空氣污染物暴露對兒童常見呼吸系統疾病住院患兒數的影響
周芳 崔玉霞 劉燁 陳恒 周浩
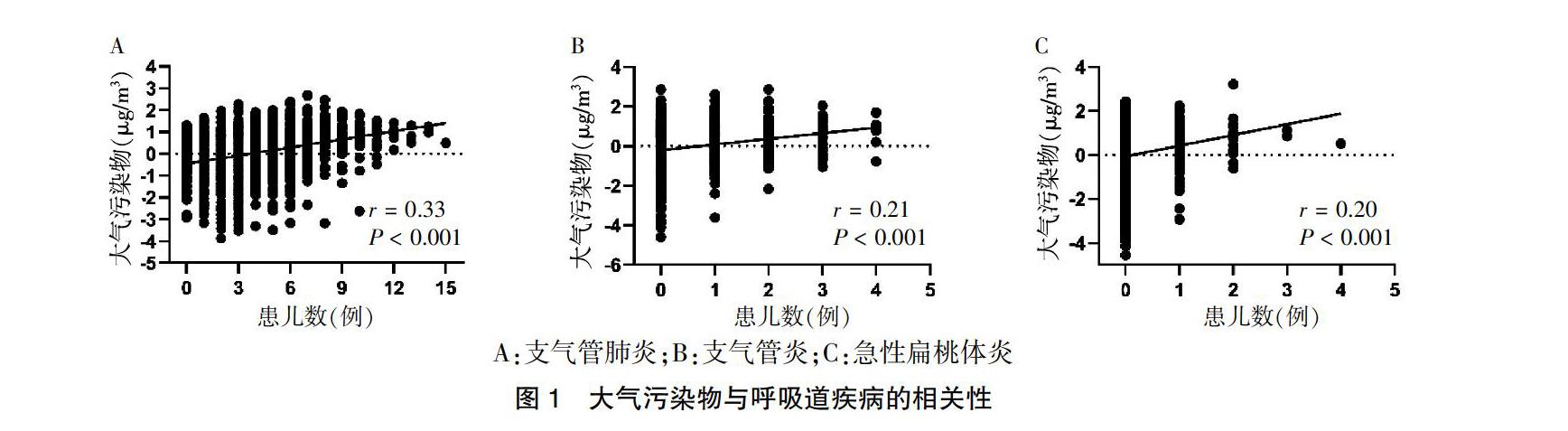

[摘要] 目的 了解空氣污染物暴露對兒童常見呼吸系統疾病住院患兒數的影響。 方法 收集貴州省人民醫院2009年1月—2016年12月兒科常見呼吸系統疾病住院患兒臨床資料及貴陽市各環境監測點空氣污染物監測數據,包括:PM2.5、PM10、一氧化氮(NO)、二氧化硫(SO2)濃度。應用典型相關分析方法分析空氣污染物對兒童常見呼吸系統疾病住院患兒數的影響。 結果 共10 876例呼吸系統疾病住院患兒納入研究,其中診斷以支氣管肺炎為主(76.31%),平均住院(9.56±6.05)d。大氣污染物與支氣管肺炎相關系數最高(r = 0.33,P < 0.001),其次為支氣管炎(r = 0.21,P < 0.001)和急性扁桃體炎(r = 0.20,P < 0.001)。PM10是影響兒童常見呼吸系統疾病住院患兒數的主要空氣污染物成分,住院前1 d空氣污染對兒童常見呼吸系統疾病住院患兒數影響最大。 結論 環境空氣污染物可影響兒童常見呼吸系統疾病的住院患兒數,其中對支氣管肺炎的住院患兒數影響最大。PM10是影響兒童常見呼吸系統疾病住院患兒數最常見的污染物,最大影響效應為住院前1 d。
[關鍵詞] 空氣污染;呼吸系統疾病;兒童;住院人數
[中圖分類號] R56? ? ? ? ? [文獻標識碼] A? ? ? ? ? [文章編號] 1673-7210(2020)07(c)-0058-04
Effect of air pollutant exposure on the number of children hospitalized for common respiratory diseases
ZHOU Fang1? ?CUI Yuxia1? ?LIU Ye2? ?CHEN Heng3? ?ZHOU Hao1
1.Department of Pediatrics, Guizhou Provincial People′s Hospital, Guizhou Province, Guiyang? ?550002, China; 2.Department of Otolaryngology, Guizhou Provincial People′s Hospital, Guizhou Province, Guiyang? ?550002, China; 3.College of Medical, Guizhou University, Guizhou Province, Guiyang? ?550025, China
[Abstract] Objective To understand the impact of air pollutant exposure on the number of children hospitalized for common respiratory diseases. Methods The clinical data of pediatric hospitalized children for common respiratory diseases from January 2009 to December 2016 in Guizhou Provincial People′s Hospital and air pollutant monitoring data at various environmental monitoring points in Guiyang City including: PM2.5, PM10, nitric oxide (NO) and the concentration of sulfur dioxide (SO2) were collected. A typical correlation analysis method was used to analyze the impact of air pollutants on the number of children hospitalized for common respiratory diseases. Results A total of 10 876 hospitalized children with respiratory diseases were included in the study, and the diagnosis was mainly bronchopneumonia (76.31%), with an average hospital stay (9.56±6.05) d. The correlation coefficient between air pollutants and bronchial pneumonia was the highest (r = 0.33, P < 0.001), followed by bronchitis (r = 0.21, P < 0.001) and acute tonsillitis (r = 0.20, P < 0.001). PM10 was the main air pollutant component that affected the number of children for common respiratory diseases. Air pollution one day before hospitalization had the greatest impact on the number of children for common respiratory diseases. Conclusion Ambient air pollutants can affect the number of children hospitalizations for common respiratory diseases, of which the number of hospitalizations for bronchopneumonia is the greatest. Among them, PM10 is the most common pollutant that affects the number of children hospitalizations for common respiratory diseases, and the largest effect is one day before hospitalization.
本研究通過典型相關分析,大氣污染物對支氣管肺炎住院患兒數影響最大,其次為支氣管炎和急性扁桃體炎。提示大氣污染物可影響兒童呼吸系統疾病住院患兒數,且對不同呼吸系統疾病患兒數的影響存在差異。根據各種大氣污染物的理化特性和兒童呼吸系統的生理特點,使下呼吸道及肺泡更容易受到大氣污染物的影響和侵害,這可能是與空氣污染對兒童支氣管肺炎的住院患兒數影響最大有關[11-13]。因此,減少兒童與大氣污染物的接觸有助于降低兒童支氣管炎及肺炎等下呼吸道疾病的發病率。
大氣污染物與呼吸系統疾病患兒數的權重分布發現,不同大氣污染物成分對呼吸系統疾病住院患兒數的影響存在差異。這可能與污染物具有不同的理化性質相關。PM2.5和PM10因粒徑小,可隨氣流進入下呼吸道,部分可達到肺泡,多次接觸大氣中的顆粒物會損害激活保護性Nrf2組織防御系統的能力[14-15],導致肺氧化損傷和全身炎癥反應,促使兒童肺功能下降,引發急慢性支氣管炎、肺炎等呼吸系統疾病。環境中NO通過誘導氣道甲氧膽堿高反應性、抗原特異性IgG1和IgE、炎癥性白細胞募集等促進氣道變應性疾病的發生,其濃度與咳嗽、哮鳴、遺傳性過敏性呼吸短促等癥狀存在關聯[16-17]。而SO2水溶性較強,易被上呼吸道和支氣管黏膜的黏液吸收,從而刺激氣管或支氣管收縮,增加氣道阻力。此外,SO2還可與飄塵產生協同作用進而被吸附于微粒表面,進入呼吸道深部,吸入SO2可導致早期肺反應,包括組織損傷、急性嗜中性肺炎癥和氣道高反應性[11,18-19]。
綜上所述,通過分析空氣污染物暴露對兒童常見呼吸系統疾病住院患兒數的影響發現,空氣污染對兒童常見呼吸系統疾病住院患兒數的影響存在差異,對支氣管肺炎的影響最大。PM10是導致兒童呼吸系統疾病的主要空氣污染物成分,住院前1天的空氣污染是影響呼吸系統疾病住院患兒數的主要原因。然而,本研究僅包含呼吸系統住院患兒病歷資料,缺少門診資料,導致受空氣質量影響較大的支氣管哮喘病例未納入本研究,這將是下一步的研究方向。
[參考文獻]
[1]? Beelen R,Raaschou-Nielsen O,Stafoggia M,et al. Effects of long-term exposure to air pollution on natural-cause mortality:an analysis of 22 European cohorts within the multicentre ESCAPE project [J]. Lancet,2014,383(9919):785-795.
[2]? Phillips D,Osmond C,Southall H,et al. Evaluating the long-term consequences of air pollution in early life: geographical correlations between coal consumption in 1951/1952 and current mortality in England and Wales [J]. BMJ Open,2018,8(4):e18231.
[3]? Tao Y,Mi S,Zhou S,et al. Air pollution and hospital admissions for respiratory diseases in Lanzhou,China [J]. Environ Pollut,2014,185:196-201.
[4]? Chi R,Li H,Wang Q,et al. Association of emergency room visits for respiratory diseases with sources of ambient PM2.5 [J]. J Environ Sci,2019,86:154-163.
[5]? Guan WJ,Zheng XY,Chung KF,et al. Impact of air pollution on the burden of chronic respiratory diseases in China:time for urgent action [J]. Lancet,2016,388(10054):1939-1951.
[6]? Zhou H,Wang T,Zhou F,et al. Ambient Air Pollution and Daily Hospital Admissions for Respiratory Disease in Children in Guiyang,China [J]. Front Pediatr,2019,7:400.
[7]? Xu M,Zhu Z,Zhang X,et al. Canonical Correlation Analysis With L2,1-Norm for Multiview Data Representation [J]. IEEE Trans Cybern,2019.
[8]? Chai G,He H,Sha Y,et al. Effect of PM2.5 on daily outpatient visits for respiratory diseases in Lanzhou,China [J]. Sci Total Environ,2019,649:1563-1572.
[9]? Liang L,Cai Y,Barratt B,et al. Associations between daily air quality and hospitalisations for acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Beijing,2013-17:an ecological analysis [J]. Lancet Planet Health,2019, 3(6):e270-e279.
[10]? 蘇志華,王建華.貴陽市大氣顆粒物的污染特征及其影響因素分析[J].中山大學學報:自然科學版,2015,54(5):77-84.
[11]? Jo EJ,Lee WS,Jo HY,et al. Effects of particulate matter on respiratory disease and the impact of meteorological factors in Busan,Korea [J]. Respir Med,2017,124:79-87.
[12]? 安愛萍,郭琳芳,董蕙青.我國大氣污染及氣象因素對人體健康影響的研究進展[J].環境與職業醫學,2005,22(3):279-282.
[13]? 張瑩.我國典型城市空氣污染特征及其健康影響和預報研究[D].蘭州:蘭州大學,2016.
[14]? Zeng Q,Wu Z,Jiang G,et al. The association between ambient inhalable particulate matter and the disease burden of respiratory disease:An ecological study based on ten-year time series data in Tianjin,China [J]. Environ Res,2017,157:71-77.
[15]? Li Y,Duan J,Yang M,et al. Transcriptomic analyses of human bronchial epithelial cells BEAS-2B exposed to atmospheric fine particulate matter PM2.5 [J]. Toxicol In Vitro,2017,42:171-181.
[16]? 李泓冰,朱琳,崔國權,等.哈爾濱市空氣污染對小學生呼吸系統疾病的影響[J].中國學校衛生,2015,36(6):884-886.
[17]? 孫賽男.蘇州市空氣污染物對兒童呼吸道病原體流行的影響[D].蘇州:蘇州大學,2018.
[18]? Polezer G,Tadano YS,Siqueira HV,et al. Assessing the impact of PM2.5 on respiratory disease using artificial neural networks [J]. Environ Pollut,2018,235:394-403.
[19]? Chen H,Uddin LQ,Guo X,et al. Parsing brain structural heterogeneity in males with autism spectrum disorder reveals distinct clinical subtypes [J]. Hum Brain Mapp,2019,40(2):628-637.
(收稿日期:2020-03-05)

