深遠海浮式風電裝備對徐聞附近海域優勢物種生理生化指標的影響
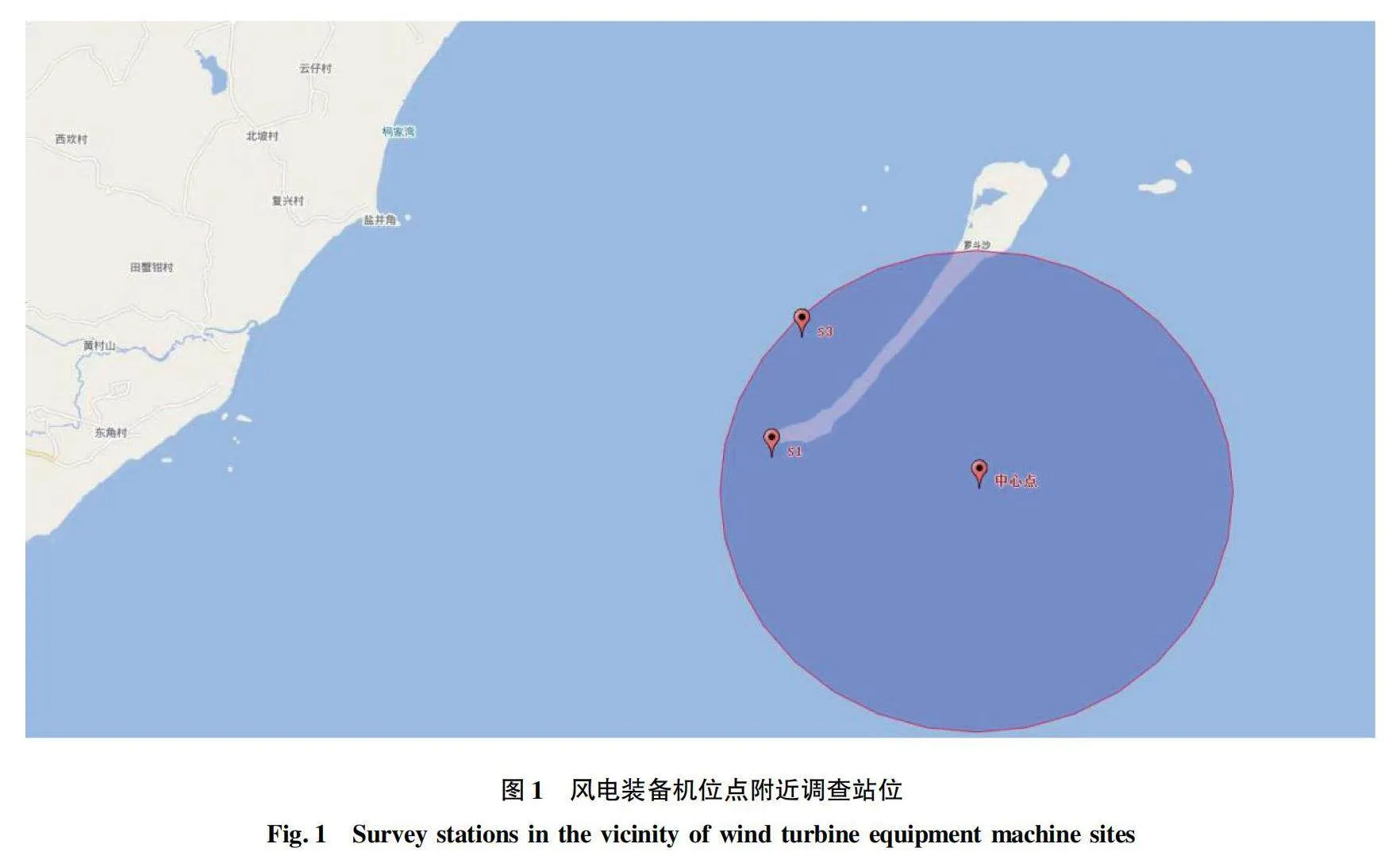
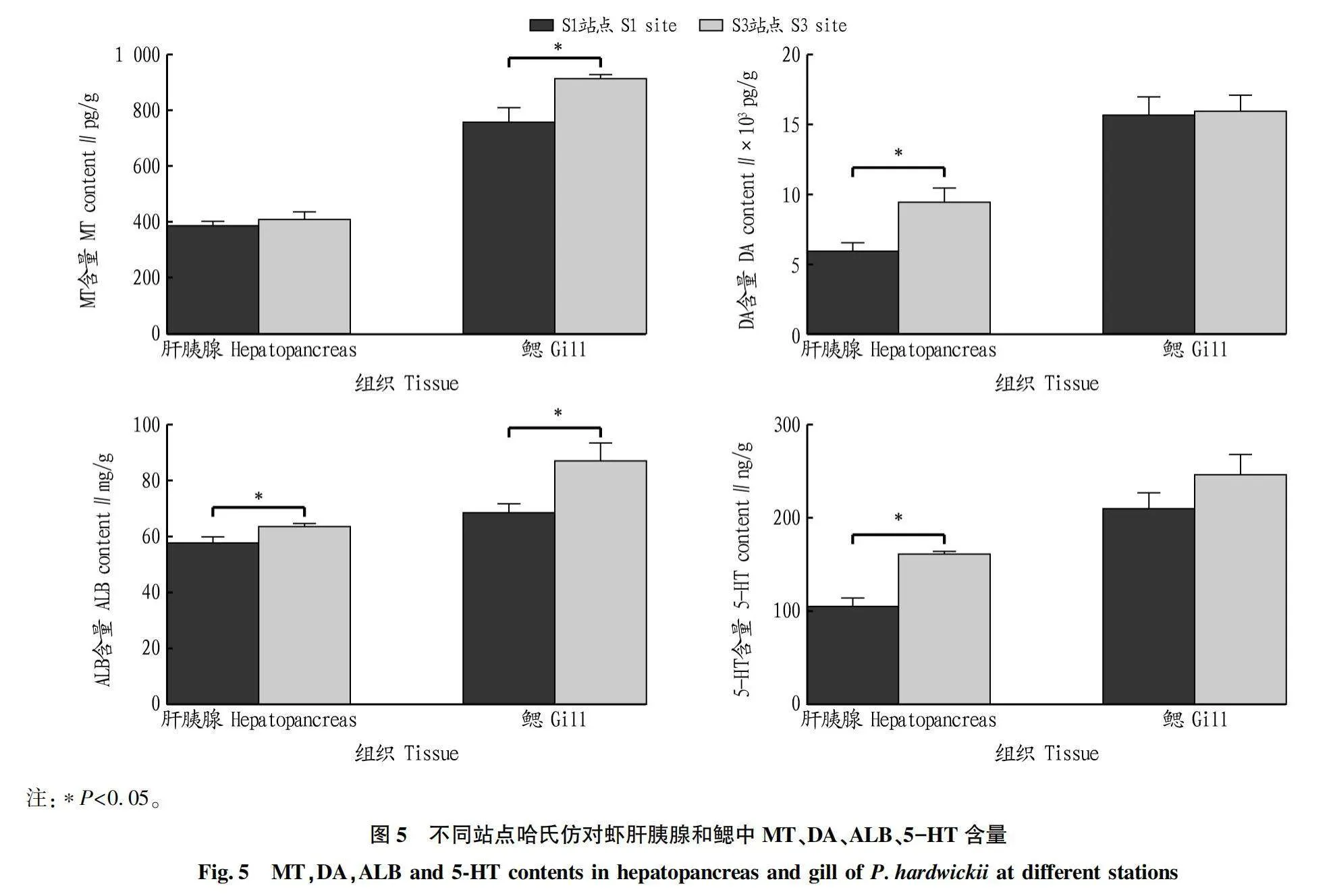

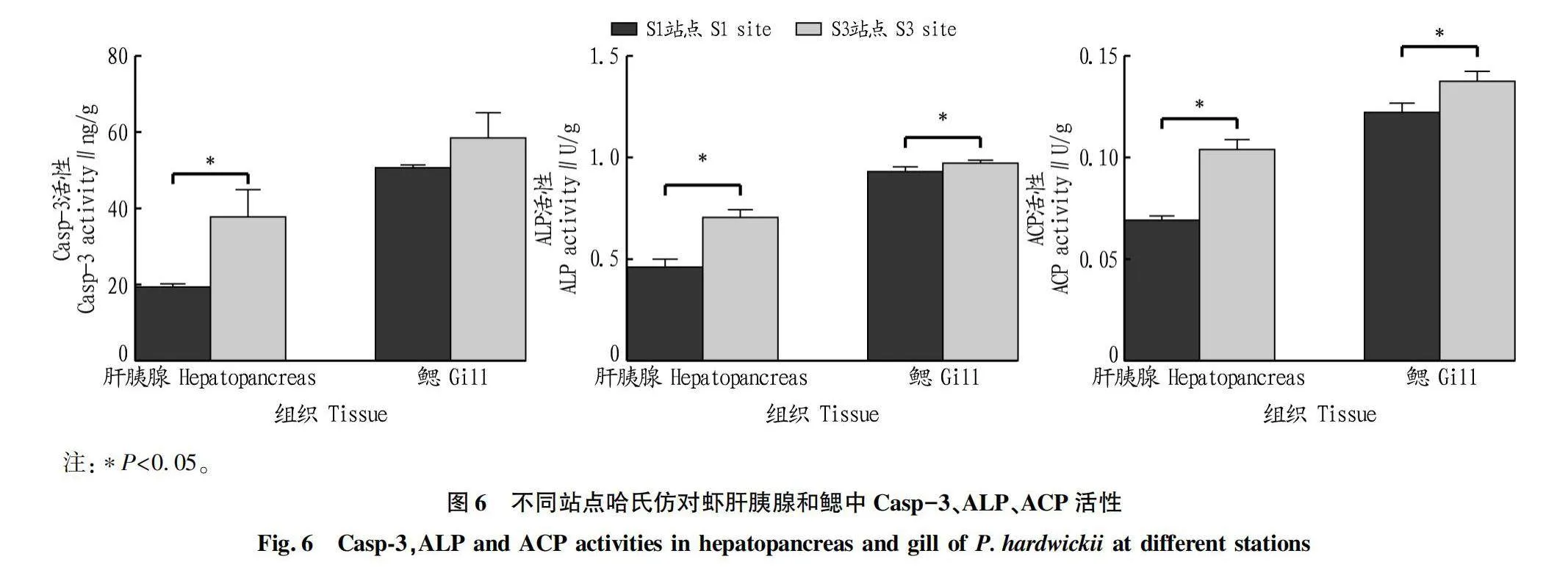
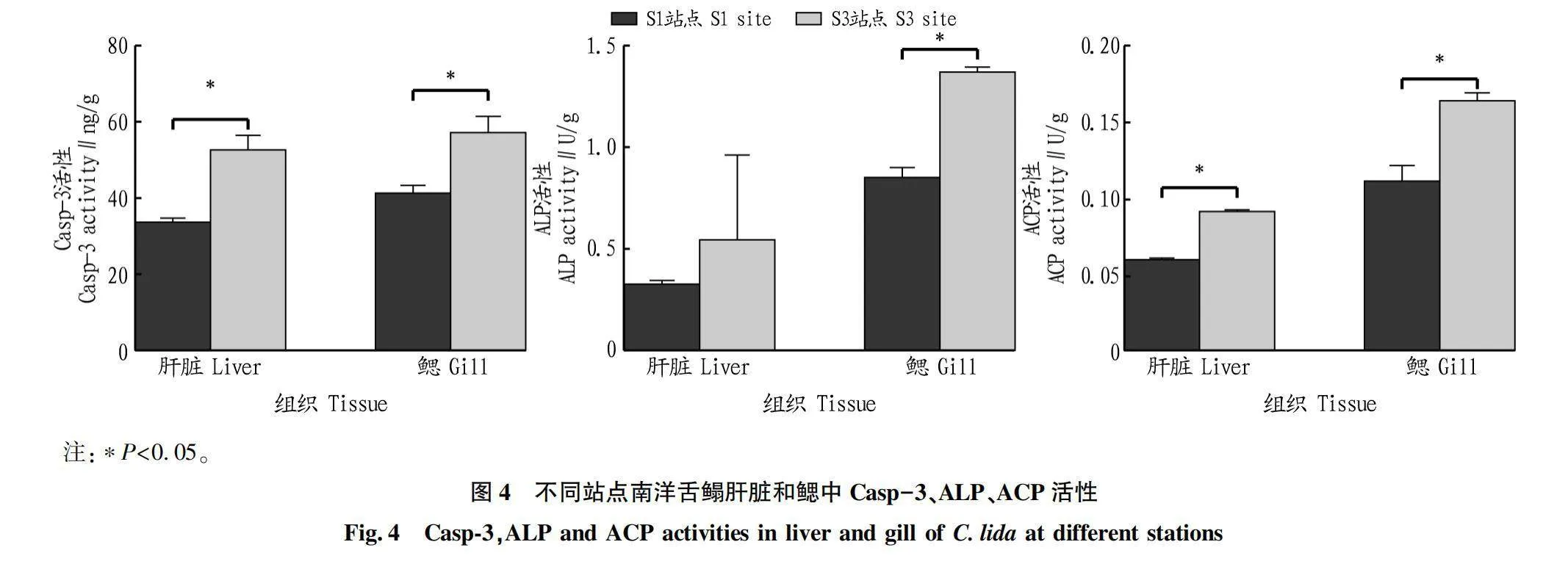
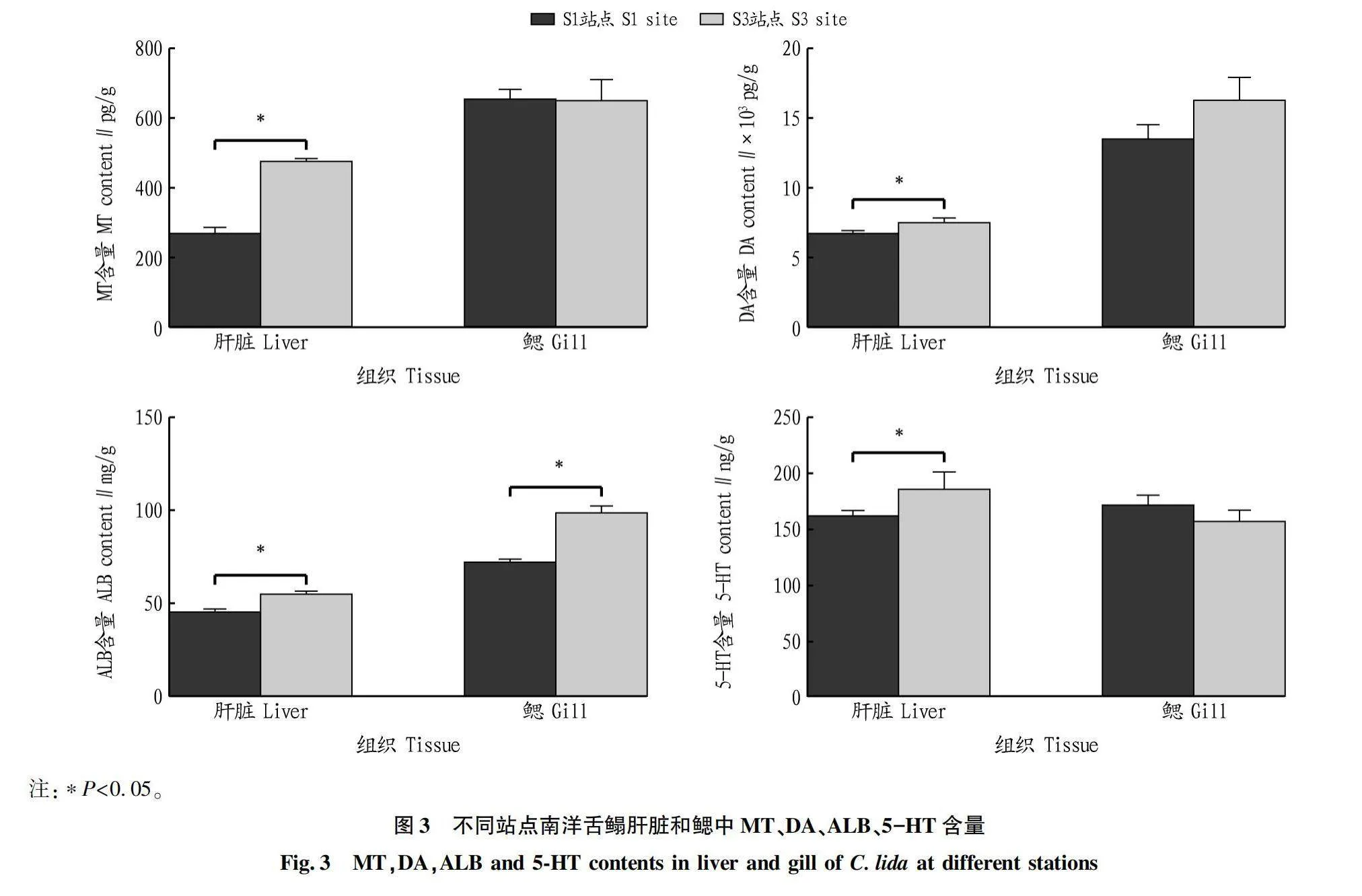
摘要 [目的]研究深遠海浮式風電的建設及運營對周邊海域漁業資源的影響。[方法]對徐聞羅斗沙海域深遠海浮式風電裝備機位點附近海域的S1站點(距機位點約4 km處)和S3站點(距機位點約5 km處)進行拖網取樣,選擇優勢物種南洋舌鰨(Cynoglossidae lida)和哈氏仿對蝦(Parapenaeopsis hardwickii)為試驗對象,探討深遠海浮式風電裝備運行對優勢物種生理生化指標的影響。[結果]S3站點南洋舌鰨肝臟中褪黑素(MT)、多巴胺(DA)、白蛋白(ALB)、5-羥色胺(5-HT)含量及半胱氨酸蛋白酶3(Casp-3)、酸性磷酸酶(ACP)活性顯著高于S1站點(P<0.05),S3站點南洋舌鰨鰓中ALB含量及Casp-3、堿性磷酸酶(ALP)、ACP活性顯著高于S1站點(P<0.05);S3站點哈氏仿對蝦肝胰腺中DA、ALB、5-HT含量及Casp-3、ALP、ACP活性顯著高于S1站點(P<0.05),S3站點哈氏仿對蝦鰓中MT、ALB含量及ALP、ACP活性顯著高于S1站點(P<0.05)。[結論]深遠海浮式風電在一定范圍內對徐聞附近海域優勢物種的生理生化指標有一定的影響。
關鍵詞 深遠海浮式風電裝備;周邊海域;海洋生物;生理生化指標
中圖分類號 X17 文獻標識碼 A 文章編號 0517-6611(2024)19-0071-06
doi:10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2024.19.016
開放科學(資源服務)標識碼(OSID):
Effects of Deep-sea Floating Wind Power Equipment on Physiological and Biochemical Indicators of Dominant Species in the Waters of Xuwen
GUO Hui1,LI Shu-hong1,LIU Zhi2 et al
(1.Key Laboratory of Marine Ecology and Aquaculture Environment of Zhanjiang,College of Fisheries,Guangdong Ocean University,Zhanjiang,Guangdong 524088;2.Guangdong Haizhuang Offshore Windpower Research Center Company Limited,Zhanjiang,Guangdong 524000)
Abstract [Objective]To study the effect of the construction and operation of deep-sea floating wind power on the fishery resources in the surrounding waters.[Method]Trawl sampling was conducted at S1 station (about 4 km from the location) and S3 station (about 5 km from the location) near the deep-sea floating wind power equipment in the Luodousha area of Xuwen.The dominant species Cynoglossidae lida and Parapenaeops hardwickei were selected as experimental subjects to explore the effects of deep-sea wind power equipment operation on the physiological and biochemical indicators of dominant species.[Result]The melatonin (MT),dopamine (DA),albumin (ALB),5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) contents,caspase-3 (Casp-3) and acid phosphatase (ACP) activities in the liver of C.lida at S3 Site were significantly higher than those at Site S1 (P<0.05),the ALB contents and Casp-3,alkaline phosphatase (ALP),ACP activities in the gills of C.lida at Site S3 were significantly higher than those at Site S1 (P<0.05).The contents of DA,ALB and 5-HT and the activities of Casp-3,ALP and ACP in the hepatopancreas of P.hardwickii at Site S3 were significantly higher than those at Site S1 (P<0.05),and the contents of MT and ALB and the activities of ALP and ACP in the gills of P.hardwickii at Site S3 were significantly higher than those at Site S1 (P<0.05).[Conclusion]The deep-sea floating wind power equipment has a certain effect on the physiological and biochemical indexes of the dominant species in the sea area near Xuwen.
Key words Deep-sea floating wind power equipment;Surrounding waters;Marine organism;Physiological and biochemical indicators
作者簡介 郭慧(1986—),女,安徽阜陽人,副教授,博士,從事水產動物健康養殖生態學研究。*通信作者,教授,博士,博士生導師,從事水產經濟動物遺傳育種及生殖生長調控研究。
收稿日期 2023-11-27
風力發電是可再生能源技術領域最成熟的發電方式之一,對解決能源危機和調整能源結構具有積極的意義[1]。作為一種可再生能源,風能具有分布廣泛和儲量豐富等優點,尤其是海上風能,相比于陸地風能,在風速、風況和發電的年利用小時數上都有明顯的優勢,且不占用土地資源[2],因此,海上風電的發展逐漸成為沿海各國海上能源資源開發的重點。……

