超聲評分在膝關節類風濕關節炎中的臨床意義*
章春來,張菁菁,雷建明
(麗水市人民醫院超聲科,浙江麗水 323000)
?
超聲評分在膝關節類風濕關節炎中的臨床意義*
章春來,張菁菁,雷建明
(麗水市人民醫院超聲科,浙江麗水 323000)
目的 探討膝關節類風濕關節炎超聲診斷的價值及超聲評分系統的臨床意義。方法 收集2013年7月至2015年12月麗水市兩家三級甲等綜合醫院膝關節類風濕關節炎患者500例作為觀察組,另收集同期健康成人500例作為對照組。觀察兩組膝關節滑膜厚度、增生滑膜內血管檢出率、超聲評分、類風濕性關節炎疾病活動度評分、C反應蛋白、紅細胞沉降率、髕上囊積液、髕下囊積液、關節腔積液、膝關節軟骨和骨表面情況。結果 與對照組比較,觀察組膝關節滑膜厚度[(0.50±0.19)cmvs.(0.13±0.05)cm,P=0.000]、髕上囊液體深度[(0.62±0.27)cmvs.(0.23±0.05)cm,P=0.000]、髕下囊液體深度[(0.58±0.12)cmvs.(0.21±0.04)cm,P=0.000]、關節腔液體深度[(0.48±0.28)cmvs.(0.12±0.08) cm,P=0.000]、紅細胞沉降率[(43.29±12.58)mm/hvs.(12.95±4.39)mm/h,P=0.000]、C反應蛋白水平[(8.95±3.29)mg/Lvs.(3.29±1.54)mg/L,P=0.000]、增生滑膜內血管檢出率(84.20%vs.13.00%,P=0.000)均明顯增加。且超聲評分與類風濕關節炎患者類風濕關節炎疾病活動度評分、C反應蛋白水平、紅細胞沉降率、髕上囊液體深度、髕下囊液體深度和關節腔液體深度均呈正相關(r=0.583、0.258、0.383、0.219、0.228、0.248,均P<0.05)。結論 超聲在類風濕性關節炎中具有良好的診斷價值,超聲評分系統可以較好地反映患者的疾病嚴重度。
膝關節;關節炎,類風濕;超聲檢查
類風濕關節炎是疼痛性的慢性炎性關節疾病,可導致嚴重骨骼改變及受累關節破壞[1-2]。類風濕關節炎患者即使臨床癥狀有所緩和,其亞臨床炎癥可能持續存在[3-4]。臨床早期診斷對后續病情的緩解及判斷非常重要[5]。常規X射線攝影技術是進展性關節損傷常用的影像學診斷技術,但是其對軟組織病變和早期侵蝕性骨病變不敏感[6-7]。超聲成像不僅能發現早期軟組織炎性病變(如滑膜炎、腱鞘炎和滑囊炎),還可以顯示關節炎的早期骨侵蝕性病灶[8-10]。研究表明,超聲和磁共振成像(MRI)具有良好的一致性[11-12]。退變性和炎癥性關節疾病以進行性關節破壞為特征,有效的、可重復的測量有助于及時掌握患者的病變情況,其中超聲的半定量評估得到越來越多的關注,但目前國內對膝關節尚缺乏具體評分系統。
1 資料與方法
1.1 一般資料 2013年7月至2015年12月收集麗水市人民醫院與麗水市中心醫院收治的膝關節類風濕性關節炎患者,膝關節類風濕性關節炎診斷標準[13]:(1)晨僵;(2)至少1個關節活動時疼痛或壓痛;(3)1個以上關節腫脹;(4)另1個關節腫脹,兩個關節腫脹時間間隔不超過3個月;(5)對稱性腫脹;(6)X線片示類風濕性關節炎;(7)類風濕因子陽性;(8)骨隆起部或關節附近伸側的皮下結節;(9)滑膜液中黏蛋白凝固不佳;(10)滑膜病理學改變;(11)皮下結節可見中心區細胞壞死等;(12)X線片示意膝關節受累;上述12項符合5項以上且持續6周以上。納入標準:(1)符合膝關節類風濕性關節炎診斷標準;(2)年齡30~60歲;(3)同意參與本研究。排除標準:(1)膝關節結核;(2)骨性關節炎;(3)其他膝關節病變;(4)不配合本研究或隨訪期間失訪。根據納入排除標準,共納入膝關節類風濕性關節炎患者500例作為觀察組,另收集同期年齡和性別匹配的健康志愿者500例作為對照組。觀察組男250例,女250例;年齡30~60歲,平均(46.38±9.83)歲;對照組男250例,女250例,年齡30~60歲,平均(46.12±8.94)歲。兩組性別、年齡等一般資料比較,差異無統計學意義(P>0.05),具有可比性。所有研究對象對本研究均知情同意并簽署知情同意書,本研究通過醫院倫理委員會審批。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 超聲檢查 應用Philips IU22、GE vivid E9 西門子S2000等超聲診斷儀,配備常規二維超聲、彩色多普勒血流顯像(CDFI)、能量多普勒功能,配備寬頻帶高頻探頭,頻率7~12 MHz。檢查時共3個體位:仰臥位腹側和側面掃描、俯臥位背側掃描和膝關節中立位或30°屈曲位。檢查內容:(1)檢查膝關節的標準切面、髕上縱切面,顯示髕上囊和股四頭肌腱;(2)檢查正中位的髕上橫切面和最大屈曲位的髕上橫切面,顯示均勻無回聲的透明軟骨和股骨關節軟骨邊界清晰的內外緣;(3)檢查內側、后內、后外、側方縱切面,可顯示相關韌帶副韌帶、半月板等;(4)檢查后方橫切,顯示覆有關節軟骨的骨髁和腘窩。
1.2.2 觀察指標 主要觀察指標為患側膝關節(對照組為同側膝關節)滑膜厚度、增生滑膜內血管檢出率、超聲評分、類風濕關節炎疾病活動度評分、C反應蛋白、紅細胞沉降率、髕上囊積液、髕下囊積液、關節腔積液、膝關節軟骨和骨表面情況。
1.2.3 判定標準 根據Hartung等[14]研究,對病變關節使用高頻超聲檢測,根據患者關節滑膜厚度、滑膜血流、關節積液和骨侵蝕等疾病嚴重度進行評分,分值范圍為0~3分,0分:滑膜厚度無異常,關節腔無積液,骨表面光滑,滑膜內無彩色血流信號;1分:滑膜輕度增厚,小關節滑膜不高出兩骨最高點連線水平,大關節滑膜厚度大于2 mm且小于5 mm,關節腔少量積液,骨表面不光滑但沒有骨質缺損,滑膜內測及少數點狀血流信號;2分:滑膜中度增厚,小關節滑膜凸出兩骨最高點連線,未達骨干,大關節滑膜厚度5~9 mm,關節腔中等積液,骨表面形成輕微骨質缺損,滑膜內測及較多點狀或點線狀血流信號;3分:滑膜重度增厚,小關節滑膜延伸達骨干,大關節滑膜厚度大于9 mm,關節腔大量積液,骨表面骨質缺損形成廣泛骨破壞,滑膜內測及豐富的樹枝狀或網狀血流信號。各個關節的評分相加為總分。膝關節不同超聲評分的彩色多普勒超聲表現見圖1。

A:超聲評分0分;B:超聲評分1分;C:超聲評分2分;D:超聲評分3分
圖1 不同膝關節超聲評分的彩色多普勒超聲表現
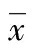
2 結 果
2.1 兩組膝關節滑膜厚度比較 與對照組比較[(0.13±0.05)cm],觀察組膝關節滑膜厚度[(0.50±0.19)cm]明顯增厚,差異有統計學意義(t=12.137,P=0.000),見圖2。

圖2 兩組膝關節滑膜厚度比較
2.2 兩組其他觀察指標比較 與對照組比較,觀察組患者髕上囊液體深度、髕下囊液體深度、關節腔液體深度、紅細胞沉降率、C反應蛋白水平及增生滑膜內血管檢出率均明顯增加,差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05),見表1。

表1 兩組其他觀察指標比較(n=500)
2.3 膝關節超聲評分在評價患者疾病嚴重度中的價值 觀察組超聲評分為(12.48±4.39)分,類風濕關節炎疾病活動度評分為(4.10±1.47)分。Pearson線性相關性分析顯示,超聲評分與患者類風濕關節炎疾病活動度評分(r=0.583,P=0.000)、C反應蛋白水平(r=0.258,P=0.005)、紅細胞沉降率(r=0.383,P=0.000)、髕上囊液體深度(r=0.219,P=0.015)、髕下囊液體深度(r=0.228,P=0.012)和關節腔液體深度(r=0.248,P=0.008)均呈正相關。
3 討 論
作為一種慢性退行性病變,膝關節類風濕關節炎主要表現為局部的慢性炎癥,為自身免疫性疾病,長期的慢性炎癥可導致關節功能障礙,病理表現為滑膜的增厚、關節積液等,可嚴重影響患者的生活質量。準確評估患者病情的嚴重程度對治療具有重要的臨床意義。目前常用的評估方法包括X射線、超聲和MRI等。其中,X射線對滑膜、軟骨等評估價值較低;而MRI價格昂貴,Schmidt等[12]研究更是顯示MRI在滑膜炎的診斷價值不如超聲檢查。既往超聲檢查的主要缺陷是缺乏定量或半定量分析,2012年Hartung等[14]提出了超聲評分系統這一概念,綜合評估患者關節滑膜厚度、滑膜血流、關節積液和骨侵蝕等情況,對類風濕關節炎患者超聲檢查進行定量評分。目前,國內對超聲的定量分析尚處于起步階段,本文綜合分析了類風濕關節炎患者的超聲診斷價值和超聲評分系統在膝關節類風濕關節炎中的作用,具有一定的臨床意義和創新性。
類風濕關節炎主要表現為關節積液和破壞,本研究顯示使用超聲可以根據患者髕上囊液體深度、關節腔液體深度、滑膜厚度、增生滑膜內血管檢出率等一系列的超聲表現區分類風濕關節炎患者和健康成人。另外,Pearson線性相關性分析顯示超聲評分與患者類風濕關節炎疾病活動度評分、C反應蛋白、紅細胞沉降率、髕上囊液體深度、髕下囊液體深度和關節腔液體深度等均呈正相關(P<0.05)。由于類風濕關節炎病情活動度評分與患者病情嚴重度緊密相關,從而被廣泛應用于臨床中[15-16]。2016年Christensen等[17]研究顯示,超聲評分與類風濕關節炎病情活動度評分緊密相關[β=0.06,95%CI(0.02,0.09),P<0.01];2016年Ciurtin等[18]研究同樣表明,超聲評分與類風濕關節炎病情活動度緊密相關,均支持本研究結果。C反應蛋白和紅細胞沉降率等是反映患者體內炎性反應的指標,局部長期的慢性炎癥是導致膝關節積液和損傷的主要原因,因此C反應蛋白和紅細胞沉降率可以在一定程度上反映膝關節功能情況[19-20]。本研究顯示超聲評分與C反應蛋白、紅細胞沉降率呈正相關,表明超聲評分可以較好地反映患者體內炎癥水平。髕上囊積液、髕下囊積液和關節腔積液深度是膝關節類風濕關節炎患者疾病嚴重程度的主要臨床表現[21],而超聲評分可以較好地反映患者局部積液情況。以上均表示,超聲評分可以較好地反映膝關節類風濕關節炎患者局部損傷情況和體內炎癥水平,可以對患者進行定量評估,具有較強的應用價值。此外,國外幾項研究也肯定了超聲評分在類風濕關節炎中的作用[22-25]。目前我國對膝關節類風濕關節炎患者滑膜厚度缺乏定量分析,本研究顯示膝關節炎類風濕關節炎患者與健康成人滑膜厚度分別為(0.50±0.19)cm和(0.13±0.05) cm,差異有統計學意義(P=0.000)。本研究樣本量較大,因此數據可為臨床超聲醫師提供參考。
綜上所述,超聲在類風濕關節炎中具有良好的診斷價值,超聲評分系統可以較好地反映患者的疾病嚴重程度。
[1]Lu JQ,Ringrose J,Gross D,et al.Multifocal inflammatory demyelination in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis and treatment complications[J].J Neurol Sci,2016,367(21):305-307.
[2]Torres Suarez E,Pinheiro R,Schrage N.Complications in the treatment of ocular surface squamous neoplasia with interferon alpha2b in rheumatoid arthritis[J].Ophthalmologe,2016,12(4):441-448.
[3]Son KM,Kim SY,Lee SH,et al.Comparison of the disease activity score using the erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein levels in Koreans with rheumatoid arthritis[J].Int J Rheum Dis,2015,8(5):997-1003.
[4]Shen R,Ren X,Jing R,et al.Rheumatoid factor,anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody,C-reactive protein,and erythrocyte sedimentation rate for the clinical diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis[J].Lab Med,2015,46(3):226-229.
[5]Nielung L,Christensen R,Danneskiold-Samsoe B,et al.Validity and agreement between the 28-joint disease activity score based on C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate in patients with rheumatoid arthritis[J].Arthritis,2015,20(12):762-771.
[6]Pfeil A,Haugeberg G,Renz DM,et al.Digital X-ray radiogrammetry and its sensitivity and specificity for the identification of rheumatoid arthritis-related cortical hand bone loss[J].J Bone Miner Metab,2016,9(12):743-752.
[7]Popescu C,Bojinca V,Opris D,et al.Dual X-ray absorptiometry whole body composition of adipose tissue in rheumatoid arthritis[J].Rom J Intern Med,2015,53(3):237-247.
[8]Forien M,Ottaviani S.Ultrasound and follow-up of rheumatoid arthritis[J].Joint Bone Spine,2016,8(6):1005-1011.
[9]Gutierrez M,Pineda C,Salaffi F,et al.Is ankle involvement underestimated in rheumatoid arthritis? Results of a multicenter ultrasound study[J].Clin Rheumatol,2016,35(11):2669-2678.
[10]Janta I,Valor L,De la Torre I,et al.Ultrasound-detected activity in rheumatoid arthritis on methotrexate therapy:Which joints and tendons should be assessed to predict unstable remission?[J].Rheumatol Int,2016,36(3):387-396.
[11]Mathew AJ,Danda D,Conaghan PG.MRI and ultrasound in rheumatoid arthritis[J].Curr Opin Rheumatol,2016,28(3):323-329.
[12]Schmidt WA,Schicke B,Ostendorf B,et al.Low-field MRI versus ultrasound:which is more sensitive in detecting inflammation and bone damage in MCP and MTP joints in mild or moderate rheumatoid arthritis?[J].Clin Exp Rheumatol,2013,31(1):91-96.
[13]Singh JA,Saag KG,Bridges SL Jr,et al.2015 American College of Rheumatology guideline for the treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis [J].Arthritis Rheumatil,2016,68(1):1-26.
[14]Hartung W,Kellner H,Strunk J,et al.Development and evaluation of a novel ultrasound score for large joints in rheumatoid arthritis:one year of experience in daily clinical practice[J].Arthritis Care Res(Hoboken),2012,64(5):675-682.
[15]Singh H,Kalra A,Talpatra P,et al.Evaluation of disease activity using DAS28- squeeze test in patients of rheumatoid arthritis[J].J Assoc Physicians India,2016,64(1):69-77.
[16]Lisbona MP,Solano A,Ares J,et al.ACR/EULAR definitions of remission are associated with lower residual inflammatory activity compared with DAS28 remission on hand MRI in rheumatoid arthritis[J].J Rheumatol,2016,43(9):1631-1636.
[17]Christensen AW,Rifbjerg-Madsen S,Christensen R,et al.Ultrasound Doppler but not temporal summation of pain predicts DAS28 response in rheumatoid arthritis:a prospective cohort study[J].Rheumatology(Oxford),2016,55(6):1091-1098.
[18]Ciurtin C,Wyszynski K,Clarke R,et al.Ultrasound-detected subclinical inflammation was better reflected by the disease activity score(DAS-28) in patients with suspicion of inflammatory arthritis compared to established rheumatoid arthritis[J].Clin Rheumatol,2016,35(10):2411-2419.
[19]Carrier N,Marotta A,de Brum-Fernandes AJ,et al.Serum levels of 14-3-3eta protein supplement C-reactive protein and rheumatoid arthritis-associated antibodies to predict clinical and radiographic outcomes in a prospective cohort of patients with recent-onset inflammatory polyarthritis[J].Arthritis Res Ther,2016,18(37):724-731.
[20]Wang J,Devenport J,Low JM,et al.Relationship between baseline and early changes in C-reactive protein and interleukin-6 levels and clinical response to tocilizumab in rheumatoid arthritis[J].Arthritis Care Res(Hoboken),2016,68(6):882-885.
[21]Gecmen C,Gecmen GG,Kahyaoglu M,et al.Pericardial effusion due to cholesterol pericarditis in case of rheumatoid arthritis[J].Echocardiography,2016,33(10):1614-1616.
[22]D′Agostino MA,Boers M,Wakefield RJ,et al.Exploring a new ultrasound score as a clinical predictive tool in patients with rheumatoid arthritis starting abatacept:results from the APPRAISE study[J].RMD Open,2016,2(1):237-244.
[23]Aga AB,Hammer HB,Olsen IC,et al.First step in the development of an ultrasound joint inflammation score for rheumatoid arthritis using a data-driven approach[J].Ann Rheum Dis,2016,75(8):1444-1451.
[24]Ohrndorf S,Messerschmidt J,Reiche BE,et al.Evaluation of a new erosion score by musculoskeletal ultrasound in patients with rheumatoid arthritis:is US ready for a new erosion score?[J].Clin Rheumatol,2014,33(9):1255-1262.
[25]Bruyn GA,Hanova P,Iagnocco A,et al.Ultrasound definition of tendon damage in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Results of a OMERACT consensus-based ultrasound score focussing on the diagnostic reliability[J].Ann Rheum Dis,2014,73(11):1929-1934.
Clinical significance of ultrasonic scoring system in rheumatoid knee arthritis*
ZhangChunlai,ZhangJingjing,LeiJianming
(DepartmentofUltrasound,LishuiMunicipalPeople′sHospital,Lishui,Zhejiang323000,China)
Objective To investigate the diagnostic values of ultrasound in rheumatoid knee arthritis and the clinical significance of ultrasonic scoring system.Methods From July 2013 to December 2015,500 cases of patients with rheumatoid knee arthritis in two grade A class 3 hospitals of Lishui City were collected as the observation group and contemporaneous 500 healthy adults were collected as the control group.The knee joint synovial thickness,vascular detection rate in hyperplasia synovium,ultrasound score,rheumatoid arthritis disease activity score,erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR),C reactive protein (CRP),suprapatellar bursa effusion,infrapatellar bursa effusion,joint effusion,knee joint cartilage and bone surface were observed in the two groups.Results Compared with the control group,the observation group got a significant increase in knee joint synovial thickness [(0.50±0.19)cmvs.(0.13±0.05) cm,P=0.000)];depth of suprapatellar bursa fluid [(0.62±0.27)cmvs.(0.23±0.05) cm,P=0.000];depth of infrapatellar bursa fluid [(0.58±0.12)cmvs.(0.21±0.04) cm,P=0.000];joint fluid depth [(0.48±0.28)cmvs.(0.12±0.08) cm,P=0.000];ESR [(43.29±12.58)mm/hvs.(12.95±4.39) mm/h,P=0.000)];CRP level [(8.95±3.29)mg/Lvs.(3.29±1.54) mg/L,P=0.000)];vascular detection rate in hyperplasia synovium (84.20%vs.13.00%,P=0.000).Moreover the ultrasound score was positively corrected with rheumatoid arthritis disease activity score,CRP level,ESR,suprapatellar bursa fluid depth,infrapatellar bursa fluid depth and joint fluid depth in the patients with rheumatoid arthritis (r=0.583,0.258,0.383,0.219,0.228,0.248;P<0.05).Conclusion Ultrasound has good diagnostic value in the patients with rheumatoid arthritis,and the ultrasonic scoring system can better reflect the severity of the disease.
knee joint;arthritis,rheumatoid;ultrasonography
10.3969/j.issn.1671-8348.2017.21.013
麗水市科技計劃項目(2014JYZB18)。 作者簡介:章春來(1975-),副主任醫師,本科,主要從事超聲介入與肌骨超聲方面的研究。
R445.1
A
1671-8348(2017)21-2923-04
2017-02-09
2017-04-14)

