荊州市城市擴張與耕地流失的EKC關系及其影響因素

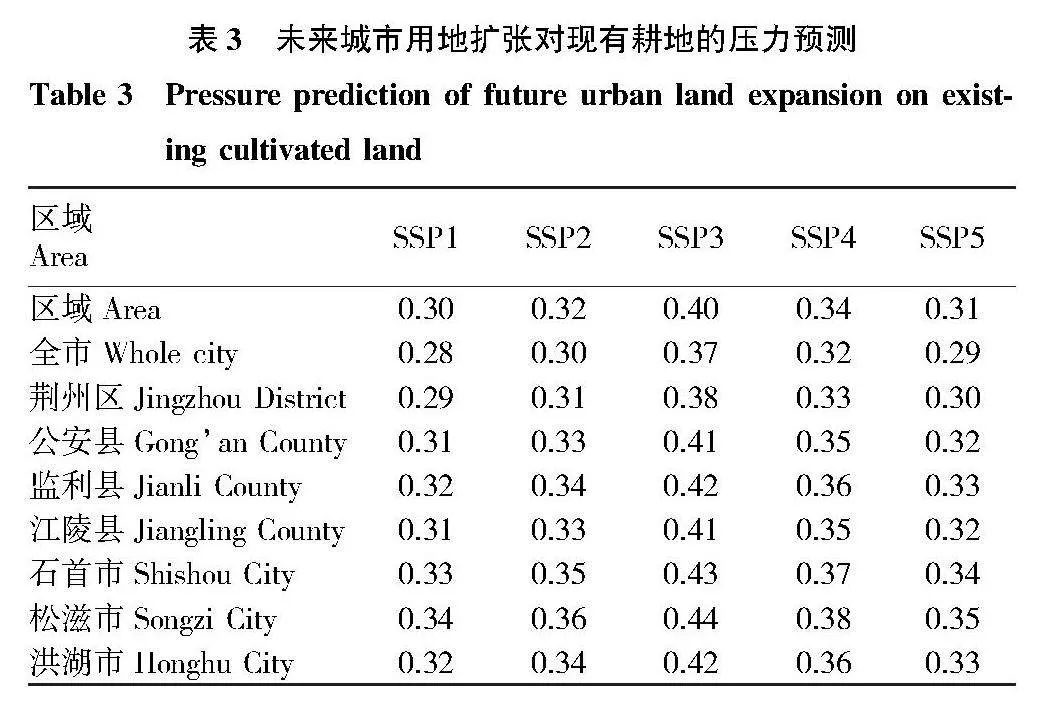
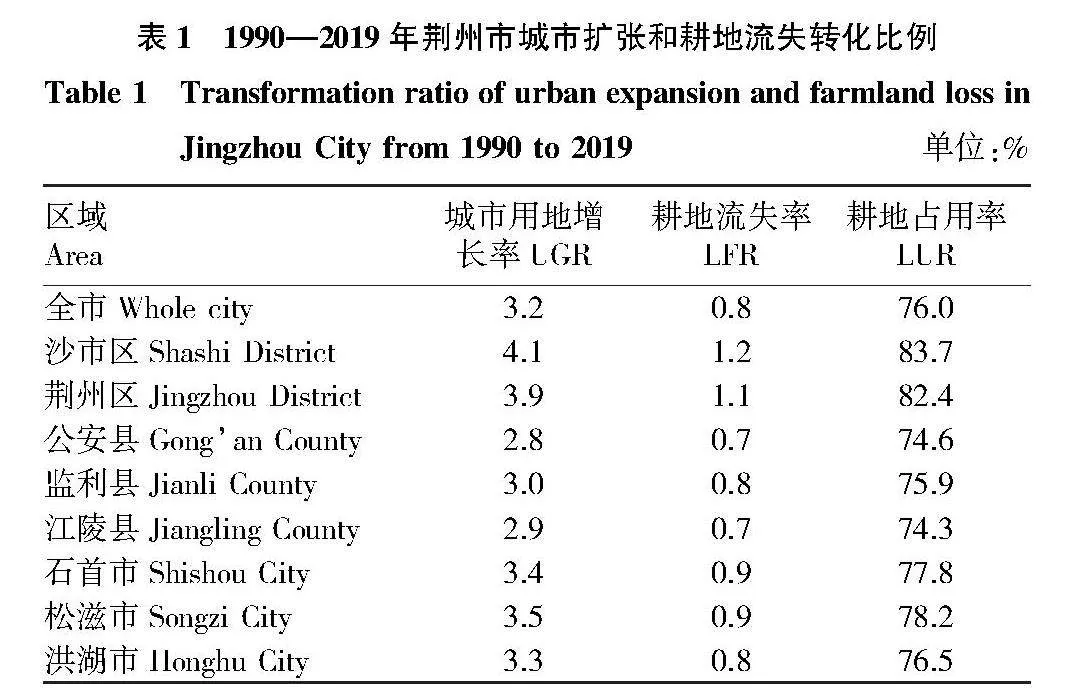
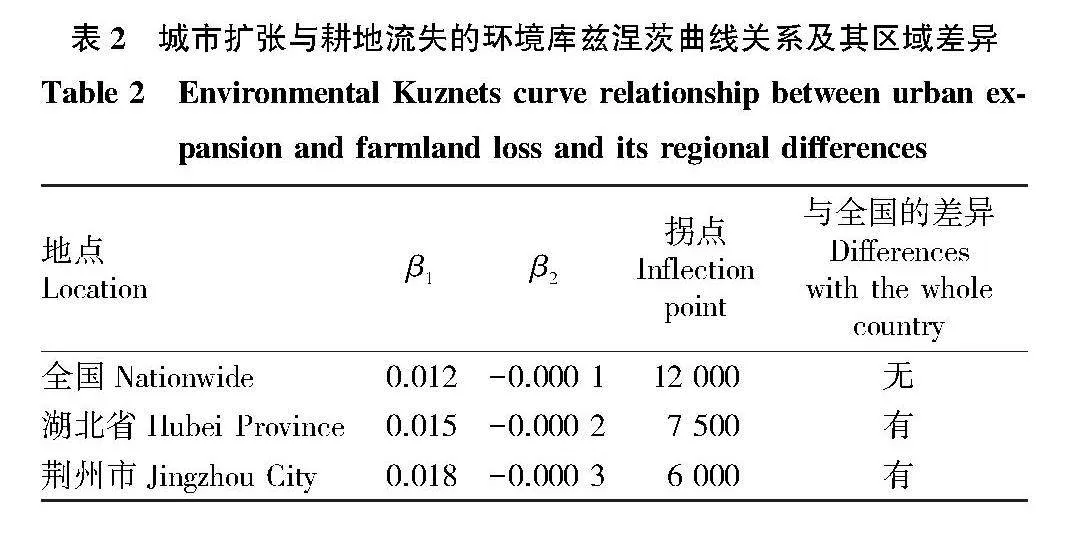
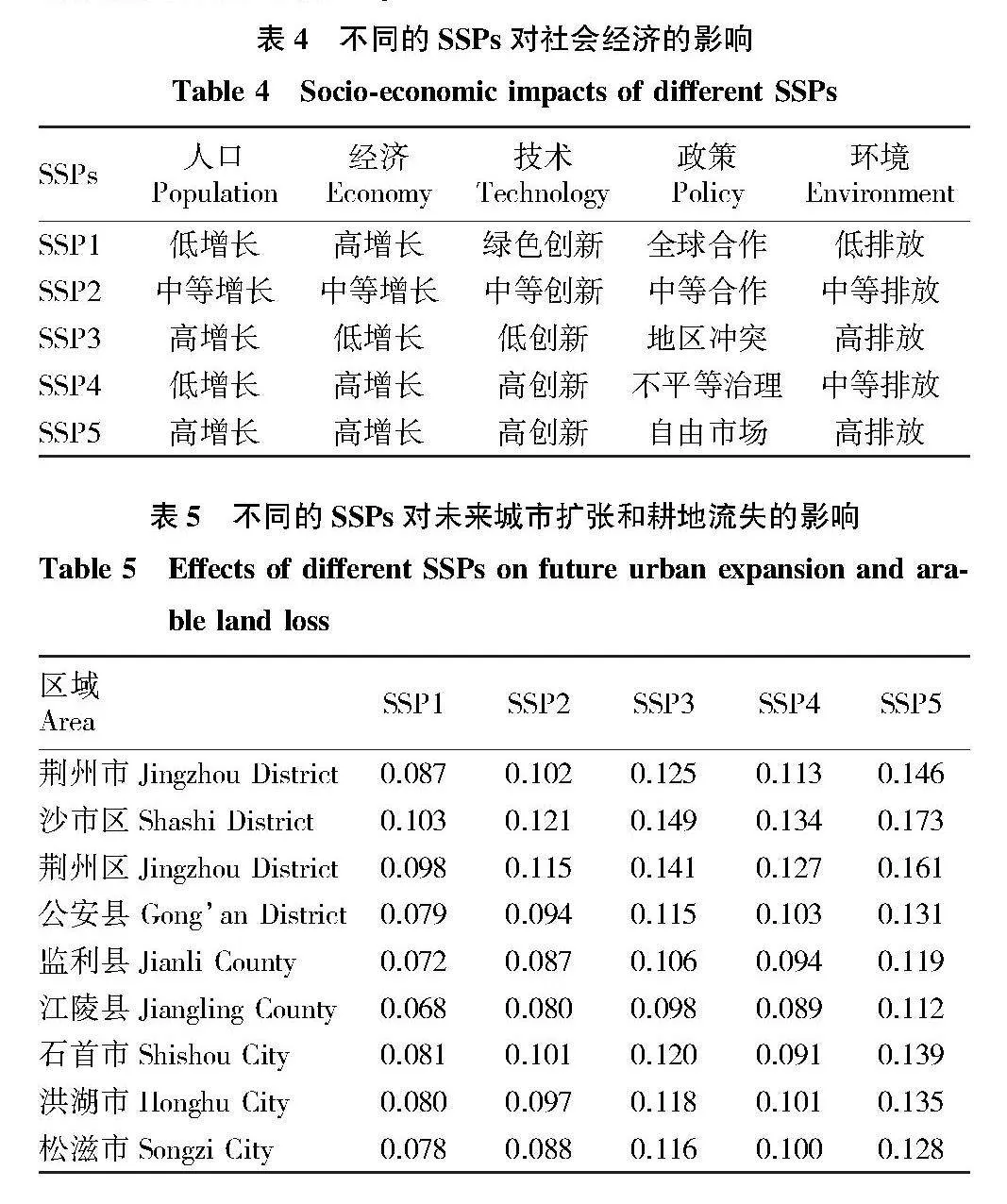
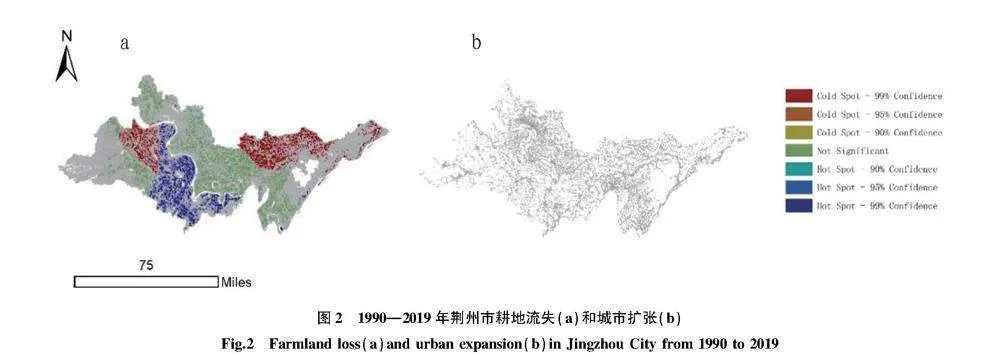
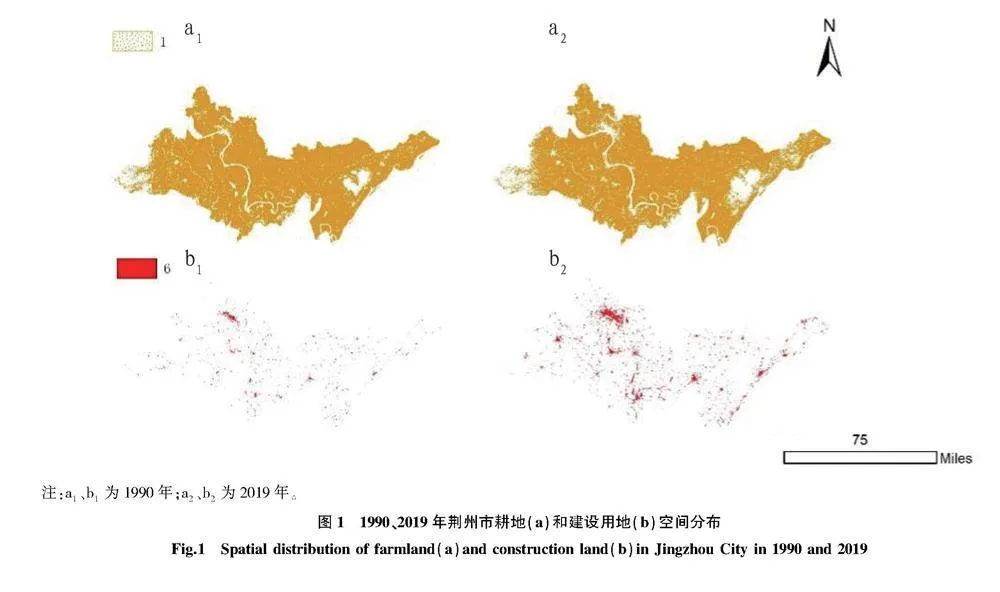
摘要 [目的]以荊州市為例,探討城市擴張與耕地流失的關系及其對經濟增長的影響。[方法]利用中國30 m年度土地覆蓋數據集,分析1990—2019年城市擴張和耕地流失的時空格局及區域差異。引入環境庫茲涅茨曲線(EKC)假設,通過省級面板數據回歸分析,檢驗城市擴張與經濟增長的關系,并利用未來城市用地擴張(FULE)數據集預測未來情景下的耕地壓力。[結果]城市擴張是耕地流失的主要原因,城市擴張的面積占新建城市用地面積的76%和耕地流失面積的28%。縣級以上城市更傾向于利用耕地進行建設,而縣級以下城市則有更多耕地轉化為其他用途。城市擴張與耕地流失之間存在倒U型關系,表明耕地流失隨經濟增長先增后減,2012年達到拐點后開始脫鉤。一些沿江和大型城市已經進入耕地流失減少的階段,而一些內陸和中小型城市仍處于耕地流失增加的階段。預計到2050年,荊州市將有30萬~40萬hm2耕地被城市用地占用,三、四線城市損失最大。[結論]建議加強土地規劃管理,控制城市擴張,優化土地利用結構,提高土地利用效率,保護耕地資源,并促進區域協調發展,實現經濟與環境的平衡。
關鍵詞 城市擴張;耕地流失;環境庫茲涅茨曲線(EKC);荊州市
中圖分類號 F293.2 文獻標識碼 A 文章編號 0517-6611(2024)18-0043-04
doi:10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2024.18.010
開放科學(資源服務)標識碼(OSID):
EKC Relationship Between Urban Expansion and Farmland Loss in Jingzhou City and Its Influencing Factors
ZANG Nan-nan, KONG Ling-cheng
(School of Economics and Management, Yangtze University, Jingzhou,Hubei 434023)
Abstract [Objective]Taking Jingzhou City as an example, this paper discussed the relationship between urban expansion and farmland loss and its impact on economic growth.[Method]Using a 30-meter annual land cover dataset in China, the spatial and temporal patterns and regional differences of urban expansion and farmland loss during 1990-2019 were analyzed. The environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) hypothesis was introduced to test the relationship between urban expansion and economic growth through regression analysis of provincial panel data, and the future urban land expansion (FULE) dataset was used to predict farmland pressure under future scenarios.[Result]Urban expansion was the main cause of farmland loss, accounting for 76% of newly built urban land and 28% of farmland loss. Cities above the county level were more inclined to use farmland for construction, while cities below the county level had more farmland converted to other uses. There was an inverted U-shaped relationship between urban expansion and farmland loss, indicating that the loss of farmland increased first and then decreased with economic growth, and began to decouple after reaching an inflection point in 2012. Some coastal and large cities had entered a stage of reduced farmland loss, while some inland and small and medium-sized cities were still in a stage of increased farmland loss.It was estimated that by 2050, 0.3-0.4 million hectares of arable land in Jingzhou will be occupied by urban land, and third-and fourth-tier cities will suffer the most losses. [Conclusion] It was recommended to strengthen land planning and management, control urban expansion, optimize land use structure, improve land use efficiency, protect arable land resources, promote regional coordinated development, and achieve a balance between economy and environment.
Key words Urban expansion;Farmland loss;Environmental Kuznets curve(EKC);Jingzhou City
作者簡介 臧南南(1989—),男,北京人,碩士研究生,研究方向:農業可持續發展。*通信作者,教授,博士,碩士生導師,從事農業可持續發展研究。
收稿日期 2023-11-09
隨著城市化進程的加速,城市擴張與耕地流失之間的關系日益引起關注。……

