New Iteration Method for a Quadratic Matrix Equation Associated with an M-Matrix
GUAN Jinrui(關晉瑞),SONG Ruying(宋儒瑛),ZUBAIR Ahmed
(1.Department of Mathematics,Taiyuan Normal University,Jinzhong 030619,China;2.Institute of Mathematics and Computer Science,University of Sindh,Sindh 76080,Pakistan)
Abstract: In this paper,we consider numerical solution of a quadratic matrix equation associated with an M-matrix,which arises in the study of noisy Wiener-Hopf problems for the Markov chain.The solution of practical interest is the M-matrix solution.By a simple transformation,this quadratic matrix equation is transformed into an M-matrix algebraic Riccati equation.We propose a new iteration method for this equation and then give the convergence analysis of it.Numerical experiments are given to show that the new iteration method is feasible and effective than some existing methods in some cases.
Key words: Quadratic matrix equation; M-matrix; Algebraic Riccati equation; Iteration method
1.Introduction
In this paper,we consider a quadratic matrix equation (QME)

where E,F ∈Rn×n,E is a diagonal matrix and F is an M-matrix.The study of equation(1.1) is motivated by noisy Wiener-Hopf problems for Markov chains.See [5,8] for more background details.
Under some conditions,it was proved in [5] that the equation (1.1) has an M-matrix solution,which is of practical interest.In addition,by transforming it into an equivalent M-matrix algebraic Riccati equation,a fixed-point iteration method and Newton method have been developed for solving the QME in [5].However,the fixed-point iteration method converges too slowly while the Newton method is too expensive at each iteration.So they are not very efficient for this problem.In this paper,our main aim is to develop an efficient method for solving the QME (1.1).
In the following,we first review some basic results of M-matrix and M-matrix algebraic Riccati equation.
Let A = (aij) ∈Rn×n.If aij≤0 for all ij,then A is called a Z-matrix.A Z-matrix A is called an M-matrix if there exists a nonnegative matrix B such that A = sI -B and s ≥ρ(B) where ρ(B) is the spectral radius of B.In particular,A is called a nonsingular M-matrix if s >ρ(B) and singular M-matrix if s=ρ(B).
The following lemmas can be found in [1,11].
Lemma 1.1Let A ∈Rn×nbe a Z-matrix.Then the following statements are equivalent:
1) A is a nonsingular M-matrix;
2) A-1≥0;
3) Av >0 for some vectors v >0;
4) All eigenvalues of A have positive real part.
Lemma 1.2Let A,B be Z-matrices.If A is a nonsingular M-matrix and A ≤B,then B is also a nonsingular M-matrix.In particular,for any nonnegative real number α,B =αI +A is a nonsingular M-matrix.
Lemma 1.3Let A be an M-matrix,B ≥A be a Z-matrix.If A is nonsingular or irreducible singular with AB,then B is also a nonsingular M-matrix.
Lemma 1.4Let A,B be nonsingular M-matrices and A ≤B,then A-1≥B-1.
M-matrix algebraic Riccati equation is of the form
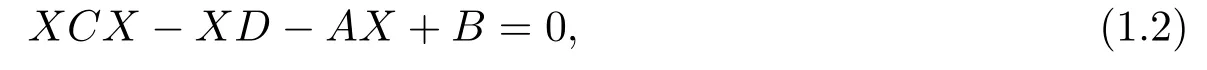
where A,B,C and D are real matrices of sizes m×m,m×n,n×m and n×n respectively.MARE appears in many branches of applied mathematics,such as transport theory,Markov chains,stochastic process,and so on.See [2-3] and the references therein for details.For the MARE (1.2),the solution of practical interest is its minimal nonnegative solution.The following basic result is obtained in [3-4].
Lemma 1.5For the MARE (1.2),if
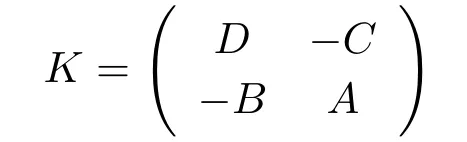
is a nonsingular M-matrix or an irreducible singular M-matrix,then (1.2) has a minimal nonnegative solution S.If K is a nonsingular M-matrix,then A-SC and D-CS are also nonsingular M-matrices.If K is irreducible M-matrix,then S >0 and A-SC and D-CS are also irreducible M-matrices.
When K is an irreducible singular M-matrix,there exist unique,up to a multiplicative constant,u >0 and v >0 such that uTK =0,Kv =0 and uTv =1.Partition the vectors u and v according to the block structure of the matrix M asLetwe have the following result.[3]
Lemma 1.6If K is an irreducible singular M-matrix and S is the minimal nonnegative solution of the MARE (1.2).Then
(i) when μ<0,D-CS is singular and A-SC is nonsingular;
(ii) when μ>0,D-CS is nonsingular and A-SC is singular;
(iii) when μ=0,both D-CS and A-SC are singular.
Efficient methods for solving the MARE (1.2) include the Schur method,the fixed-point iteration,the Newton iteration,the doubling algorithms and etc.[2-3,6-7,9-10]
2.A New Iteration Method
In this section,we first briefly introduce the fixed-point iteration method in[5]for solving the QME (1.1),and then propose a new iteration method for solving (1.1).
By introducing X =αI -Y,the equation (1.1) can be transformed into
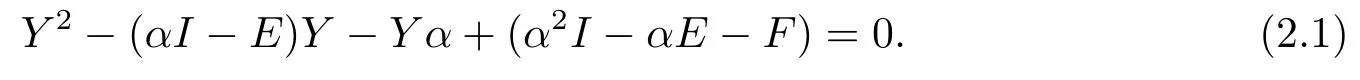
It was proved in [5] that when α satisty
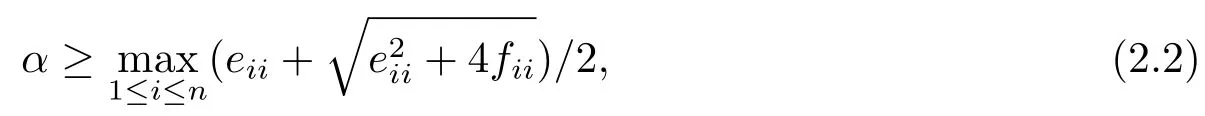
α2I-αE-F is a nonnegative matrix.In addition,if F is a nonsingular M-matrix,then
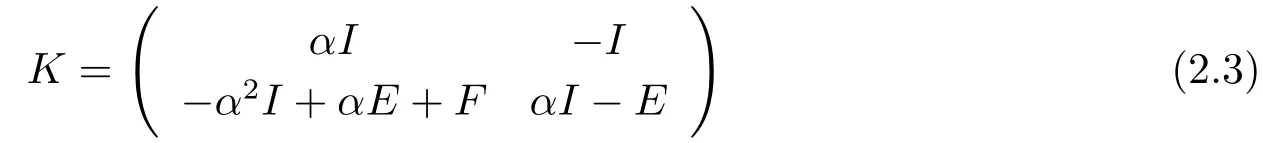
is a nonsingular M-matrix,and if F is an irreducible singular M-matrix,then K is an irreducible singular M-matrix.
By the above analysis and the theory of MARE,the following results were obtained in[5].
Theorem 2.1If F is a nonsingular M-matrix,then (1.1) has exactly one M-matrix as its solution and the M-matrix is nonsingular.If F is an irreducible singular M-matrix,then(1.1) has M-matrix solutions and all elements of each M-matrix solution are nonzero.In addition,let u,v be positive vectors such that Fv =0 and uTF =0,then
1) if uTEv ≤0,then (1.1) has exactly one M-matrix as its solution and the M-matrix is singular.
2) if uTEv >0,then (1.1) has exactly one nonsingular M-matrix as its solution but may also have singular M-matrices as its solutions.
For solving the QME(1.1),a fixed-point iteration method was proposed in[5]as follows.
Fixed-point iteration method:
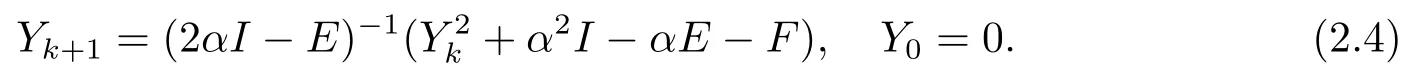
Convergence analysis showed that the sequence {Yk} in (2.4) is monotonically increasingly and converges to the minimal nonnegative solution of the equation (2.1).In addition,the convergence rate of the fixed-point iteration method is linear for the noncritical case,and is sublinear for the critical case.However,experiments in [5] showed that the fixed-point iteration needs a large numbers of iterations to converge,though at each iteration it is very cheap.
In the following,we will propose a new iteration method for computing the minimal nonnegative solution of the equation (2.1).
First,write the equation (2.1) as
(2αI -E-Y)Y =α2I-αE-F.
Then we can get the following iterations
(2αI -E-Yk)Yk+1=α2I-αE-F.
Thus the new iteration method can be stated as follows.
New iteration method:
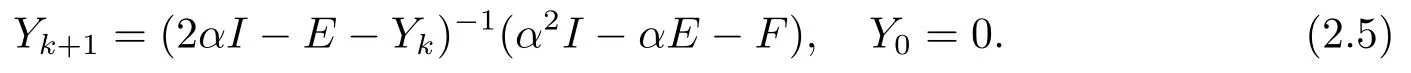
Compared with the fixed-point iteration method (2.4),the new iteration method (2.5) is a little expensive,since at each iteration a matrix inverse is required to compute.However,the new iteration method may need less iterations than the fixed-point iteration method,which will be confirmed by the numerical experiments.So it is feasible.
3.Convergence Analysis
In the following,we give convergence analysis of the new iteration method (2.5).
The following lemma can be concluded from Theorem 2.1,Lemma 1.5 and Lemma 1.6.
Lemma 3.1Let the parameter α satisfy (2.2).If F in (1.1) is a nonsingular Mmatrix,then the equation (2.1) has a unique minimal nonnegative solution Sα,and αI-Sα,αI-E-Sαare nonsingular M-matrices.If F in(1.1)is an irreducible singular M-matrix,then the equation(2.1)has a unique minimal nonnegative solution Sα,and αI-Sα,αI-E-Sαare irreducible M-matrices.In addition,let u,v be positive vectors such that Fv =0,uTF =0,then
1) If uTEv =0,then both αI-Sαand αI -E-Sαare singular M-matrices;
2) If uTEv <0,then αI -Sαis nonsingular and αI -E-Sαis singular;
3) If uTEv >0,then αI -Sαis singular and αI -E-Sαis nonsingular.
ProofWhen F is a nonsingular M-matrix or an irreducible singular M-matrix,equation(2.1) has a unique minimal nonnegative solution Sαby Lemma 1.5.When F is nonsingular,then both αI -Sαand αI -E-Sαare nonsingular M-matrices.
When F is irreducible singular,take= (uT(αI -E),uT)Tand= (vT,αvT)T,then we haveTK =0,K=0 and μ=-uTEv.By Lemma 1.6,the conclusion follows.
Theorem 3.1Let F in (1.1) be a nonsingular M-matrix or an irreducible singular M-matrix and the parameter α satisfy (2.2).Then the sequence {Yk} generated by (2.5) is well defined,converges to Sα,and satisfy

where Sαis the unique minimal nonnegative solution of the equation (2.1).
ProofWe first prove (3.1) by induction.
When k = 0,we have Y1= (2αI -E)-1(α2I -αE -F).Since α satisfies (2.2),we have 2αI >E and α2I - αE - F ≥0.It is clear that 0 = Y0≤Y1.Since Sαis the minimal nonnegative solution of (2.1),it holds that (2αI -E-Sα)Sα=α2I -αE-F.By Lemma 3.1,we know αI-E-Sαis an M-matrix,and hence,by Lemma 1.2,2αI-E-Sαis a nonsingular M-matrix.Thus Sα= (2αI - E - Sα)-1(α2I - αE - F).It is evident(2αI-E)-1≤(2αI -E-Sα)-1,thus Y1≤Sα.
Suppose that the assertions (3.1) hold for k =l-1,i.e.0 ≤Yl-1≤Yl,Yl≤Sα.
Since Yl≤Sα,we know 2αI -E -Yl≥2αI -E -Sαis a nonsingular M-matrix by Lemma 1.3.Thus Yl+1is well defined.From 0 ≤Yl-1≤Yl≤Sαand Lemma 1.4,we know(2αI-E-Yl-1)-1≤(2αI -E-Yl)-1≤(2αI -E-Sα)-1.We have
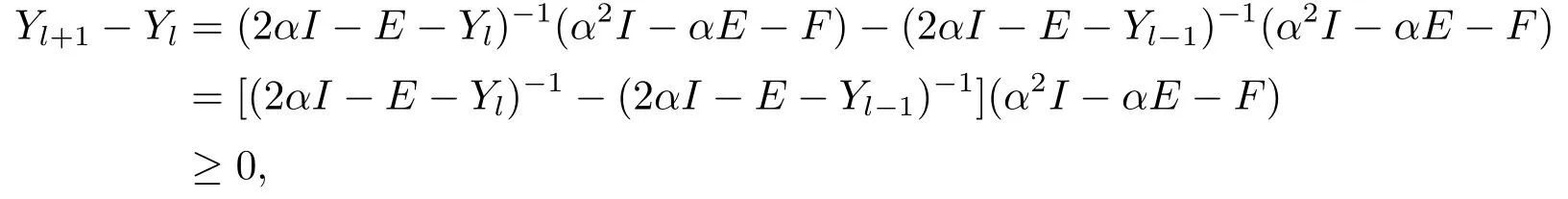
and
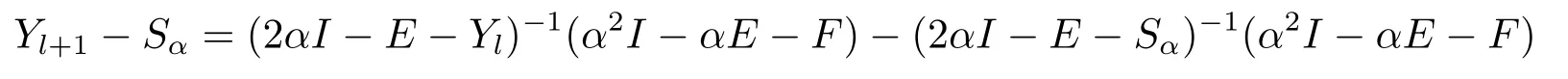
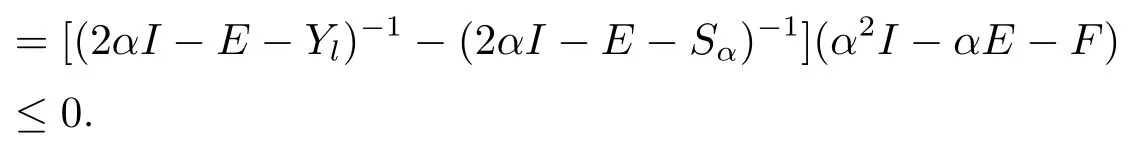
Hence the assertions (3.1) hold for k = l+1.Thus we have proved by induction that the assertions (3.1) hold for all k ≥0.
Since {Yk} is nonnegative,monotonically increasing and bounded from above,there is a nonnegative matrix Y such that limk→∞Yk=Y.From (3.1) we know Y ≤Sα.On the other hand,taking the limit in(2.5),we know Y is a solution of(2.1),thus Sα≤Y.Hence Sα=Y.
Theorem 3.2Let F in (1.1) be a nonsingular M-matrix or an irreducible singular M-matrix and the parameter α satisfy (2.2).Then the convergence rate of (2.5) is given by
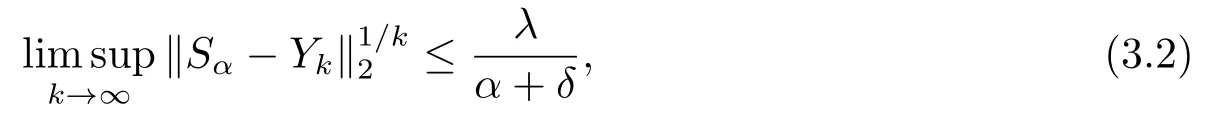
where λ=ρ(Sα) and δ is the minimum eigenvalue of the M-matrix αI -E-Sα.
ProofWe have
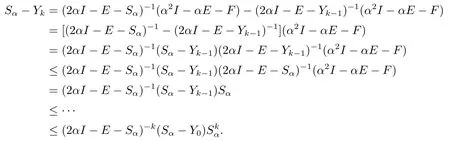
Hence
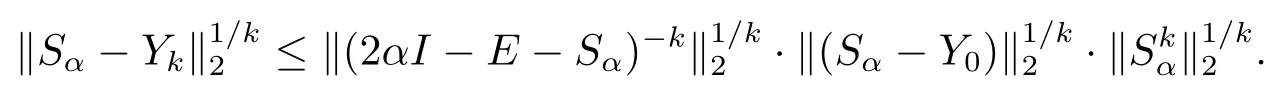
Taking limit on both side and noting thatwe have
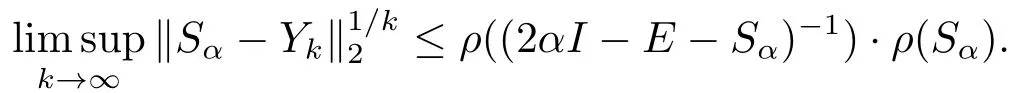
Since αI -E-Sαis an M-matrix and Sαis a nonnegative matrix,we can easily verify that
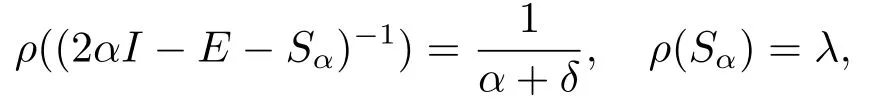
where δ is the minimum nonnegative eigenvalue of αI-E-Sαand λ is the Perron eigenvalue of Sα.Thus the conclusion (3.2) holds.
Corollary 3.1If F in (1.1) is a nonsingular M-matrix,then the convergence rate of(2.5)is linear.If F is an irreducible singular M-matrix,then for the cases 2)and 3)in Lemma 3.1,the convergence rate of (2.5) is linear; for the case 1) the convergence rate of (2.5) is sublinear.
ProofWhen F is a nonsingular M-matrix,αI -Sαand αI -E-Sαare nonsingular M-matrices.Hence α >λ and δ >0.Thus<1,the convergence rate of (2.5) is linear.
If F is an irreducible singular M-matrix,and the cases 2) and 3) happen,then one of αI-Sαand αI-E-Sαis a nonsingular M-matrix.We have<1,the convergence rate of (2.5) in this case is still linear.
If F is an irreducible singular M-matrix and the case 1) happens,then αI -Sαand αI -E -Sαare both singular M-matrices.Thus we have α = ρ(Sα) and δ = 0.Hence=1,the convergence rate of (2.5) is sublinear in this case.
Corollary 3.2The optimal parameter of the new iteration method (2.5) is given by
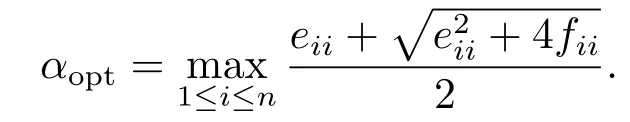
ProofLet α1>0,α2>0 be two parameters that satisfy (2.2) and α1>α2.Then the convergence factor of the new iteration method (2.5) are respectively
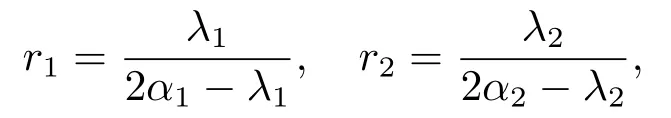
where λ1=ρ(Sα1),λ2=ρ(Sα2) and Sα1,Sα2are the minimal nonnegative solutions of (2.1)respectively.Since α1I-S1=α2I-S2,we have S1=(α1-α2)I+S2and λ1=(α1-α2)+λ2.Thus
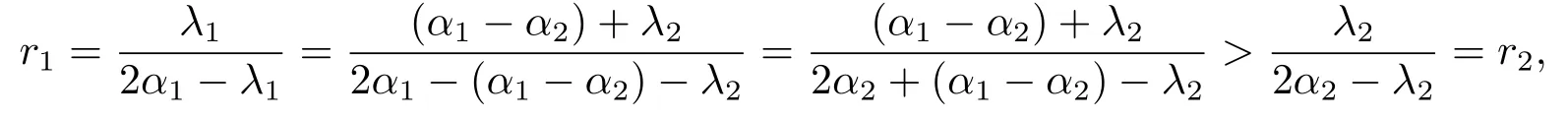
and the conclusion follows.
4.Numerical Experiments
In this section,numerical experiments are given to show the feasibility and effectiveness of the new iteration method.We compare the new iteration method (NM) with the fixedpoint iteration method(FP)in[5],and present numerical results of each experiment in terms of iteration numbers (IT),CPU time (CPU) in seconds and residue (Res),where the residue is defined to be
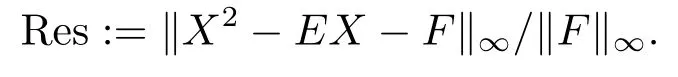
In our implementations,all iterations are run in MATLAB (R2012a) on a personal computer and are terminated when the current iterate satisfies
Example 4.1[5]Consider the equation (1.1) with
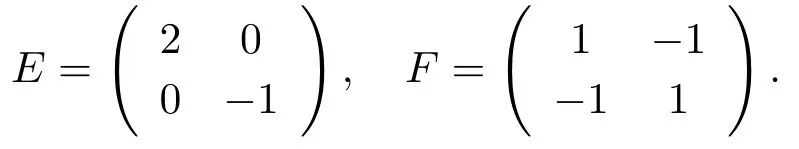
The numerical result is summarized in Tab.4.1.
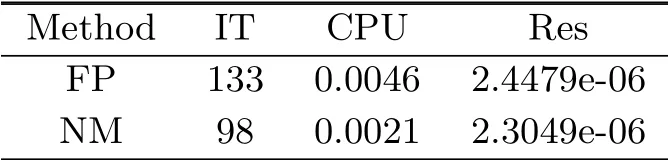
Tab.4.1 Numerical Results of Example 4.1
Example 4.2[5]Consider the equation (1.1) with
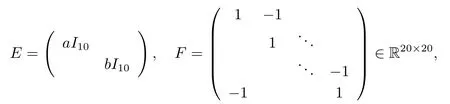
where we take a=2,b=1.The numerical result is summarized in Tab.4.2.
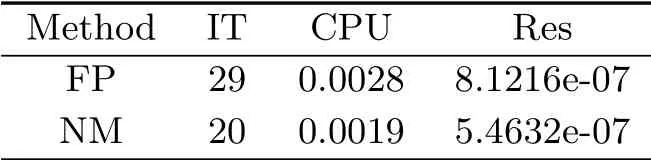
Tab.4.2 Numerical Results of Example 4.2
Example 4.3Consider the equation (1.1) with coefficient matrices defined as
E =diag(1:n); F =rand(n,n); F =diag(Fe)-F,
where e=(1,1,··· ,1)T.For different sizes of n,we list the numerical results in Tab.4.3.

Tab.4.3 Numerical Results of Example 4.3
From Tabs.4.1-4.3,we can conclude that the new iteration method needs less iteration number and CPU time than the fixed-point iteration method.Hence it is feasible and effective.
- 應用數學的其它文章
- 一種新的二次約束二次規劃問題的分支定界算法
- 一類分數階Kirchhoff型方程Schwarz對稱基態解的存在性
- 矩陣偽譜的新定位集及其在土壤生態系統的應用
- The Uniform Boundedness and Convergence for the Core Inverses of Linear Operators in Banach Spaces
- Impulsive Control for One Class of the Incommensurate Conformable Fractional Order System with Discontinuous Right Side
- Existence and Stability of Positive Solutions to Nonlinear Delay Integro-Differential Equation on Time Scales

