不同類型的膝關節假體對站立時靜態穩定性的影響研究
米爾阿里木·木爾提扎,趙巍,王利,袁宏*
(1.新疆醫科大學研究生學院,新疆 烏魯木齊 830011;2.新疆自治區人民醫院骨科中心關節外科,新疆 烏魯木齊 830001)
不同類型的膝關節假體對站立時靜態穩定性的影響研究
米爾阿里木·木爾提扎1,趙巍2,王利2,袁宏2*
(1.新疆醫科大學研究生學院,新疆 烏魯木齊 830011;2.新疆自治區人民醫院骨科中心關節外科,新疆 烏魯木齊 830001)
目的 探討人工全膝關節置換術(total knee arthroplasty,TKA)中選用固定平臺(fixed-bearing)型(PFC-sigma)和旋轉平臺(rotating-platform)型(PFC-RP)膝關節假體對膝關節骨關節炎(knee osteoarthritis,OA)患者術后軀體靜態穩定性產生的影響。方法 對2011年1月至2013年12月在我院接受單側TKA的OA患者45 例(選用旋轉平臺型假體PFC-RP的患者21 例,選用固定平臺型假體PFC-Sigma的患者24 例)進行分析。術前、術后6個月和術后1年時采用HSS評分標準對術側膝關節進行功能評估,并用重心測量儀對患者進行站立平衡試驗,連續記錄軀體重心位置(gravity center position,GCP)。對GCP在水平方向上轉移程度(medio-lateral displacement,ML-X range)以及GCP漂移軌跡(locus of GCP,LG)進行量化并分析兩組患者之間的靜態穩定性、術側膝關節恢復情況以及術后并發癥發生率的差異性。結果 TKA后單位時間內GCP在水平方向上平均位置由初始位置逐漸向術側轉移,且兩組患者之間ML-X range上變化程度差異均無統計學意義(P>0.05),而選用PFC-RP型假體的患者LG水平明顯較選用PFC-Sigma的患者小,且差異性有統計學意義(P<0.05)。結論 兩組患者術后術側膝關節恢復情況、并發癥發生率無明顯差異性,而選PFC-RP型假體的患者較PFC-Sigma的患者具有更好的靜態時穩定性。
人工全膝關節置換術;骨關節炎;旋轉平臺型;固定平臺型;靜態時穩定性
人工全膝關節置換術(total knee arthroplasty,TKA)已在治療晚期膝關節骨關節炎(osteoarthritis,OA)疾病中取得了良好的療效。OA的病理性改變能夠影響到膝關節本體感覺,從而影響到患者維持軀體平衡的能力[1]。而人體維持軀體平衡能力對順利進行日常活動、維持靜態時姿勢穩定性極為重要[2]。有關報道指出患者經TKA后膝關節本體感覺能夠部分恢復[3],這樣患者運動協調功能和膝關節穩定性較術前得到明顯改善[4]。隨著生物材料技術的進一步成熟,目前 TKA中已普遍使用固定平臺型(fixed-bearing)假體PFC-Sigma與旋轉平臺型(rotating-platform)假體PFC-RP等第三代人工關節假體,并取得令人滿意的療效[5-9]。在實際臨床中骨溶解、假體無菌性松動以及聚乙烯墊片的磨損等均是影響TKA長期療效以及增大TKA翻修難度的重要因素,國內外學界一致認為以上因素與術中選用的假體類型密切相關[10-12]。目前國內外大部分研究中僅以術后膝關節活動功能和假體長期存活率作為判斷手術是否成功的金標準。有關研究指出選用PFC-Sigma型或PFC-RP型假體對術后關節功能、假體長期存活率以及解除疼痛等均無明顯差異性[13]。而尚無詳細臨床研究對選用PFC-Sigma型或PFC-RP型假體對患者靜態時穩定性的影響進行比較。本研究目的在于比較采用PFC-Siga型假體與PFC-RP型假體的患者在TKA術后6個月、術后1年時的關節疼痛、活動功能恢復情況以及患者靜態穩定性的差異性,并對其原因進行初步分析。
1 資料與方法
1.1 一般資料 本研究通過我院倫理委員會審批通過,所有患者被納入之前均給予詳細解釋,術前每位患者均與手術醫師進行詳細談話,自愿地選擇術中選用的假體類型,并簽署本研究知情同意書。分析2011年1月至2013年12月在我院接受單側TKA的45 例患者,其中選用旋轉平臺型假體(PFC-RP,Depuy)的患者21 例,選用固定平臺型假體(PFC-Sigma,Depuy)的患者24 例。本研究納入標準為:所有患者均為右側膝關節骨關節炎,對側膝關節無明顯異常。排除標準為:膝關節重度外翻或內翻畸形超過15°,患有神經系統或嚴重的內科基礎性疾病,類風濕病,術側下肢接受過手術治療,雙下肢不等長,隨訪期間服用影響軀體平衡性及視力的藥物的患者。
1.2 手術方法 所有手術均在垂直層流性手術室全麻狀態下完成。手術入路均取標準的膝關節正中髕旁切口,使用髓外導向進行脛骨截骨,用髓外導向進行股骨髁截骨。股骨與脛骨假體均使用骨水泥固定。所有手術均未進行髕骨表面置換。裝完假體后均對膝關節周圍的軟組織進行適當地調整。所有患者圍手術期預防性應用抗生素,預防術后靜脈血栓。在術后1 d開始逐漸進行康復訓練,包括下肢連續被動運動,主動或輔助下進行逐漸增大膝關節活動幅度以及行走步態訓練等專業功能康復鍛煉。
1.3 臨床評價 根據美國特種外科醫院(hospital special knee scores,HSS)評分標準對患者術前、術后6個月,術后1年時的膝關節功能恢復情況進行評定[14]。本研究中通過重心測量儀對患者軀體重心(gravity center position,GCP)進行測定。讓每位患者在重心測量儀上無扶助條件下站立1 min,并讓患者注視前方3 m遠處固定目標物。在測量時間內確保無外物進入患者視線干擾(見圖1)。每2秒進行一次GCP測定,連續記錄1 min內的GCP位置。分別對GCP在單位時間內水平方向上轉移程度(medio-lateral displacement,ML-X range) 和GCP漂移軌跡(locus of GCP,LG)進行量化分析。單位時間內LG能夠表示由人本體感受性反射控制的維持軀體平衡性能力[15-16]。若在進行上述試驗的過程中,患者在規定的時間內無法站立平穩或要求停頓時該次操作視為無效,進行重新測取。

圖1 患者在術后6個月時進行站立平衡試驗
1.4 統計學方法 利用SPSS 17.0統計學軟件進行處理研究有關的數據。根據術中選用的假體類型分PFC-RP組和PFC-Sigma組。兩組患者術前、術后6個月、術后1年時的相關變量進行配對t檢驗。為較客觀描述患者術后GCP轉移情況,需算出患者在測量時間內的所有GCP的橫軸平均位置,故在研究中描述平準值與表均差時利用95%的可信區間。用卡方檢驗來比較兩組之間總的并發癥發生率差異性。為使研究中混淆因素降低,我們盡可能地排除在骨質、對疼痛耐受程度、術后康復過程等方面存在差異性的患者,且均選用同一家公司的兩種假體。本研究有關GCP數據均取上圖中平移距離,以圖中單元格為計量單位(見圖2~3)。從圖中獲取有關數據時,以患者術側(右側)為水平軸(X軸)方向上的正方向(+),左側為負方向(*),患者站在測量儀上面對方向為縱軸(Y軸)方向上的正方向(+),后側為負方向(*)。以P<0.05為差異具有統計學意義。
2 結 果
本研究中45 例患者,其中選用PFC-RP的患者21 例,選用PFC-Sigma的患者24 例。兩組患者平均年齡、術前體重、身高、體重指數(body mass index,BMI),術前術側膝關節HSS評分之間的差異性均無統計學意義(見表1)。
2.1 術側膝關節HSS評分 本研究中PFC-Sigma組與PFC-RP組之間在術前、術后6個月及術后1年時,術側膝關節HSS評分差異均無統計學意義。術后患側膝關節HSS評分均較術前時有明顯變化,且差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05,見表2)。

a 術 前 b 術后6個月 c 術后1年
圖2 1 例選用PFC-Sigma型假體的患者在術前、術后6個月、術后1年時行GCP飄移軌跡LG

a 術 前 b 術后6個月 c 術后1年
圖3 1 例選用PFC-RP型假體的患者在術前、術后6個月、術后1年時行GCP飄移軌跡LG
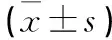
表1 兩組患者術前一般情況比較

表2 兩組患者HSS功能評分對比分)
2.2 并發癥
2.2.1 切口感染 兩組中均有2 例患者術后早期(術后3~7 d)出現膝關節術區發紅,皮溫持續高等感染癥狀。以上4 例患者均積極進行抗炎或切開清創對癥處理后癥狀明顯好轉或消失。對切口周圍滲出液進行一般細菌培養,培養結果均為無菌生長。2 例PFC-RP組患者術后出現膝關節腫脹,對其進行消腫或關節腔穿刺抽出對癥處理后,癥狀明顯好轉。并對患者進行凝血相關檢查。兩組患者術后早期出現切口愈合有關的并發癥率之間差異無統計學意義(P>0.05)。
2.2.2 術后疼痛 14%的PFC-Sigma組患者和9.5%的PFC-RP組患者術后出現膝關節周圍疼痛癥狀,給予止痛并康復對癥治療后疼痛癥狀有效緩解并逐漸消失。
2.2.3 其他并發癥 研究中兩組患者均未出現術后膝關節脫位,明顯骨溶解等癥狀。1 例PFC-Sigma患者出現術側下肢深靜脈血栓,給予抬高患肢并進行抗凝對癥處理3周后再次進行下肢血管彩超檢查,未發現下肢靜脈血栓(見表3)。

表3 兩組患者術后出現的并發癥(例)
2.3 穩定性 研究中發現兩組患者在術后6個月和術后1年時,在水平方向上患者GCP均由初始位置逐漸向術側方向轉移,與術前時平均位置比較其轉移差異均有統計學意義(P<0.01)。而術后6個月和術后1年時,水平方向上GCP較術前轉移程度兩組患者之間差異無統計學意義(P>0.05,見表4)。
術后6個月、術后1年時,兩組患者LG水平均較術前逐漸變小。跟術前時LG水平比較差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05)。而術后6個月、術后1年時,兩組患者之間LG水平的差異均無統計學意義(P>0.05,見表4,見圖2~3)。

表4 兩組患者之間穩定性指標對比
3 討 論
TKA選用PFC-Sigma型假體已取得較好的臨床療效[17-21],在術后10~15年的隨訪中發現假體存活率甚至高達90%以上[22-23],并且在年輕和高齡患者中均有較好的效果[24-25]。然而,因傳統PFC-Sigma型假體設計原因,可能出現的假體聚乙烯墊片磨損、骨溶解等現象均可能導致假體松動甚至可能需要二次手術[26]。從假體設計理論上分析,PFC-RP型假體與PFC-Sigma型假體相比,脛骨平臺處有旋轉軸,更能改善術后膝關節活動,允許脛骨平臺在縱軸上旋轉,有效減少聚乙烯墊片磨損,減輕假體骨水泥界面受到的壓力,從而減少發生骨溶解和假體松動的可能[27-28]。目前許多文獻從TKA后臨床療效、假體存活壽命、術后影像學以及關節活動功能等方面比較PFC-RP型假體與PFC-Sigma型假體的區別,結果顯示兩種假體之間均無明顯差異性[29-35]。而目前國內外尚無研究分析出選用兩種假體對患者術后靜態穩定性的影響。本研究中兩組患者術后膝關節恢復程度差異無統計學意義。
我們可以推測隨著患者術后關節功能恢復,術側膝關節負重量逐漸增大,而對側膝關節負重量逐漸減少,術側膝關節疼痛逐漸減輕,患者逐步恢復軀體的平衡。本研究中,TKA后患者GCP由初始位置逐漸向術側方向轉移,且患者維持軀體平衡性能力逐漸得到改善。
影響軀體穩定性的主要因素有膝關節疼痛、下肢肌力減弱及本體感覺減退等[16]。膝OA患者下肢肌力及膝關節本體感與同性別和年齡段的人群相比減弱較明顯,故膝OA患者軀體不穩定性更顯著[36]。隨膝OA病程進展,關節腔及周圍組織中的感受器數量減少,導致患者膝關節本體感覺減退,從而影響患者軀體平衡性[36-38]。TKA目的在于長期緩解或消除關節疼痛,改善膝關節功能,從而提高生活質量。目前關于TKA對關節本體感覺及軀體平衡性的影響存在較多的爭議。有些學者認為患者本體感覺通過TKA能夠得到改善,從而患者維持軀體平衡性較術前有所提高[39-40],相反有文獻指出TKA后,患者減退的本體感覺和軀體穩定性未見明顯改善[41-43]。本研究中所有患者術后LG均較術前時明顯變小,表明術后患者軀體平衡性經TKA逐漸好轉,其中PFC-RP組患者LG變化程度較PFC-Sigma組較為明顯。筆者認為原因可能為與PFC-RP假體設計中脛骨平臺處有旋轉軸,允許脛骨在縱軸上旋轉,這樣幫助患者站立時更好地維持靜態穩定性。而本研究中假體均選用同一家公司產品,除脛骨平臺處是否有旋轉軸外,兩種假體其余部分均相同,故我們可以排除TKA中由于選用假體類型不同而導致的對關節本體感覺影響。
本研究存在的局限性有:a)我們前瞻性地對兩種設計相似的假體類型進行隊列比較分析。雖然兩組之間年齡、性別、術前一般臨床特征、術前關節功能等變量均無明顯差異,但由于本研究中選擇假體時不能夠嚴格按盲法執行,故前瞻性研究可能未能夠更有效地限制選擇偏倚和其他潛在的混淆變量。b)由于研究樣本量較小,且取95%的可信區間,故本研究方案可能不能夠有效地識別兩組患者之間的變量差異性,這樣容易導致Ⅱ型錯誤。比較兩組患者術后發生的并發癥時,由于樣本量和并發癥發生的數量較小,且隨訪時間較短。故我們認為還需進一步擴大樣本量和隨訪時間,以便研究結果更為精確。c)本研究由于條件有限,故研究方案較為簡略。因患者前庭神經、視線以及認知能力等因素均能夠影響到患者的本體感覺,從而影響到患者維持軀體平衡性能力。本研究未能夠像類似研究中一樣分別對患者在閉眼和睜眼時進行測量[16],或對患者雙下肢分別進行單側下肢站立平衡試驗[44],這樣對患者本體感覺、術后軀體穩定性變化的分析結果可能更為精確。d)未能對患者術前特點進行更詳細地分類并分析,如術前不同內外翻程度、病程長短、對側膝關節情況及其本體感覺等因素。研究中未對隨訪期不同階段的患者體重是否有變化及體重變化對患者軀體中心是否產生相應地影響做出更深度地分析。
研究中兩種假體組患者膝關節功能及軀體靜態穩定性均較術前明顯改善,其中PFC-RP組患者較PFC-Sigma組患者軀體穩定性變化更為明顯。TKA圍手術期極為重要,尤其是膝OA患者軀體穩定性退變較同年齡段人群更明顯。TKA術后前幾個月內患者軀體穩定性甚至較術前更弱,故筆者認為選用PFC-RP型假體也許能夠有效減少老年患者術后跌倒摔傷的概率。然而,本研究隨訪時間較短,至于兩種假體的長期療效和對患者關節功能恢復以及軀體穩定性的影響需進行長期隨訪,有待進一步細致的研究。
[1]Gage WH,Frank JS,Prentice SD.Organization of postural responses following a rotational support surface perturbation,after TKA:sagittal plane rotations[J].Gait Posture,2007,25(1):112-120.
[2]Hinman RS,Bennell KL,Metcalf BR.Balance impairments in individuals with symptomatic knee osteoarthritis:a comparison with matched controls using clinical tests[J].Rheumatology(Oxford),2002,41(12):1388-1394.
[3]Leitch KK,Dalgorf D,Borkhoff CM.Bilateral total knee arthroplasty-staged or simultaneous?Ontario′s orthopedic surgeons reply[J].Can J Surg,2005,48(7):273-276.
[4]Swanik CB,Lephart SM,Rubash HE.Proprioception,kinesthesia,and balance after total knee arthroplasty with cruciate-retaining and posterior stabilized prostheses[J].J Bone Joint Surg(Am),2004,86(2):328-334.
[5]Kim YH,Kim JS,Choe JW.Long-term comparison of fixed-bearing and mobile-bearing total knee replacements in patients younger than fifty-one years of age with osteoarthritis[J].J Bone Joint Surg(Am),2012,94(10):866-870.
[6]Kim YH,Yoon SH,Kim JS.The long-term results of simultaneous fixed bearing and mobile-bearing total knee replacements performed in the same patient[J].J Bone Joint Surg(Br),2007,89(10):1317-1320.
[7]Callaghan JJ,Wells CW,Liu SS.Cemented rotating-platform total knee replacement:A concise follow-up,at a minimum of twenty years,of a previous report[J].J Bone Joint Surg(Am),2010,92(7):1635-1638.
[8]Ritter MA.The anatomic graduated component total knee replacement:a long-term evaluation with 20-year survival analysis[J].J Bone Joint Surg(Br),2009,91(6):745-749.
[9]Rodriguez JA,Bhende H,Ranawat CS.Total condylar knee replacement:A 20-year followup study[J].Clin Orthop Relat Res,2001(5):388-391.
[10]Duffy GP,Crowder AR,Trousdale RR,etal.Cemented total knee arthroplasty using a modern prosthesis in young patients with osteoarthritis[J].J Arthroplasty,2007,22(2):67-71.
[11]Gioe TJ,Glynn J,Sembrano J.Mobile and fixed-bearing (all-polyethylene tibial component) total knee arthroplsaty designs.A prospective randomized trial[J].J Bone Joint Surg(Am),2009,91(2):2104-2107.
[12]Sharkey P,Hozack W,Rothman R.Why are total knee arthroplasties failing today?[J].Clin Orthop Relat Res,2002,5(7):404-407.
[13]O.Bailey K,Ferguson E,Crawfurd P.No clinical difference between fixed-and mobile-bearing cruciate-retaining total knee arthroplasty:a prospective randomized study[J].Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc,2014,24(5):42-48.
[14]Slupik A,Bialoszewski D.A comparative analysis of the clinical utility of the Staffelstein-score and the hospital for special surgery knee score (HSS) in monitoring physiotherapy of total knee replacement patients-preliminary study[J].Ortop Traumatol Rehabil,2009,11(1):37-45.
[15]Swanik CB,Lephart SM,Rubash HE.Proprioception,kinesthesia,and balance after total knee arthroplasty with cruciateretaining and posterior stabilized prostheses[J].J Bone Joint Surg(Am),2004,5(86):328-334.
[16]Bakirhan S,Angin S,Karatosun V.A comparison of static and dynamic balance in patients with unilateral and bilateral total knee arthroplasty[J].Eklem Cerrahisi,2009,20(4):93-101.
[17]Insall JN,Hood RW,Flawn LB.The total condylar knee prosthesis ingonarthrosis.A five to nine-year follow-up of the first one hundred consecutive replacement[J].J Bone Joint Surg(Am),1983,65(5):619-628.
[18]Callahan CM,Drake BG,Heck DA.Patient outcomes following tri-compartmental total knee replacement.A meta-analysis[J].JAMA,271(17):1349-1357.
[19]Tarkin IS,Bridgeman JT.Successful biologic fixation with mobile-bearing total knee arthroplasty[J].J Arthroplasty,2005,20(4):481-486.
[20]Buechel FF Sr.Long-term follow up after mobile-bearing total knee replacement[J].Clin Orthop Relat Res,2002,14(3):40-50.
[21]Stern SH,Insall JN.Posterior stabilized prosthesis.Results after follow-up of nine to twelve years[J].J Bone Joint Surg(Am),1992,74(7):980-986.
[22]Dixon MC,Brown RR,Parsch D.Modular fixed-bearing total knee arthroplasty with retention of the posterior cruciate ligament.A study of patients followed for a minimum of fifteen years[J].J Bone Joint Surg(Am),2005,87(3):598-603.
[23]Dennis DA,Clayton ML.Posterior cruciate condylar total knee arthroplasty.Average 11-year follow-up evaluation[J].Clin Orthop Relat Res,1992,13(281):168-176.
[24]Diduch DR,Insall JN,Scott WN.Total knee replacement in young,active patients.Long term follow-up and functional outcomes.[J]J Bone Joint Surg(Am),1997,79(4):575-582.
[25]Parsch D,Krüger M,Moser MT.Follow-up of 11-16 years after modular fixed-bearing TKA[J].Int Orthop,2009,33(2):431-435.
[26]Colizza WA,Insall JN,Scuderi GR.The posterior stabilized total knee prosthesis.Assessment of polyethylene damage and osteolysis after a ten-year-minimum follow-up[J].J Bone Joint Surg(Am),1995,77(11):1713-1720.
[27]Alessandro Bistolfi,Giuseppe Massazza,Gwo-Chin Lee.Comparison of fixed and mobile-bearing total knee arthroplasty at a mean follow-up of 116 months[J].J Bone Joint Surg(Am),2013,95(16):11-18.
[28]Nakamura E,Banks SA,Tanaka A.Three-dimensional tibio-femoral kinematics during deep flexion kneeling in a mobile-bearing total knee arthroplasty[J].J Arthroplasty,2009,24(7):1120-1124.
[29]Kim YH,Koo HK,Kim JS.Comparison of fixed-bearing and mobile-bearing total knee arthroplasties[J].Clin Orthop Relat,2007,92(12):101-115.
[30]Smith H,Jan M,Mahomed NN.Meta-analysis and systematic review of clinical outcomes comparing mobile bearing and fixed bearing total knee arthroplasty[J].J Arthroplasty,2011,26(8):1205-1213.
[31]Kelly NH,Fu RH,Wright TM,etal.Wear damage in mobile-bearing TKA is as severe as that in fixed-bearing TKA[J].Clin Orthop Relat Res,2003,5(1):123-130.
[32]Geiger F,Mau H,Kru¨ger M.Comparison of a new mobile-bearing total knee prosthesis with a fixed-bearing prosthesis:a matched pair analysis[J].Arch Orthop Trauma Surg,128(3):285-291.
[33]Matsuda S,Mizu-uchi H,Fukagawa S.Mobile-bearing prosthesis did not improve mid-term clinical results of total knee arthroplasty[J].Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc,18(10):1311-1316.
[34]Kim YH,Choi Y,Kim JS.Osteolysis in well-functioning fixed-and mobile-bearing TKAs in younger patients[J].Clin Orthop Relat Res,1999,468(11):3084-3093.
[35]Jacobs W,Anderson P,Limbeek J.Mobile bearing vs fixed bearing prostheses for total knee arthroplasty for post-operative functional status in patients with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis[J].Cochrane Database Syst Rev,2012,10(3):31-34.
[36]Marks R,Quinney HA,Wessel J.Proprioceptive sensibility in women with normal and osteoarthritic knee joints[J].Clin Rheumatol,1993,12(2):170-175.
[37]Brandt KD,Dieppe P,Radin EL.Etiopathogenesis of osteoarthritis[J].Rheum Dis Clin North Am,2008,34(3):531-559.
[38]Barrett DS,Cobb AG,Bentley G.Joint proprioception in normal osteoarthritic and replaced knees[J].J Bone Joint Surg(Br),1991,73(1):53-56.
[39]Swanik CB,Lephart SM,Rubash HE.Proprioception,kinaesthesia,and balance after total knee arthroplasty with cruciate retaining and posterior stabilized prostheses[J].J Bone Joint Surg(Am),2004,86(2):328-334.
[40]Wada M,Kawahara H,Shimada S.Joint proprioception before and after total knee arthroplasty[J].Clin Orthop Relat Res,2002,3(8):161-167.
[41]Farquhar S,Snyder-Mackler L.The chitranjan ranawat award:the non-operated knee predicts function 3 years after unilateral total knee arthroplasty[J].Clin Orthop Relat-Res,2010(468):37-44..
[42]Pap G,Meyer M,Weiler HAT.Proprioception after total knee arthroplasty:a comparison with clinical outcome[J].Acta Orthop Scand,2000,71(2):153-159.
[43]Fuchs MD,Thorwesten L,Niewerth S.Proprioceptive function in knees with and without total knee arthroplasty[J].Am J Phys Med Rehabil,1999,78(1):39-45.
[44]Sung Do Cho,Chang Ho Hwang.Improved single-limb balance after total knee arthroplasty[J].Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc,2013(21):2744-.2750.
[45]Stan G,Orban H,Orban C.The influence of total knee arthroplasty on postural control[J].Chirurgia,2013,6(10):874-878.
The Influence of Fixed-bearing and Rotating-platform Total Knee Arthroplasty on Static Body Balance in knee osteoarthritis
Mieralimu Muertizha1,Zhao Wei2,Wang Li2,etal
(1.The Postgraduate School of Xinjiang Medical University,Urumqi 830011,China;2.Department of Joine Surgery,Orthopaedic Center,People′s of Xinjiang,Urum 830011,China)
Objective To compare the static body balance between fixed -bearing total knee arthroplasty (PFC-Sigma) and rotating-platform total knee arthroplasty(PFC-RP) in patients′ who suffered from unilateral knee osteoarthritis.Methods Forty-five patients with single osteoarthritis of right knee who underwent TKA at our department from January 2011 to December 2013 were prospectively analyzed.21consecutive patients were replaced with rotating-platform total knee design (PFC-RP)and the others with fixed-bearing design (PFC-Sigma).The measurements were performed using the corresponding instrument and subjects completed consecutive double-limb standing balance trials for three times.The Medio-lateral displacements and Locus Length of GCP (LG) in unit-time were derived from the instrument.All the patients were evaluated with HSS and complete balance trails pre-operatively,sixth month and one year postoperatively.Clinical outcome complication rates and body static balance were compared.Results The mean GCP in the medio-lateral direction shifted to the operative side in both groups after surgery,there was no significant difference in ML-Xrange between the groups(P>0.05).The value of Locus of GCP(LG) was smaller in PFC-RP group than PFC-Sigma group(P<0.05).Conclusion Our study demonstrated no advantage of the rotating-platform arthroplasty over fixed-bearing arthroplasty with regard to clinical results and complication rates at one year follow-up.However,rotating-platform arthroplasty has a better body static balance than fixed-bearing arthroplasty.
total knee arthroplasty;osteoarthritis;rotating-platform;fixed-bearing;body static balance
新疆維吾爾自治區研究生科研創新項目基金(XJGRI 2014093);*本文通訊作者:袁宏
1008-5572(2015)01-0020-06
R687.4+2
B
2014-09-11
米爾阿里木·木爾提扎(1988- ),男,醫師,新疆醫科大學研究生學院,830011。

