血紅素加氧酶-1在高氧肺損傷小鼠中的表達及作用*
羅喜鋼,王 毅,張鳳香
(1.錦州醫科大學附屬第三醫院檢驗中心,遼寧錦州 121001;2.錦州醫科大學附屬第一醫院胸外科,遼寧錦州 121001)
論著·基礎研究
血紅素加氧酶-1在高氧肺損傷小鼠中的表達及作用*
羅喜鋼1,王 毅1,張鳳香2△
(1.錦州醫科大學附屬第三醫院檢驗中心,遼寧錦州 121001;2.錦州醫科大學附屬第一醫院胸外科,遼寧錦州 121001)
目的探討血紅素加氧酶-1(HO-1)在高氧造成的肺損傷轉基因小鼠和正常小鼠中的肺部表達水平及其作用。方法把32只新生小鼠分成4組:野生型組(WT組),特異性轉基因小鼠全身高水平表達HO-1組[HO-1-FL(H)組,細胞質]、特異性轉基因小鼠全身低水平表達HO-1組[HO-1-FL(L)組,細胞質]和切去C末端HO-1(Nuc-HO-1-TR組,細胞核)。把4組小鼠暴露在高氧環境中3 d,然后放到正常空氣環境中,通過免疫組織化學、免疫熒光等實驗技術來觀察小鼠3 d、7 d和14 d肺泡發育情況及HO-1在小鼠肺部表達情況。結果HO-1在HO-1-FL(H)組小鼠肺部高表達,高氧暴露3 d后4組小鼠肺部肺泡發育都受到了損害,在正常空氣環境中7、14 d時HO-1-FL(H)組小鼠的肺泡發育恢復得最好。結論小鼠肺部適度高水平的HO-1表達有助于高氧環境造成的小鼠肺損傷的恢復。
肺損傷;血紅素加氧酶-1;基因敲除小鼠
血紅素加氧酶-1(HO-1)是內質網的錨定蛋白[1],在新生兒肺中含量豐富,但不響應于高氧的誘導[2-3]。HO-1高水平的超表達與體外氧的細胞毒性相關聯[4-5]。同成人比較,暴露高氧中的新生小鼠HO-1局限于細胞核中[6-7]。本研究對HO-1表達水平與亞細胞定位進行研究,現報道如下。
1 材料與方法
1.1材料
1.1.1主要實驗儀器設備及耗材 全自動生化分析儀(日立7600-110),液氮冰箱(海爾),生物組織自動包埋機(KH-BL),切片機(KH-Q380),氣相色譜儀(北京恒通瑞利 GC6891N),熒光顯微鏡(奧林巴斯)。
1.1.2主要試劑及藥品 鹽酸氯胺酮(西安漢豐藥業),甲苯噻嗪鹽酸鹽、磷酸鹽緩沖液(PBS,武漢普諾賽),抗血凝素(HA)、抗小鼠肺表面活性物質蛋白(SP-C)抗體、抗波形蛋白抗體、抗α-平滑肌肌動蛋白抗體、抗CD45,核質提取試劑盒(NE-PER,Sigma)。
1.1.3實驗對象 實驗動物為錦州醫科大學實驗動物中心提供的SPF級新生小鼠。小鼠分成4組,每組8只,即野生型組(WT組),特異性轉基因小鼠全身高水平表達HO-1組[HO-1-FL(H)組,細胞質],特異性轉基因小鼠全身低水平表達HO-1組[HO-1-FL(L)組,細胞質]和轉基因小鼠切去C末端HO-1組(Nuc-HO-1-TR組,細胞核)。
1.2方法 (1)本研究把4組新生的小鼠幼崽分到含正常空氣容器和含95%氧氣的容器內,其中95%氧氣的容器能夠連續監測、調節氧和二氧化碳的含量,在此容器內小鼠被暴露于高氧環境中3 d,然后放到正常環境中恢復,一直持續到第2周結束。(2)肺組織收集:小鼠被腹腔注射鹽酸氯胺酮(100 mg/kg)和甲苯噻嗪鹽酸鹽(10 mg/kg)進行麻醉,肺動脈用PBS進行灌注后,切下右肺放入液氮中冷凍保存并進行蛋白質分析,左肺膨脹并用10%中性甲醛固定24 h[8]。肺組織被石蠟包埋制成5 mm厚切片,固定在載玻片上。(3)免疫組織化學:本研究使用生物素化抗增殖細胞核抗原(PCNA)免疫組織化學染色作為細胞增殖的一般標記,蛋白印記分析作為細胞凋亡的標記。石蠟包埋的組織切片用免疫熒光或修飾后的生物素進行間接染色,切片在4 ℃的溫度下和抗血凝素(HA)、PCNA、抗SP-C、抗波形蛋白、抗α-平滑肌肌動蛋白及抗CD45抗體一起過夜孵育,然后在熒光顯微鏡下進行觀察。(4)免疫沉淀,使用NE-PER核質提取試劑盒,抗HA結合到瓊脂糖珠上進行免疫沉淀反應[8]:組織裂解液轉移至旋轉柱,接著加入抗HA瓊脂糖珠上4 ℃孵育過夜。旋轉柱子移除組織裂解物,洗滌珠子。還有一部分和鈣連蛋白(calnexin)抗體進行免疫沉淀,免疫沉淀得到的蛋白質進行洗滌和免疫印記。(5)HO-1活性測定:以 CO 產生量用氣相色譜儀進去測定,間接測定出 HO-1活性[9]。
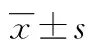
2 結 果
2.1HA標記肺組織的HO-1的表達 用HA標記的HO-1在HO-1-FL(H)組小鼠肺部特異性的高表達,而在其他類型小鼠少量表達或無表達,見圖1、2。通過免疫熒光方法觀察HA染色的肺泡上皮細胞的表達與分布,在HO-1-FL(H)組中能看到大量的綠色熒光,而在HO-1-FL(L)組和Nuc-HO-1-TR組上有少量的綠色熒光,WT組上沒有綠色熒光,HO-1在HO-1-FL(H)組肺泡上皮細胞上大量分布,見圖2。

1:WT組;2:Nuc-HO-1TR-組;3:HO-1-FL(L)組;4:HO-1-FL(H)組
圖1 HO-1在小鼠肺部的表達

圖2 小鼠HA染色(綠色)圖和細胞核DAPI染色
2.2肺部HO-1酶活性的測定 總HO-1酶活性HO-1-FL(H)組高于WT組(P<0.05),HO-1酶活性在HO-1-FL(L)和Nuc-HO-1-TR組與WT組比較差異無統計學意義(P>0.05),見圖3。
2.3在高氧和恢復之后肺泡發育受到損害程度的比較 在正常空氣環境中,WT組小鼠發展成有序的通氣道,與之相反,WT組新生小鼠暴露高氧環境中3 d,肺泡的發育受到損害,導致肺泡簡化和肺組織輻射狀肺泡計數(RAC)均顯著降低。HO-1-FL(L)組在高氧環境中的RAC也較差,但同暴露在高氧中WT組相比,在正常空氣中恢復后,RAC得到了顯著的提高。與此相反,Nuc-HO-1-TR組和HO-1-FL(H)組在14 d時后,RAC均得到了顯著提高,見圖4。

圖3 14 d小鼠肺部HO-1酶活性計數

圖4 肺泡發育受損程度的比較
2.4高氧暴露后肺細胞增殖和細胞凋亡情況 在正常空氣環境中,4組小鼠肺部PCNA陽性細胞數量相差不多。而在高氧環境中,除HO-1-FL(H)組外,其余3組細胞數大量減少,見圖5。

圖5 高氧暴露3 d 后PCNA免疫組織化學染色(綠色)
3 討 論
雖然,高氧環境在自然界中尚未證實存在,但是在臨床環境和適應性反應中存在這種挑戰[10-11]。 暴露在高氧環境中成年嚙類目動物被觀察到的HO-1的誘發是一種保護作用,但是新生小鼠在同樣的條件下,肺部的HO-1沒有被誘導[12-13]。本研究先前已經表明,低水平的HO-1表達是有益的[14-15],但是在體外研究表明HO-1表達的增加也是有益的[8,12],這就暗示HO-1的有益表達是有閾值的。本課題組的研究表明,HO-1的表達的程度和它細胞內表達定位改變著它在小鼠體內的保護能力。
本研究模擬臨床環境,新生轉基因小鼠暴露高氧中3 d后,然后放在正常空氣中恢復,這個模型用來評估新生小鼠急性肺損傷和修復。同經過3 d高氧環境的WT組相比,HO-1-FL(H)組在第14 d從肺損傷中完全恢復。這表明HO-1在肺上皮細胞中的適度表達在高氧引起的肺損傷的恢復起著至關重要的作用。
綜上所述,本研究構建出一種新生小鼠對高氧環境應激反應模型,通過HO-1在轉基因小鼠和野生型小鼠肺部表達的對比,研究得出適度的HO-1在肺部表達有益小鼠急性肺損傷的恢復,為進一步的研究工作奠定了堅實的基礎。
[1]An J,Li T,Dong Y,et al.Terminalia chebulanin attenuates psoriatic skin lesion via regulation of heme oxygenase-1[J].Cell Physiol Biochem,2016,39(2):531-543.
[2]Noda M,Doi Y,Liang J,et al.Fractalkine attenuates excito-neurotoxicity via microglial clearance of damaged neurons and antioxidant enzyme heme oxygenase-1 expression[J].J Biol Chem,2016,291(27):14388.
[3]Go H,La P,Namba F,et al.MiR-196a regulates heme oxygenase-1 by silencing Bach1 in the neonatal mouse lung[J].Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol,2016,311(2):L400-411.
[4]Iho S,Maeyama J,Suzuki F.CpG oligodeoxynucleotides as mucosal adjuvants[J].Hum Vaccin Immunother,2015,11(4):755-760.
[5]Ko SH,Rhoda J.Bacteroides fragilis enterotoxin upregulates heme oxygenase-1 in intestinal epithelial cells via a mitogen-activated protein kinase- and NF-κB-dependent pathway,leading to modulation of apoptosis[J].Infect Immun,2016,84(9):2541-2554.
[6]Prado E.Antimicrobial peptide elicitors:new hope for the post-antibiotic era[J].Innate immunity,2013,19(1):227-241.
[7]Cheng X,Gao D,Chen B,et al.Endotoxin-binding peptides derived from casein glycomacropeptide inhibit lipopolysaccharide-stimulated inflammatory responses via blockade of NF-κB activation in macrophages[J].Nutrients,2015,7(8):3119-3137.
[8]Negi G,Nakkina V,Kamble P,et al.Heme oxygenase-1,a novel target for the treatment of diabetic complications:focus on diabetic peripheral neuropathy[J].Pharmacol Res,2015(102):158-167.
[9]Russell Cruz C,Bollard CM.T-cell and natural killer cell therapies for hemato-logic malign-ancies after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation:enhancing the graft-versus-leukemia effect[J].Haematologica,2015,100(6):709-719.
[10]Lee HS,Lee JG,Yeom HJ,et al.The Introduction of human heme oxygenase-1 and soluble tumor necrosis factor-α receptor type Ⅰ with human IgG1 Fc in porcine islets prolongs islet xenograft survival in humanized mice[J].Am J Transplant,2016,16(1):44-57.
[11]Allin KH,Nordestgaard BG,Zacho J,et al.C-reacti-ve protein and the risk of cancer:a mendelian randomization study[J].J Natl Cancer Inst,2010,102(11):202-206.
[12]Cheng HT,Yen CJ,Chang CC,et al.Ferritin heavy chain mediates the protective effect of heme oxygenase-1 against oxidative stress[J].Biochim Biophys Acta,2015,1850(12):2506-2517.
[13]Wu MM,Chiou HY,Lee TC,et al.GT-repeat polymorphism in the heme oxygenase-1 gene promoter and the risk of carotid at herosclerosis related to arsenic exposure [J].J Bio Med Sci,2010,17(6):70.
[14]Matthay MA,Ware LB,Zimmerman GA.The acute respiratory distress syndrome[J].J Clin Invest,2012,122(8):2731-2740.
[15]Aird WC,Mosnier LO,Fairhurst RM.Plasmodium falciparum picks on EPCR[J].Blood,2014,123(2):163-167.
Expressionandroleofhemeoxygenase-1inmouselunginjuryinducedbyhyperoxia*
LuoXigang1,WangYi1,ZhangFengxiang2△
(1.LaboratoryCenter,ThirdAffiliatedHospitalofJinzhouMedicalUniversity,Jinzhou,Liaoning121001,China;2.DepartmentofThoracicSurgery,FirstAffiliatedHospitalofJinzhouMedicalUniversity,Jinzhou,Liaoning121001,China)
ObjectiveTo investigate the expression of heme oxygenase-1 in lungs of transgenic mice and normal mice and its effects.Methods32 newborn mice were divided into four groups:wild-type group (WT group),specific transgenic mice expressed hemoglobin oxygenase-1 high level group[HO-1-FL(H) group,cytoplasm],low level WT group[HO-1-FL(L) group,cytoplasm] and the C-terminal heme oxygenase-1 group(Nuc-HO-1-TR group,nucleus).Then four groups of mice were exposed to high oxygen for 3 days,after that placed in normal air environment.Immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence were used to observe the alveolar development and hemoglobin addition at 3 days,7 days and 14 days oxygenase-1 expression in the lungs of mice.ResultsThe levels of heme oxygenase-1 were significantly higher in the lungs of HO-1-FL (H) group,and the alveolar development in the lungs of the four groups after 3 days of hyperoxia exposure was impaired.In the normal air environment,the recovery of alveolar development in HO-1-FL (H) group on the 7th and 14th day was the best.ConclusionThe moderately high levels of heme oxygenase-1 expression in the lungs contribute to the recovery of lung injury in mice caused by hyperoxic environments.
pulmonary injury;heme oxygenase-1;knockout mice
R-332
A
1671-8348(2017)26-3614-03
2017-02-21
2017-06-06)
10.3969/j.issn.1671-8348.2017.26.005
國家自然科學基金資助項目(81541099)。
羅喜鋼(1980-),碩士,主管檢驗師,主要從事體液酶學方面研究。△
,Email:zhangfengxiang64@163.com。

