二甲醚/甲醇混合燃料HCCI燃燒特性數值模擬
王鑫 談嶺 陳朝陽
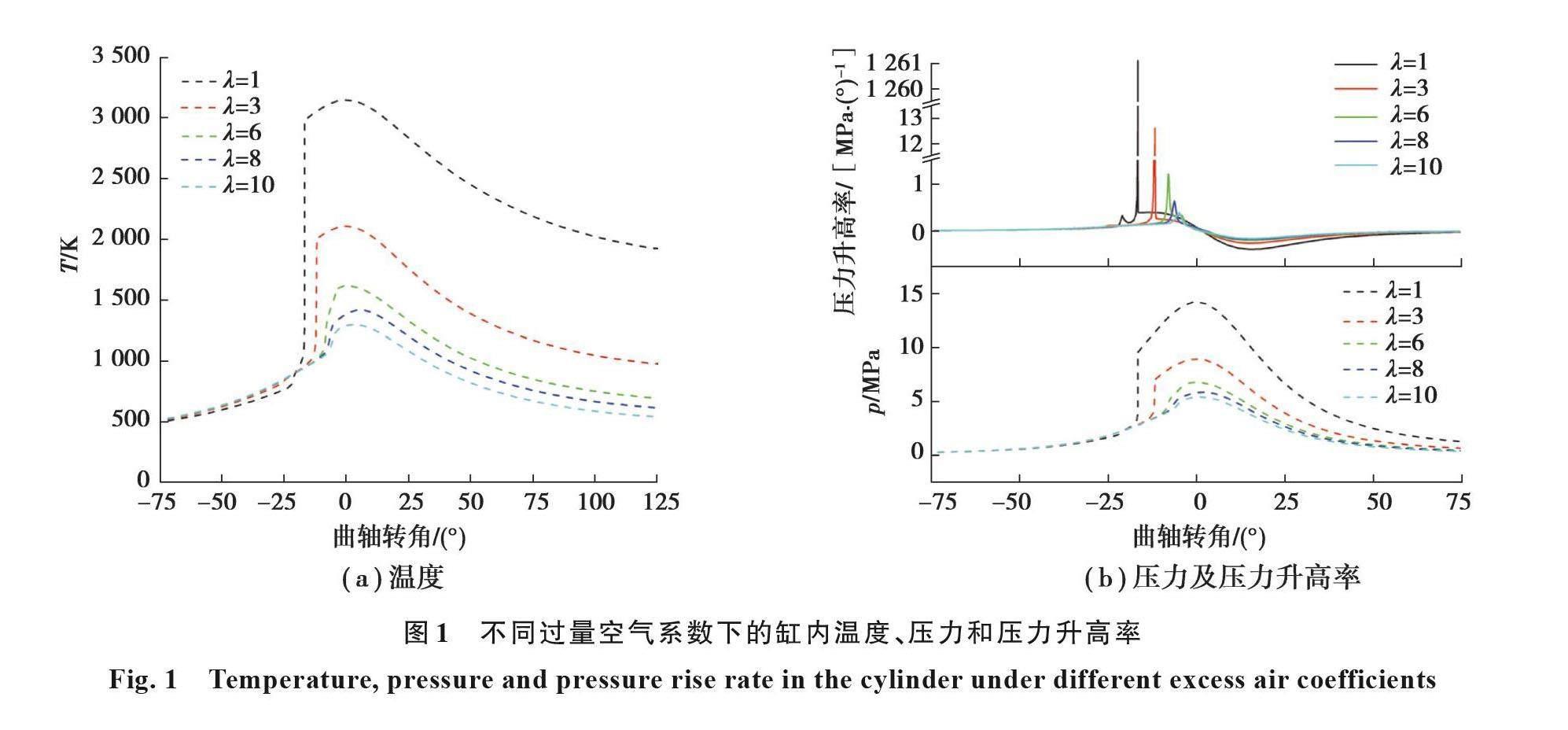
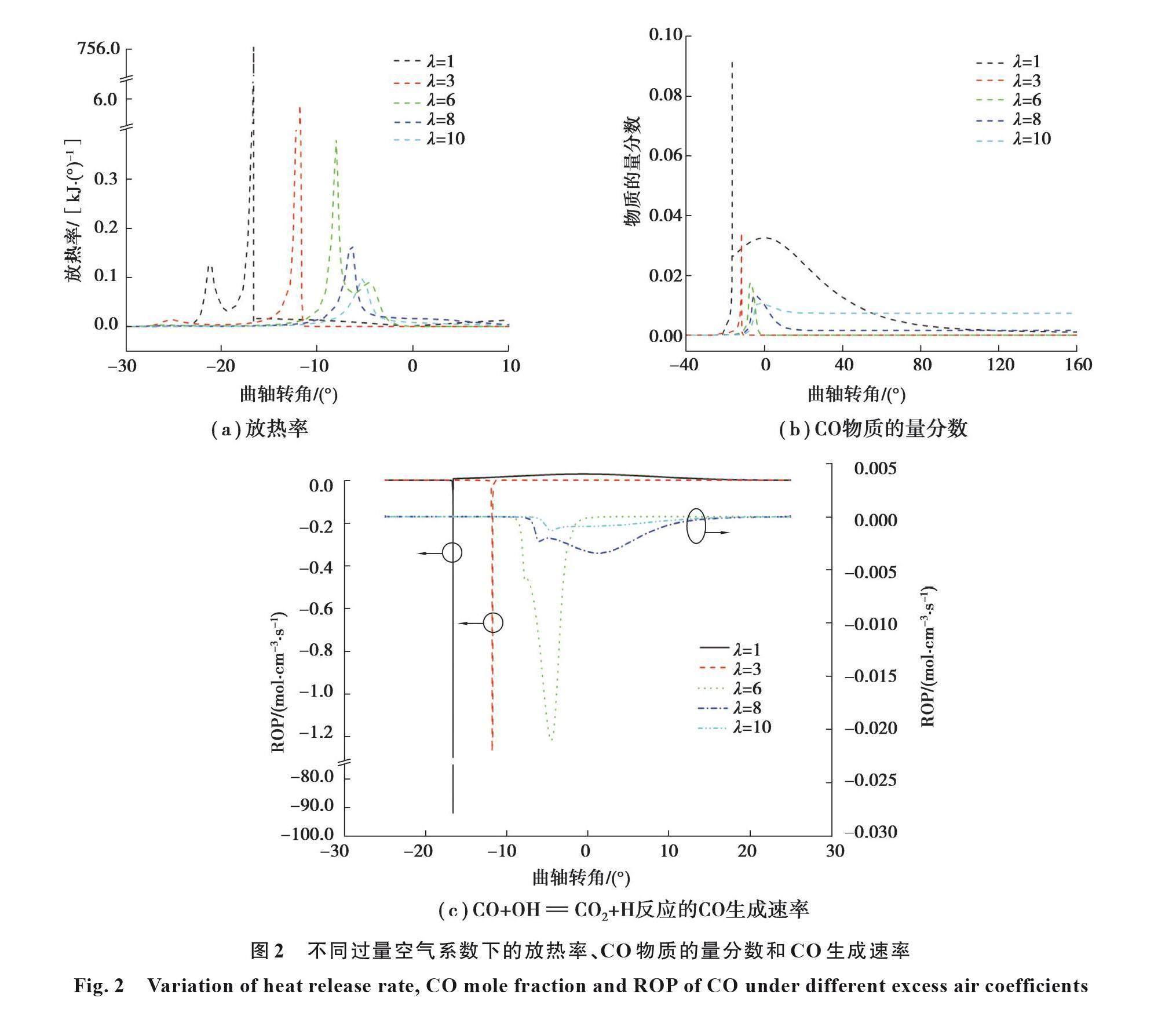
摘要:為了研究混合氣濃度及燃料摻混對二甲醚/甲醇混合燃料HCCI(homogeneous charge compression ignition)燃燒特性的影響,對不同過量空氣系數和二甲醚摻混比下的醇醚混合燃料HCCI燃燒過程進行了模擬計算,分析了缸內溫度、壓力、壓力升高率、放熱率和燃料消耗路徑隨過量空氣系數和二甲醚摻混比的變化關系。結果表明,隨過量空氣系數增大,缸內壓力、溫度、放熱率和壓力升高率峰值減小,相位推遲,過量空氣系數太大時,CO的進一步氧化反應會受到阻礙,使缸內產生大量的CO殘留;隨二甲醚摻混比的增大,缸內壓力、溫度峰值增大,相位提前,壓力升高率和放熱率峰值減小;二甲醚HCCI燃燒放熱率曲線存在3個峰值,第1個峰值出現上止點前曲軸轉角30°,為二甲醚低溫氧化放熱,對應缸內溫度為804 K,第2個峰值出現在上止點前曲軸轉角15°,對應缸內溫度為1 193 K,為甲醛等中間產物氧化生成CO時放熱,第3個峰值為CO氧化,生成CO2時放熱,第2和第3個放熱率峰值為二甲醚的高溫氧化放熱階段,與甲醇摻混燃燒時,二甲醚的低溫氧化反應對混合氣的燃燒起到了促進作用。
關鍵詞:內燃機;數值模擬;二甲醚;甲醇;均質混合壓燃
中圖分類號:TK421.2????????? 文獻標志碼:A????????? 文章編號:1000-582X(2024)01-001-08
Simulation study on HCCI combustion of DME/methanol fueled engine
WANG Xin, TAN Ling, CHEN Zhaoyang
(School of Automobile, Changan University, Xian 710064, P. R. China)
Abstract: To determine the effects of mixture concentration and fuel blending on the combustion performance of a dimethyl ether/methanol fueled HCCI engine, the combustion process under different excess air coefficients and dimethyl ether addition ratios was simulated. Parameters such as temperature, pressure, pressure rise rate and the heat release rate were examined, as well as the fuel consumption path. The results show that the peak values of the pressure, temperature, heat release rate and pressure rise rate decrease with the increase of the excess air coefficient, while the phases are delayed. Excessive excess air coefficient hinders the further oxidation reaction of CO, resulting in high CO residue. On the other hand, increasing the dimethyl ether (DME) addition ratio leads to higher peak values of pressure and temperature in the cylinder, advancing their phases, while the peak values of pressure rise rate and heat release rate decrease. The combustion heat release rate curve of dimethyl ether homogeneous charge compression ignition (HCCI) combustion exhibits three peaks. The first peak, occurring at a crane angle of 30° before topdead center (BTDC) with a temperature of 804 K, corresponds to the low-temperature-oxidation heat release of dimethyl ether. The second peak, appearing at a crane angle of 15° BTDC with a temperature of 1 193 K, corresponds to the heat release from reactions forming CO through formaldehyde and other intermediates. The third peak represents the heat release from CO oxidation when CO2 is generated. The second and third exothermic rate peaks indicate the high-temperature oxidation exothermic stage of dimethyl ether. Additionally, when mixed with methanol, the low-temperature oxidation reaction of dimethyl ether promotes the combustion of the mixture.
Keywords: internal combustion engine; simulation; dimethyl ether (DME); methanol; homogeneous charge compression ignition (HCCI)
隨著化石能源短缺和環境污染問題的日益突出,尋找新型可替代燃料,探索清潔高效燃燒方式成為內燃機工作者所面臨的最緊迫任務之一。低溫燃燒發動機因其高的熱效率和優良的排放性能成了研究熱點。均質充量壓縮著……

