Morphological variation of Trametes gallica
SUN Xun,REN Shao-ting,CHEN Zhi-wei
(Life Science Department,Heze University,Heze 274015,China)
It is well known that morphogenesis is the biological process that causes an organism to develop its shape.So far,a lot of researches on the developmental biology of fungal morphogenesis have been undertaken and great progress has been made[1-2].However,the previous research conventionally employed taxonomic,anatomic and biochemical methods.No detailed reports are available on this field in which cultivating a higher fungus on distinctive conditions was used as a research method.White-rot basidiomycete Trametes gallica,with a strong capacity to degrade lignocellulose[3],belongs to higher fungi,has simple structure,and is suitable for the morphological research.In the study,we tried to investigate the morphological variation of the fungus by cultivating it in different media.
1 Materials and Methods
1.1 Organism
The strain used in the study was initially isolated in Heze,China,from a poplar stump in autumn of 1997,preliminarily identified as Trametes gallicaFr.,and collected at Molecular Biology Lab of Heze University.It was ordinarily maintained at 4℃on potato dextrose agar(PDA)slants.Subculture was routinely made every 2 months.
1.2 Nutrient salt fluid
One liter of nutrient salt fluid,lacking a carbon source,containedthefollowingingredients:(NH4)2SO43.0 g,KH2PO41.0 g,MgSO4·7H2O 0.5 g,CaCl2·2H2O 0.1 g and trace minerals solution 2 mL(MnSO4·H2O 0.5 g,FeSO4·7H2O 0.5 g,CuSO4·5H2O 0.6 g,ZnSO4·7H2O 0.05 g,H3BO30.2 g,Na2MoO4·2H2O 0.2 g,CoCl2·6H2O 0.1 g,distilled H2O 1 000 mL).
In the study,the fungus was cultured by four procedures which varied to some extent in the medium formulation and types of growth conditions that included agitated fluid culture,static liquid fostering,sawdust planting and wood stick cultivation.
1.3 Cultivation in agitated fluid medium
The eutrophic medium at natural pH,contained glucose(1.5%),yeast extract(0.15%),tryptone(0.3%)and the nutrient salt fluid.One hundred and fifty milliliters of the medium was placed into a 500-mL Erlenmeyer flask and sterilized(121℃,20 min).Three mycelia disks(1 cm in diam.)were punched from the fungus grown for 6 days on PDA plate at 26℃and used as inoculum for each culture.The fungus was cultured for 9 days in a shaker(190 r/min)at 29℃.
1.4 Cultivation in static liquid media
The composition of the dystrophic medium was:glucose,1.5%;yeast extract,0.05%;the nutrient salt fluid,in which(NH4)2SO4was removed and replaced by 0.12%ammonium tartrate;at natural pH.If yeast extract was increased to 0.15%,then we regard the medium as semi-eutrophic liquid.Two hundred ml of the medium was placed into a 1-liter Erlenmeyer flask and sterilized(121℃,20 min).Each flask was sealed with 8 layers of gauze for air exchange.The liquid medium was used for the surface stationary cultivation of the fungus at 26℃.
1.5 Cultivation on sawdust
Air-dried wheat straw powder or pine sawdust was passed through a 10-mesh sieve.Mix four hundred grams of wheat straw powder with 800 ml of the nutrient salt fluid,put intensively the mixture into a polypropylene bag(12.7 cm in diam.),tie the bag with rope,and autoclave for 1.5 hr at 121℃.Each bag was punched two pores spaced 8 cm,and each pore was inoculated 3 mycelia disks from the fungus.While using pine sawdust,then mix 500 g of the powder with 1 000 mL of the nutrient salt fluid and use the same size bag as above.
1.6 Cultivation on poplar wood sticks
Immerse poplar wood sticks(about 20 cm long,7~8 cm in diam.)in the nutrient salt fluid overnight,put separately the sticks in polypropylene bags(about 25 cm long,12.7 cm in diam.),tie the bag with rope,and sterilize(121℃,1.5 hr).Erect the stick and soak its one end in appropriate amount of the sterile nutrient fluid contained in a plastic box.Disperse 3 mycelia disks and inoculate at all sides of the upper parts and on the cross-section of every stick,respectively.
2 Result and discussion
2.1 T.gallica in agitated nutrient fluid
In agitated nutrient fluid,the vegetative mycelia of T.gallica were formed into hollow pellets(Fig.A),which were filled with medium.The hollow structure will make the aerobe T.gallica to efficiently use oxygen in water.Under shaking conditions,the pellets were fractured into mycelium pieces which again grew up into new pellets.
2.2 T.gallica in static liquid medium
When cultured for 60 days in static dystrophic liquid,T.gallica exhibited honeycomb-like structure in appearance,with its pore surface somewhat similar to those on straw powder or sawdust(Fig.C,F and J).From an evolutionary perspective,it perhaps can be supposed that the native habitat of the fungus had undergone significant changes.Due to large scale crustal movement and climate variation,the primary marine environments were trans-formed into shallow water beaches,lakes,ponds,puddles,swamps,or wetlands where the fungus was stranded.With gradual decrease of nutrient and oxygen in the relatively static nutrition soup,a mass of aerial hyphae were slowly and firstly differentiated into the flower cluster-like structure(Fig.B)and then the honeycomb-like shape(Fig.C).We guess that the“honeycomb”may be a structure with which the fungus was faced to adapt to the stress environments and actually the prototype of basidiocarp of the existing species T.gallica Fr.We believe the cavities in the“honeycomb”will be evolved into tubes,in which spores will be spawned.Therefore,from the evolutionary point of view,the fungus at that time had got ready for leaving from the static waters and further landing.
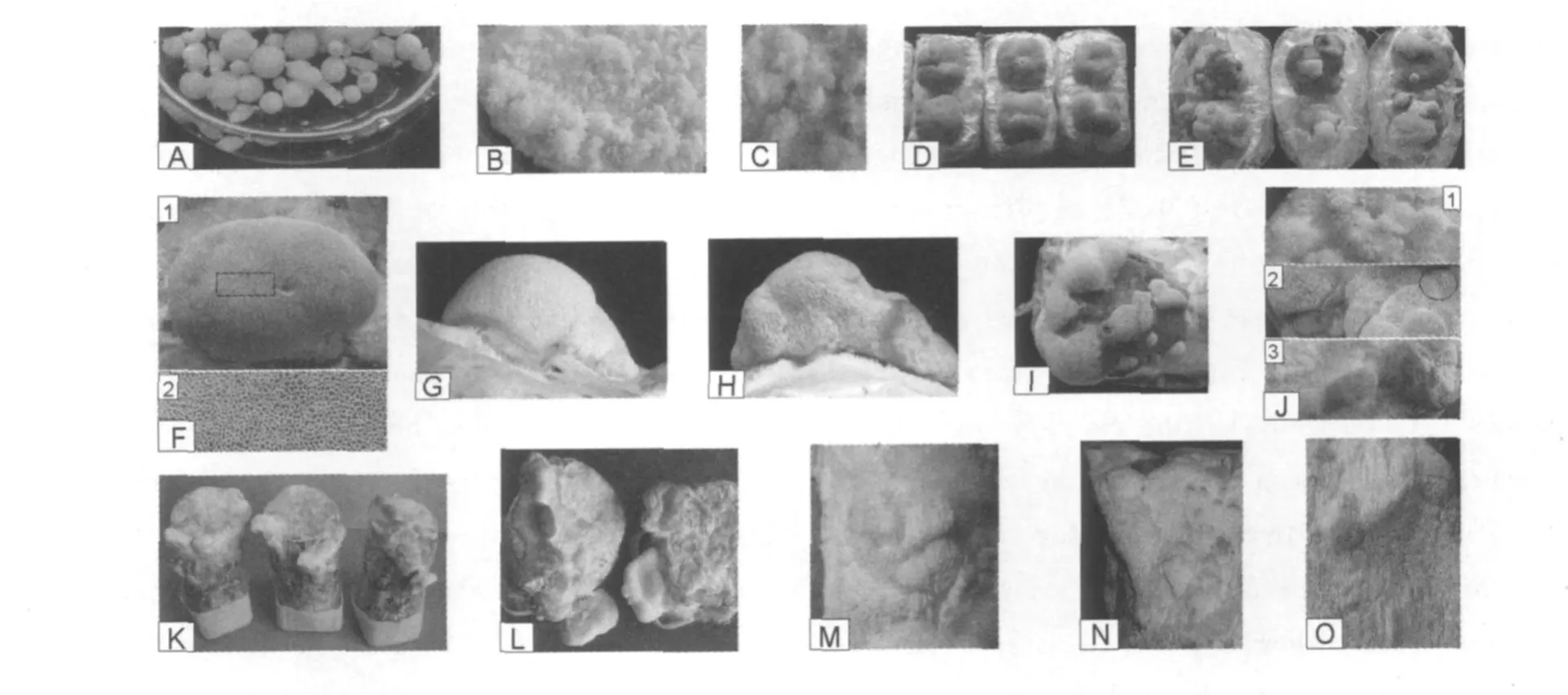
Fig.1 Trametes gallica Fr.cultivated under different conditions
2.3 T.gallica cultivated on saw dust
The results showed that,it took about 90 days for T.gallica to develop its fungus-bud when cultured on pine sawdust,almost 3 times as long as on wheat straw powder,meaning its selectivity in habitat or host.According to historical records,the fungus mainly grows on the trunks of broad-leaved trees such as willows,poplar,oak,elm,walnut and apple trees[4].Our previous study has proved that,when cultured on wheat straw powder,the fungus produced all of the 5 main lignocellulolytic enzymes including cellulase,hemicellulase,laccase,manganese-dependent peroxidase(MnP)and lignin peroxidase(LiP)[5].This study again proved that T.gallica can efficiently use straw powder as its nutrients.When cultured on wheat straw powder and pine sawdust,respectively,the morphological characteristics of the fungus were shown in Fig.D~I.
2.4 T.gallica cultivated on poplar sticks
When cultivated on poplar wood sticks,the specimens mainly showed procumbent or imbricate shapes(Fig.K~O)which were similar to the wild types.
Like many other large fungi,T.gallica also exhibits a good amount of variation in the appearance of its fruit bodies,no two wild individuals in nature are of exactly the same shape even in the same habitat.In general,under the same conditions,the morphological differences between the two fruit bodies were not significant.Our result showed that the fungus displayed significant morphological differences in distinctively different conditions.For example,when cultured in static dystrophic liquid,T.gallica exhibited a honeycomb-like structure(Fig.C),which was quite different from those on wheat straw powder(Fig.D)and those on poplar wood sticks(Fig.K~O).
In the study,a certain distinct shape of T.gallica was the reflection of the corresponding culture condition.From the evolutionary point of view,if possible primitive ecological environments be simulated accurately,the morphogenesis of the fungus will be further understood.The fungus was ever treated as Coriolopsis gallica(GenBank:DQ119335.1),but we still believe it is Trametes gallica Fr.Anyway the disagreement does not hamper us to research the morphogenesis of the fungus.Its taxonomic status needs to be further studied by using cultural characters[6-7].In addition,whether the honeycomb-like structure produces spores in its cavities is still to be investigated.
AcknowledgementsWe thank the senior experimentalist Mr.Qi-Ming Ma(Biology Institute of Shandong Academy of Sciences,Jinan,China)for further identification of Trametes gallica Fr.
Reference
[1] Chiu,S-W,Moore,D.Patterns in Fungal Development[M].Cambridge University Press,1996.
[2] Moore,D.Fungal morphogenesis[M].Cambridge University Press,1998.
[3] Sun,X.,Ren,S-T.,Bi,R-M.Lignocellulose degradation of wheat straw by Trametes gallica[J].J.Microbiol(in Chinese),2002,22(1):24-26.
[4] Deng,S.Fungi in China(in Chinese)[M].Beijing:Science Press,1963:513.
[5] Sun,X.,Zhang,R.,Zhang,Y.Production of lignocellulolytic enzymes by Trametes gallica and detection of polysaccharide hydrolase and laccase activities in polyacrylamide gels[J].J.Basic Microbiol,2004,44(3):220-231.
[6] Nobles,M.K.Cultural characters as a guide to the taxonomy of the Polyporaceae.In:Petersen R.H.,ed.Evolution in the higher basidiomycetes[M].Knoxville:The University of Tennessee Press,1971:169-196.
[7] Stalpers,J.A.Identification of wood inhabiting Aphyllophorales in pure culture[M].Centraalbureau voor Schimmelcultures,Baarn,Studies in Mycology,1978,16:1-248.

