基于雙(1,2,4-三氮唑基)剛性配體和芳香羧酸的兩個配位聚合物的合成、晶體結構及熒光性質
王嘵嘵 劉永光 葛 明 崔廣華
(華北理工大學化學工程學院,唐山063009)
基于雙(1,2,4-三氮唑基)剛性配體和芳香羧酸的兩個配位聚合物的合成、晶體結構及熒光性質
王嘵嘵 劉永光 葛 明 崔廣華*
(華北理工大學化學工程學院,唐山063009)
水熱條件下,合成了2個結構新穎的金屬配位聚合物:[Co1.5(btb)2(nbta)(H2O)2]n(1),[Cd(btb)0.5(nph)(H2O)]n(2)(btb=4,4′-二(1,2,4-三氮唑-1-基)聯苯,H3nbta=5-硝基-1,2,3-苯三甲酸,H2nph=3-硝基鄰苯二甲酸)并對它們進行了元素分析,紅外光譜及X-射線單晶衍射等表征。結構分析表明,化合物1是一個二維(3,4)-連接3,4L90拓撲結構,并進一步通過O-H…O氫鍵作用構筑成三維超分子結構。而配合物2是一個三維(3,4,4)-連接的sqc69網絡,它的拓撲符號為(4.82)2(42.82.102)(8.104.12)。此外,還研究了這兩個配合物的熱重和熒光性質。
雙(三氮唑)配體;晶體結構;配位聚合物;混合配體;熒光
0 Introduction
The rational design and synthesis of novel metalorganic coordination polymers(MOCPs)is currently attractingconsiderableinterestbecauseoftheir intriguing structures and potential applications as functional materials in luminescence,conductivity, magnetism,porosity,and so on[1-4].In recent years,agreatnumberofMOCPswithmiscellaneous topological architectures and promising applications have been successfully obtained through self-assembly strategy[5-8].According to previously reported,judicious selectionofmultifunctionalN-donorand polycarboxylate mixed ligands is crucial to direct the synthesis of desirable MOCPs.Triazole-containing ligands as good candidates for the construction of metal coordination polymers,have aroused a great dealofattentionduetotheirdiversitiesin coordination modes and conformations[9-11].Specifically, the bis(1,2,4-triazole)ligands can donate four N-donor atoms,which can enhance their coordination ability with metal ions and consequently contribute the formation of complexes[12-14].From the viewpoint of crystal engineering and supermolecular chemistry. 4,4′-bis(1,2,4-triazolyl-1-yl)-biphenyl(btb)rigid ligand could be introduced as an attractive building block owing to its strong coordinating ability and planar πconjugated system.However,only a few examples of metal coordination polymers with btb ligand have been previously reported[15-18].
Herein,in order to investigate the influence of organic carboxylate co-ligands and metal ions on the structures and properties of MOCPs derived from rigid btb ligand,twonew coordination polymers were fortunatelyisolatedandcharacterized,namely, [Co1.5(btb)2(nbta)(H2O)2]n(1),and[Cd(btb)0.5(nph)(H2O)]n(2)(H3nbta=5-nitro-1,2,3-benzenetricarboxylic acid, H2nph=3-nitrophthalic acid).Structural diversification and the related properties such as fluorescence, thermal stability of two MOCPs were also investigated.
1 Experimental
1.1 Materials and general methods
Reagents and solvents employed were commercially available and used as received without further purification.Ligand btb was prepared according to literature procedure[19].Elemental analyses for C,H and N were performed on a Perkin-Elmer automatic analyzer.IR spectra were recorded from KBr pellets in the range of 4 000~400 cm-1on a Nicolet FTIR Avatar360spectrophotometer.Thermogravimetric analysis for complexes 1 and 2 were determined on a NETZSCH TG 209 thermal analyzer from room temperature to 800°C with a heating rate of 10℃·min-1under N2atmosphere.The solid samples for photoluminescentmeasurementswereperformedwitha Hitachi F-7000 spectrophotometer at room temperature.Powder X-ray diffraction(PXRD)patterns were collected on a Rigaku D/Max-2500PC X-ray diffractometer using Cu Kα radiation(λ=0.154 2 nm)and ω-2θ scan mode at 293 K.
1.2 Synthesis of the complex[Co1.5(btb)2(nbta) (H2O)2]n(1)
A mixture of CoCl2·6H2O(240 mg,1 mmol),btb (290 mg,1 mmol),NaOH(120 mg,3 mmol),H3nbta (760 mg,3 mmol)and 10 mL water was heated at 140℃for 3 days in a Teflon-lined vessel(25 mL).After the mixture cooled to room temperature at a rate of 5℃·h-1.Purple block single crystals of 1,suitable for X-ray diffraction,were collected by filtration,washed with distilled water,and dried at ambient temperature. Yield:43%(based on CoCl2·6H2O).Anal.Calcd.for C82H60Co3N26O20(%):C,51.66;H,3.17;N,19.10. Found(%):C,51.88;H,2.95;N,19.36.IR(KBr,cm-1): 3 432(s),3 124(m),1 589(s),1 506(s),1 394(s),1 357 (m),1 324(m),1 217(w),1 155(w),967(m),824(m), 725(s),649(m),574(w).
1.3 Synthesis of the complex[Cd(btb)0.5(nph) (H2O)]n(2)
Complex 2 was prepared in the similar way to 1 except that Cd(OAc)2(799 mg,3 mmol)and H2nph (630 mg,3 mmol)were used instead of CoCl2·6H2O and H3nbta.Crystals of 2 were obtained in 65%yield. Anal.Calcd.for C16H11CdN4O7(%):C,39.73;H,2.29; N,11.58.Found(%):C,39.49;H,2.55;N,11.36.IR (KBr,cm-1):3 415(m),3 134(w),1 601(s),1 520(s), 1 454(m),1 387(s),1 281(w),1 154(w),973(w),826 (m),713(m),513(w).
1.4 X-ray crystallography
Single crystal X-ray diffraction data for the title complexes were collected on a Bruker Smart 1000 CCD diffractometer with Mo Kα radiation(λ=0.071 073 nm) by using an ω scan mode.An empirical absorption correction was applied to the collected reflections withSADABS[20].The structures were solved by direct methods using SHELXS-97 and were refined on F2by thefull-matrixleast-squarestechniqueusingthe program SHELXL-97 program package[21].The hydrogen atoms of water molecule were added by difference Fourier maps and refined with isotropic displacement parameters.Crystal data of 1 and 2 are summarized in Table 1.Selected bond distances and angles of the complexes are listed in Table 2.
CCDC:1055345,1;1063802,2.
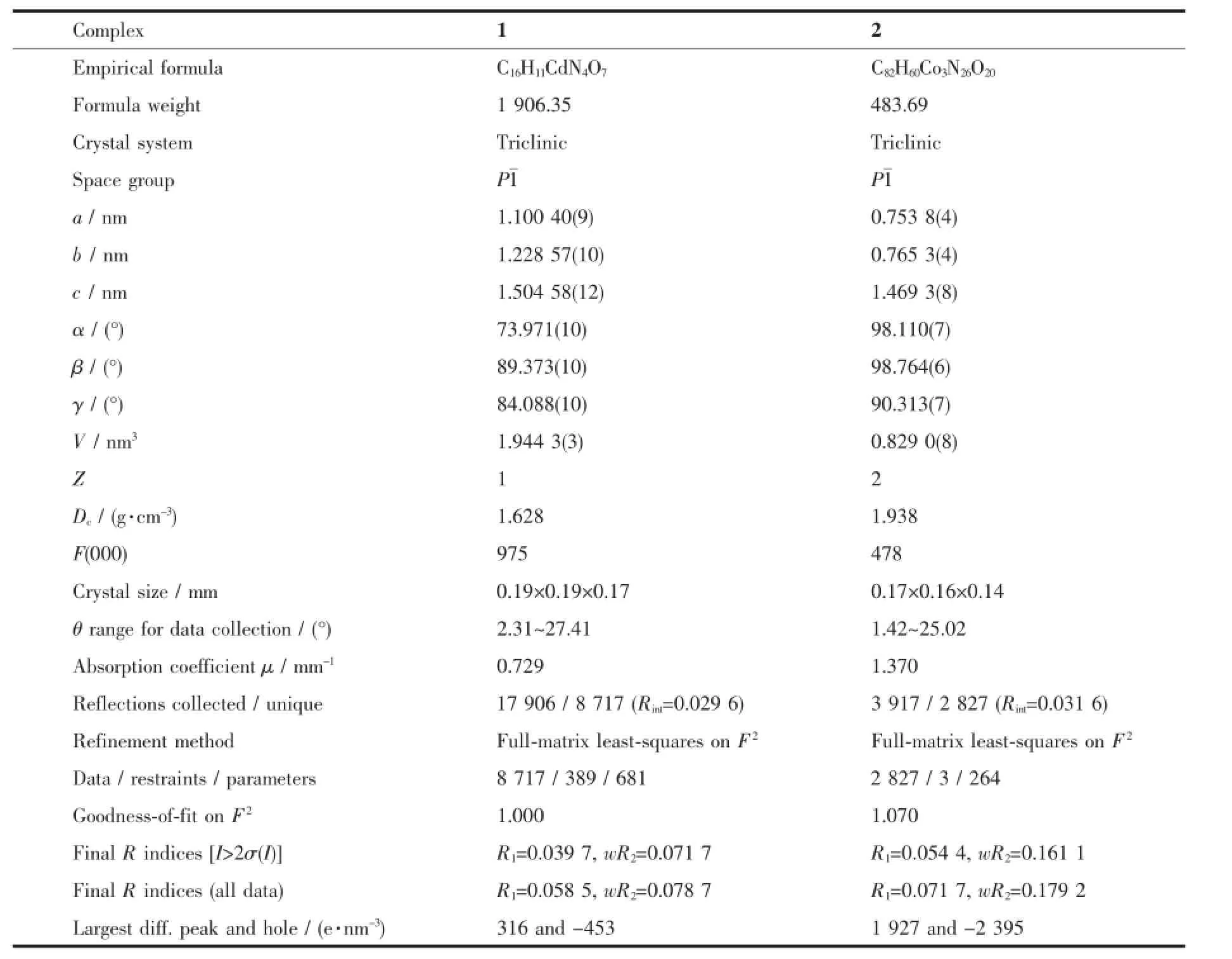
Table 1Crystallographic data and structural refinement of complexes 1 and 2
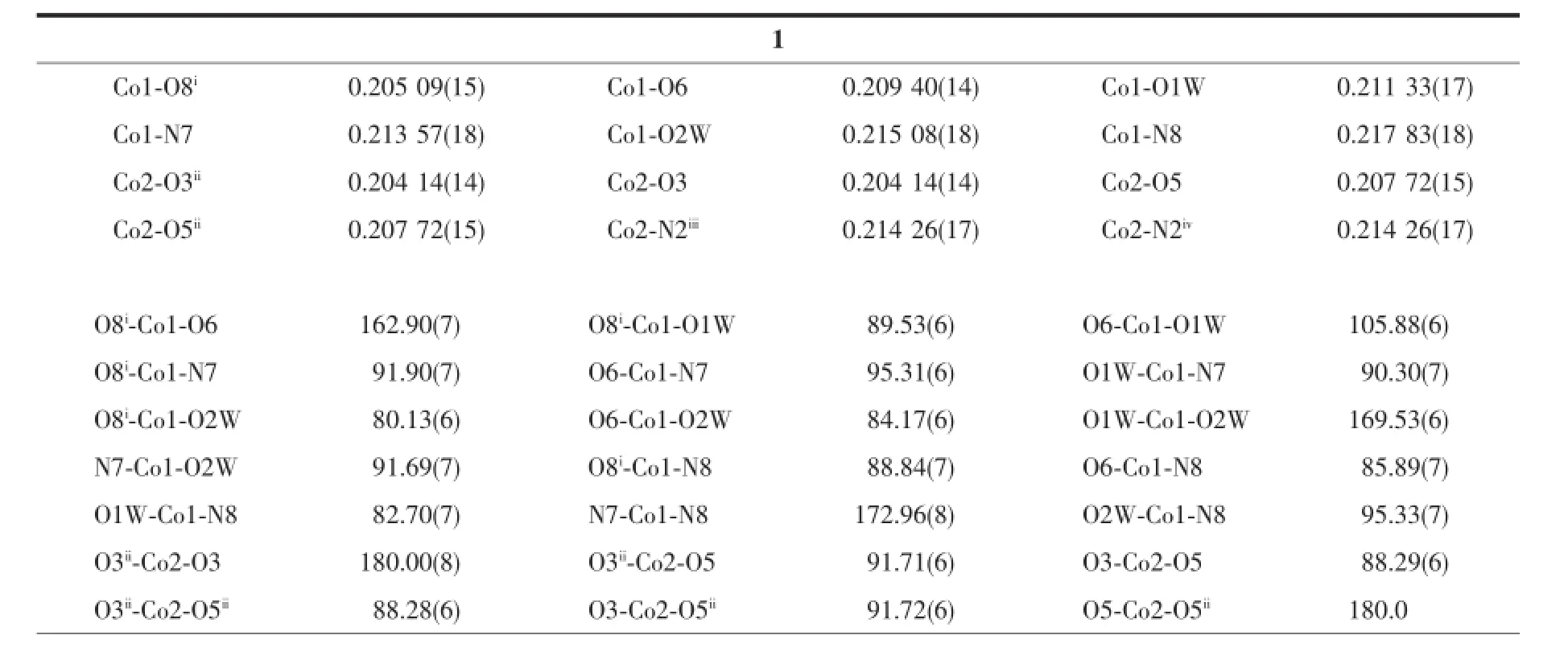
Table 2Selected bond lengths(nm)and angles(°)for complexes 1 and 2
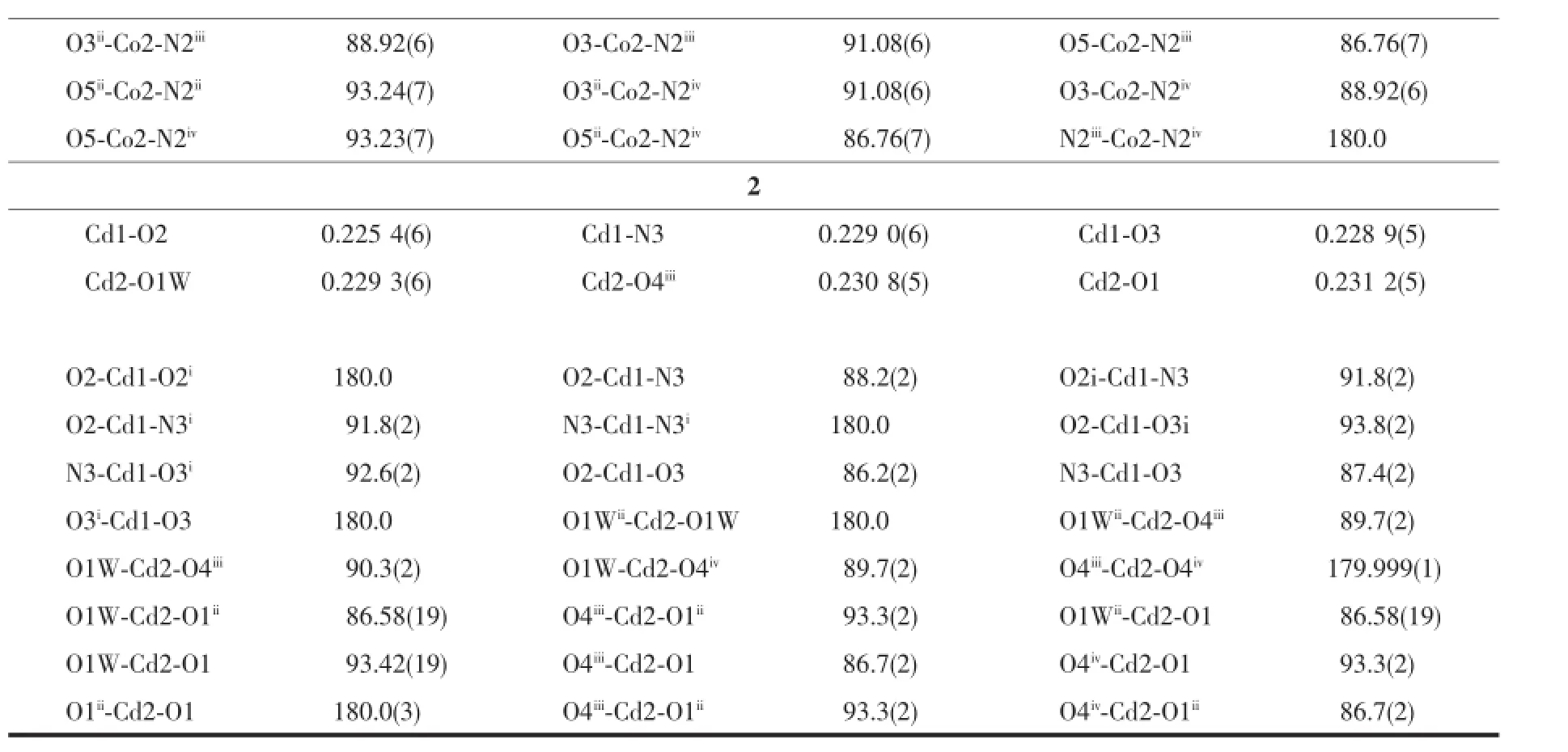
Continued Table 1
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Crystal structure of[Co1.5(btb)2(nbta)(H2O)2]n(1)
Structureanalysisexhibitsthatcomplex1 crystallizes in the triclinic space group P1.The asymmetry unit contains one and half Co atoms(The Co2 atom lies on an inversion centre and therefore has an occupancy of 0.5),two btb ligands,one nbta anionandtwocoordinatedwatermolecules.As illustrated in Fig.1a,the two unique cobalt centres including Co1,Co2 exhibit octahedral coordination geometry.Co1 ion is in a distorted octahedron,in which two nitrogen atoms(N7,N8)from different btb ligands comprise the apical position,four oxygen atoms(O1W,O2W,O6,and O8i,Symmetry code:ix-1,y,z)from two nbta ligands and two coordinated water molecules occupy the equatorial plane.Co2 is coordinated by four carboxyl oxygen atoms(O3,O3ii, O5,O5ii,Symmetry code:ii-x+2,-y,-z)from different nbta3-anions,two nitrogen atoms(N2iiiand N2iv, Symmetry code:iii-x+1,-y,-z-1;ivx+1,y,z+1)from twobtbligandstogiveaperfectoctahedron geometry.The Co-N distances range from 0.213 57(18) to 0.217 83(18)nm,and the Co-O lengths are in the range of 0.204 14(14)~0.215 08(18)nm,which are all comparable to those observed in related Co(Ⅱ)coordination compounds[22].
In the structure of 1,each nbta3-anion is completely deprotonated and displays μ3-η2∶η1∶η1coordination mode connecting neighboring Co atoms to generate a 1D linear chain along the a-axis with a throughligand Co…Co distances of 1.10 nm.It is noteworthy thatthetwocrystallographicallyindependentbtb ligands exhibit distinct coordination behaviors when coordinated to cobalt atoms,one acts as a terminal ligand(N2-N7)and the other one acts as a linker(N8-N13).Each μ2-bridging btb ligand further extended neighboring 1D chains into a 2D sheet(Fig.1b).To better understand the nature of thisnetwork,a topological analysis was performed with the TOPOS 4.0 software[23].If the Co1 and Co2 atoms are considered as 3-connected nodesand the nbta ligandsare considered as 4-connected nodes,the μ2-bridging btb ligands could act as connectors.Hence,the 2D structure of 1 can be represented to be a rarely(3,4)-connected 3,4L90 topology with the Schl?fli symbol of (62.84)(62.8)4(Fig.1c).Moreover,the 2D layer is further extended by the classical O-H…O hydrogen bonding interactions(O2W-H2B…O2Wv:0.302 6(2) nm,153(3)°,Symmetry code:v-x+1,-y+1,-z)between coordinatedwatermoleculestoconstructa3Dsupramolecularframework.Therelatedhydrogen bonding geometries are given in Table 3.
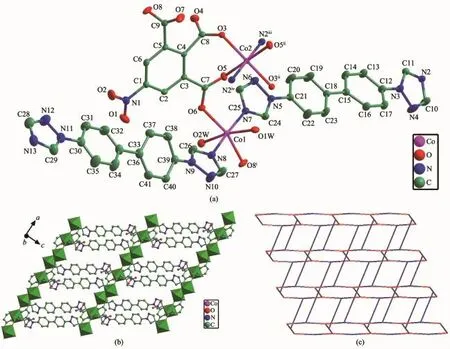
Fig.1(a)Coordination environment of Co(Ⅱ)ion in 1(30%ellipsoid probability);(b)2D layer for 1; (c)(3,4)-connected 3,4L90 topology for 1

Table 3Hydrogen bond distances(nm)and angles(°)for complex 1
2.2 Crystal structure of[Cd(btb)0.5(nph)(H2O)]n(2)
X-ray single crystal structure analysis reveals that 2 crystallizes in the triclinic space group P1.Two coordination cadmium and C6(from btb)atoms lie on centers of inversion.As shown in Fig.2a,both Cd1 and Cd2 ions take on distorted octahedron geometries. Cd1 is coordinated by four carboxyl oxygen atoms of two nph2-ligands,two nitrogen atoms from different btb ligands.Cd2 binds with four carboxyl oxygen atoms from four nph2-ligands,together with two oxygen atoms from two coordinated water molecules.The distances of Cd-O bonds range from 0.225 4(6)to 0.231 2(5)nm and Cd-N length is 0.229 0(6)nm, respectively,both of which are in the normal range[8].
The nph2-ligands are completely deprotonated, whose two carboxylic groups exist in types of bridging bidentateandmonodentatefashions,respectively. Each nph2-ligand linking neighboring three Cd(II) ions(one Cd1 and two Cd2)with its two carboxylates to build a 2D layer(Fig.2b).The btb ligands exhibit the anti-conformation and acts as a μ2-mode bridging adjacent Cd1 atoms to pillar 2D layer into a 3D framework,in which the Cd…Cd distance through btb ligand is 1.816 nm(Fig.2c).In the topology view, each Cd1 atom is connected by two btb and two nph2-ligands in a tetrahedral geometry and can be regarded as a tetrahedral node;each Cd2 is linked to four nph2-ligands and can be considered as a four-connected node;each nph anion bridges three Cd(Ⅱ)ions and thus can be regarded as a three-connected node.In such a case,the 3D framework of 2 can be described as a(3,4,4)-connected sqc69 network with the Schlfli symbol of(4.82)2(42.82.102)(8.104.12)(Fig.2d).Further, the 3D structure was further reinforced byπ-π interactions between benzene rings from nph2-ligands and triazole rings from btb ligands with the Cg1…Cg3i(Cg1 containing N1,N2,C1,N3,C2 atoms and Cg2 holding C9i,C10i,C11i,C12i,C13iand C14iatoms, Symmetry code:i-x,-y+2,-z.The x,y and z coordinates of centroid of the specified atoms are(0.263 75, -0.019 14,0.211 74)for Cg1,(-0.166 50,2.075 35, 0.282 78)for Cg2,respectively.)center-to-center separation of 0.360 2(5)nm and the inter-planar angle α of 14.5(4)°,slipping angles β(γ)of 9.43°(5.78°).
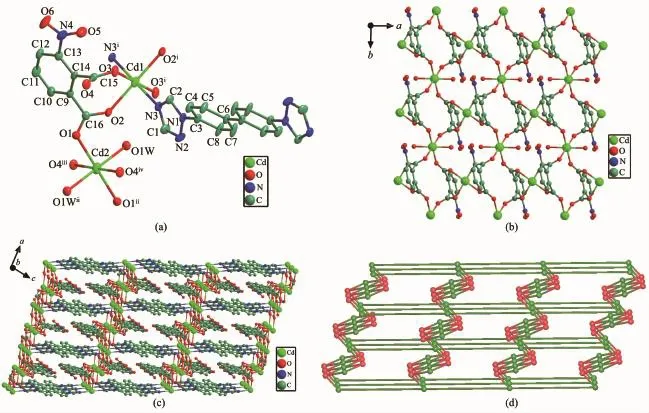
Fig.2(a)Coordination environment of Cd(Ⅱ)ion in 2(30%ellipsoid probability);(b)View of the 2D network assembled by Cd(Ⅱ)and nph2-ligands for 2;(c)3D framework for 2;(d)(3,4,4)-connected sqc69 network with the Schl?fli symbol(4.82)2(42.82.102)(8.104.12)for 2
2.3 IR spectroscopy
The IR spectra of the complexes show broad bands at about 3 432 cm-1for 1,3 415 cm-1for 2, which can be ascribed to the presence of water molecules.There is no band in the region of 1 690~1 730 cm-1,indicating complete deprotonation of the carboxyl groups[24].The asymmetric and symmetric stretching vibrations of carboxyl groups are observed at 1 589 and 1 394 cm-1for 1,1 601,1 454 and 1 387 cm-1for 2,respectively.The separations(Δν[νas(COO) -νs(COO)])between these bands indicate the presence of bridging(195 cm-1for 1,147 cm-1for 2)and monodentate(214 cm-1for 2)coordination modes of carboxyl groups[25].The bands at 1 506 cm-1for 1,1 520 cm-1for 2 can be assigned to the νC=Nabsorption of triazole ring of btb ligand.
2.4 Thermal analysis and PXRD results
Thethermalstabilitieswereinvestigatedas shown in Fig.3.The TGA curve of 1 shows a two-step weight loss process.The first weight loss of 4.5% occurs in the range of 80~135℃corresponding to the loss of the coordinated water molecules(Calcd.3.8%). The second weight loss may be assigned to the loss oforganic ligands,which begins at 205℃and completes at 520℃.The remaining weight(11.5%)corresponds to the percentage(11.8%)of Co and O components, indicating that the final residue is CoO.While for complex 2,the first weight loss step from 127 to 160℃is attributed to the loss of the coordinated water molecule.The weight loss is about 3.1%,in correspondence with the calculated value of 3.7%.The second step with a weight-loss occurred in a temperature range from 256 to 435℃for corresponding to the decomposition of the btb and nph2-ligands.Finally, the residue weight of 25.6%for 2 is due to the Cd and O components in CdO(Calcd.26.4%).
Toconfirmthephasepurityofthenew compounds,PXRD patterns have been carried out at room temperature(Fig.4).The peak positions of the experimental PXRD are well in agreement with the simulated data,demonstrating the phase purity of the bulk compounds.
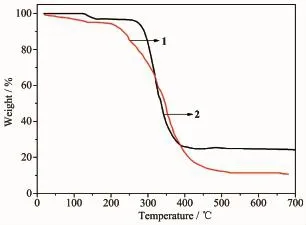
Fig.3TGA curves of complexes 1 and 2
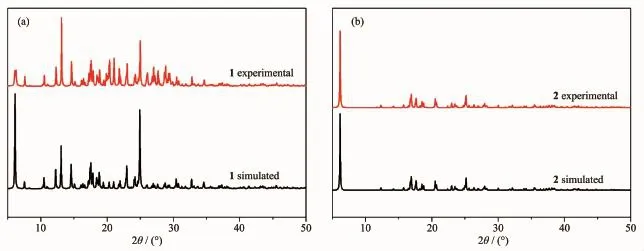
Fig.4(a)X-ray powder diffraction patterns of 1;(b)X-ray powder diffraction patterns of 2
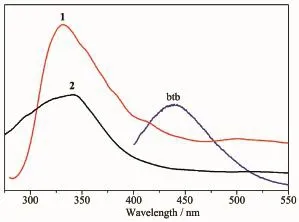
Fig.5Emission spectra of the free btb ligand as well as complexes 1 and 2
2.5 Fluorescence properties
The fluorescence properties of two complexes and the free btb ligand have been investigated in the solid state at room temperature.As shown in Fig.5,the free btb ligand exhibits fluorescent emission peaks at 439 nm(λex=380 nm),which may be assigned to the intraligand n→π*or π→π*transition[26].Excitation of the as-synthesized 1 at 280 nm leads to the maximum emission peak at 328 nm.Upon excitation at 230 nm the maximum emission peaks of 2 are observed at 340 nm.On comparison with the free btb ligand,the maximum emission peak of 1 shows a blue shift of 111 nm and that of 2 shows a blue shift of 99 nm,which may tentatively be assigned to the ligand-to -metal charge transfer(LMCT).The emission discrepancy of these complexes is probably due to the differences of organic ligands and coordination environments of central metal ions,which have a closerelationship to the photoluminescence behavior[27].
3 Conclusions
In summary,two metal coordination polymers based on rigid btb ligand have been synthesized and characterized.The results of this work suggest that the metal centers and organic carboxylate ligands can greatly affect the construction of MOCPs with btb ligand.In addition,complexes 1 and 2 show intense fluorescence emission,signifying that the title MOCPs maybepromisingcandidatesforuseasopticalmaterials.
[1]Van de Voorde B,Bueken B,Denayer J,et al.Coord.Chem. Rev.,2014,43:5766-5788
[2]Hao J M,Yu B Y,Van Hecke K,et al.CrystEngComm, 2015,17:2279-229386
[3]ZHANG Qi(張琦),YU Liang-Min(于良民),XIA Shu-Wei(夏樹偉),et al.Chinese J.Inorg.Chem.(無機化學學報),2015, 31(3):585-593
[4]Wang X X,Yu B Y,Van Hecke K,et al.RSC Adv.,2014,4: 61281-61289
[5]Li J R,Yu Q,Saudo E C,Tao Y,et al.Chem.Commun., 2007,25:2602-2604
[6]Hao J M,Yu B Y,Van Hecke K,et al.CrystEngComm, 2015,17:2279-2293
[7]Li J R,Zhang R H,Bu X H.Cryst.Growth Des.,2003,3: 829-835
[8]HAO Jin-Ming(郝金明),LI Huan-Huan(李歡歡),LI Guang-Yue(李光躍)et al.Chinese J.Inorg.Chem.(無機化學學報), 2013,29(11):2450-2454
[9]Li M,Peng Y F,Zhao S,et al.RSC Adv.,2014,4(27):14241-14247
[10]Cui G H,He C H,Jiao C H,et al.CrystEngComm,2012,14 (12):4210-4216
[11]Yang E C,Zhang C H,Liu Z Y,et al.Polyhedron,2012,40 (1):65-71
[12]Ming C L,Wang L N,Van Hecke K,et al.Spectrochim. Acta Part A:Mol.Biomol.Spectrosc.,2014,129:125-130
[13]Wang X L,Li J,Tian A X,et al.Cryst.Growth Des.,2011, 11(8):3456-3462
[14]Li M,Zhao S,Peng Y F,et al.Dalton Trans.,2013,42(26): 9771-9776
[15]Wang X X,Li Z X,Yu B Y,et al.Inorg.Chem.Commun., 2015,54:9-11
[16]Wang X X,Li Z X,Yu B Y,et al.Spectrochim.Acta Part A:Mol.Biomol.Spectrosc.,2015,149:109-115
[17]Wang X X,Li Z X,Yu B Y,et al.Bull.Korean Chem.Soc., 2015,36:1848-1853
[18]Wang X X,Zhang S,Van Hecke K,et al.Trans.Met.Chem., 2015,40:565-571
[19]Aakeroy C B,Desper J,Elisabeth E,et al.Z.Kristallogr., 2005,220:325-332
[20]Sheldrick G M.SADABS,University of G?ttingen,Germany, 1996.
[21]Sheldrick G M.Acta Cryst.,2008,A64:112-122
[22]Zhu X F,Wang N,Luo Y H,et al.Aust.J.Chem.,2011,64: 1346-1354
[23]Blatov V A.Struct.Chem.,2012,23:955-963
[24]Liang M X,Ruan C Z,Sun D,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2014,53: 897-902
[25]Deacon G B,Phillips R J.Coord.Chem.Rev.,1980,33:227-250
[26]Zuo Y,Fang M,Xiong G,et al.Cryst.Growth Des.,2012, 12:3917-3926
[27]Li F F,Ma J F,Song S Y,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2005,44:9374-9383
Syntheses,Crystal Structures and Fluorescence Properties of Two Metal-Organic Coordination Polymers Derived from Rigid Bis(1,2,4-triazolyl) and Aromatic Carboxylic Acid Ligands
WANG Xiao-XiaoLIU Yong-GuangGE MingCUI Guang-Hua*
(College of Chemical Engineering,North China University of Science and Technology,Tangshan,Hebei 063009,China)
Two metal-organic coordination polymers with novel structural based on a rigid bis(triazole)ligand, namely,[Co1.5(btb)2(nbta)(H2O)2]n(1),and[Cd(btb)0.5(nph)(H2O)]n(2)(btb=4,4′-bis(1,2,4-triazolyl-1-yl)-biphenyl, H3nbta=5-nitro-1,2,3-benzenetricarboxylic acid,H2nph=3-nitrophthalic acid)were synthesized hydrothermally and characterized by IR,elemental analysis,as well as single-crystal X-ray diffraction.Compound 1 features a 2D structure with a(3,4)-connected 3,4L90 topology,which ultimately is extended into a 3D supramolecular framework via O-H…O hydrogen bonding interactions.While complex 2 exhibits a 3D(3,4,4)-connected sqc69 network with the Schl?fli symbol of(4.82)2(42.82.102)(8.104.12).Furthermore,the thermal stability and fluorescence properties of the complexes have been investigated.CCDC:1055345,1;1063802,2.
bis(triazole);crystal structure;coordination polymer;mixed-ligand;fluorescence
O614.81+2;O614.24+2
A
1001-4861(2015)10-2065-08
10.11862/CJIC.2015.273
2015-03-23。收修改稿日期:2015-07-13。
國家自然科學基金(No.51474086),河北省自然科學基金-鋼鐵聯合研究基金(No.B2015209299)資助項目。
*通訊聯系人。E-mail:tscghua@126.com

