南京新濟(jì)洲國家濕地公園植被類型?區(qū)系及多樣性研究
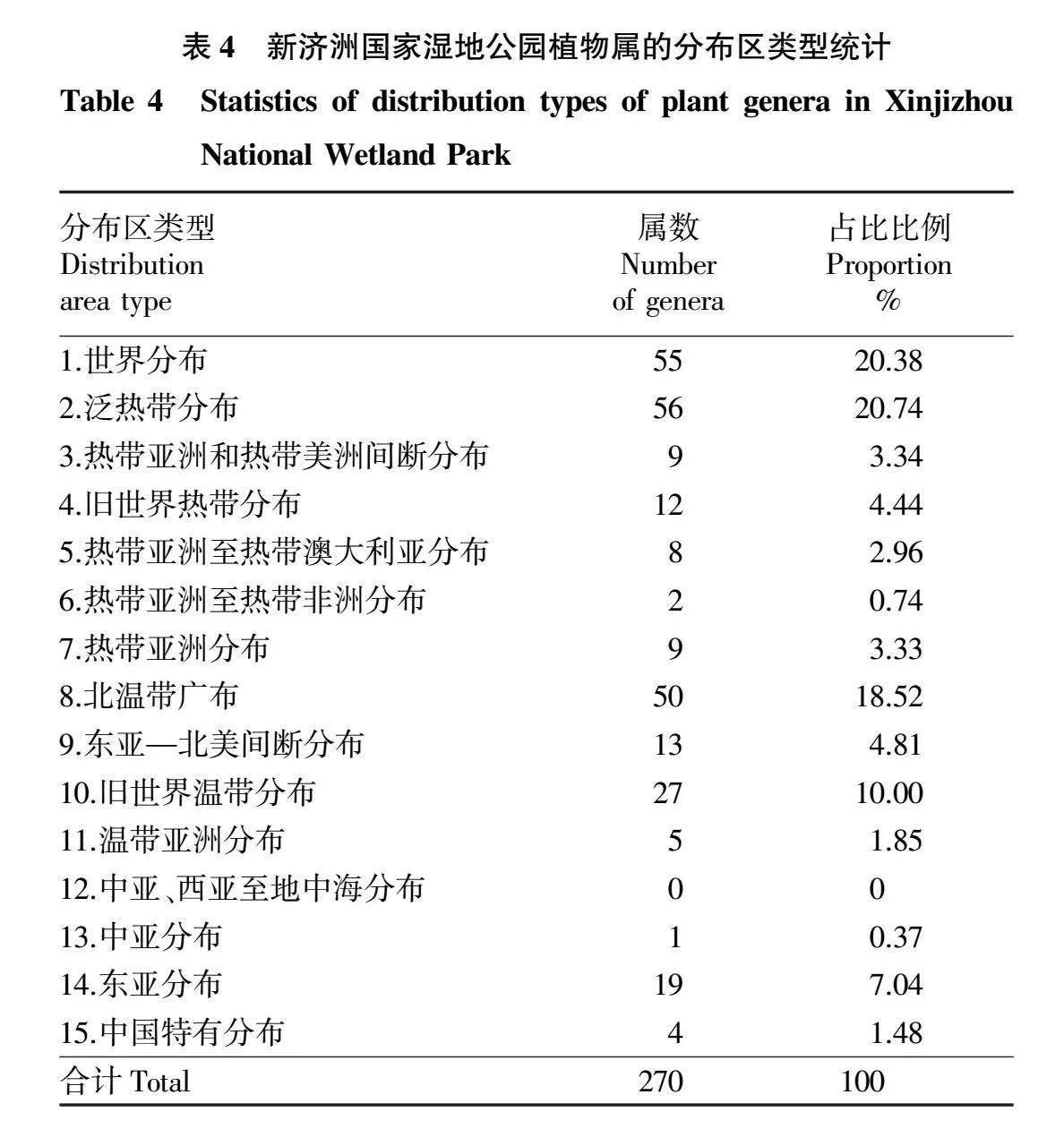
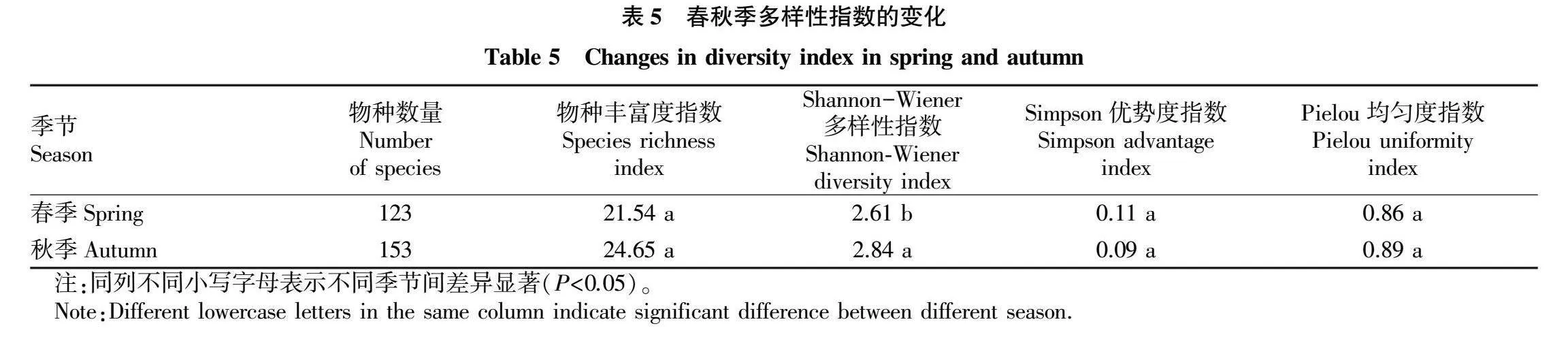

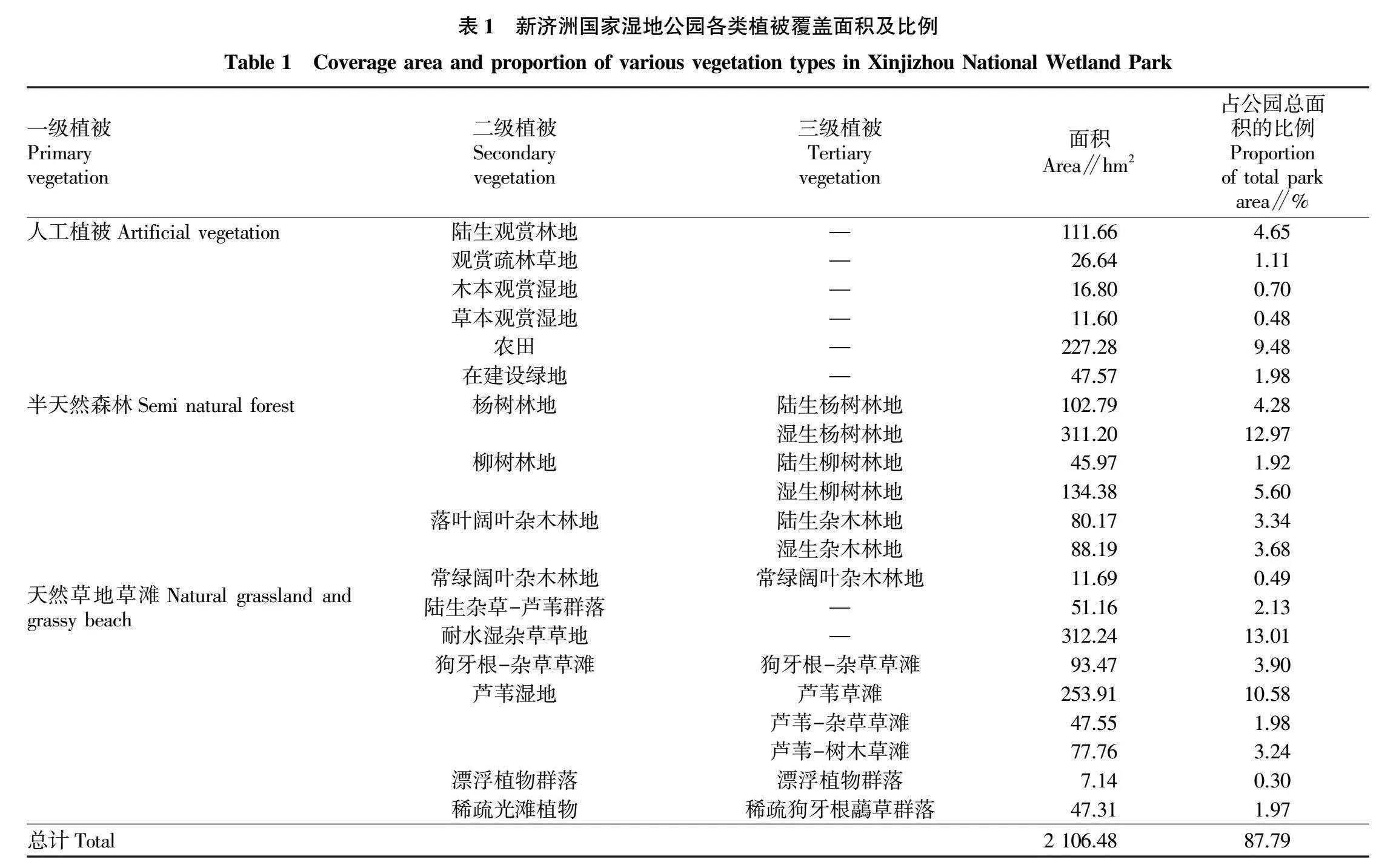
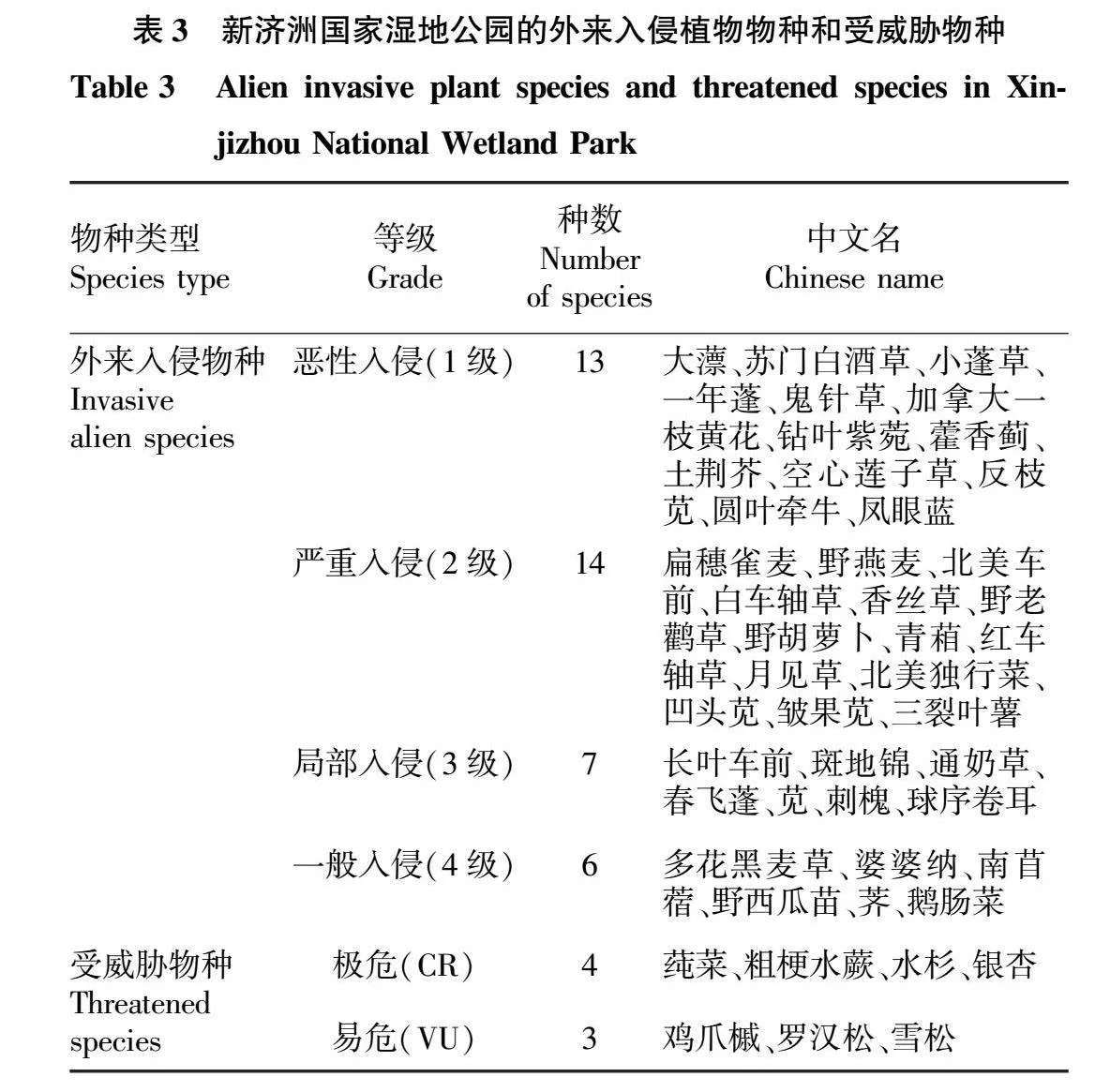

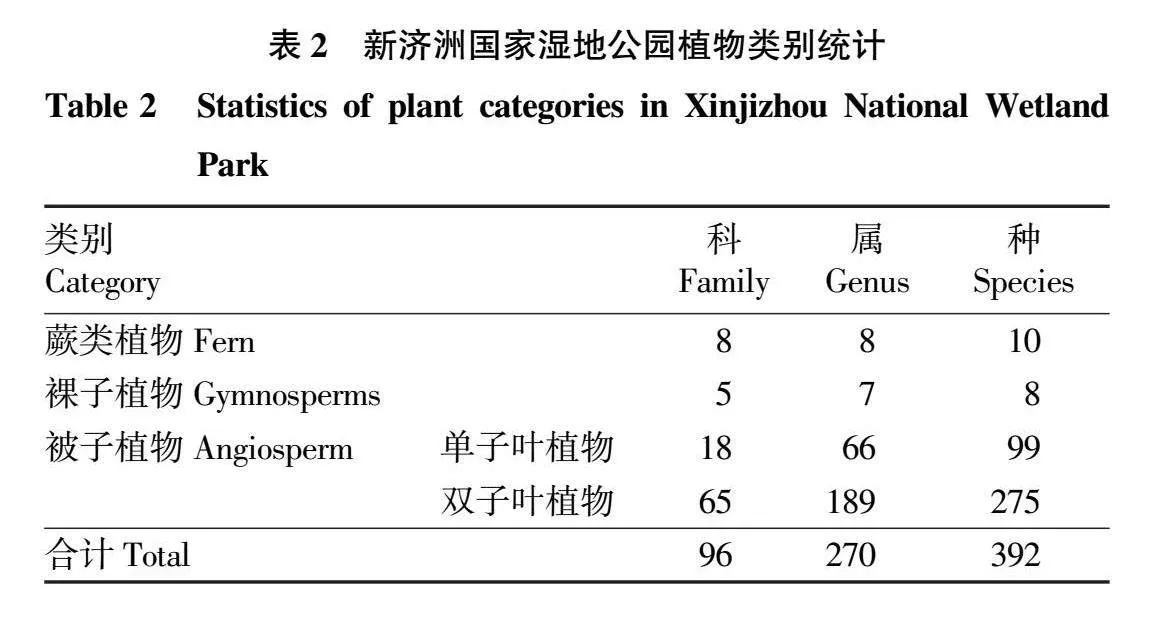
摘要 為研究新濟(jì)洲國家濕地公園的植被類型、區(qū)系組成和物種多樣性特征,2020年春季和秋季對濕地公園開展了遙感影像分析和植物野外調(diào)查監(jiān)測。結(jié)果表明:濕地公園的植被面積占總面積的87.79%,可分為3個一級植被類型(人工植被、半天然森林、天然草地草灘)和16個二級植被類型;有植物96科270屬392種,其中蕨類植物8科8屬10種,裸子植物5科7屬8種,被子植物83科255屬374 種,禾本科、菊科和莎草科為優(yōu)勢科。植物區(qū)系分析表明,屬的地理分布類型有14種,以溫帶分布和熱帶分布為主。植被樣點(diǎn)監(jiān)測結(jié)果表明,秋季的平均Shannon-Wiener多樣性指數(shù)顯著高于春季,且各監(jiān)測樣點(diǎn)的 Shannon-Wiener多樣性指數(shù)差異顯著,而春季、秋季的平均Patrick豐富度指數(shù)、Simpson優(yōu)勢度指數(shù)和Pielou均勻度指數(shù)差異不顯著,各監(jiān)測點(diǎn)表現(xiàn)出相似的變化規(guī)律。
關(guān)鍵詞 國家濕地公園;植被類型;植物區(qū)系;植物多樣性
中圖分類號 Q 948 文獻(xiàn)標(biāo)識碼 A
文章編號 0517-6611(2024)22-0102-05
doi:10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2024.22.020
開放科學(xué)(資源服務(wù))標(biāo)識碼(OSID):
Study on Vegetation Type,F(xiàn)lora and Diversity in Xinjizhou National Wetland Park
SHAO Jing,WANG Hong,XU Jing et al
(Nanjing Insititute of Landscape Architecture and Forestry,Nanjing,Jiangsu 210019)
Abstract In the spring and autumn of 2020,remote sensing image analysis and plant field survey and monitoring were carried out to fully understand the vegetation type,flora,and species diversity characteristics of plant in Xinjizhou national wetland park,Nanjing,China.The results showed that vegetation accounted for 87.79% of the total area.Vegetation can be divided into three primary vegetation types (artificial vegetation,semi-natural forest,natural grassland) and 16 secondary vegetation types. The study demostrated that there were 96 families,270 genera and 392 species.Among them,there existed ferns plants of 8 families,8 genera and 10 species,gymnosperms plants of 5 families,7 genera and 8 species,angiosperms plants of 83 families and 255 genera and 374 species. Poaceae,Asteraceae and Cyperaceae were the dominant families.The geographic distribution of the genera of plants existed 14 distribution types,and they were mainly in a tropical and temperate distribution.Monitoring results of vegetation sampling sites showed that the mean Shannon-Wiener diversity index was significantly higher in autumn than in spring.Among the 24 vegetation sampling sites,the Shannon-Wiener diversity index varied significantly,the mean Patrick richness index,Simpson dominance index and Pielou evenness index did not differ significantly in spring and autumn,and showed a similar trend.
Key words National wetland park;Vegetation type;Flora;Diversity of plant
作為國家自然保護(hù)體系的重要組成部分,國家濕地公園的發(fā)展建設(shè)對于改善生態(tài)環(huán)境,調(diào)節(jié)區(qū)域氣候及保護(hù)生態(tài)多樣性等具有重要意義[1]。而植物作為濕地生態(tài)系統(tǒng)中的生產(chǎn)者,維護(hù)著濕地生態(tài)系統(tǒng)的正常運(yùn)行,對濕地恢復(fù)起著主要的調(diào)控作用,同時指示著濕地生態(tài)環(huán)境狀況及其變化,是反映濕地自然生態(tài)的重要指標(biāo)[2-4]。因此,對國家濕地公園植物資源進(jìn)行調(diào)查研究,可為濕地公園生物多樣性保護(hù)和濕地生態(tài)環(huán)境保護(hù)修復(fù)提供重要的科學(xué)依據(jù)。當(dāng)前,已有眾多研究者對國家濕地公園植物多樣性開展了調(diào)查研究,一方面豐富了生物多樣性數(shù)據(jù),另一方面也為科學(xué)、規(guī)范地評價濕地的生物多樣性提供了參考[5-7]。……
 安徽農(nóng)業(yè)科學(xué)
2024年22期
安徽農(nóng)業(yè)科學(xué)
2024年22期
- 安徽農(nóng)業(yè)科學(xué)的其它文章
- 農(nóng)業(yè)教育?科技?人才一體化協(xié)同發(fā)展研究——以廣西為例
- 農(nóng)民學(xué)院發(fā)展視角下的海南鄉(xiāng)村振興大學(xué)發(fā)展研究
- 涉農(nóng)高校信息類專業(yè)“知農(nóng)愛農(nóng)”情懷的培育價值和路徑研究
- 差序格局視域下農(nóng)民生態(tài)倫理困境及對策研究
- 蘇州農(nóng)村人居環(huán)境整治及日常管護(hù)費(fèi)用支出現(xiàn)狀與改進(jìn)策略
- 鄉(xiāng)村振興背景下我國農(nóng)村環(huán)境治理的可視化分析
