湘中典型礦區(qū)土壤對銻的吸附特征
李寧 任伯幟 周瑩瑩 張堯
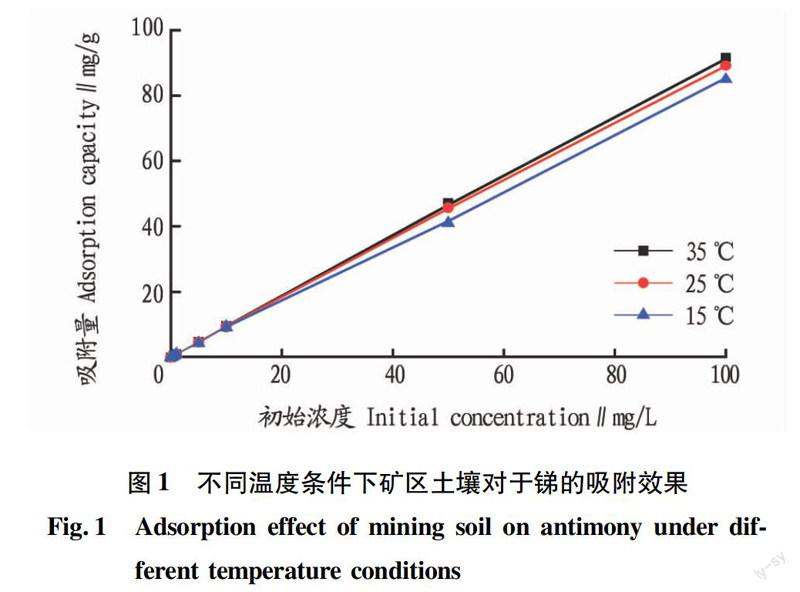
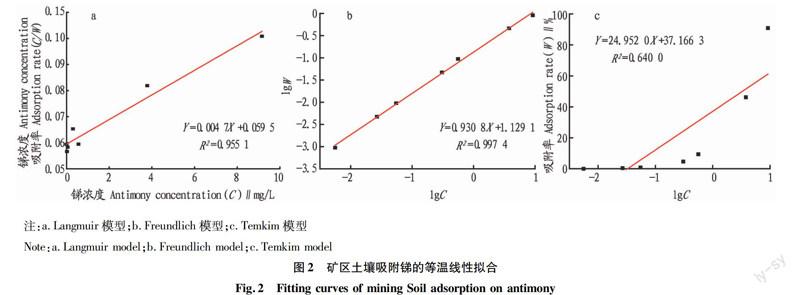
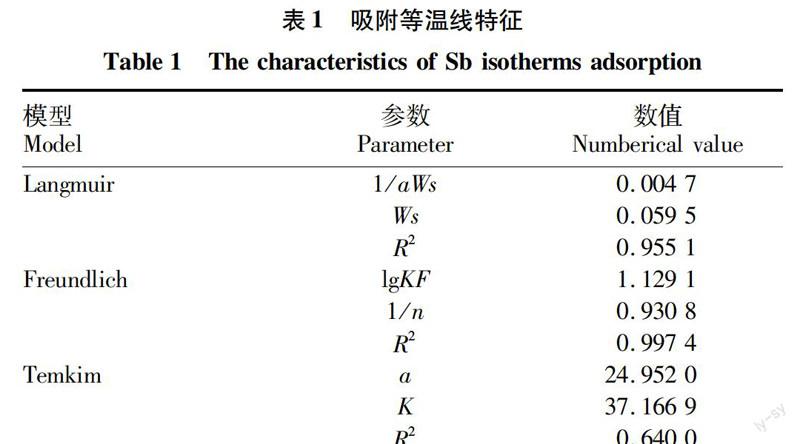
摘要[目的]研究礦區(qū)土壤對重金屬銻的吸附行為。[方法]采取動態(tài)吸附的方法,通過改變污染物濃度、pH、吸附時間、溫度等條件,研究礦區(qū)土壤對重金屬銻的吸附特征。[結(jié)果]礦區(qū)土壤對重金屬銻的吸附可以用Langmuir方程、Freundlich方程、Temkin方程進行較好地擬合,其中Langmuir方程的描述效果最優(yōu)。不同溫度試驗中,礦區(qū)土壤對銻的吸附量的影響從大到小依次為35、25、15 ℃。隨pH的升高,礦區(qū)土壤對重金屬銻的吸附量逐漸遞減。與雙常數(shù)速率方程相比,Elovich方程更適合描述礦區(qū)土壤的動力學(xué)吸附過程。[結(jié)論]該研究可為預(yù)防和治理污染土壤提供科學(xué)依據(jù)。
關(guān)鍵詞銻;礦區(qū)土壤;吸附
中圖分類號S181.3文獻標(biāo)識碼A文章編號0517-6611(2017)11-0047-03
Abstract[Objective]In order to study the adsorption behavior of mine soil on heavy metal antimony. [Method]Using the dynamic adsorption method to obtain the adsorption characteristics of heavy metals in the mine soil by changing the pollutant concentration, pH value, adsorption time, temperature and other conditions. [Result] The results showed the the adsorption of heavy metal antimony in mine soil can be well fitted by Langmuir equation, Freundlich equation and Temkin equation, in which the Langmuir equation was the best.In the three groups of different temperature control experiments, the adsorption capacity increased with the rise of temperature. In the experimental range, with the increase of pH value, the adsorption capacity of heavy metals antimony in the mine soil was gradually decreased.The Elovich equation was more suitable to describe the dynamic adsorption process. [Conclusion]This study can provide scientific basis for prevention and treatment of contaminated soil.
Key wordsAntimony;Mine soil;Adsorption
銻是一種對生物體有毒害作用的重金屬元素[1],近年來銻污染越來越受到人們的關(guān)注。銻普遍應(yīng)用于各類制造行業(yè),長期接觸會刺激、損害人體器官。銻及其復(fù)合產(chǎn)物已被美國國家環(huán)境保護局(USEPA)及歐盟(EU)確定為重點防控污染物,在巴塞爾公約中把銻列為可越境遷移的危險廢物[2-4]。土壤中的銻污染主要來自城市廢棄物以及礦山開采[5]。銻作為常用阻燃劑廣泛應(yīng)用于建筑、電子、紡織等行業(yè),這些行業(yè)產(chǎn)生的垃圾廢物會引起銻的聚集,研究表明,城市垃圾廢棄物中銻的平均濃度可達29 mg/kg(WW)和52 mg/kg(DW)。在銻礦區(qū)及銻作為主要伴生重金屬的礦區(qū)開采過程中往往產(chǎn)生含銻廢棄物,如廢礦石、尾礦渣等,這些廢棄物的長期堆放會致使離子態(tài)銻隨降雨和地表水滲入地下,對周邊地表水、地下水及土壤造成嚴(yán)重污染。……

