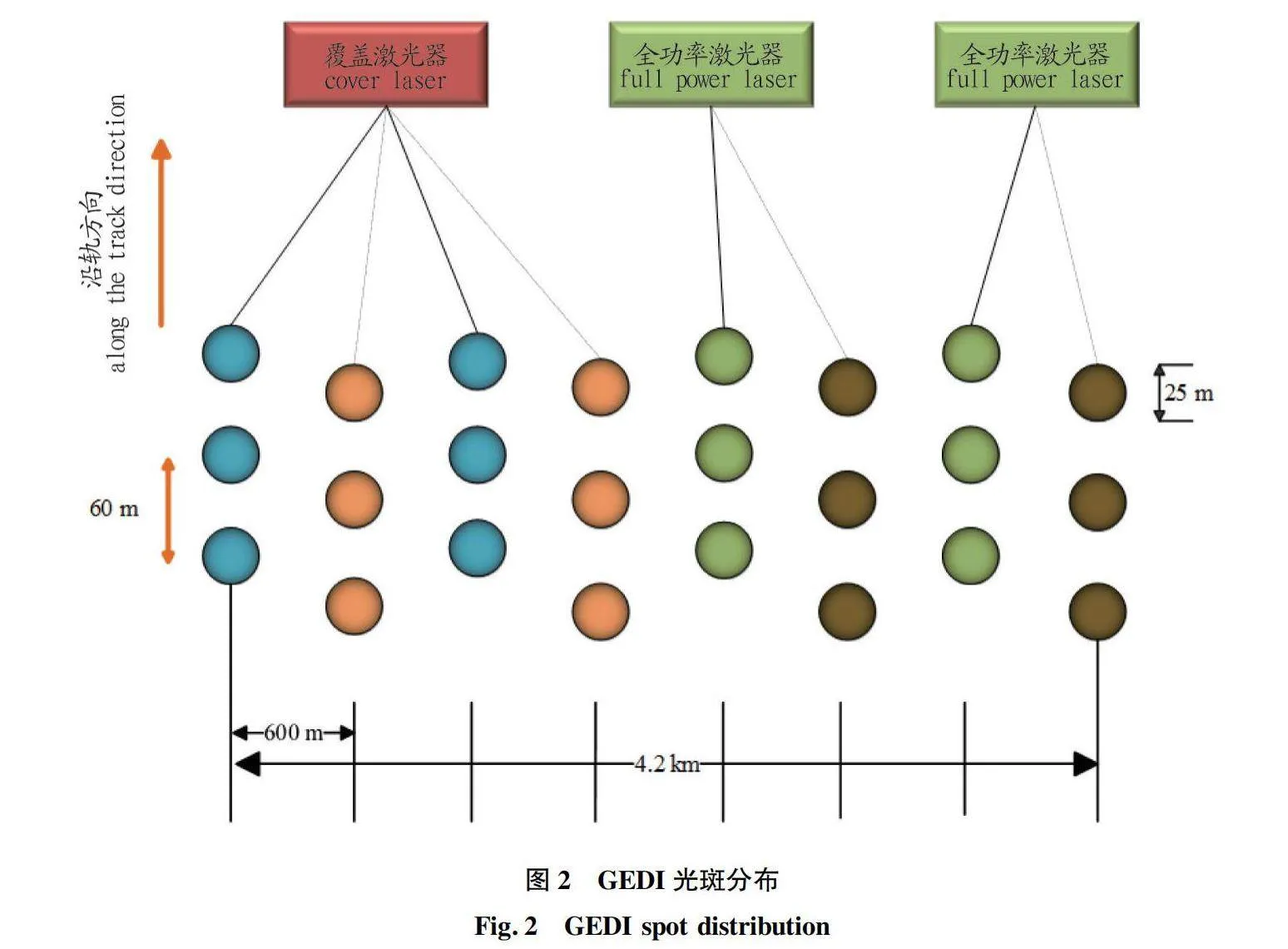
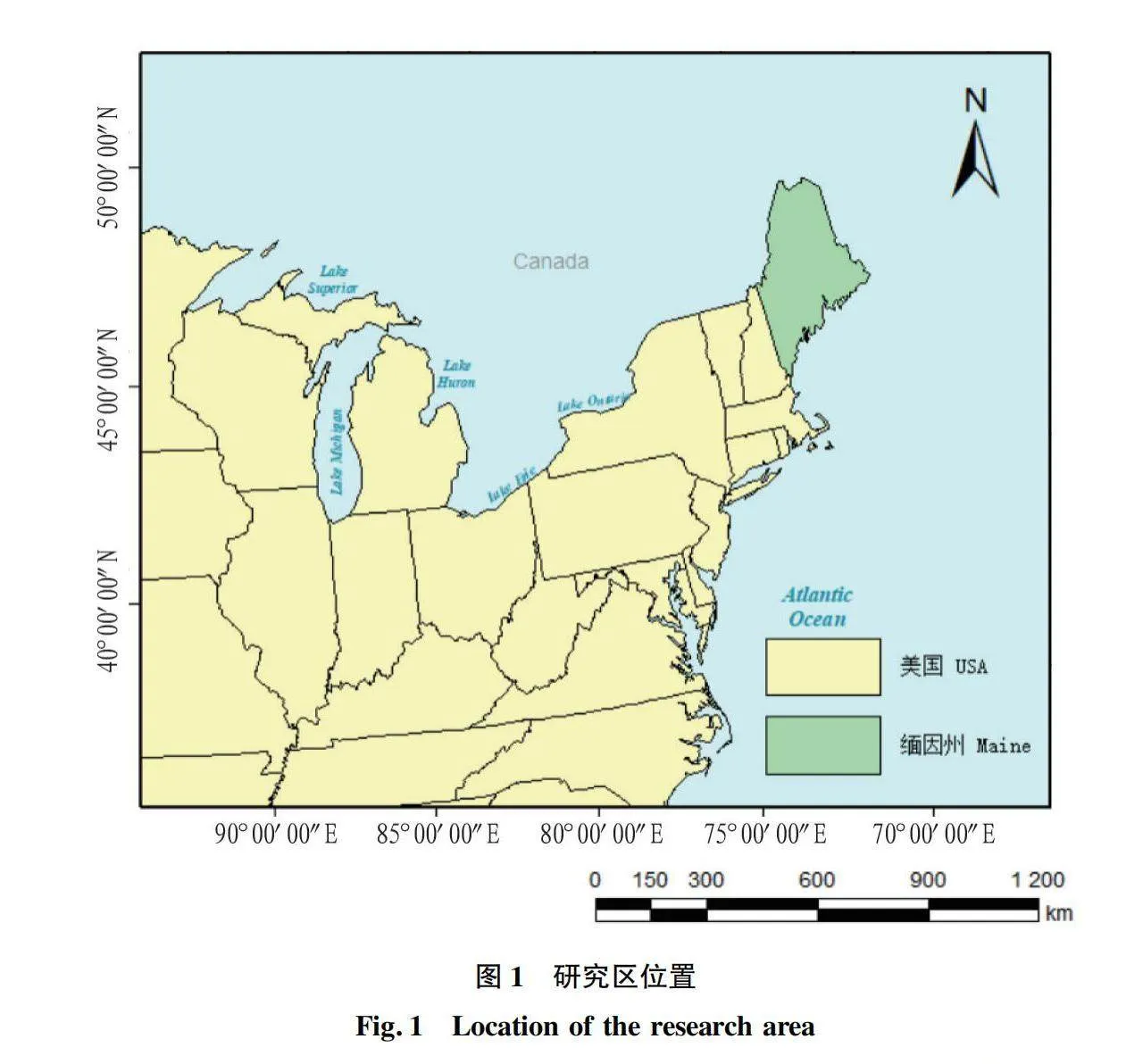
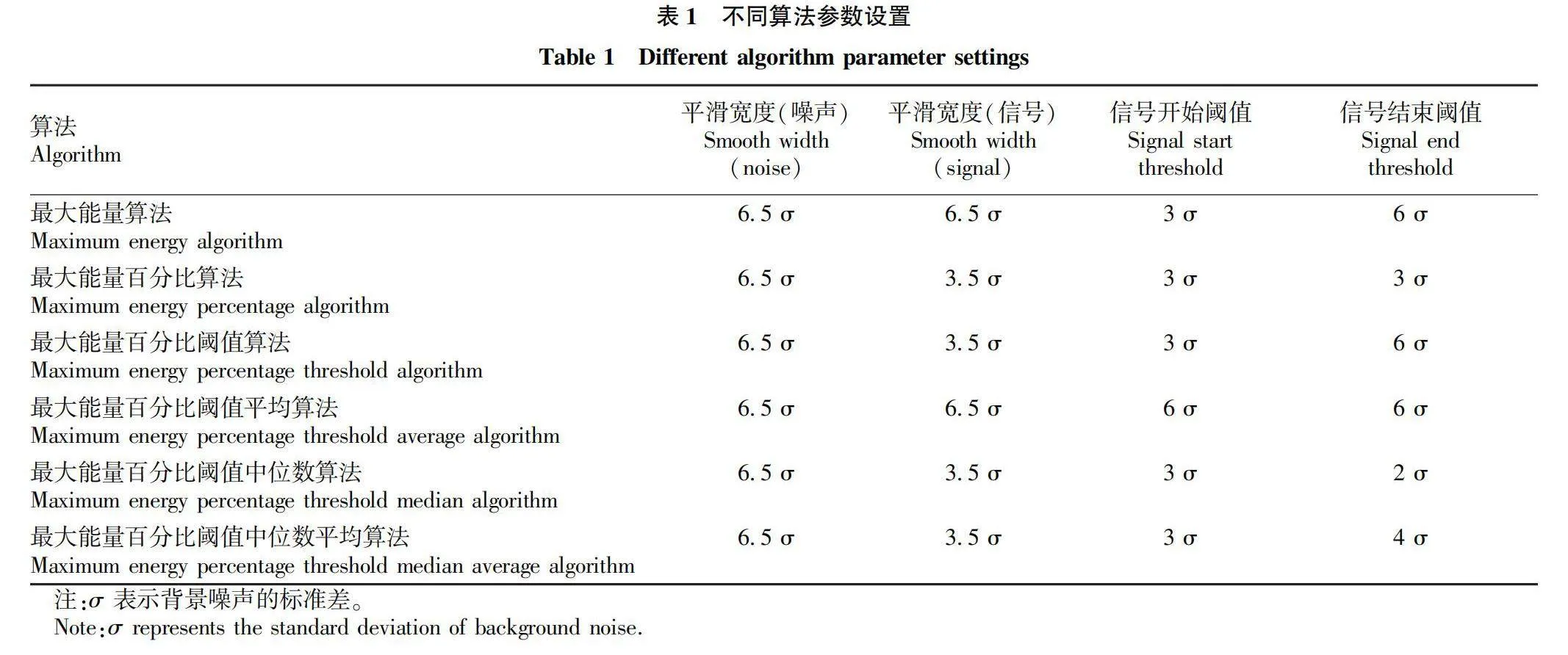

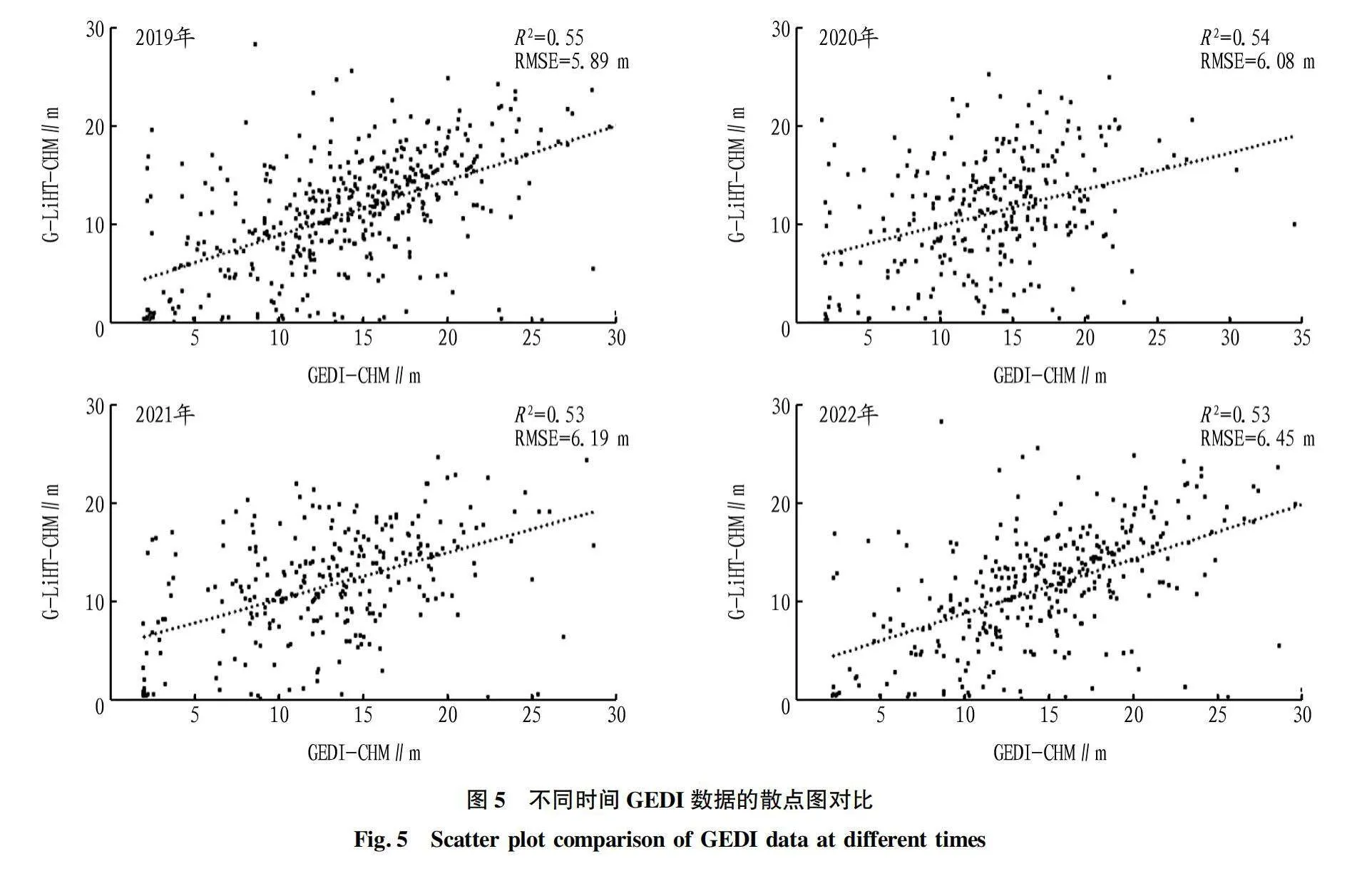

摘要 為解決現有研究針對GEDI 數據產品不同算法估測森林冠層高度不充分的問題,利用機載激光雷達數據探究GEDI 提取的佩諾布斯科特森林冠層高度精度,計算兩數據的R2、RMSE并開展顯著性檢驗分析,用以探究不同算法以及數據獲取時間對估測精度的影響。結果表明:6種算法中,算法4的精度最高,R2=0.61,RMSE=5.74 m。對于不同時間獲取的GEDI數據,與機載數據獲取時間接近的GEDI數據估測精度較高。
關鍵詞 全波形激光雷達;GEDI;森林冠層高度;G-LiHT;精度評估
中圖分類號 S758 文獻標識碼 A 文章編號 0517-6611(2024)19-0097-06
doi:10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2024.19.021
開放科學(資源服務)標識碼(OSID):
Assessing GEDI LiDAR Data Estimation Accuracy of Canopy Height
HUANG Jia-peng,QIAO Jun-qiu,WANG Yong
(School of Geomatics, Liaoning Technical University, Fuxin, Liaoning 123000)
Abstract Existing research on the selection of Global Ecosystem Dynamics Investigation (GEDI) different algorithms to estimate accuracy of canopy height is insufficient. Based on this, this article uses airborne LiDAR data to verify the accuracy of the canopy height extracted by GEDI for the Penobscot experimental forest and calculate the R2 and RMSE of two sets of data and conduct significance test analysis to explore the impact of different algorithm selection and data acquisition time on estimation accuracy. The results show that among the six algorithms, Algorithm four has the highest accuracy, with R2=0.61, RMSE=5.74 m. For GEDI data obtained at different times, the estimation accuracy of GEDI data obtained at a time similar to that of airborne data is higher.
Key words Full waveform lidar;GEDI;Canopy height;G-LiHT;Accuracy assessment
基金項目 遼寧省博士科研啟動基金計劃項目(2023-BS-202);大學生創新創業訓練計劃項目(S202210147007);遼寧省教育廳基本科研項目(JYTQN2023202)。
作者簡介 黃佳鵬(1993—),男,湖南永州人,副教授,博士,從事林業定量遙感研究。
收稿日期 2023-12-04
森林作為陸地生態系統的主體,在地球生態系統中占有重要地位[1]。森林通過調節氣候,涵養水源,提供生物多樣性和資源等方式,對環境和生態具有重要的作用,因此準確地獲取植被參數至關重要。傳統的方式是通過外業實地進行測量,這種方法比較簡單,精度也相對較高。但獲取的數據量非常小,耗時耗力,同時還需要高昂的人工費用,難以滿足大范圍高效率獲取數據的要求。相比而言,星載激光雷達技術可以較好地克服實地調查方法的不足。與傳統衛星光學遙感相比,激光雷達可以克服大氣與夜間觀測限制,為估測地表高程與植被冠層高度提供科學數據[2],這使其成為研究森林垂直結構參數的理想遙感手段。……

