基于二次轉(zhuǎn)角約束的改進(jìn)RRT路徑規(guī)劃算法研究
鮑家定 鐘國安 馬果 徐海軍 景暉

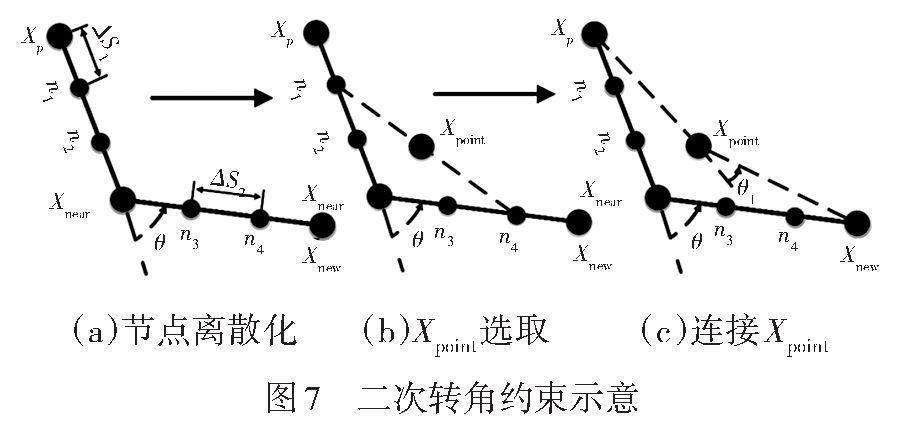
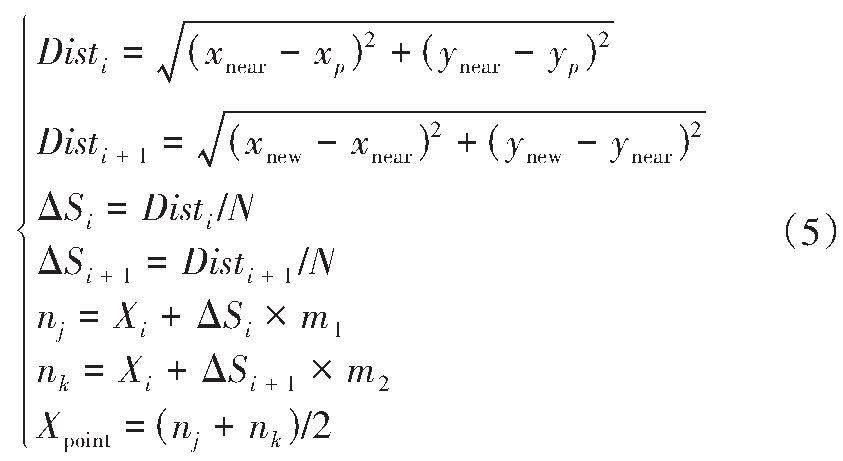
【摘要】針對(duì)快速隨機(jī)搜索樹(RRT)算法存在節(jié)點(diǎn)擴(kuò)展冗余、生成路徑不滿足車輛轉(zhuǎn)角條件等問題,提出一種改進(jìn)的二次轉(zhuǎn)角約束RRT算法。首先,在傳統(tǒng)RRT算法基礎(chǔ)上對(duì)采樣空間進(jìn)行裁剪,引入目標(biāo)導(dǎo)向策略減少采樣時(shí)間;然后采用車輛膨脹處理和直線方法檢測(cè)障礙物,并引入第一次轉(zhuǎn)角約束得到粗解路徑;接著對(duì)粗解路徑建立二次轉(zhuǎn)角約束并進(jìn)行優(yōu)化處理,獲取優(yōu)化路徑后擬合,并進(jìn)行仿真驗(yàn)證。結(jié)果表明,相比于引入目標(biāo)導(dǎo)向策略的RRT算法,所提出的算法路徑最大曲率降低了34.33%,平均曲率降低47.36%,擴(kuò)展節(jié)點(diǎn)數(shù)降低47.62%,路徑距離降低7.76%,規(guī)劃時(shí)間縮短14.98%。
主題詞:改進(jìn)RRT算法 轉(zhuǎn)向角度約束 路徑規(guī)劃 路徑曲率 路徑平滑性
中圖分類號(hào):U461.99? ?文獻(xiàn)標(biāo)志碼:A? ?DOI: 10.19620/j.cnki.1000-3703.20230371
Research on Improved RRT Path Planning Algorithm Based on Two-Time Steer Angel Constraint
【Abstract】Aiming at the problems that the Rapid-exploration Random Tree (RRT) algorithm is easy to lead to node expansion redundancy and the generated path does not meet the vehicle rotation angle constraint, an improved secondary rotation angle constraint RRT algorithm is proposed. Based on the traditional RRT algorithm, the sampling space is first cut, and the target offset strategy is introduced to reduce the sampling time. Then, the vehicle expansion processing and the straight line method are used to detect the obstacle collision, and the first rotation angle constraint is introduced to obtain the coarse solution path. Then, the secondary angle constraint optimization processing is established for the rough solution path, and the vehicle optimization path is obtained and fitted, and the simulation verification is carried out. The results show that compared with the biased RRT algorithm with the goal-oriented strategy, the maximum curvature of the path is reduced by 34.33 %, the average curvature is reduced by 47.36 %, the number of extended nodes is reduced by 47.62 %, the path distance is reduced by 7.76 %, and the planning time is reduced by 14.98 %.
Key words: Improved RRT algorithm, Steering angle constrain, Path planning, Path curvature, Path smoothness
1 前言
路徑規(guī)劃技術(shù)作為無人駕駛汽車實(shí)現(xiàn)自主導(dǎo)航的關(guān)鍵技術(shù)之一,對(duì)車輛安全行駛起著至關(guān)重要的作用,逐漸成為無人駕駛車輛領(lǐng)域研究熱點(diǎn)[1-2]。
路徑規(guī)劃算法可分為基于圖搜索的算法(如A*算法、Dijkstra算法等)、基于隨機(jī)采樣的算法(如快速隨機(jī)搜索樹(Rapid-exploration Random Tree,RRT)算法、蒙特卡洛隨機(jī)采樣算法等),以及深度學(xué)習(xí)算法、蟻群算法等[3-7]。
RRT算法作為一種常用的路徑規(guī)劃算法,通過隨機(jī)采樣狀態(tài)空間生成新節(jié)點(diǎn),并不斷擴(kuò)展樹形結(jié)構(gòu),搜索可行路徑,具有較強(qiáng)的靈活性。欒添添等[8]提出了一種動(dòng)態(tài)變采樣區(qū)域RRT路徑規(guī)劃算法,減少了節(jié)點(diǎn)的采樣次數(shù)并降低了搜索的盲目性。Zhang等[9]利用人工勢(shì)場(chǎng)法,對(duì)采樣目標(biāo)進(jìn)行啟發(fā)式引導(dǎo),再根據(jù)障礙物密度動(dòng)態(tài)調(diào)整步長,提出了動(dòng)態(tài)步長RRT算法。……

