基質金屬蛋白酶-8與肺結核復發的相關性研究
陳伊 翁瓊琳 鄧君麗
【摘要】 目的 探討基質金屬蛋白酶-8(MMP-8)與肺結核復發的相關性及評估其臨床價值。方法 選取初治活動性肺結核患者86例(初治活動性肺結核組)、復發肺結核患者46例(復發肺結核組)、健康體檢者56例(健康對照組), 采用酶聯免疫吸附實驗(ELISA)法檢測三組的血清MMP-8濃度, 并作比較, 分析復發肺結核患者的診斷臨界值、敏感度、特異度。結果 初治活動性肺結核組的血清MMP-8濃度高于健康對照組, 差異有統計學意義(Z=-8.145, P=0.000<0.05)。復發肺結核組的血清MMP-8濃度高于健康對照組, 差異有統計學意義(Z=-6.528, P=0.000<0.05)。初治活動性肺結核組與復發肺結核組的血清MMP-8濃度比較差異無統計學意義(Z=-0.236, P=0.813>0.05)。根據復發肺結核組及健康對照組血清MMP-8 濃度繪制受試者工作特征曲線(ROC)曲線, 得出復發肺結核患者的診斷臨界值為1.88 ng/ml、敏感度為91.3%和特異度為69.6%。表明血清MMP-8 濃度在復發肺結核的診斷中有一定的準確度[曲線下面積(AUC)=0.875, 95%CI=(0.811, 0.940), P=0.000<0.05]。結論 MMP-8與肺結核復發有一定的相關性并具有一定的臨床價值。
【關鍵詞】 基質金屬蛋白酶-8;肺結核;復發
【Abstract】 Objective ? To discuss the correlation between matrix metalloproteinase-8 (MMP-8) and recurrence of tuberculosis and evaluate its clinical value. Methods ? 86 patients with newly diagnosed active pulmonary tuberculosis (initial active pulmonary tuberculosis group), 46 patients with recurrent pulmonary tuberculosis (recurrent pulmonary tuberculosis group), and 56 healthy subjects (healthy control group) were selected. The serum MMP-8 concentrations of the three groups were tested by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and compared to analyze the diagnostic threshold, sensitivity and specificity of patients with recurrent pulmonary tuberculosis. Results ? Initial active pulmonary tuberculosis group had higher concentrations of serum MMP-8 than healthy control group, and the difference was statistically significant (Z=-8.145, P=0.000<0.05). Recurrent pulmonary tuberculosis group had higher concentrations of serum MMP-8 than healthy control group, and the difference was statistically significant (Z=-6.528, P=0.000<0.05). Initial active pulmonary tuberculosis group and recurrent pulmonary tuberculosis group had no statistically significant in concentrations of serum MMP-8 (Z=-0.236, P=0.813>0.05). The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was drawn according to the serum MMP-8 concentration in the recurrent pulmonary tuberculosis group and the healthy control group. The diagnostic threshold, sensitivity and specificity of patients with recurrent pulmonary tuberculosis were 1.88 ng/ml,?91.3% and 69.6% respectively. The serum MMP-8 concentration showed a certain degree of accuracy in the diagnosis of recurrent pulmonary tuberculosis [area under curve (AUC)=0.875, 95%CI=(0.811, 0.940), P=0.000<0.05]. Conclusion ? MMP-8 is related to the recurrence of pulmonary tuberculosis and has certain clinical value.
【Key words】 Matrix metalloproteinase-8; Tuberculosis; Recurrence
流動人口的增加以及耐藥結核尤其是耐多藥結核的出現等多種原因, 使得結核病仍然是全球性的嚴重健康問題。肺結核為結核病的主要常見發病形式, 對于肺結核致病機制及病理過程的深入研究有助于結核病的防控。基質金屬蛋白酶(matrix metalloproteinases, MMPs)是一組有鋅鈣依賴性的催化激活的蛋白酶, 其主要作用是參與炎癥反應、組織重塑、降解細胞外基質等, 目前已發現有20多種。研究表明MMPs與結核病的發病機理有關, 是結核病組織損傷的效應因子, 與結核病的發病程度及愈后有關[1-7]。MMP-8主要來源于中性粒細胞, 是MMPs中的一員, 在結核病的免疫病理學中起著重要作用[8-11]。本研究通過對初治活動性肺結核患者、復發肺結核患者及健康對照人群的血清MMP-8濃度分析, 探討MMP-8與肺結核復發的相關性及臨床應用價值。
1 資料與方法
1. 1 一般資料 選取本院2017~2018年收治的初治活動性肺結核患者86例(初治活動性肺結核組)、復發肺結核患者46例(復發肺結核組)、健康體檢者56例(健康對照組)。
1. 2 方法
1. 2. 1 儀器與試劑 酶標儀:匯松科技發展有限公司, MMP-8 ELISA試劑盒:江萊生物。
1. 2. 2 檢測方法 采用ELISA法檢測三組的血清MMP-8濃度。設置標準品孔、標本孔及空白對照孔, 標準品孔加入50 μl標準品, 標本孔加入50 μl標本, 若標本濃度過高需樣品稀釋液稀釋后加入。每孔加100 μl酶標試劑, 空白孔不加標品及酶標試劑, 封板膜封板, 37℃溫育60 min, 洗滌5次, 拍干, 先加50 μl顯色劑A, 再加50 μl顯色劑B, 37℃避光15 min, 加50 μl終止液, 450 nm波長測量吸光度(空白孔調零), 計算樣品濃度。
1. 3 觀察指標 比較三組血清MMP-8濃度, 分析復發肺結核患者的診斷臨界值、敏感度和特異度。
1. 4 統計學方法 采用SPSS20.0對實驗數據進行統計分析。計量資料經正態性檢驗, 數據呈非正態分布, 采用中位數(四分位數間距)表示, 數據比較采用Mann-Whitney U檢驗;計數資料采用χ2檢驗。應用ROC曲線確定診斷臨界值、敏感度和特異度, AUC比較采用Z檢驗。P<0.05為差異有統計學意義。
2 結果
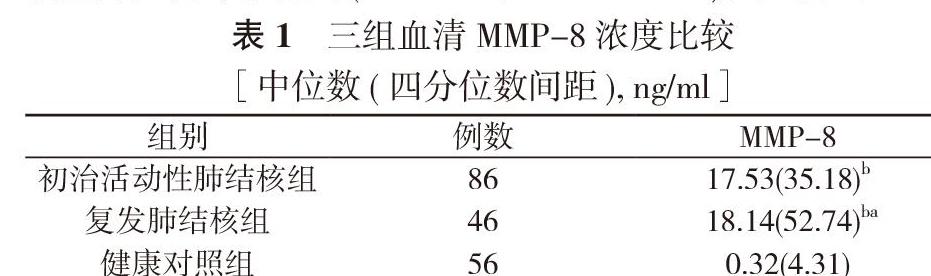
2. 1 三組血清MMP-8濃度比較 初治活動性肺結核組的血清MMP-8濃度高于健康對照組, 差異有統計學意義(Z=-8.145, P=0.000<0.05)。復發肺結核組的血清MMP-8濃度高于健康對照組, 差異有統計學意義(Z=-6.528, P=0.000<0.05)。初治活動性肺結核組與復發肺結核組的血清MMP-8濃度比較差異無統計學意義(Z=-0.236, P=0.813>0.05)。見表1。
2. 2 復發肺結核患者的診斷臨界值、敏感度和特異度 根據復發肺結核組及健康對照組血清MMP-8 濃度繪制ROC曲線, 得出復發肺結核患者的診斷臨界值為1.88 ng/ml、敏感度為91.3%和特異度為69.6%。表明血清MMP-8 濃度在復發肺結核的診斷中有一定的準確度[AUC=0.875, 95%CI=(0.811, 0.940), P=0.000<0.05]。
3 討論
結核病是由結核分枝桿菌引起的慢性傳染性高負擔性疾病。肺結核的病理過程主要包括炎性滲出、增生、干酪樣壞死等, 對于這些過程的研究有助于揭示結核病致病機制及篩選發現新的分子標志物。
MMPs具有重要的免疫調節功能, 可以作用于促炎細胞因子、趨化因子和其他蛋白質, 以調節炎癥和免疫的各個方面并在生理性組織重構中起著重要作用, 是結核病發病的主要因素之一[10]。MMP-8是基質金屬蛋白酶家族中的一類膠原酶, 具有降解細胞外基質, 參與肉芽腫形成及炎性反應等作用。本研究結果顯示, 初治活動性肺結核組的血清MMP-8濃度高于健康對照組, 差異有統計學意義(Z=-8.145, P=0.000<0.05)。這與國外的研究結果相似[11], 表明MMP-8有可能成為肺結核診斷中的潛在分子標志物。
肉芽腫、空洞和干酪樣壞死是結核病的重要特征, 其中空洞是感染傳播, 治療后復發和耐藥性出現的公認風險因素, 與結核分枝桿菌菌量負荷有關, 聯系MMP-8的生物作用, MMP-8含量的高低或可具有預測結核病危險程度的作用。Lee 等[12]的研究也證實了MMP-8具有預測結核病風險作用。Ong等[9]的研究顯示MMP-8是結核病潛在的定向治療靶標。本研究通過分析不同時期治療的肺結核患者, 即初治活動性肺結核和復發肺結核患者的血清MMP-8濃度, 進一完善了MMP-8與肺結核的關系, 研究顯示, 初治活動性肺結核組與復發肺結核組的血清MMP-8濃度比較差異無統計學意義(Z=-0.236, P=0.813>0.05)。這對于MMP-8作為潛在治療方案時提供一定的臨床數據。
肺結核的復發不僅給肺結核患者帶來了巨大的負擔與痛苦, 同時也增加了結核病防治的難度, 如何能急時快捷的預測肺結核的復發, 對于防治肺結核具有重要意義。本研究結果顯示, 復發肺結核組的血清MMP-8濃度高于健康對照組, 差異有統計學意義(Z=-6.528, P=0.000<0.05)。MMP-8在復發肺結核患者中的敏感度為91.3%和特異度為69.6%, 這表明MMP-8與肺結核復發有一定的相關性, MMP-8濃度的變化或可預示肺結核復發的風險程度。
綜上所述, MMP-8與肺結核復發有一定的相關性并具有一定的臨床價值, 但仍需進一步的研究。
參考文獻
[1] Kumar NP, Moideen K, Viswanathan V, et al. Elevated levels of matrix metalloproteinases reflect severity and extent of disease in tuberculosis-diabetes co-morbidity and are predominantly reversed following standard anti-tuberculosis or metformin treatment. Bmc Infectious Diseases, 2018, 18(1):345.
[2] Parasa VR, Muvva JR, Rosé J, et al. Inhibition of tissue matrix metalloproteinases interferes with mycobacterium tuberculosis-induced granuloma formation and reduces bacterial load in a human lung tissue model. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2017(8):2370.
[3] Xu Y, Wang L, Zimmerman MD, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors enhance the efficacy of frontline drugs against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Plos Pathogens, 2018, 14(4):e1006974.
[4] Esmedlyaeva DS, Alexeyeva NP, Sapozhnikova NV, et al. The system of matrix metalloproteinases and their role in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. Biomeditsinskaia Khimiia, 2016, 62(5):593.
[5] Walker NF, Wilkinson KA, Meintjes G, et al. Matrix degradation in human immunodeficiency virus type 1-associated tuberculosis and tuberculosis immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome: a prospective observational study. Clinical Infectious Diseases An Official Publication of the Infectious Diseases Society of America, 2017, 65(1):121-132.
[6] Teixeira LR, Dias MB, Sales RK, et al. Profile of Metalloproteinases and Their Association with Inflammatory Markers in Pleural Effusions. Lung, 2016, 194(6):1021-1027.
[7] Shiryaev SA, Cieplak P, Aleshin AE, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase proteolysis of the mycobacterial HSP65 protein as a potential source of immunogenic peptides in human tuberculosis. Febs Journal, 2011, 278(18):3277-3286.
[8] Lyadova IV, Tsiganov EN, Kapina MA, et al. In mice, tuberculosis progression is associated with intensive inflammatory response and the accumulation of Gr-1 cells in the lungs. Plos One, 2010, 5(5):e10469.
[9] Ong CWM, Elkington PT, Brilha S, et al. Neutrophil-Derived MMP-8 Drives AMPK-Dependent Matrix Destruction in Human Pulmonary Tuberculosis. Plos Pathogens, 2015, 11(5):e1004917.
[10] Ong CWM, Fox K, Ettorre A, et al. Hypoxia increases neutrophil-driven matrix destruction after exposure to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1):11475.
[11] Sathyamoorthy T, Sandhu G, Tezera LB, et al. Gender-dependent differences in plasma matrix metalloproteinase-8 elevated in pulmonary tuberculosis. Plos One, 2015, 10(1):e0117605.
[12] Lee MR, Tsai CJ, Wang WJ, et al. Plasma Biomarkers Can Predict Treatment Response in Tuberculosis Patients: A Prospective Observational Study. Medicine, 2015, 94(39):e1628.
[收稿日期:2019-01-07]

