基于區間數的直覺模糊多屬性決策研究
段 傳 慶
(1.合肥工業大學 管理學院, 安徽 合肥 230009; 2.合肥工業大學 數學學院, 安徽 合肥 230009)
基于區間數的直覺模糊多屬性決策研究
段 傳 慶1,2
(1.合肥工業大學 管理學院, 安徽 合肥 230009; 2.合肥工業大學 數學學院, 安徽 合肥 230009)
研究一類屬性權重未知的直覺模糊多屬性決策問題. 將直覺模糊數的屬性值轉由雙區間數表示,根據決策方案屬性值間的離差確定屬性權重. 根據各方案屬性加權綜合值及區間直覺模糊數的得分函數,對2套方案分別進行排序和比較, 并通過實例說明了該方法的有效性.
直覺模糊數;區間數;多屬性決策;權重
0 引 言
1965年,ZADEH[1]提出了模糊集理論,在此基礎上,ATANASSOV[2]又提出了直覺模糊集概念. 直覺模糊集在模糊集理論的基礎上提出了隸屬度、非隸屬度及猶豫度3個概念,從而更準確地反映事物的本質.但是決策者提供的信息有時很難用隸屬度、非隸屬度及猶豫度的精確數值來表達,而用區間數可以更方便、準確地描述其意圖及想法.
受時間、空間等客觀因素及自身知識結構和專業水平等主觀因素的限制,決策者無法給予決策方案精確的信息. 對于屬性權重的描述更是如此. 因此,如何確定屬性權重一直是模糊多屬性決策的熱點. 熵權法是一種客觀賦權法,不少學者對其進行過研究[3-8].文獻[9]根據屬性值的均值、方差及屬性間的關聯度,建立模型描述屬性. 文獻[10]通過集成主、客觀權重求得屬性綜合權重. 文獻[11]利用熵和離差確定屬性權重,既考慮了數據本身的重要性,又兼顧到數據間的聯系.關于區間數權重的確定問題, 文獻[12]引入了偏差的概念,利用偏差和最小建立目標規劃模型計算屬性權重. 文獻[13]依據主客觀信息偏差最小化原則,通過構造線性模型求得屬性最大、最小值,從而得到屬性權重區間信息. 文獻[14]運用誤差傳遞公式確定屬性的權重. 文獻[15]依據相對優勢度的概念對屬性權重進行兩兩比較,從而得到了屬性權重排序向量. 文獻[16]將區間數轉化為聯系數,以確定屬性權重.
直覺模糊集中的隸屬度、非隸屬度及猶豫度所提供的信息是點估計,在很多情況下無法準確反映決策者的真實意圖. 因此,屬性權重的確定及最終的方案排序很可能出現與事實不符的情況. 針對上述情況,本文將直覺模糊數轉化為用2個區間數來表示,同時引入風險因子k. 而風險因子k與猶豫度相對應,反映了猶豫度對決策過程的影響. 本文所提供的轉化公式既體現了隸屬度、非隸屬度及猶豫度在決策中的作用,又規避了點估計無法準確反映決策者意圖的弊端. 利用屬性值間離差最大化方法建立新模型求得屬性權重.用文獻[16]中主值模型的綜合值及區間直覺模糊集的得分函數2套方案分別進行排序,并討論其結果.
1 基本理論
1.1 基本定義
定義1[2]設X是一個非空集合,A={〈x,μA(x),νA(x)〉|x∈X}為直覺模糊集,其中μA(x)和νA(x)分別表示X中的元素x屬于X隸屬度μA:X→[0,1]和非隸屬度vA:X→[0,1],且滿足0≤μA(x)+vA(x)≤1,?x∈X.此外,πA(x)=1-μA(x)-vA(x)表示X中的元素x屬于X的猶豫度.
定義2[17]設X是一個給定的論域,則X上的一個區間直覺模糊集A定義為:
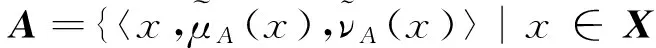


定義3[18-19]設a1=(μa1,νa1)和a2=(μa2,νa2)為直覺模糊數,s(a1)=μa1-νa1和s(a2)=μa2-νa2分別為a1和a2的得分函數,h(a1)=μa1+νa1和h(a2)=μa2+νa2分別為a1和a2的精確函數:
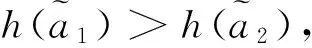
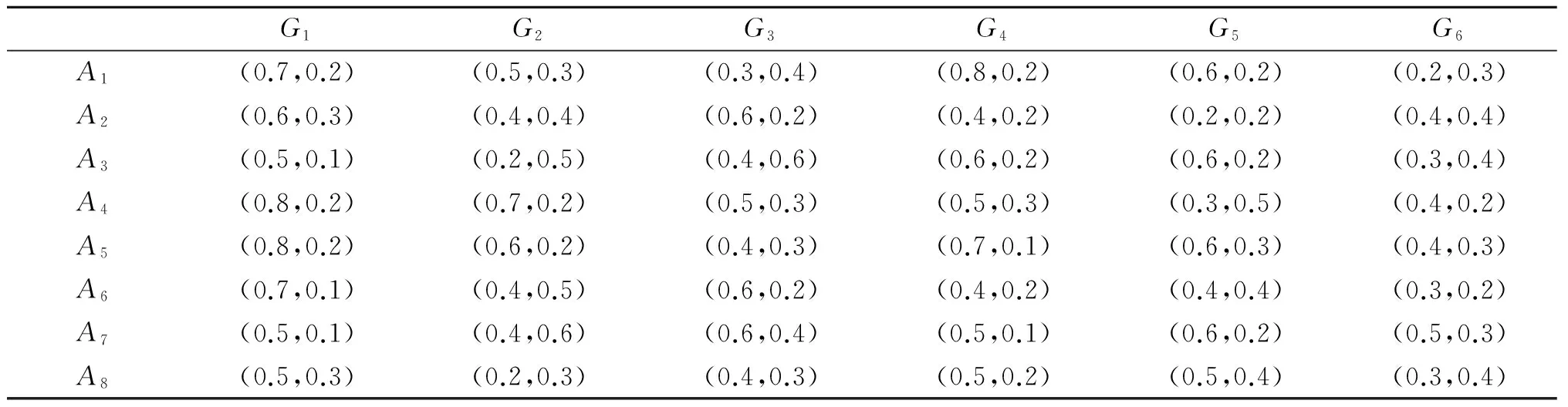
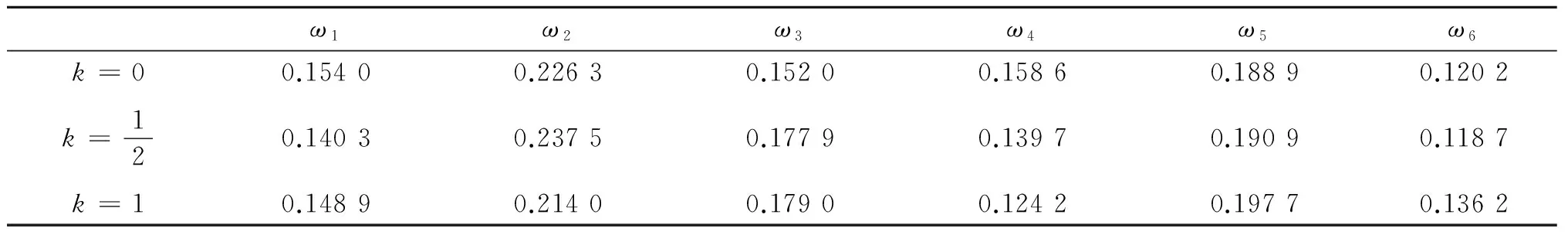
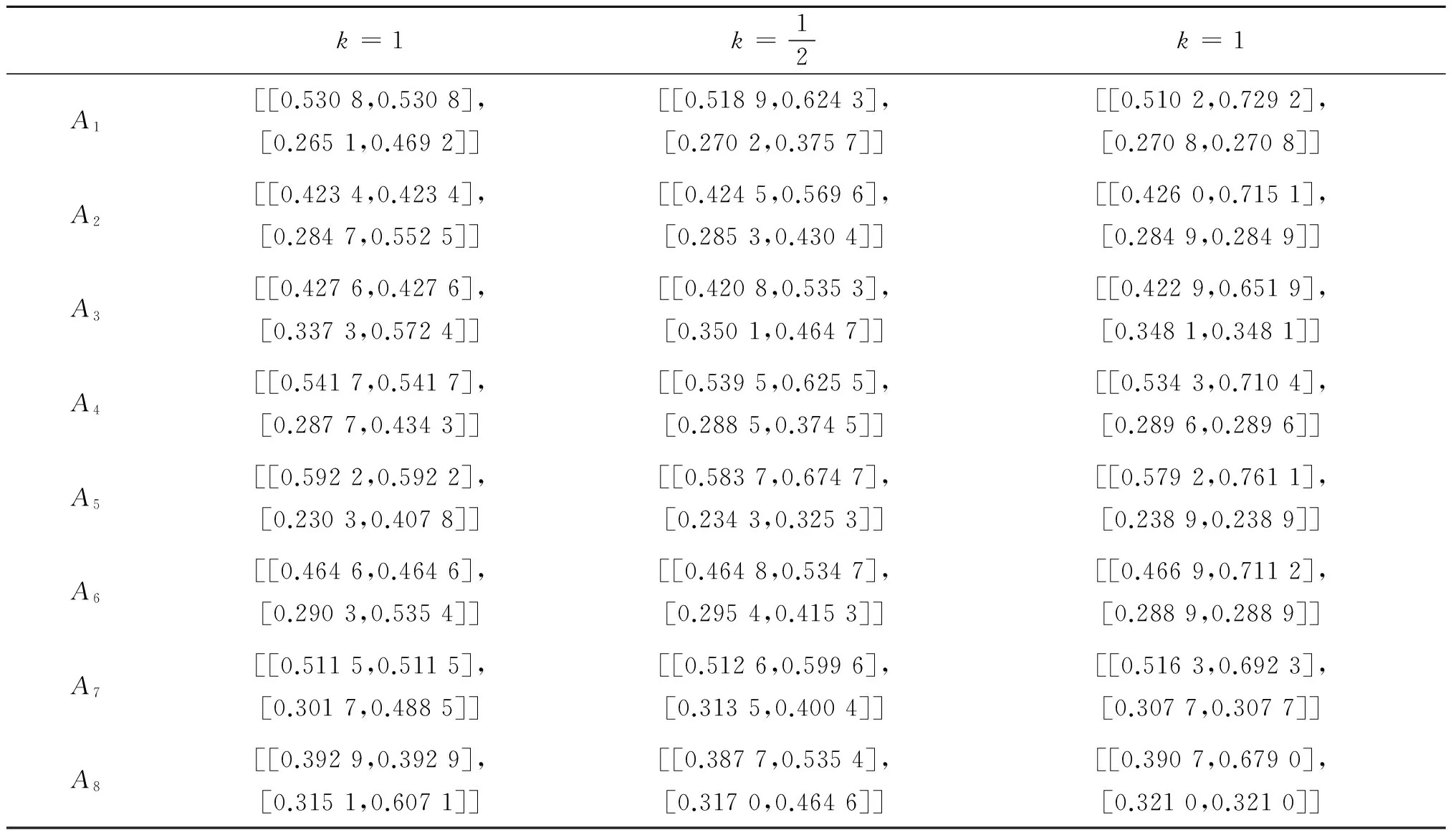
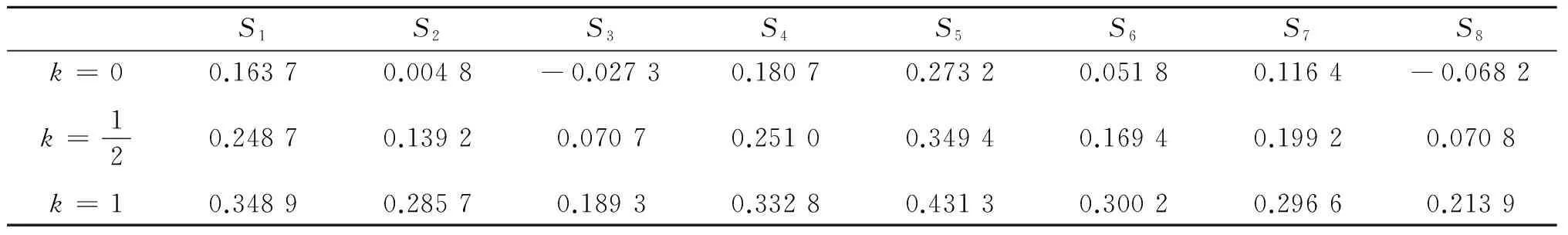
若s(a1) 若s(a1)=s(a2),則 1)若h(a1)=h(a2),則a1和a2相等,即μa1=μa2和νa2=νa1,記為a1=a2; 2)若h(a1) 3)若h(a1)>h(a2),則a1大于a2,記為a1>a2. (1) (2) (3) 1.2 區間數轉化為三角函數的方法 其中: (4) 稱為區間數的模; (5) 稱為幅角. 1.3 將直覺模糊數轉化為區間數的方法 (6) 對于效益型屬性,采用公式: (7) 對于成本型屬性,采用公式: (8) (9) (10) 綜合考慮,則 (11) 綜合2種情形,記 (12) 則M(Si)越大,Ai越優. 綜上所述,給出如下算法: 步驟1 將直覺模糊矩陣R=(μij,νij)mn轉化為二元區間數矩陣[[μij,μij+kπij],[νij,νij+(πij-kπij)]]mn; 步驟2 利用式(11)計算屬性權重ωj; 步驟3 利用式(12)計算M(Si),并根據k的取值和M(Si)的大小對Ai進行排序; 中汕廠的訂單保住了,景花廠生產穩定了。阿花說這幾天我心都操干了,我要美容。天天往美容院跑,臉蛋越發俏麗,身材越發魔鬼了。周末,她來廠里晃一下,交代了工作,就開車出去了。 經計算,每個方案最終都對應2個區間數,按照其所代表的意義,這2個區間數可以理解為1個區間直覺模糊數.因此,可以按區間直覺模糊數的得分函數及k的取值情況對各個選項進行排序. 例2 某公司準備提拔一名部門經理,現有8名候選人A=(A1,A2,A3,A4,A5,A6,A7,A8)符合提拔條件.公司分別從6個方面G=(G1,G2,G3,G4,G5,G6)進行評估,并將結果以直覺模糊信息形式給出[24](見表1). 表1 直覺模糊決策矩陣Table 1 Intuitionistic fuzzy decision matrix 步驟1 由于該表中屬性值均為效益型,故無需再對其進行規范化處理.將上述直覺模糊矩陣轉化為二元區間數矩陣(見表2). 表2 二元區間數矩陣表Table 2 Binary interval number matrix table 屬性權重,如表3所示. 表3 各屬性權重值表格Table 3 Table of weight values of each attribute 步驟3 對應上述k值,分別計算M(Si),見表4. 表4 各方案的綜合主值表格Table 4 Consolidated master value table for each program k=0時,選項排序為: A5>A4>A1>A7>A6>A2>A8>A3; k=1時,選項排序為: A5>A1>A4>A6>A2>A7>A8>A3. 表5 二元區間數加權綜合值表格Table 5 Weighted comprehensive value table for binary interval numbers 表6 各方案綜合得分值表格Table 6 Comprehensive score table k=0時,其選項排序為: A5>A4>A1>A7>A6>A2>A3>A8; A5>A4>A1>A7>A6>A2>A8>A3; k=1時,排序為: A5>A1>A4>A6>A7>A2>A8>A3. [1]ZADEHLA.Fuzzyset[J]. Information and Control,1965,8(3):338-356. [2] ATANASSOV K. Intuitionistic fuzzy sets[J]. Fuzzy Sets and Systems,1986,20(1):87-96. [3] MAO J J, YAO D B, WANG C C. A novel crossentropy and entropy measures of IFSs and their applications[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems,2013, 48:37-45. [4] 王曉杰,魏翠萍,郭婷婷.基于交叉熵和熵的直覺模糊多屬性群決策專家權重的確定[J].曲阜師范大學學報,2011,37(3):35-40. WANG X J,WEI C P,GUO T T. A method to drive experts’ weights in intuitionistic fuzzy multi-attribute group decision making based on cross entropy and entropy[J]. Journal of Qufu Normal University,2011,37(3):35-40. [5] 趙萌,任嶸嶸.基于模糊熵的直覺模糊多屬性群決策方法[J].數學的實踐與認識,2014,44(23):153-159. ZHAO M, REN R R. Method based on fuzzy entropy with intuitionistic fuzzy set for group multi-attribute decision making[J]. Journal of Mathematics in Practice and Theory, 2014,44(23):153-159. [6] 戚曉雯,梁昌勇,張恩橋,等.基于熵最大化的區間直覺模糊多屬性群決策方法[J].系統工程理論與實踐,2011,31(10):1940-1948. QI X W, LIANG C Y, ZHANG E Q, et al. Approach to interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy multiple attributes group decision making based on maximum entropy[J].Systems Engineering Theory & Practice, 2011,31(10):1940-1948. [7] 陳曉紅.基于熵和關聯系數的區間直覺模糊決策方法[J].系統工程與電子技術,2013,35(4):791-794. CHEN X H. Approach to interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy decision making based on entropy and correlation coefficient[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics,2013,35(4):791-794. [8] 李蘭平.基于一類新的直覺模糊熵的直覺模糊多屬性決策法[J].齊齊哈爾大學學報,2014,30(2):83-86. LI L P. Intuitionistic fuzzy multi-attribute decision making based on a new intuitionistic fuzzy entropy measure[J].Journal of Qiqihar University,2014,30(2):83-86. [9] 劉小弟,朱建軍,張世濤,等.考慮屬性權重優化的猶豫模糊多屬性決策方法[J].控制與決策,2016,31(2):297-302. LIU X D, ZHU J J, ZHANG S T, et al. Hesitant fuzzy multiple attribute decision making method based on optimization of attribute weight[J]. Control and Decision,2016,31(2):297-302. [10] 韓二東,郭鵬,趙靜.主客觀權重集成及擴展VIKOR的多屬性群決策方法[J].計算機工程與應用,2015,51(11):1-6. HAN E D, GUO P, ZHAO J. Method for multiple attribute group decision maling based on subjective-objective weight integrated and extended VIKOR[J].Computer Engineering and Applications, 2015,51(11):1-6. [11] 段傳慶.一種對方案有偏好的區間直覺模糊多屬性算法[J].中國科學技術大學學報,2015,45(12):100-105. DUAN C Q. Approach to interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy multiple attribute decision making with preference information[J].Journal of University of Science and Technology of China, 2015,45(12):100-105. [12] XU Z S. Multiple attribute group decision making with different formats of preference information on attributes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics-Part B,2007,37:1500-1511. [13] XU Z S, CHEN J. MAGDM linear programming models with distinct uncertain preference structures[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems,Man,and Cyber-netics-Part B,2008,38:1356-1370. [14] YOON K. The propagation of errors in multiple-attribute decision analysis:A practical approach[J]. Journal of the Operational Research Society,1989, 40(7): 681-686. [15] 張吉軍. 區間數多指標決策問題的模糊層次分析法[J]. 工業工程與管理,2003(6):20-23. ZHANG J J. Fuzzy AHP in multiple attribute decision making with interval numbers[J]. Industrial Engineering and Management,2003(6):20-23. [16] 劉秀梅,趙克勤. 基于聯系數的屬性權重未知的區間數多屬性決策研究[J]. 數學的實踐與認識,2013,43(3):143-148. LIU X M, ZHAO K Q. Interval multi-attribute decision making with the attribute weight unknown based on connection number[J]. Journal of Mathematics in Practice and Theory, 2013,43(3):143-148. [17] ATANASSOV K, GARGOV G. Interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy sets[J]. Fuzzy Sets and Systems,1989,31(3):343-349. [18] XU Z S. Intuitionistic fuzzy aggregation operators [J]. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems,2007,15(6):1179-1187. [19] XU Z S, YAGER R R. Some geometric aggregation operators based on intuitionistic fuzzy sets[J]. International Journal of General Systems,2006,35(4):417-433. [20] 徐澤水.區間直覺模糊信息的集成方法及其在決策中的應用[J].控制與決策,2007,22(2):215-219. XU Z S. Methods for aggregating interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy information and their application to decision making [J]. Control and Decision,2007,22(2):215-219. [21] 徐澤水.不確定多屬性決策方法及應用[M].北京:清華大學出版社,2004:105-117. XU Z S. Uncertain Multiple Attribute Decision Making:Methods and Applications[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press,2004:105-117. [22] 劉秀梅,趙克勤.基于聯系數復運算的區間數多屬性決策方法及應用[J].數學的實踐與認識,2008,38(23):57-64. LIU X M, ZHAO K Q. Multiple attribute decision making and its applications based on complex number arithmetic operation of connection number with interval numbers[J]. Journal of Mathematics in Practice and Theory,2008,38(23):57-64. [23] XU Z S, HU H. Projection models for intuitionistic fuzzy multiple decision making[J]. International Journal of Information Technology and Decision Making,2010,9(2):267-280. [24] 王翠翠,姚登寶,毛軍軍,等.基于熵和相關系數的直覺模糊多屬性決策方法[J].計算機應用,2012,32(11):3002-3004. WANG C C, YAO D B, MAO J J, et al. Intuitionistic fuzzy multiple attributes decision making method based on entropy and correlation coefficient[J]. Journal of Computer Applications,2012,32(11):3002-3004. DUAN Chuanqing1,2 (1.SchoolofBusinessAdministration,HefeiUniversityofTechnology,Hefei230009,China; 2.SchoolofMathematics,HefeiUniversityofTechnology,Hefei230009,China) This paper discusses the multiple attribute decision making problems, in which the information about attribute weights is totally unknown and the attribute values are expressed by intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Two interval numbers are used to take the place of attribute values. A new method is proposed to gain the weights of the attributes based on the deviations between the values of the attributes. We make the ranking of projects by the weighted comprehensive values of all projects and the score function of interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy numbers, respectively, and then compared with the results of the two methods. Finally,an illustrative example is given to verify the effectiveness of the method. intuitionistic fuzzy number; interval number;multiple attribute decision making;entropy 2016-05-19. 中央高校基本科研業務費專項資金資助(J2014HGXJ0080). 段傳慶(1978-),ORCID:http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3096-3479,男,博士,講師,主要從事決策分析研究,E-mail:dcqhn@126.com. 10.3785/j.issn.1008-9497.2017.02.009 C 934 A 1008-9497(2017)02-174-07 Intuitionistic fuzzy multiple attribute decision making based on interval numbers. Journal of Zhejiang University(Science Edition), 2017,44(2):174-180


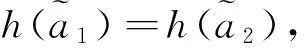

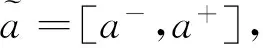
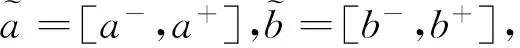
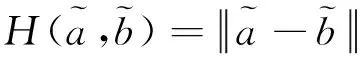
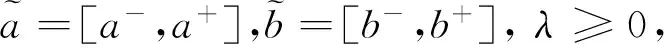

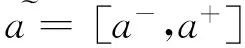

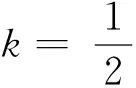

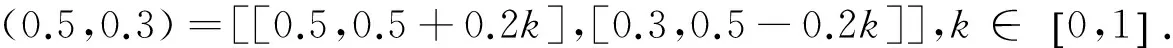
2 決策方法
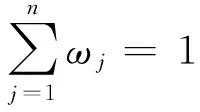


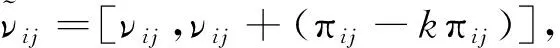
3 算例分析


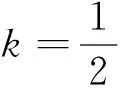


4 結果比較
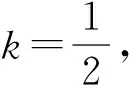
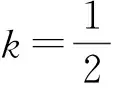
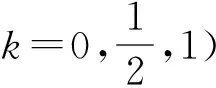
5 結 論