營(yíng)林措施對(duì)森林土壤甲烷吸收的影響*
王會(huì)來(lái) 劉 娟 姜培坤 周?chē)?guó)模 李永夫 吳家森
(浙江農(nóng)林大學(xué) 亞熱帶森林培育國(guó)家重點(diǎn)實(shí)驗(yàn)室 浙江省森林生態(tài)系統(tǒng)碳循環(huán)與固碳減排重點(diǎn)實(shí)驗(yàn)室 臨安 311300)
?
營(yíng)林措施對(duì)森林土壤甲烷吸收的影響*
王會(huì)來(lái) 劉 娟 姜培坤 周?chē)?guó)模 李永夫 吳家森
(浙江農(nóng)林大學(xué) 亞熱帶森林培育國(guó)家重點(diǎn)實(shí)驗(yàn)室 浙江省森林生態(tài)系統(tǒng)碳循環(huán)與固碳減排重點(diǎn)實(shí)驗(yàn)室 臨安 311300)
以期為全球氣候變暖背景下的林地合理經(jīng)營(yíng)管理提供依據(jù)。 利用Scopus,Web of Science,SDOS,CNKI 等數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù),查詢(xún)林地土壤CH4的相關(guān)文獻(xiàn),對(duì)不同營(yíng)林措施(施肥、采伐、火燒、林下植被管理)森林土壤CH4吸收通量方面的研究進(jìn)行綜述。 施加N肥對(duì)于富氮森林土壤CH4吸收有抑制作用,但可以顯著促進(jìn)貧氮森林土壤CH4吸收; 火燒后土壤CH4吸收通量受到多種因素的影響,因此存在一定的不確定性,多數(shù)研究表明,火燒減少土壤CH4吸收通量; 皆伐改變土壤溫度、含水量、有機(jī)碳的分解和利用等,從而減弱森林土壤CH4吸收能力; 擇伐對(duì)森林土壤CH4吸收的影響表現(xiàn)為抑制、促進(jìn)和無(wú)影響; 剔除林下植被提高土壤溫度,加快土壤水分蒸發(fā)散失,增強(qiáng)CH4氧化菌的活性,促進(jìn)土壤CH4吸收; 種植固氮植物使森林土壤轉(zhuǎn)變?yōu)镃H4的排放源。 目前經(jīng)營(yíng)措施對(duì)森林土壤CH4吸收影響的研究結(jié)果還存在較大差異,對(duì)營(yíng)林措施影響森林土壤CH4吸收的內(nèi)在機(jī)理的認(rèn)識(shí)還不充分。隨著研究方法和觀測(cè)手段的不斷發(fā)展,今后應(yīng)深入研究多種因素和氣候變化對(duì)林地土壤CH4吸收影響的內(nèi)在機(jī)理以及甲烷氧化菌對(duì)各種干擾因素的響應(yīng)機(jī)制。
人為干擾; 土壤甲烷吸收; 經(jīng)營(yíng)管理; 施肥; 采伐; 火燒; 林下植被管理
甲烷是引起全球氣候變化的第二大溫室氣體,單位質(zhì)量CH4的增溫潛勢(shì)是CO2的25倍(IPCC, 2007),對(duì)全球氣候變暖的貢獻(xiàn)率約為20%(Duttaetal., 2015)。截止到2011年,大氣中CH4的濃度相較于工業(yè)革命前提高了150%(IPCC, 2013),目前仍以每年0.8%的速度不斷遞增(IPCC, 2007)。大氣中CH4通常來(lái)源于水稻田、濕地、海洋以及化石燃料的開(kāi)采和燃燒,全球大氣CH4年排放量為548 Tg·a-1,其中濕地、水稻田等自然排放源占30%~50%(Heimann, 2010; Kirschkeetal., 2013)。森林土壤是大氣CH4的重要吸收匯,全球土壤CH4年吸收量為 26~36 Tg·a-1,其中森林土壤CH4年吸收量占52%(Denmanetal., 2007; Borkenetal., 2009)。中國(guó)森林覆蓋面積為2.08×108hm2,占國(guó)土總面積的22%,蘊(yùn)含著巨大的CH4吸收能力。據(jù)統(tǒng)計(jì),我國(guó)森林土壤CH4年吸收量為0.675 Tg·a-1,其中東部濕潤(rùn)、半濕潤(rùn)地區(qū)土壤CH4年吸收量占82%(Cai, 2012; Wangetal., 2014)。
施肥、采伐、火燒、林下植被管理等營(yíng)林措施改變了土壤含水量、土壤pH值、土壤碳含量和土壤氮含量等基本理化性質(zhì)和土壤微生物的群落組成、活性等,顯著影響了森林土壤CH4吸收。近年來(lái),開(kāi)展了大量營(yíng)林措施對(duì)森林土壤CH4吸收影響研究,但因管理措施、森林類(lèi)型、土壤狀況以及氣候因素的不同,營(yíng)林措施對(duì)林地土壤CH4吸收影響的研究結(jié)果存在較大差異; 同一種營(yíng)林措施在不同森林類(lèi)型、土壤狀況和氣候條件下,也會(huì)產(chǎn)生抑制、促進(jìn)和不變3種結(jié)果。這種研究結(jié)果的差異性及其作用機(jī)理的認(rèn)識(shí)還不充分(Zhangetal., 2015; Iwataetal., 2015; Hoyos-Santillanetal., 2016)。本文綜述了營(yíng)林措施(施肥、采伐、火燒和林下植被管理)影響林地土壤甲烷(CH4)吸收通量的研究進(jìn)展,探討了營(yíng)林措施影響土壤CH4吸收的主要機(jī)理,并提出未來(lái)研究的重點(diǎn),以期對(duì)全球氣候變暖背景下林地的合理經(jīng)營(yíng)管理起到借鑒和啟示作用。
1 施肥
施肥直接改變土壤有機(jī)碳含量和植物根系生物量,同時(shí)影響土壤微生物活性、土壤pH值等土壤理化性質(zhì),從而顯著影響森林土壤CH4吸收。施肥特別是施加N肥對(duì)森林土壤CH4吸收的影響機(jī)制主要包括: 氮素累積產(chǎn)生的抑制作用、土壤酸化、代謝產(chǎn)物的毒害作用、NH4+和CH4競(jìng)爭(zhēng)甲烷單氧酶等(程淑蘭等, 2012)。施肥對(duì)林地土壤CH4吸收的影響受植被類(lèi)型、施肥種類(lèi)和地帶氣候等因素的共同影響,因此產(chǎn)生抑制、促進(jìn)和不變3種結(jié)果,但以抑制的研究結(jié)果居多(表1)。
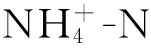
與此相反的是,在貧N的森林土壤中,N肥施用對(duì)土壤CH4吸收通量的影響多表現(xiàn)為不變或促進(jìn)(表1)。貧N的寒溫帶森林土壤,外源氮很容易被植被和土壤微生物吸收利用(高文龍等, 2013),而且地表長(zhǎng)期覆蓋凍土導(dǎo)致外源氮難以穿透到土壤CH4氧化區(qū)域(Sj?gerstenetal., 2007),從而導(dǎo)致施加N肥后土壤CH4氧化速率沒(méi)有顯著變化(Whalenetal., 2000)。高文龍等(2013)對(duì)寒溫帶針葉林和Whalen等(2000)對(duì)北方針葉林的研究表明,N肥的輸入沒(méi)有顯著改變土壤CH4吸收能力。貧N 森林土壤由于缺乏礦質(zhì)氮,土壤CH4氧化能力較弱,施加少量N肥后,Ⅰ,Ⅱ和X型甲烷氧化菌的活性增強(qiáng)(Aumanetal., 2001),從而促進(jìn)林地土壤CH4的吸收。少數(shù)研究表明,短時(shí)間N肥的施加促進(jìn)了土壤CH4的吸收(Veldkampetal., 2013)。
2 火燒
火燒一方面釋放大量的溫室氣體,造成森林生態(tài)系統(tǒng)碳損失,另一方面影響森林生態(tài)系統(tǒng)的形成與演化,改變森林生態(tài)系統(tǒng)的碳、氮循環(huán)過(guò)程。火燒改變土壤溫度、濕度和pH值,并通過(guò)有機(jī)碳燃燒和改變黏土礦物來(lái)影響土壤結(jié)構(gòu),使得土壤CH4吸收通量發(fā)生改變(任樂(lè)等, 2014)。此外,火燒后土壤微生物以及土壤酶活性也會(huì)影響土壤CH4吸收(Zhaoetal., 2015)。
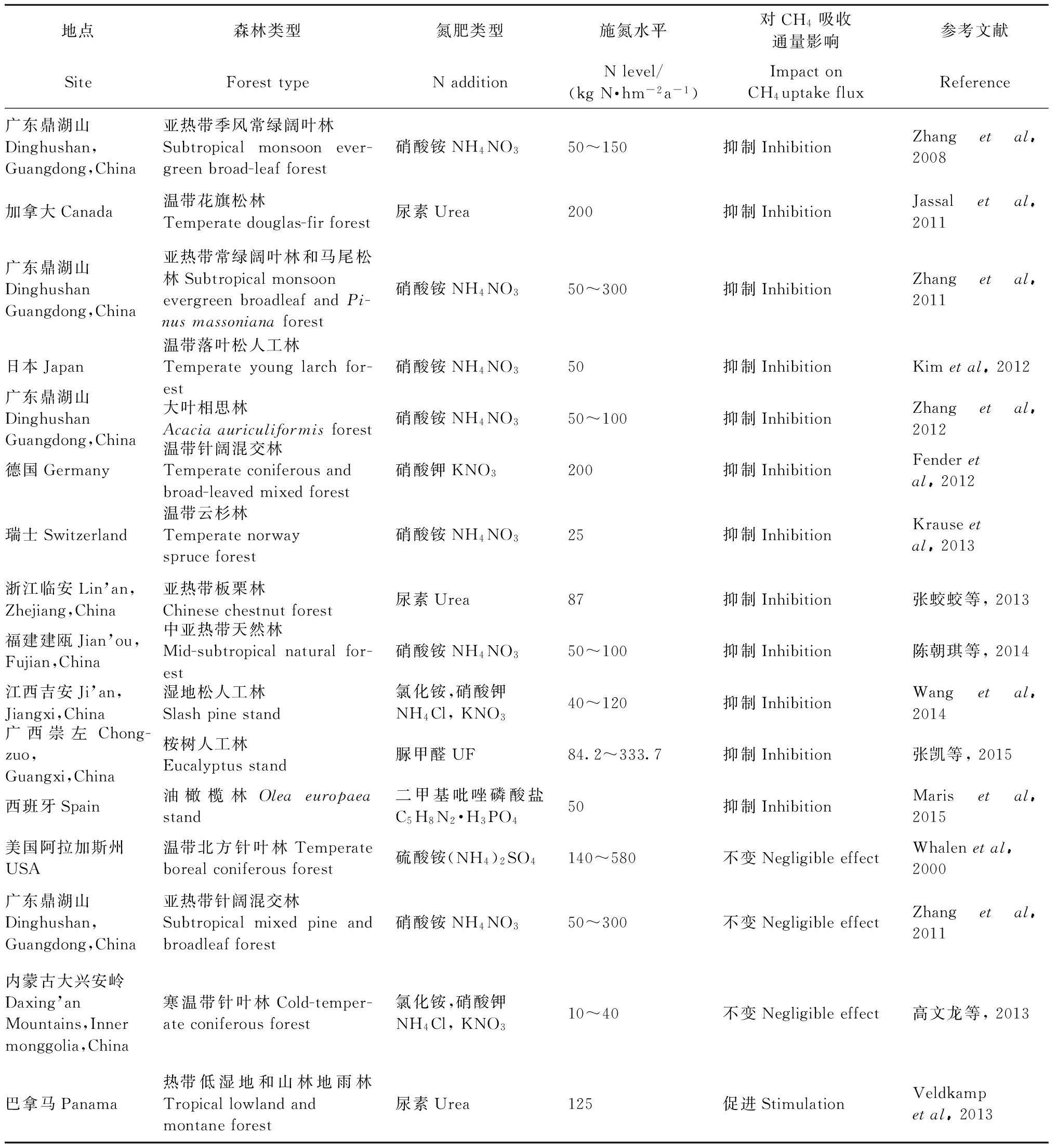
表1 不同林分土壤CH4吸收對(duì)增氮的響應(yīng)Tab.1 Responses of CH4 uptake flux to N fertilizer addition in typical stand soils
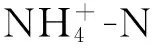
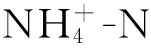
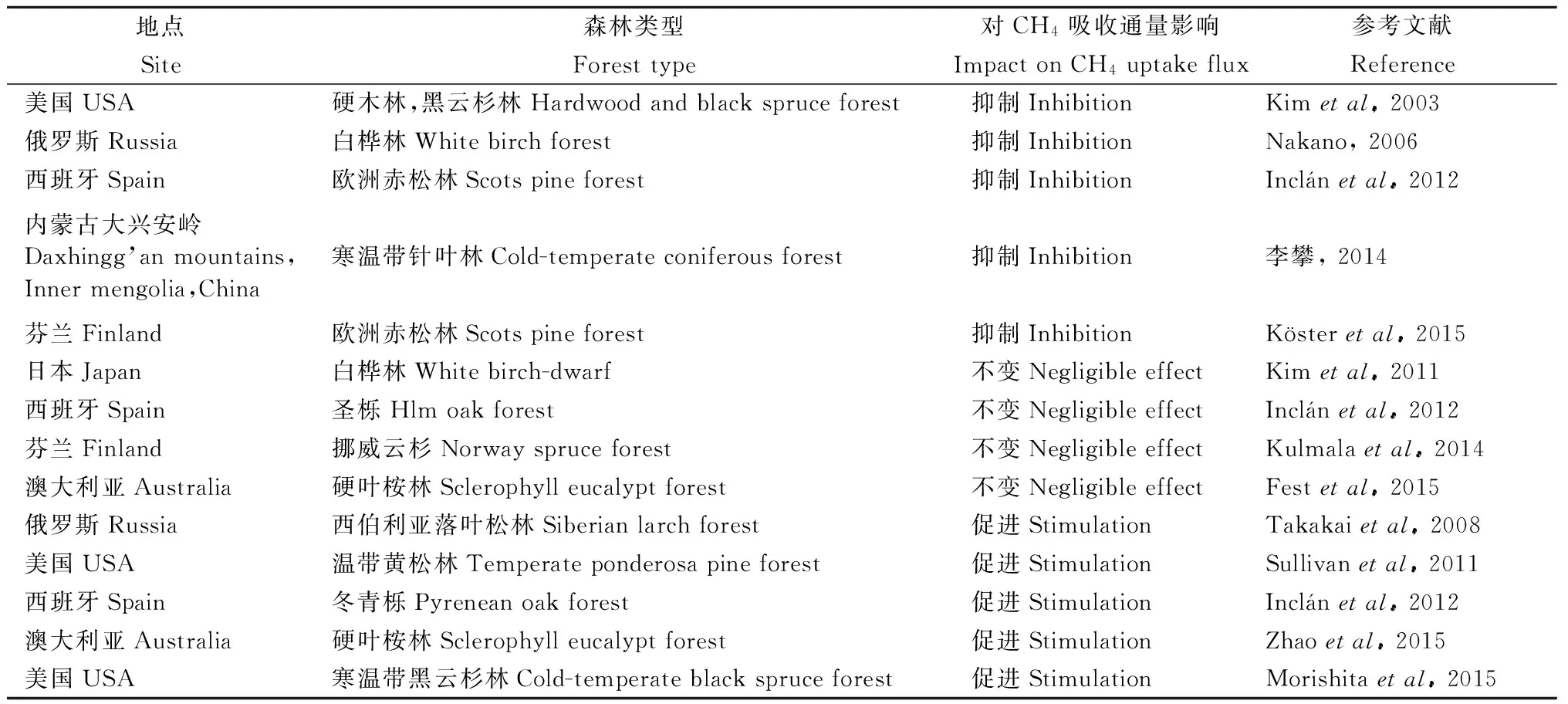
表2 不同林分土壤CH4吸收對(duì)火燒的響應(yīng)Tab.2 Responses of CH4 uptake to burning in typical forest soils
3 采伐
森林采伐后,地表植被和凋落物減少,土壤裸露在地表,土壤侵蝕和淋溶作用加強(qiáng),加快有機(jī)碳分解速率,減弱森林碳匯能力(閆美芳等, 2010; Zhouetal., 2015)。采伐改變森林土壤水熱條件,樹(shù)木對(duì)土壤水分吸收能力的減弱使得地下水位上升,從而減弱土壤的通氣透水性,進(jìn)而影響森林土壤CH4吸收(Gaoetal., 2015)。
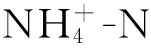
擇伐是森林采伐中最常見(jiàn)方式之一。擇伐可以?xún)?yōu)化森林林齡結(jié)構(gòu),提高林木生產(chǎn)力,增加光照利用率,改善土壤水熱條件,維持植物根系和微生物群落的穩(wěn)定,減少林火風(fēng)險(xiǎn),是維持森林健康的重要措施。目前,擇伐對(duì)土壤CH4吸收速率影響的研究還沒(méi)有統(tǒng)一的結(jié)論(表4)。Bradford等(2000)研究發(fā)現(xiàn),溫帶山毛櫸(Quercusrobur)人工林擇伐2年后土壤CH4吸收速率增加。Yoshiyuki等(2004)發(fā)現(xiàn)日本扁柏(Chamaecyparisobtusa)人工林擇伐8個(gè)月后土壤密度增加,土壤通氣性減弱導(dǎo)致土壤CH4吸收通量下降。Sundqvist等(2014)發(fā)現(xiàn)擇伐1年后土壤CH4吸收速率下降了50%。Sullivan等(2008)發(fā)現(xiàn)擇伐1年后促進(jìn)了林下植被生長(zhǎng),森林土壤有機(jī)碳沒(méi)有顯著減少,對(duì)甲烷氧化菌影響較小(Wuetal., 2011),土壤CH4吸收速率沒(méi)有顯著變化。由此可見(jiàn),擇伐后采樣時(shí)間可能是影響土壤CH4吸收速率變化的原因之一。
4 林下植被管理
林下植被是林下生態(tài)系統(tǒng)的重要組成部分,林下植被管理通過(guò)改變土壤有機(jī)物的輸入、小氣候和土壤理化性質(zhì),對(duì)土壤CH4吸收有著重要的影響(表5)。林下種植固氮植物能增強(qiáng)植物根系活性,提高作物生產(chǎn)力,同時(shí)增加了土壤凋落物輸入,促進(jìn)土壤碳的積累(Wangetal., 2014)。在土壤濕度較高的條件下,林下種植固氮植物,刺激了CH4產(chǎn)生菌的活性,使森林土壤轉(zhuǎn)變?yōu)镃H4的排放源(Qiao,etal., 2011)。Li(2010)發(fā)現(xiàn)種植翅莢決明(Cassiaalata)后抑制了尾葉桉(Eucalyptusurophylla)林土壤CH4吸收。
剔除尾葉桉林下灌草增大森林表層土的通透度,地表溫度升高加快土壤水分蒸發(fā)散失,使土壤濕度降低刺激了甲烷氧化菌的活性,從而增加土壤CH4吸收(Wuetal., 2011; Wangetal., 2011)。劉娟等(2015)研究發(fā)現(xiàn),留養(yǎng)雜草和剔除雜草的山核桃(Caryacathayensis)林均表現(xiàn)為土壤CH4的匯,剔除雜草后土壤CH4吸收通量顯著增加。
除草劑改變土壤微生物數(shù)量和群落活性,進(jìn)而影響土壤CH4吸收(丁洪等, 2011; 張仕穎等, 2013)。如Chen等(2009)發(fā)現(xiàn),丁草胺加快了土壤甲烷吸收速率。
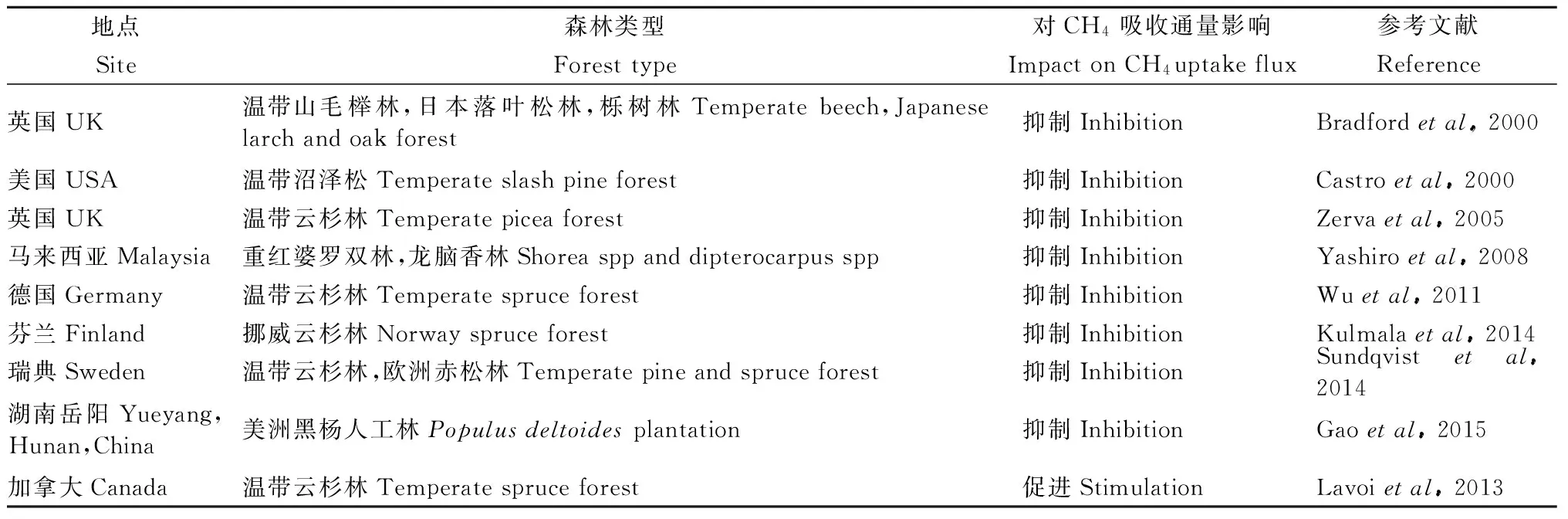
表3 不同林分土壤CH4吸收對(duì)皆伐的響應(yīng)Tab.3 Responses of CH4 uptake to clear-cutting in typical stand soils
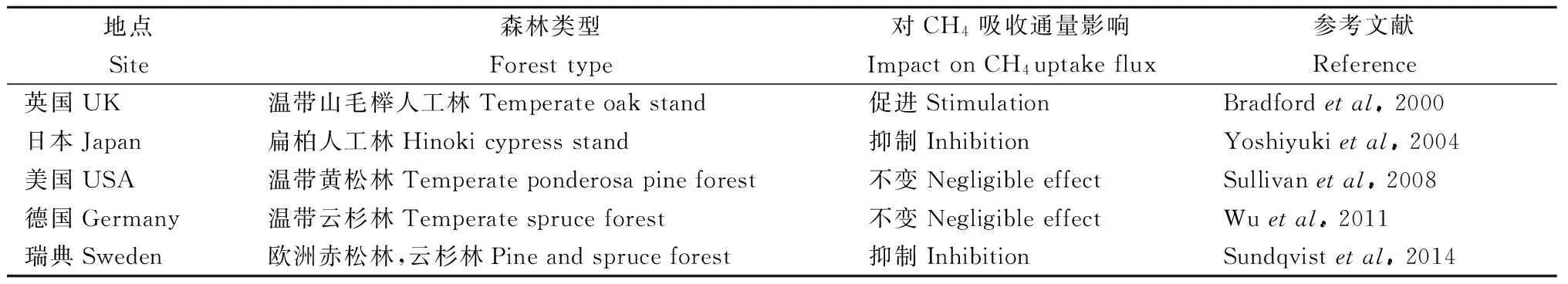
表4 不同林分土壤CH4吸收對(duì)擇伐的響應(yīng)Tab.4 Responses of CH4 uptake to thinning in typical stand soils
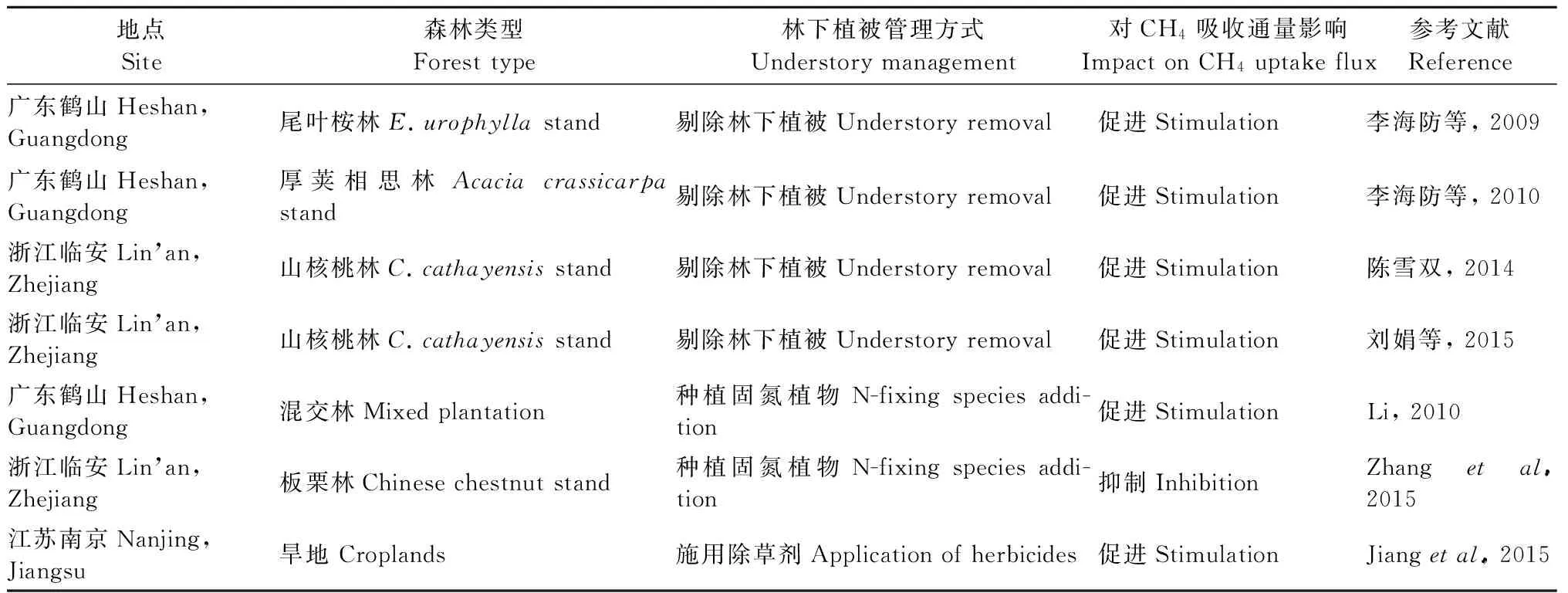
表5 不同林分土壤CH4吸收對(duì)林下植被管理的響應(yīng)Tab.5 Responses of CH4 uptake to understory management in typical stand soils
5 展望

今后應(yīng)加強(qiáng)以下4方面研究: 1)森林土壤CH4吸收對(duì)N輸入響應(yīng)機(jī)制的研究; 2)多種因素對(duì)林地土壤CH4吸收影響的長(zhǎng)期定位試驗(yàn)的研究; 3)甲烷氧化菌對(duì)各種干擾因素響應(yīng)模式的研究; 4)氣候變化對(duì)林地土壤CH4吸收的影響及其響應(yīng)機(jī)制的研究。
陳雪雙.2014.施肥及林下雜草管理對(duì)山核桃林地土壤溫室氣體排放的影響.臨安: 浙江農(nóng)林大學(xué)碩士學(xué)位論文.
(Chen X S.2014.Effects of fertilization and understory management on soil Greenhouse gases emissions in ChineseCaryacathayensisstands. Lin’an: MS thesis of Zhejiang A & F University.[in Chinese])
陳朝琪,楊智杰,劉小飛,等.2014.中亞熱帶天然林土壤CH4吸收速率對(duì)模擬N沉降的響應(yīng).生態(tài)學(xué)報(bào),34(10): 2498-2508.
(Chen Z Q,Yang Z J,Liu X F,etal.2014. Responses of CH4uptake rates to simulated N deposition in a nature forest in mid-subtropical China. Acta Ecologica Sinca,34(10): 2498-2508.[in Chinese])
程淑蘭,方華軍,于貴瑞,等.2012.森林土壤甲烷吸收的主控因子及其對(duì)增氮的響應(yīng)研究進(jìn)展.生態(tài)學(xué)報(bào),32(15): 4914-4923.
(Cheng S L,F(xiàn)ang H J,Yu G R,etal.2012.The primary factors controlling methane uptake from forest soils and their responses to increased atmospheric nitrogen deposition: a review. Acta Ecologica Sinica,32(15): 4914-4923.[in Chinese])
丁 洪,張玉樹(shù),鄭祥洲.2011.除草劑對(duì)土壤氮素循環(huán)的影響.生態(tài)環(huán)境學(xué)報(bào), 20(4): 767-772.
(Ding H,Zhang Y S,Zheng X Z,etal.2011.Review on the effect of herbicides on soil nitrogen cycle. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 20(4): 767-772.[in Chinese])
高升華,張旭東,湯玉喜,等. 2013.灘地美洲黑楊人工林皆伐對(duì)地表甲烷通量的短期影響.林業(yè)科學(xué),49(1): 7-13.
(Gao S H,Zhang X D,Tang Y X,etal.2013.Short-term effects of clear-cutting ofPopulusdeltoidesplantation on methane flux on the beach land of Yangtze River. Scientia Silvae Sinicae,49(1): 7-13.[in Chinese])
高文龍,程淑蘭,方華軍,等.2013.寒溫帶針葉林土壤CH4吸收對(duì)模擬大氣氮沉降增加的初期響應(yīng).生態(tài)學(xué)報(bào),33(23): 7505-7515.
(Gao W L,Cheng S L,F(xiàn)ang H J,etal.2013.Early responses of soil CH4uptake to increased atmospheric nitrogen deposition in a cold-temperate coniferous forest. Acta Ecologica Sinica,33(23): 7505-7515.[in Chinese])
李海防,夏漢平,傅聲雷,等.2009.剔除林下灌草和添加翅莢決明對(duì)尾葉桉林土壤溫室氣體排放的影響.植物生態(tài)學(xué)報(bào),33(6): 1015-1022.
(Li H F,Xia H P,F(xiàn)u S L,etal.2009.Emissions of soil greenhouse gases in response to under-story removal andCassiaalataaddition inEucalyptusurophyllaplantation in Guangdong Province,China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology,33(6): 1015-1022.[in Chinese])
李海防,張杏鋒.2010.剔除灌草和添加翅莢決明對(duì)厚莢相思林土壤溫室氣體排放的影響.應(yīng)用生態(tài)學(xué)報(bào),21(3): 563-568.
(Li H F,Zhang X F.2010.Soil greenhouse gases emission from anAcaciacrassicarpaplantation under effects of under-story removal andCassiaalataaddition. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,21(3): 563-568.[in Chinese])
李 攀.2014.寒溫帶針葉林火燒跡地土壤溫室氣體通量研究.呼和浩特: 內(nèi)蒙古農(nóng)業(yè)大學(xué)博士學(xué)位論文.
(Li P.2014.Soil greenhouse gases effluxes and its relationships with effect factors in the burned areas of Daxing′an Mountain. Hohhot: PhD thesis of Inner Mongolia Agricultural University.[in Chinese])
劉 娟,陳雪雙,吳家森,等.2015.剔除雜草對(duì)山核桃林地土壤溫室氣體排放的影響.應(yīng)用生態(tài)學(xué)報(bào),26(3): 666-674.
(Liu J,Chen X S,Wu J S,etal.2015.Effects of understory removal on soil greenhouse gas emissions inCaryacathayensisstands. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,26(3): 666-674.[in Chinese])
任 樂(lè),馬秀枝,李長(zhǎng)生.2014.林火干擾對(duì)土壤性質(zhì)及溫室氣體通量的影響.生態(tài)學(xué)雜志,33(2): 502-509.
(Ren L,Ma X Z,Li C S.2014.Effects of forest fire on soil property and greenhouse gas flux. Chinese Journal of Ecology,33(2): 502-509. [in Chinese])
王海淇.2011.大興安嶺北部實(shí)驗(yàn)林火影響下土壤碳、氮、水的時(shí)空變化.長(zhǎng)春: 東北林業(yè)大學(xué)碩士學(xué)位論文.
(Wang H Q.2011.Special and temporal variations of soil carbon,nitrogen and water as affected by an experimental forest fire in the Great Xing′an Mountains. Changchun: MS thesis of Northeast Forestry University.[in Chinese])
閆美芳,張新時(shí),江 源,等. 2010.主要管理措施對(duì)人工林土壤碳的影響.生態(tài)學(xué)雜志,29(11): 2265-2271.
(Yan M F,Zhang X S,Jiang Y,etal.2013.Effects of management practices on forest plantation soil carbon: a review. Chinese Journal of Ecology,29(11): 2265-2271.[in Chinese])
張蛟蛟,李永夫,姜培坤,等.2013.施肥對(duì)板栗林土壤CH4吸收通量動(dòng)態(tài)的影響.植物營(yíng)養(yǎng)與肥料學(xué)報(bào), 19(6): 1428-1437.
(Zhang J J,Li Y F,Jiang P K,etal.2013.Effects of fertilization on seasonal variations of soil CH4uptake fluxes in Chinese chestnut stands. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 19(6): 1428-1437.[in Chinese])
張 凱,鄭 華,歐陽(yáng)志云,等.2015.施氮對(duì)桉樹(shù)人工林生長(zhǎng)季和非生長(zhǎng)季土壤溫室氣體通量的影響.生態(tài)學(xué)雜志,34(7): 1779-1784.
(Zhang K,Zheng H,Ouyang Z Y,etal.2015. Effects of nitrogen fertilization on greenhouse gas fluxes of soil-atmosphere interface in growing and non-growing season in eucalyptus plantations in southern China. Chinese Journal of Ecology,34(7): 1779-1784.[in Chinese])
張仕穎,夏運(yùn)生,肖 煒,等.2013.除草劑丁草胺對(duì)高產(chǎn)水稻土微生物群落功能多樣性的影響.生態(tài)環(huán)境學(xué)報(bào),22(5): 815-819.
(Zhang S Y,Xia Y S,Xiao W,etal.2013.Effects of butachlor on the functional diversity of microbial communities in high-yield paddy soil. Ecology and Environmental Sciences,22(5): 815-819.[in Chinese])
Aronson E L,Helliker B R.2010.Methane flux in non-wetland soils in response to nitrogen addition: a meta-analysis. Ecology, 91(11): 3242-3251.
Auman A J,Speake C C,Lidstrom M E.2001. nifH sequences and nitrogen fixation in type I and type II methanotrophs. Applied & Environmental Microbiology,67(9): 4009-4016.
Becker H,Uri V,Aosaar J,etal.2015. The effects of clear-cut on net nitrogen mineralization and nitrogen losses in a grey alder stand. Ecological Engineering,85: 237-246.
Borken W,Brumme R.2009.Methane uptake by temperate forest soils∥functioning and management of european beech ecosystems. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer,369-385.
Bradford M A,Ineson P,Wookey P A,etal.2000.Soil CH4oxidation: response to forest clearcutting and thinning. Soil Biology & Biochemistry,32(7): 1035-1038.
Cai Z C. 2012.Greenhouse gas budget for terrestrial ecosystems in China. Science China Earth Sciences,55(2): 173-182.
Castro M S,Gholz H L,Clark K L,etal.2000. Effects of forest harvesting on soil methane fluxes in florida slash pine plantations. Canadian Journal of Forest Research,30(10): 1534-1542.
Chen W C,Yen J H,Chang C S,etal.2009. Effects of herbicide butachlor on soil microorganisms and on nitrogen-fixing abilities in paddy soil. Ecotoxicology & Environmental Safety,72(1): 120-127.
Denman K L,Brasseur G,Chidthaisong A,etal.2007. Couplings between changes in the climate system and biogeochemistry. London: Cambridge University Press,499-587.
Dutta M K,Ray R,Mukherjee R,etal.2015.Atmospheric fluxes and photo-oxidation of methane in the mangrove environment of the Sundarbans,NE coast of India: a case study from Lothian Island. Agricultural & Forest Meteorology,213: 33-41.
Fender A C,Birgit P,Gansert D,etal.2012. The inhibiting effect of nitrate fertilisation on methane uptake of a temperate forest soil is influenced by labile carbon. Biology & Fertility of Soils,48(6): 621-631.
Fernández-Fernández M,Gómez-Rey M X,González-Prieto S J.2015. Effects of fire and three fire-fighting chemicals on main soil properties, plant nutrient content and vegetation growth and cover after 10 years. Science of the Total Environment,515/516: 92-100.
Fest B J,Livesley S J,F(xiàn)ischer J C V,etal.2015. Repeated fuel reduction burns have little long-term impact on soil greenhouse gas exchange in a dry sclerophyll eucalypt forest. Agricultural & Forest Meteorology, 201: 17-25.
Gao S H,Chen J Q,Tang Y X,etal.2015. Ecosystem carbon (CO2and CH4) fluxes of aPopulusdeltoidesplantation in subtropical China during and post clear-cutting. Forest Ecology & Management,357: 206-219.
Heimann M. 2010. How stable is the methane cycle. Science,327(5970): 1211-1212.
Hoyos-Santillan J,Lomax B H,Large D,etal.2016. Quality not quantity: organic matter composition controls of CO2, and CH4, fluxes in neotropical peat profiles. Soil Biology & Biochemistry,103: 86-96.
Inclán R,Uribe C,Sánchez L,etal.2012.N2O and CH4fluxes in undisturbed and burned Holm oak,Scots pine andPyreneanoakforests in central Spain. Biogeochemistry,107 (1/3): 19-41.
Intergovemental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC).2007.Climate change 2007: the physical science basis. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Intergovemental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC).2013.Climate change 2013: the physics science basis. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Iwata H,Harazono Y,Ueyama M,etal.2015. Methane exchange in a poorly-drained black spruce forest over permafrost observed using the eddy covariance technique. Agricultural & Forest Meteorology,214/215: 157-168.
Jassal R S,Black T A,Roy R,etal.2011.Effect of nitrogen fertilization on soil CH4and N2O fluxes,and soil and bole respiration. Geoderma,162(1/2): 182-186.
Jiang J Y,Chen L M,Sun Q,etal.2015. Application of herbicides is likely to reduce greenhouse gas (N2O and CH4) emissions from rice-wheat cropping systems. Atmospheric Environment,107: 62-69.
K?ster E,K?ster K,Berninger F,etal.2015.Carbon dioxide,methane and nitrous oxide fluxes from podzols of a fire chronosequence in the boreal forests in V?rri?,F(xiàn)innish Lapland. Geoderma Regional,5: 181-187.
Kim Y S,Makoto K,Takakai F,etal.2011.Greenhouse gas emissions after a prescribed fire in white birch dwarf bamboo stands in Northern Japan,focusing on the role of charcoal. European Journal of Forest Research,130(6): 1031-1044.
Kim Y,Tanaka N.2003.Effect of forest fire on the fluxes of CO2,CH4and N2O in boreal forest soils,interior Alaska. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres,108(1): 1-12.
Kim Y S,Imori M,Watanabe M,etal.2012. Simulated nitrogen inputs influence methane and nitrous oxide fluxes from a young larch plantation in northern Japan. Atmospheric Environment,46: 36-44.
Kirschke S,Bousquet P,Ciais P,etal. 2013. Three decades of global methane sources and sinks. Nature Geoscience,6(10): 813-823.
Krause K,Niklaus P A,Schleppi P.2013.Soil-atmosphere fluxes of the greenhouse gases CO2,CH4and N2O in a mountain spruce forest subjected to long-term N addition and to tree girdling. Agricultural & Forest Meteorology,181: 61-68.
Kulmalaa L,Aaltonen H,Berninger F,etal.2014. Changes in biogeochemistry and carbon fluxes in a boreal forest after the clear-cutting and partial burning of slash. Agricultural & Forest Meteorology,188: 33-44.
Lavoie M,Kellman L,Risk D.2013.The effects of clear-cutting on soil CO2,CH4,and N2O flux,storage and concentration in two Atlantic temperate forests in Nova Scotia,Canada. Forest Ecology & Management,304: 355-369.
Li H F.2010.Soil CH4fluxes response to understory removal and N-fixing species addition in four forest plantations in Southern China. Journal of Forestry Research,21(3): 301-310.
Maris S C,Teira-Esmatges M R,Arbonés A,etal.2015. Effect of irrigation, nitrogen application, and a nitrification inhibitor on nitrous oxide, carbon dioxide and methane emissions from an olive (OleaeuropaeaL.) orchard. Science of the Total Environment,538: 966-978.
Morishita T,Noguchi K,Kim Y,etal.2015.CO2,CH4and N2O fluxes of upland black spruce (Piceamariana) forest soils after forest fires of different intensity in interior Alaska. Soil Science & Plant Nutrition,61(1): 98-105.
Nakano T.2006.Changes in surface methane flux after a forest fire in West Siberia//Hatano R,Guggenberger G. Symptom of environmental change in Siberian Permafrost Region. Sapporo: Hokkaido University Press,55-63.
Qiao Y F,Miao S J,Silva L C R,etal.2014.Understory species regulate litter decomposition and accumulation of C and N in forest soils: a long-term dual-isotope experiment. Forest Ecology & Management,329: 318-327.
Shrestha R K,Strahm B D,Sucre E B.2015. Greenhouse gas emissions in response to nitrogen fertilization in managed forest ecosystems. New Forests,46(2): 167-193.
Sj?gersten S,Melander E,Wookey P A.2007.Depth distribution of net methanotrophic activity at a mountain birch forest-tundra heath ecotone,Northern Sweden. Arctic Antarctic & Alpine Research,39(3): 477-480.
Sullivan B W,Kolb T E,Hart S C,etal.2008. Thinning reduces soil carbon dioxide but not methane flux from southwestern USA ponderosa pine forests. Forest Ecology & Management,255(12): 4047-4055.
Sullivan B W,Kolb T E,Hart S C,etal.2011. Wildfire reduces carbon dioxide efflux and increases methane uptake in ponderosa pine forest soils of the southwestern USA. Biogeochemistry,104(1/3): 251-265.
Sundqvist E,Vestin P,Crill P,etal.2014.Short-term effects of thinning,clear-cutting and stump harvesting on methane exchange in a boreal forest. Biogeosciences,11(21): 4637-4667.
Takakai F,Desyatkin A R,Lopez C M L,etal.2008.Influence of forest disturbance on CO2,CH4and N2O fluxes from larch forest soil in the permafrost taiga region of eastern Siberia. Soil Science & Plant Nutrition,54(6): 938-949.
Veldkamp E, Koehler B, Corre M D.2013.Indications of nitrogen limited methane uptake in tropical forest soils.Biogeosciences,10(3):5367-5379.
Wang F M,Zou B,Li H F,etal.2014. The effect of understory removal on microclimate and soil properties in two subtropical lumber plantations. Journal of Forest Research, 19(1): 238-243.
Wang Q K,Wang S L.2011. Response of labile soil organic matter to changes in forest vegetation in subtropical regions. Applied Soil Ecology,47(3): 210-216.
Wang Y F,Chen H,Zhu Q,etal.2014. Soil methane uptake by grasslands and forests in China. Soil Biology & Biochemistry,74: 70-81.
Wang Y S,Cheng S L,F(xiàn)ang H J,etal.2014. Simulated nitrogen deposition reduces CH4uptake and increases N2O emission from a subtropical plantation forest soil in southern China. Plos One,9(4): e93571.
Whalen S C,Reeburgh W S.2000. Effect of nitrogen fertilization on atmospheric methane oxidation in boreal forest soils. Chemosphere-Global Change Science,2(2): 151-155.
Wu J P,Liu Z F,Wang X L,etal.2011. Effects of understory removal and tree girdling on soil microbial community composition and litter decomposition in two Eucalyptus plantations in South China. Functional Ecology,25(4): 921-931.
Wu X,Nicolas B,Rainer G,etal.2011. Long-term effects of clear-cutting and selective cutting on soil methane fluxes in a temperate spruce forest in southern Germany. Environmental Pollution,159(10): 2467-2475.
Yashiro Y,Wan R K,Okuda T,etal.2008.The effects of logging on soil greenhouse gas (CO2,CH4,N2O) flux in a tropical rain forest, Peninsular Malaysia. Agricultural & Forest Meteorology,148(5): 799-806.
Yoshiyuki I,Shigehiro I,Masamichi T,etal.2004. The effect of thinning on carbon dioxide emission and methane uptake by forest soils in Hinoki cypress (Chamaecyparisobtusa) plantations. Applied Forest Science,13(2): 91-96.
Zerva A,Mencuccini M.2005.Short-term effects of clearfelling on soil CO2,CH4,and N2O fluxes in a Sitka spruce plantation. Soil Biology & Biochemistry,37(11): 2025-2036.
Zhang J J,Li Y F,Chang S X,etal.2015. Understory management and fertilization affected soil greenhouse gas emissions and labile organic carbon pools in a Chinese chestnut plantation. Forest Ecology & Management,337: 126-134.
Zhang T,Zhu W,Mo J M,etal.2011.Increased phosphorus availability mitigates the inhibition of nitrogen deposition on CH4uptake in an old-growth tropical forest,southern China. Biogeosciences,8(9): 2805-2813.
Zhang W,Mo J M,Zhou G Y,etal.2008. Methane uptake responses to nitrogen deposition in three tropical forests in southern China. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres,113(11): 1-10.
Zhang W,Zhu X,Liu L,etal.2012. Large difference of inhibitive effect of nitrogen deposition on soil methane oxidation between plantations with N-fixing tree species and non-N-fixing tree species. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences,117(4): 1-9.
Zhao Y,Wang Y Z,Xu Z H,etal.2015.Impacts of prescribed burning on soil greenhouse gas fluxes in a suburban native forest of south-eastern Queensland,Australia. Biogeosciences,12(21): 6279-6290.
Zhou Y,Zheng L F,Zhou X N,etal.2015. Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and the optimum operation model of timber production systems in Southern China. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin,24(11): 3743-3753.
(責(zé)任編輯 于靜嫻)
Effect of Management Practices on Methane Uptake in Forest Soils
Wang Huilai Liu Juan Jiang Peikun Zhou Guomo Li Yongfu Wu Jiasen
(State Key Laboratory of Subtropical Silviculture Zhejiang Provincial Key Laboratory of Carbon Cycling in Forest Ecosystems and Carbon Sequestration Zhejiang A & F University Lin’An 311300)
Forest soils are the main sinks of atmospheric CH4. This study is aimed to provide a basis for forest management practices under climate change. The databases of Scopus, Web of Science, SDOS and China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) were used to review current status of studies on CH4uptake from forest soils. The review highlighted the effect of forest management practices (fertilization, cutting, burning, and understory management) on soil CH4uptake, and explained its main mechanism. Fertilization tended to inhibit soil CH4uptake in N-rich forest soils, but obviously promoted soil CH4uptake in N-poor forest soils. It was generally believed that slash burning reduced soil CH4uptake. Clear-cutting changed soil temperature, water content, decomposition of organic carbon, and thus weakened the capability of methanotrophs to oxidize methane. Selective-cutting could stimulate, suppress, or show no effect on forest soil CH4uptake. Understory removal increased soil temperature, sped up evaporation of soil water and increased the activity of methanotrophs, which promoted soil CH4uptake. Nitrogen fixing plants reduced soil CH4uptake. There were significant differences of management practices on forest soil CH4uptake among the previous studies. Additionally, the inherent mechanism is still not sufficient. With the development of research theory and technology, the interactive effects of various factors and climate change on forest soil CH4uptake and its mechanism, the response model of methanotrophs to various interference factors will become the main direction in the future.Key words: human disturbance; soil CH4uptake; management practices; fertilization; cutting; burning; understory management
10.11707/j.1001-7488.20170518
2015-11-18;
2017-01-19。
浙江省自然科學(xué)基金項(xiàng)目(LY15C160004); 浙江省科技創(chuàng)新團(tuán)隊(duì)項(xiàng)目(2012R10030-11)。
S718.5
A
1001-7488(2017)05-0156-08
* 劉娟為通訊作者。

