土層置換對馬鈴薯葉片酶活性及晚疫病的影響
張丁 蒼真名 白雪靜 王秋菊 劉峰 高中超 焦峰 翟瑞常
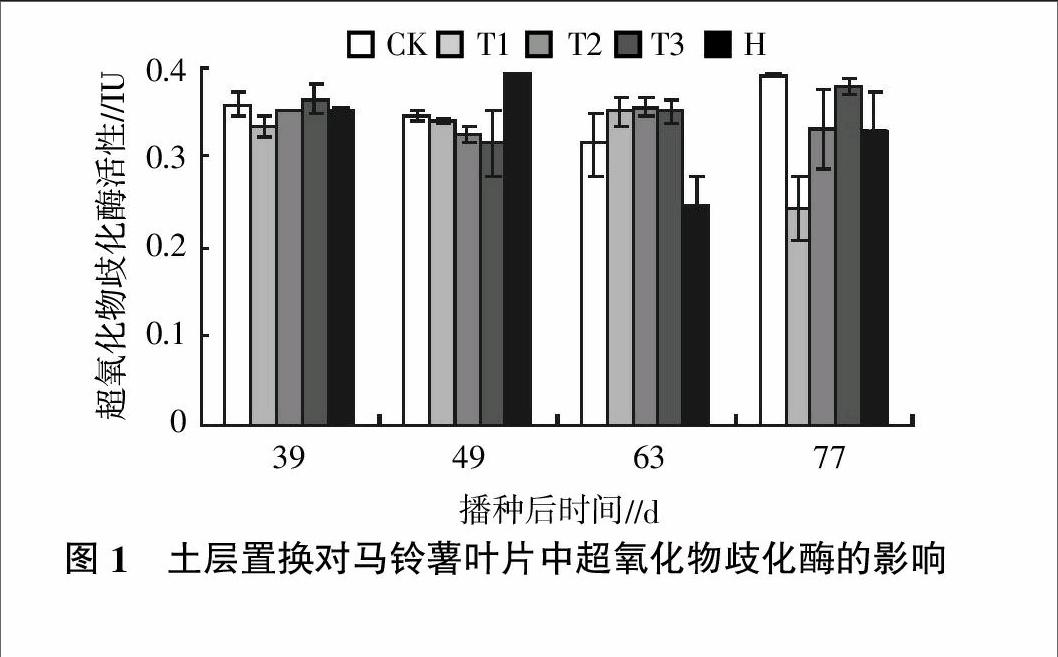
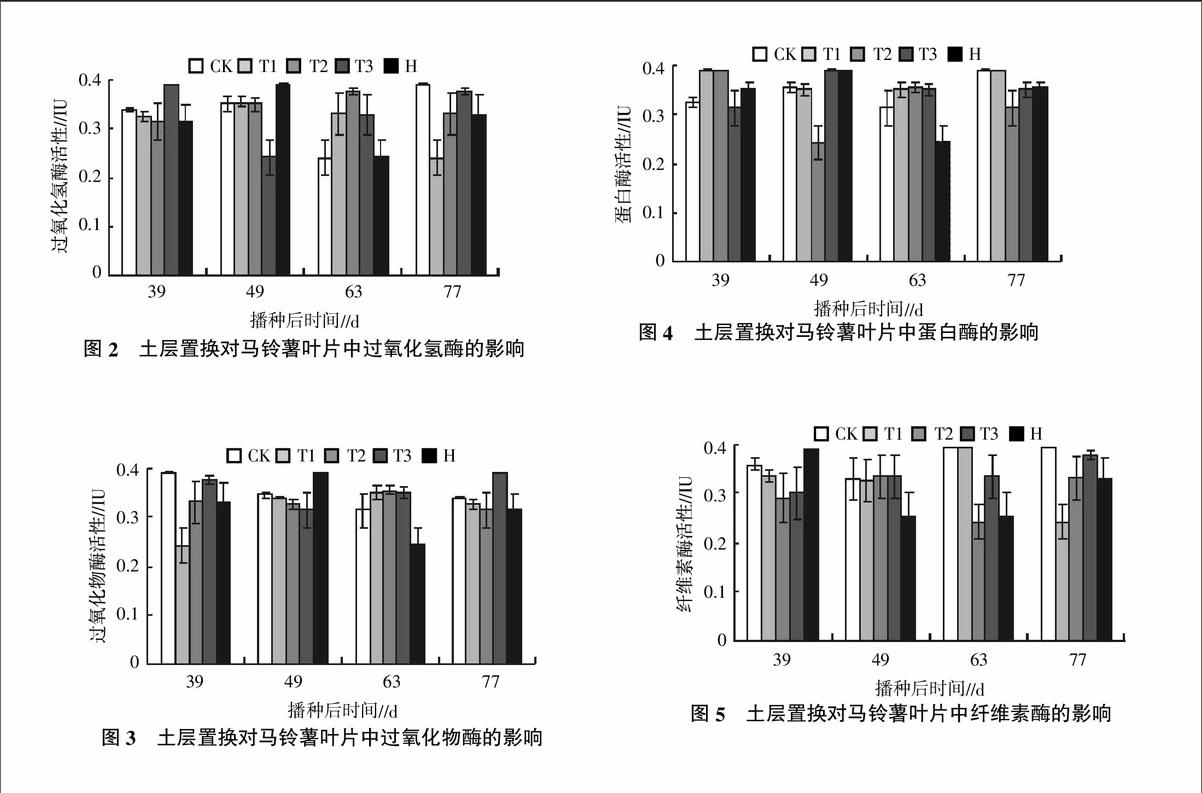
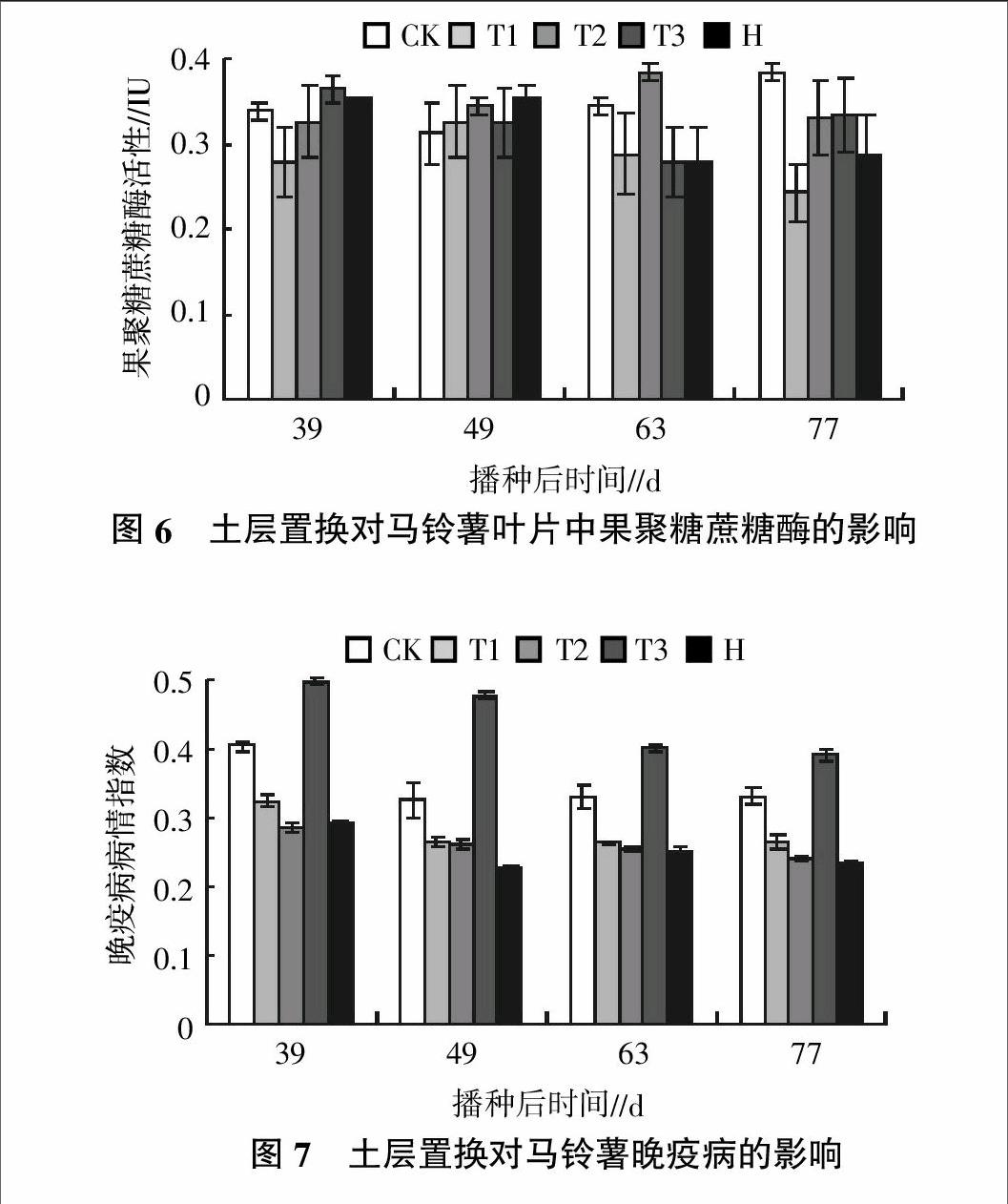
摘要:研究了土層置換及土壤滅菌措施對馬鈴薯葉片酶活性的影響。結果表明,土層置換或土壤滅菌處理提高了馬鈴薯葉片中保護酶(超氧化物歧化酶、過氧化物酶和過氧化氫酶)的活性,降低了葉片中纖維素酶和蛋白酶的活性,提高了馬鈴薯對晚疫病的抵抗能力。土層置換和土壤滅菌處理可以消除馬鈴薯由于連作障礙而產生的晚疫病的發病率,其中增施磷肥15%且置換土壤(T2)與施殺菌靈且不置換土壤(H)處理在消除馬鈴薯由于連作而產生的晚疫病方面效果最佳。而土壤經過土壤置換并加有機肥處理后(T3處理),馬鈴薯的晚疫病的病情指數在整個馬鈴薯的生長期內都顯著高于其他4個處理,在77 d時分別比CK、T1(置換土壤)、T2和H 4個處理高出17.5%、47.1%、60.8%和66.6%,表明在土壤置換后使用有機肥不利于降低馬鈴薯的晚疫病。
關鍵詞:馬鈴薯(Solarium tuberosum L.);土層置換;酶活性;晚疫病
中圖分類號:S432.4+4 文獻標識碼:A 文章編號:0439-8114(2015)21-5281-04
DOI:10.14088/j.cnki.issn0439-8114.2015.21.019
Effects of Soil Replacement of Potato Leaf Enzyme Activity and Late Blight Disease Index
ZHANG Ding1,CANG Zhen-ming1,BAI Xue-jing1,WANG Qiu-ju2,LIU Feng2,
GAO Zhong-chao2,JIAO Feng1,ZHAI Rui-chang1
(1.Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University,Daqing 163319,Heilongjiang,China;2. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences,Harbin 150086,China)
Abstract: The analysis of the effects of soil displacement and soil sterilization measures on enzyme activity in leaves of potato, and provide the technical support of sciencefor the elimination of potato continuous cropping obstacle was reaseached. The results showed that soil replacement or soil sterilization treatment increased the activity of protective enzyme in potato leaves (superoxide dismutase, peroxidase and catalase), and reduced the activity of cellulase and protease, which improved the resistance of potato to late blight. Soil replacement and soil sterilization treatment eliminates the potato late blight caused by continuous cropping obstacles incidence,and Phasphate 15% and the replacement of soil(T2) and Application of soil fungicide antiseptic spirit and no replacement of soil(H) treatment in eliminating due to continuous cropping potato late blightbest effect. But the soil through?soil replacement and add organic fertilizer after treatment (T3 treatment), the disease index of potato late blight of potato during the growing period of the whole inner were significantly higher than the other four treatments,and the replacement of soil(T1),T2 and H treatment was 17.5%,47.1%,60.8% and 66.6% higher than the CK in 77 days respectively,which showed that the use of organic manure was not conducive to the reduction of potato late blight in soil after replacement.
Key words: potato(Solarium tuberosum L); soil displacement; enzyme activity; late blight
馬鈴薯(Solarium tuberosum L.)又名土豆、地豆、地蛋、番薯、洋芋及荷蘭薯,起源于南美秘魯和智利的安第斯山一帶[1],是茄科(Solanaceae)茄屬(Solarium)一年生的草本植物,被聯合國譽為“未來的糧食”[2],隨著種植面積的不斷增加,已經躍居成為全球第四大糧食作物,產量僅次于小麥、水稻和玉米[3],在保證全球糧食安全方面發揮著至關重要的作用。在中國,馬鈴薯的主要種植地區包括東北、華北、西北和西南四大產區。其鮮薯產量和種植面積占全球的25%,居世界第一位[4-7]。……

