歐洲船舶工業的低碳行動
韓光 劉嘯波
歐洲船舶工業的低碳行動
韓光 劉嘯波

近年來,盡管歐洲三大造船指標全面下滑,世界造船重心轉向韓國、中國、日本,但憑借其強大的技術優勢,歐洲仍處在世界船舶工業的領先地位。究其原因,是歐洲造船業始終堅持技術引領的發展戰略,始終將關注重點放在科技開發上。在歐盟委員會的推動下,歐洲先后出臺了一系列船舶技術研發政策,并開展了大量研發項目,如《船舶領袖2015計劃》(《Leadership 2015》)、《歐盟第六研發框架計劃》(FP6)、《歐盟第七研發框架計劃》(FP7)、船用超低排放燃燒高效率柴油機研發項目(Hercules),歐洲突破船舶和造船技術研究項目(BESST)等。受益于這些政策和項目,歐洲船舶工業在船舶設計建造技術,船舶配套設備如船舶動力設備、船舶控制設備等關鍵設備技術領域始終保持著世界先進水平和主導地位。在全球倡導低碳經濟的大背景下,歐洲各國大力開展船舶綠色、環保技術研發,以期進一步鞏固其優勢地位。
船舶動力技術
2004年,在歐盟推動下,船用超低排放燃燒高效率柴油機研發項目(Hercules)正式啟動。截止2007年,第一階段Hercules-α項目的研發工作已成功結束,研究經費總計3300萬歐元(其中1500萬歐元由歐盟提供資助)。與2003年船用柴油機最先進的技術相比, Hercules-α項目實現燃料消耗降低1.4%,NOx減排50%(與IMO2000年制定的排放標準相比),SOx減排90%,顆粒物質(PM)減排40%,碳氫化合物(HC)減排20%,可靠性達到8000小時以上。在Hercules-α項目基礎上,世界兩大船用柴油機巨頭MAN柴油機公司和瓦錫蘭公司共同牽頭開展Hercules-β項目,其研究方向也代表著環保型船用柴油機的研發趨勢。該項目目標主要有提高船用柴油推進效率60%以上,降低船用柴油消耗(SFC)10%,煙塵減排50%,NOx減排70%,達到IMO規定最高排放限值。該項目自2008年起實施,計劃研究周期36個月。
自2003年挪威船級社啟動FellowSHIP項目——全面試驗船上燃料電池以來,挪威船級社一直致力于船舶和海洋平臺用燃料電池的研究及商業化推廣。如果項目取得成功,將極大地降低二氧化碳排放量,提高能效,實現危險物質的零排放。該項目在2009年9月取得階段性進展,在一艘海洋工程供應船“海盜夫人”號上成功安裝320KW功率的燃料電池,作出了一次世界級創新。德國、冰島等歐盟國家也對第二代動力之一的燃料電池十分積極。德國通過“ZEM項目”開發了可以乘坐100人的內河專用燃料電池船舶,冰島也成功設計出全球首款氫能商用船。
此外,歐洲各國還致力于研究利用風能、太陽能、液化天然氣等清潔能源為船舶提供動力的技術。德國開發出世界第一艘風動力貨船“白鯨天帆(Beluga SkySails)”號和第一艘風動力漁船“瑪特杰迪多拉(Maartje·Theadora)”號。德國還研制出以太陽能為動力的“星球陽光”號雙體船(如圖1所示)。挪威船級社設計一艘能利用液化天然(LNG)作為船舶燃料的新概念集裝箱(如圖2所示)。

船舶減阻技術
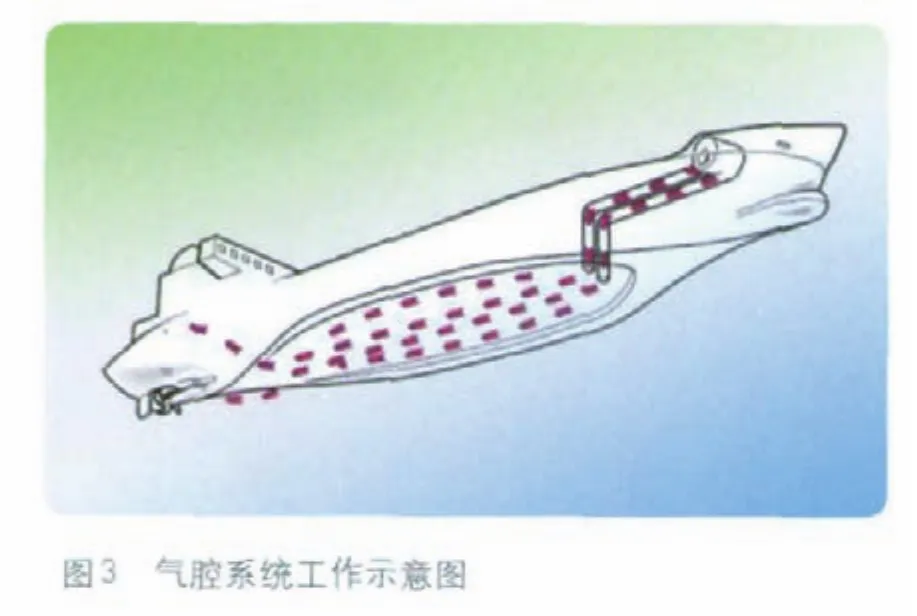
荷蘭船舶氣腔系統(ACS)技術開發商DK集團開發出氣腔系統技術,并成功在一艘超大型油輪(VLCC)上進行了相關測試。氣腔系統技術利用氣腔替代船底表面,能減少船底摩擦阻力,從而提高船舶的燃油效率。氣腔系統包括氣腔、噴氣系統和控制系統。如圖3所示,安裝在船底的氣腔,能減少船體與水接觸面積,從而減少船體阻力;自動壓縮機和閥門組成的噴氣系統能向氣腔內注入空氣,而控制系統則用于監控空氣數量和氣壓,并維持氣腔內的空氣處于最佳水平。船舶安裝氣腔系統后,最多能降低15%燃油消耗量,相應也就減少了二氧化碳排放量。
英國科學家研制出可有效清除藤壺而不對海洋環境造成污染的船舶涂料。他們將一種比人類頭發細一千倍的碳納米管融進油漆中,該碳納米管可在分子層面改變油漆表面。當船舶移動時,附著生物可輕易被沖走。該船舶涂料的研究成功,不僅帶來了巨大經濟效益,也具有重要的環保意義。因為,多年來船舶上附著生物的問題一直困擾著全球船東,每年為清除此類生物大約要花費數十億英鎊。不僅是航運業,就連私人游艇、海水淡化廠也深受其害。由于船舶附著藻類會增加船體阻力,從而增加船舶油耗,進而導致碳排放增加。研究表明,一艘船舶粘附上藻類或藤壺,其速度會減少10%,而耗油量會上升40%,全球船舶業每年為此需耗資近一百億美元。
復合環保技術
法國造船集團——歐洲世騰造船集團設計出環保概念郵輪“Eoseas”號。該郵輪主要使用可再生能源,限制溫室氣體排放量,其設計充分體現了節能環保的理念。桅桿上的風帆在為船舶提供風能動力的同時,能將收集的空氣導入船底產生氣泡形成氣墊,從而減少船底阻力,提高船舶水動效力;該郵輪使用液化天然氣(LNG)作為燃料,同時,郵輪上還安裝了太陽能儲電板,能利用太陽能供電;其雙重外殼板設計更有作為天然空調系統之效;此外該郵輪會循環使用水、回收上層甲板的雨水、以及使用從處理廢物時回收的能源。

In 2004, driven by the European Union, the research and development project (Hercules) for marine diesel engine with ultra-low emission and high efficiency was launched formally. By 2007, the first stage work of Hercules-α project has successfully concluded,which costs a total of 33 million Euros including 15 million Euros provided by EU. Compared with the most advanced technology of marine diesel engine in 2003,the Hercules-α project realized a 1.4% reduction of fuel consumption, a 50% reduction in NOxemissions compared with the emission standard enacted by IMO in 2000,a 90% reduction in SOxemission, a 40% reduction in particle material (PM) emissions and a 20% reduction in hydrocarbon (HC) emissions, the reliability could last more than 8000 hours. On the basis of Hercules-α project, two marine diesel engine giants, MAN diesel engine company and Wartsila company jointly lead the development of Hercules-β project, whose research direction also represents the development trend of environmental marine diesel engine. The main targets of this project are to improve the propulsive eff i ciency of marine diesel engine by more than 60%, to reduce ship fuel consumption (SFC)by 10%, to reduce smoke dust emission by 50%, and to reduce NOxemission by 70% to achieve the highest emission limit set by IMO. This project was started in 2008,and is planned to last 36 months.
Since 2003 when DNV started the Fellow SHIP project which focused on comprehensive testing on marine fuel cell, DNV has been committed to the research and commercial promotion of fuel cell used on ships and marine platforms. If the project succeeds, the carbon dioxide emission will be dramatically reduced, the eff i ciency will be improved, and the zero discharge of hazardous substances will be realized. This project made a periodical progress in September 2009, the fuel cell of 320KW power was successfully installed onboard an oceaneering supply ship “Madam Pirate”, which made an innovation of a world-class. Germany, Iceland and other EU countries are also positive for the fuel cell which is considered to be one type of the second generation of power. Through the“ZEM project”, Germany has developed the fuel cell ship specialized in navigating in incoming rivers, which can accommodate 100 people. Iceland has also successfully designed the world's first hydrogen-powered commercial ship.
In addition, the European countries are also committed to the study and the use of the clean energy, like wind energy,solar energy and liquefied natural gas to provide power for ships. Germany developed the world’s fi rst cargo ship powered by wind, “Beluga SkySails” and the first fishing vessel powered by wind, “Maartje Theadora”. Germany also developed the catamaran powered by solar energy,“planet sunshine”. DNV designed a new concept container,which can be fuelled by liquef i ed natural gas (LNG).
The Dutch developer of ship air cavity system (ACS)technology, DK group developed the air cavity system technology, and carried out related testing on a VLCC successfully. The air cavity system technology replaces the surface of ship bottom with gas cavity to reduce the friction resistance of ship bottom, so as to improve the fuel efficiency. With the installation of air cavity system,fuel consumption can be reduced by 15%, and the carbon dioxide emission will also be correspondingly reduced.
Low Carbon Action of European Shipbuilding Industry
By Han Guang & Liu Xiaobo

