不同晝夜節律高血壓患者心率減速力檢測的臨床意義
周麗++王興德+申淑榮++程培++陳彬+陳忠

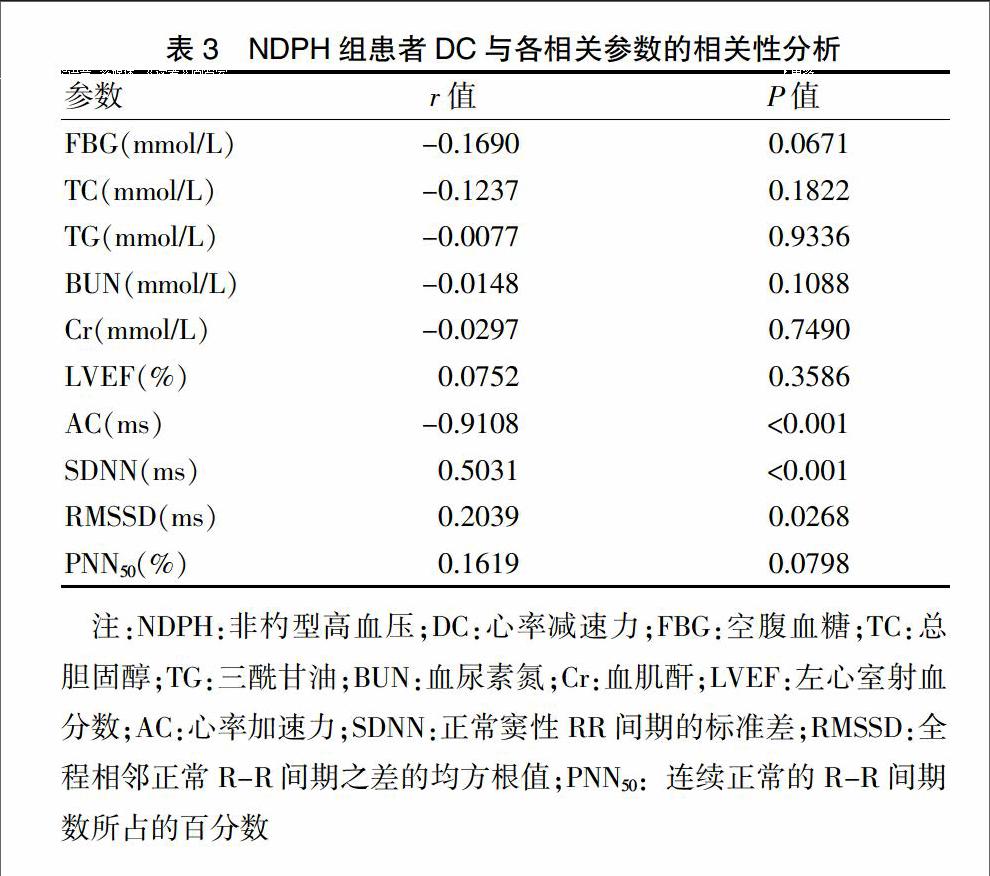
[摘要] 目的 探討不同晝夜節律高血壓患者心率減速力(DC)改變的臨床意義。 方法 選擇2014年1月~2016年12月在上海交通大學附屬第六人民醫院(以下簡稱“我院”)診治的原發性高血壓患者184例,給予動態血壓監測,根據其夜間血壓下降率結果分為兩組:<10%為非杓型高血壓組(NDPH組,118例),≥10%為杓型高血壓組(DPH組,66例)。選擇我院同期健康體檢者50名為對照組。應用24 h Holter檢測并比較三組入選者的DC、心率加速力(AC)及心率變異性(HRV)水平,并分析其相關性。 結果 DPH組及NDPH組DC和正常竇性RR間期的標準差(SDNN)值均明顯低于對照組,AC值明顯高于對照組(均P < 0.01);NDPH組全程相鄰正常R-R間期之差的均方根值(RMSSD)、24 h內差值>50 ms的連續正常的R-R間期數所占的百分數(PNN50)值也明顯低于對照組(P < 0.05)。同時與DPH組比較,NDPH組DC、SDNN也明顯降低,AC明顯增高(P < 0.05)。NDPH組患者DC與SDNN、RMSSD呈明顯正相關(P < 0.01、P < 0.05),與AC呈明顯負相關(P < 0.01)。 結論 不同晝夜節律高血壓患者均存在自主神經功能損害,其中NDPH組較DPH組自主神經功能失衡更加明顯,在臨床工作中不僅要關心高血壓患者的血壓控制,還應注意其自主神經功能的變化和血壓晝夜節律的改變。
[關鍵詞] 自主神經系統;晝夜節律;高血壓;心率減速力
[中圖分類號] R544.1 [文獻標識碼] A [文章編號] 1673-7210(2017)10(b)-0061-04
Clinical significance of detection of deceleration capacity of rate in patients with primary hypertension of different circadian rhythm
ZHOU Li WANG Xingde SHEN Shurong CHENG Pei CHEN Bin CHEN Zhong
Department of Cardiology, the Sixth People′s Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 201306, China
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the clinical significance of the changes of deceleration capacity of rate (DC) in patients with primary hypertension of different circadian rhythm. Methods One hundred and eighty-four patients with primary hypertension treated in the Sixth People′s Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University (“our hospital” for short) from January 2014 to December 2016 were selected and given ambulatory blood pressure monitoring. According to the descent rate of nighttime blood pressure, they were divided into two groups: the patients with descent rate of <10% were taken as non-dipper pattern hypertension group (NDPH group, 118 cases), the patients with descent rate of ≥10% were taken as dipper pattern hypertension group (DPH group, 66 cases). 50 healthy subjects taken physical examination in our hospital at the same time were taken as control group. 24 h Holter was used to detect and compare the levels of DC, acceleration capacity of rate (AC), heart rate variability (HRV) among the three groups, and their relevance was analyzed. Results The DC and standard deviation of normal sinus RR intervals (SDNN) in NDPH group and DPH group were significantly lower than that of control group, and AC was significantly higher than that of control group (all P < 0.01); the root mean square of standard deviations of differences between adjacent normal RR intervals (RMSSD) and the proportion derived by dividing NN50 by the total number of NN intervals (PNN50) in NDPH group were significantly lower than that of control group (P < 0.05). DC and SDNN in NDPH group were significantly lower than that of DPH group, and AC was significantly higher than that of DPH group (P < 0.05). In NDPH group, DC was significantly positively correlated with SDNN, RMSSD (P < 0.01, P < 0.05) and negatively correlated with AC (P < 0.01). Conclusion The patients with primary hypertension of different circadian rhythm have impaired autonomic nerve function, and its imbalance in NDPH group is more obvious than that in DPH group. In clinical practice, physicians should not only care for the blood pressure control, but also pay attention to the changes of autonomic function and circadian blood pressure rhythm in the diagnosis and treatment of hypertension.endprint
[Key words] Autonomic nervous system; Circadian rhythm; Hypertension; Deceleration capacity of rate
正常生理狀態下,人體24 h的血壓變化呈明顯的晝夜節律,表現為“雙峰一谷”節律改變[1-2]。根據夜間血壓下降是否超過白天平均血壓的10%,可以將高血壓患者分為兩類:≥10%定義為杓型高血壓(dipper pattern hypertension,DPH),而<10%定義為非杓型高血壓(non-dipper pattern hypertension,NDPH)[3-6]。有研究表明,NDPH患者可發生更嚴重的心、腦、腎等靶器官損害和心血管事件[7-8],可能跟迷走神經活動受損和交感神經興奮有關[9-10]。心率減速力(deceleration capacity of rate,DC)檢測能定量評估受檢者迷走和交感神經張力的高低,可作為其自主神經功能異常的檢測指標[11-12]。本研究旨在觀察不同晝夜節律高血壓患者心率減速力的變化,探討其在心臟自主神經功能損害中的作用,為臨床診斷和治療提供幫助。
1 資料與方法
1.1 一般資料
選擇2014年1月~2016年12月在上海交通大學附屬第六人民醫院(以下簡稱“我院”)診治的高血壓患者184例(男126例,女58例)作為高血壓組,均符合中國高血壓防治指南修訂委員會[13]所制訂的高血壓診斷標準。排除標準:急性心肌梗死、嚴重肝腎功能不全、腫瘤患者;心力衰竭以及合并糖尿病、甲狀腺功能亢進者;繼發性高血壓患者;服用可能影響心率變異性(HRV)的藥物者;非竇性心律(如心房顫動、心房撲動);心臟起搏器植入患者。根據晝夜節律將高血壓組分為DPH組(66例)和NDPH組(118例)。選擇我院同期健康體檢者50名作為對照組,經心電圖、X線胸片、生化檢查、葡萄糖耐量試驗及超聲心動圖等,排除高血壓等相關疾病,無長期飲酒和吸煙史,年齡39~73歲。本研究經醫院倫理委員會批準,且經過入選者知情同意。……

