蘇北農村小學生結核病防治專題網站干預效果評價
周惠+李智+張楊+胡彩紅

【中圖分類號】R72.6 【文獻標識碼】A 【文章編號】2095-6851(2016)11-0-01
The Evaluation of the Intervention Effects of Special Website about Prevention and Treatment of Tuberculosis among the Primary School Students in Rural Area of Northern Jiangsu Province
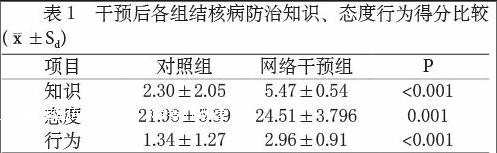
Abstract:Objective To explore the intervention effects of the website education ,and to provide theory basis for developing intervention strategies on TB. Methods Two primary schools were selected by stratified random sampling in rural areas of northern Jiangsu Province, 100 students per school .one school was website group, and the other was control group. One months intervention later, comparing the intervention effect. Results The website education group is statistically significant on the score of knowledge, attitude and behavior about TB compared with the control group. It wasnt statistically significant before and after intervention about the control group, while the website group was statistically significant. And it was statistically significant between the control group and the website group after intervention.
Key Words: Tuberculosis; primary school students; special website; intervention effects
我國是世界上22個結核病高負擔國家之一,患者人數僅次于印度居全球第二,死亡率位于我國傳染病之首,已成為一個嚴重的公共衛生問題和社會問題。第4次全國結核病流行病學抽樣調查報告:0~14歲兒童結核感染率為9.0%[1],說明兒童結核病仍然是常見病,及時發現感染者并控制發病迫切需要研究和實踐。
結核病控制措施一是通過發現和治愈結核病傳染源,以減少人群受感染的機會。二是對結核菌易感人群采取干預措施,減少發病。兒童免疫抵抗力低,是結核病高發人群,也是結核病控制工作的重點人群,學生又是一個特殊的群體,人員密度大、相互接觸密切,又正值易感年齡,一旦發生排菌者或肺結核病人,如處理不及時,易造成集團感染進而暴發式流行[2-5]。因而,對小學生采取結核病防治知識的宣傳教育,對結核病防治意義重大。近年來我國在學校開展結核病健康促進的活動越來越多,并取得了較好的效果[6-8]。網絡教育模式在一些領域已經得到廣泛的應用并以其獨特的優勢取得了明顯的效果[9-10]。本研究嘗試對網絡教育在小學生核病防病知識中的應用進行深入探索。
1.對象與方法
1.1對象 隨機選定蘇北農村地區2所小學,在每所學校里隨機抽取100名五年級學生作為研究對象。其中一所為網站式健康教育組,另一所作為對照組,于干預后1個月進行效果比較和評價。對照組與干預組年齡、性別、文化程度經統計學處理,差異無顯著性(P>0.05),具有可比性。……

