含分布式電源和電動(dòng)汽車的配電網(wǎng)可靠性評(píng)估
王輝 李旭陽(yáng) 王寶全 王一凡 方航 金子蓉

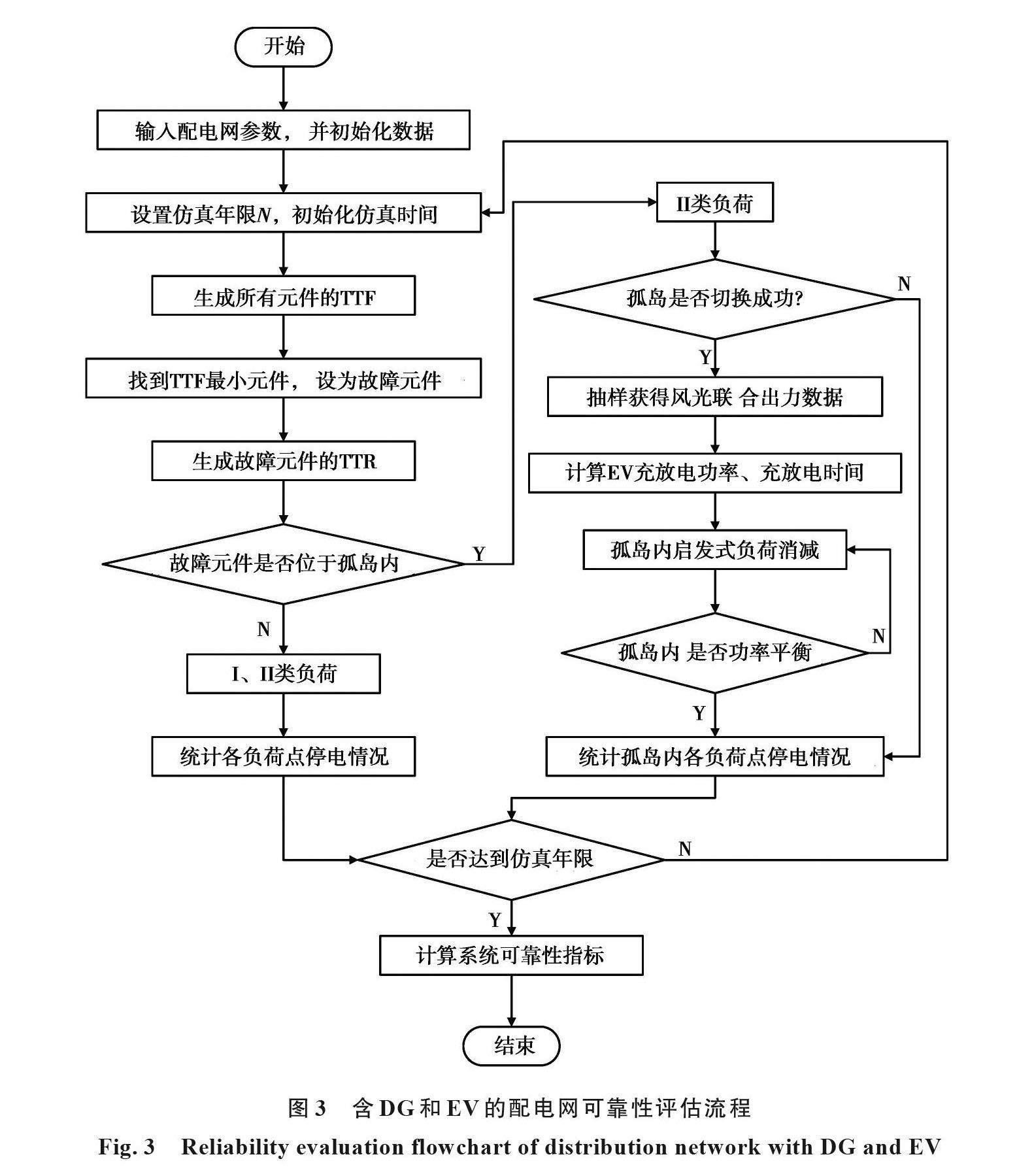
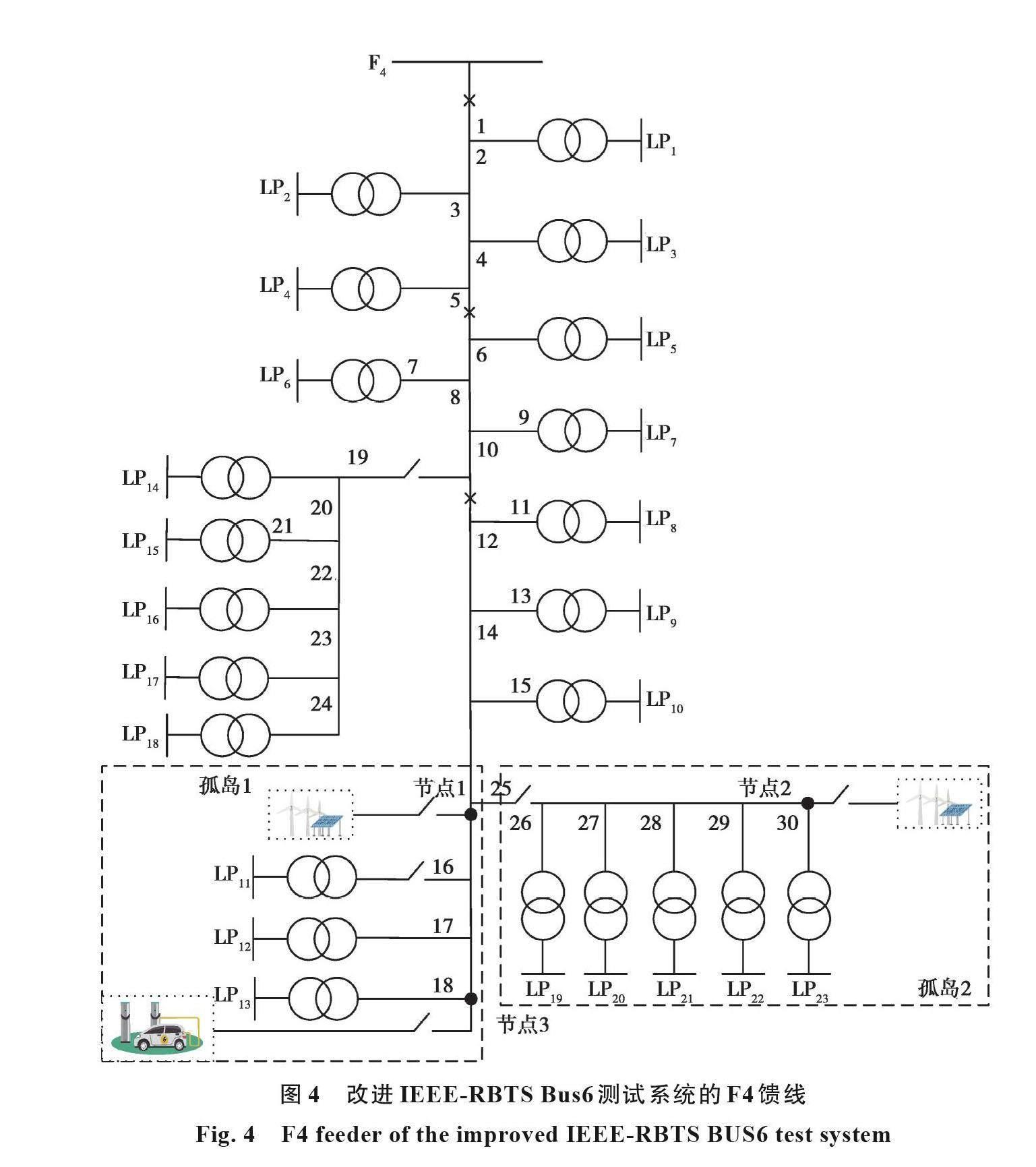
摘要:針對(duì)目前大規(guī)模分布式電源和電動(dòng)汽車接入配電網(wǎng)后,給配電網(wǎng)可靠性帶來(lái)一定影響的問(wèn)題,提出了一種含有分布式電源和電動(dòng)汽車的新型配電網(wǎng)的可靠性評(píng)估方法。首先,考慮到風(fēng)光出力的不確定性和相關(guān)性,選擇擬合性最優(yōu)的Frank-Copula函數(shù),建立了風(fēng)光聯(lián)合出力概率模型。其次,分析了電動(dòng)汽車用戶行為特征,提出了基于動(dòng)態(tài)分時(shí)電價(jià)的電動(dòng)汽車有序充放電控制策略。最后,基于改進(jìn)IEEE-RBTS Bus6測(cè)試系統(tǒng)的主饋線F4,對(duì)系統(tǒng)的可靠性指標(biāo)進(jìn)行計(jì)算分析,結(jié)果表明所提的風(fēng)光聯(lián)合出力模型和有序充放電控制策略可以有效降低對(duì)配電網(wǎng)可靠性的影響。
關(guān)鍵詞:分布式電源;風(fēng)光聯(lián)合出力;電動(dòng)汽車;有序充放電;配電網(wǎng);可靠性評(píng)估
中圖分類號(hào):TM732????????? 文獻(xiàn)標(biāo)志碼:A????????? 文章編號(hào):1000-582X(2024)01-115-12
Reliability evaluation of distribution network with distributed generation and electric vehicle
WANG Huia,b, LI Xuyanga, WANG Baoquana, WANG Yifana, FANG Hanga, JIN Zironga
(a. College of Electrical Engineering & New Energy; b. Hubei Provincial Engineering Technology Research Center for Microgrid, China Three Gorges University, Yichang, Hubei 443002, P. R. China)
Abstract: The integration of large-scale distributed generation and electric vehicles into the distribution network can have an impact on its reliability. To address this issue, a reliability evaluation method for a new distribution network containing distributed generation and electric vehicles was proposed. Firstly, with considering the uncertainty and correlation of wind and power output, the best fitting Frank-Copula function was selected and a joint probability model of wind and solar power was established. Secondly, the behavior characteristics of electric vehicle users were analyzed, and an orderly charge and discharge control strategy of electric vehicle was proposed based on dynamic time-of-use pricing. Finally, using the main feeder F4 of the improved IEEE-RBTS Bus6 test system, the reliability index of the system was calculated and analyzed. The results show that the proposed wind solar joint output model and orderly charge-discharge control strategy can effectively reduce the impact on the reliability of the distribution network.
Keywords: distributed generation; wind-solar joint power output; electric vehicle; orderly charging and discharging; distribution network; reliability evaluation
在“碳達(dá)峰”和“碳中和”的目標(biāo)驅(qū)動(dòng)下,以風(fēng)力、光伏發(fā)電為主的分布式電源(distributed generation,DG)在全球范圍內(nèi)得到大力發(fā)展,根據(jù)國(guó)際可再生能源署(International Renewable Energy Agency,IRENA)發(fā)布的《2022年可再生能源發(fā)電量統(tǒng)計(jì)報(bào)告》,全球風(fēng)力、光伏發(fā)電裝機(jī)分別達(dá)到825 GW、849 GW。電動(dòng)汽車(electric vehicle,EV)作為一種具有廣闊發(fā)展前景的綠色交通工具,也是實(shí)現(xiàn)“雙碳”目標(biāo)的重要途徑之一,得到了大力發(fā)展。但是,風(fēng)電、光伏機(jī)組的出力受到光照強(qiáng)度、溫度、風(fēng)速等自然條件的影響,具有較強(qiáng)的隨機(jī)性、間歇性及波動(dòng)性,EV無(wú)序充電行為在時(shí)空上具有較強(qiáng)的隨機(jī)性,其充電負(fù)荷會(huì)改變?nèi)肇?fù)荷變化趨勢(shì),進(jìn)而影響配電網(wǎng)的可靠性。大規(guī)模的DG和EV接入配電網(wǎng),勢(shì)必會(huì)給配電網(wǎng)的可靠性帶來(lái)影響,因此,需要對(duì)含DG和EV的配電網(wǎng)的可靠性進(jìn)行評(píng)估。……

