Factors affecting single-step transepithelial photorefractive keratectomy outcome in the treatment of mild, moderate,and high myopia: a cohort study
INTRODUCTION
Uncorrected refractive errors are one of the major causes of preventable vision impairment worldwide. A systematic review by Naidoo
showed that in 2010 about 7 million people were blind and over 100 million people were visually impaired due to uncorrected refractive errors. Uncorrected refractive disorders pose a significant financial burden;according to a study by Smith
global economic productivity loss due to uncorrected refractive errors was an astounding $268 billion. The estimated pool prevalence of myopia in adults is 26.5% and the prevalence ranges from 4%to 51%
. A study by Holden
predicted that by 2050 about 49.8% (4758 million) of the world population will have myopia and about 10% world population (938 million) will have high myopia. The combined prevalence of myopia and astigmatism in adults in the Middle East region is 54%, posing a significant financial burden
.
這種模式在我省占比比較高,也是肉牛糞污處理的主要方式,大、中、小肉牛場(chǎng)均適用。建設(shè)固體糞污堆漚場(chǎng)和污水處理池,固體糞污采取條垛式堆肥發(fā)酵,每周3~5次翻拋增氧,發(fā)酵周期需要40~60天。污水進(jìn)入污水處理池,3~6個(gè)月完成腐熟。腐熟后的固體肥和液體肥就近施入農(nóng)田。該處理模式優(yōu)點(diǎn)是工藝簡(jiǎn)單,操作簡(jiǎn)便,投資少;缺點(diǎn)是發(fā)酵周期長(zhǎng),占地面積大,臭氣不易控制。
以某大橋?yàn)槔M(jìn)行模板的選型。該橋位于某江下游末端,河床平坦、開闊、穩(wěn)定,枯水期主河槽灣流偏南岸,出現(xiàn)在每年2~3月,枯水期約5個(gè)月。按設(shè)計(jì)要求墩身高49m,采用薄壁空心結(jié)構(gòu),雙向控制墩身垂直度及各部位尺寸較為困難。
The consecutive patients with myopia and myopic astigmatism who underwent t-PRK from August 2019 to February 2020 were included in the present study. Patients aged 18 years and older and with at least 6mo follow-up after t-PRK were included. The surgeries were performed only if stable refraction was noted for at least one year prior to scheduling surgery. In all patients, contact lens usage was discontinued for at least three weeks, and postoperative residual corneal thickness of all eyes was more than 350 μm at the thinnest location. Patients with a history of ocular surgery, active ocular diseases, corneal dystrophy, retinal disease, dry eye, severe eye trauma, irregular astigmatism, or suspected keratoconus, systemic ailments like diabetes mellitus, autoimmune diseases, pregnant or lactating ladies were excluded. A single experienced corneal surgeon operated on all patients.
Photorefractive keratectomy (PRK) was the first laser refractive technique used to treat refractive errors and it is a two-step procedure where the epithelium is first removed manually,followed by laser refractive ablation to remove the stroma
.However, PRK became less popular as the surgery had long postoperative recovery time, caused postoperative pain,and was associated with the development of secondary complications like stromal haze. Over the years, with the development of newer generation lasers and improved ablation techniques, many advances have been made to this procedure giving rise to better options that circumvent the above complications. These options include, laser-assisted
keratomileusis (LASIK)
, laser-assisted subepithelial keratectomy (LASEK)
, and single-step transepithelial PRK(t-PRK)
.
LASIK, though a popular laser refractive surgery, may not be right for everyone, especially for people who have thin corneas, glaucoma, and other diabetes-related problems
.LASEK is an alternate procedure that can be used to treat patients who have thin corneas
. However, LASIK and LASEK both can develop procedure-related complications in patients
.
Single-step t-PRK is a more recent advancement that is unique in that it involves removal of the epithelium and stroma in one single step by an Amaris laser, and studies have found it to be generally safe and efficacious
. Gadde
compared single-step t-PRK to conventional PRK in eyes with low to high myopia and myopic astigmatism and found that both procedures had similar results with respect to safety and efficacy, though there was a higher incidence of postoperative haze in eyes that underwent single-step t-PRK. Higher-order aberrations (HOAs) are a common complication that often develops after refractive surgeries. ?zülken and ?lhan
compared visual acuity and HOAs in eyes with myopia and myopic astigmatism treated with t-PRK or alcohol-assisted PRK and found both of these techniques to have comparable outcomes in all parameters, except aberration coefficient,which seemed to have a better outcome in alcohol-assisted PRK. Another study investigated the relationship between preoperative and surgical factors and postoperative HOAs in low to moderate myopic eyes. It found that HOAs were positively correlated to age and increased when pupil diameter was 6 mm as compared to when it was 3 mm
. A recent study investigated the role of demographics and other preoperative factors following single-step t-PRK to treat myopia and myopic astigmatism and found age to be a strong risk factor for developing ametropia after single-step t-PRK
.
Our study was conducted in Saudi Arabia. This region has a high prevalence of myopia. Moreover, year-round extreme hot and dry weather makes it difficult to wear contact lenses, and as such, refractive surgeries become necessary and are widely practiced in Middle Eastern countries. Hence, it was important to optimize alternative methods, such as single-step t-PRK of correcting vision. We present outcomes of single-step t-PRK to treat myopia and myopic astigmatism at an institution in central Saudi Arabia. In this study, we collectively analyzed various preoperative and operative factors such as age,ablation zone, and HOAs within three grades of myopia
.mild, moderate, and severe, and carried out correlation studies between the factors. Single-step t-PRK is a relatively new technique and our study will enrich the literature on this new procedure.
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
This one-armed cohort study was carried out after the approval of the institution research board. All tenets of the Helsinki Declaration were strictly followed in each stage of the research. This being a retrospective cohort study, the consent of the participants was waived.
Available treatments for correcting myopia include eyeglasses,contact lenses, corneal refractive surgeries, and intraocular lens implantation. High refractive errors usually cannot be corrected by prescription glasses or contact lenses alone.Moreover, many people develop intolerance to contact lenses due to infections, allergies, or improper use of contact lenses.In such cases, alternative methods like refractive surgeries or intraocular lens implantation become necessary.
Demographic information of patients included age, gender, and eye operated. We used Open-Epi’s Stat-calculator for estimating the sample size for this cohort study
. The logMAR notations were used to document both uncorrected visual acuity (UCVA)and best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA). We used a Pentacam camera (OCULUS-Netzteil Art., Pentacam HR, Germany) for corneal topography. Sirius (SCHWIND eye-tech-solutions,GmbH, Kleinostheim, Germany) was used for tomography.HOAs like third-order coma value, third-order trefoil value,fourth-order spherical aberration value, aberration coefficient,and
value were documented. The myopia was graded as mild (<-3.0 D), moderate (-3.0 to -5.9 D), or severe (≥-6.0 D)based on spherical equivalent (SE) values in diopters. The following measurements for each eye were noted for the enrolled patients in the study: UCVA, BCVA, central corneal thickness, keratometry (K
and K
), spherical, cylindrical, and SE refractive power in diopters, cycloplegic refraction, and pupillary diameter in normal daytime illumination in a room.The ablation was performed using an Amaris 500 Hz excimer laser (SCHWIND eye-tech-solutions, GmbH, Kleinostheim,Germany). Antiseptic chlorhexidine gluconate 0.05% solution(Saudi Medical Solution Company) was used to clean theeyelids before surgery and moxifloxacin 0.5% (Vigamox,Alcon Co.) drops were applied. A wire lid speculum was used to keep the eyes open during surgery. Both the epithelium and the stroma were ablated in a single continuous session using an aberration-free and aspheric profile. The ablation plan utilized 55 μm centrally and 65 μm peripherally based on a population-based epithelium thickness profile. Eye movements throughout the ablation were compensated by static and dynamic cyclotorsion corrections. A sponge soaked with 0.02% mitomycin-C was placed over the ablated stroma for 25-35s. The eye was irrigated using copious amounts of balanced salt solution (BSS; Alcon Laboratories, Fort Worth,TX, USA). A soft bandage contact lens with a high diffusion constant of oxygen permeability (Bausch & Lomb, New York,USA) was placed on the cornea until the complete healing of the epithelium. The treatment aimed at achieving emmetropia.The accuracy of the refractive correction was considered as excellent if achieved SE was within 1 D of intended SE for all treated eyes
. The efficiency was defined as postoperative UDVA in logMAR/preoperative CDVA in logMAR. The safety was defined as CDVA 6mo after T-PRK/preoperative CDVA.To calculate S.IOS, we used the formula, spherical difference/SE correction targeted
.
結(jié)合承德市實(shí)際情況,確立水資源開發(fā)利用控制、用水效率控制、水功能區(qū)限制納污“三條紅線”和控制指標(biāo)、實(shí)時(shí)監(jiān)控、考核評(píng)估“三個(gè)體系”,基本形成最嚴(yán)格水資源管理制度框架的總體目標(biāo)。把構(gòu)建水資源監(jiān)控體系作為實(shí)行最嚴(yán)格水資源管理制度的基礎(chǔ)手段和技術(shù)支撐,盡快建成以各縣區(qū)城鎮(zhèn)地表水水源地、規(guī)模以上取用水戶、重要水功能區(qū)、大中型水庫(kù)、省市界和縣區(qū)界河道控制斷面為重點(diǎn)的水資源監(jiān)控體系,實(shí)現(xiàn)監(jiān)測(cè)覆蓋化、網(wǎng)絡(luò)化、信息化,為水資源嚴(yán)格管理提供技術(shù)支撐。
Surgery-induced HOAs are a common complication following refractive surgeries; these are more subtle errors that cannot be easily corrected by the use of simple lenses
. These HOAs are often responsible for halos, blurring, glares, and ghost images, and poor night vision in patients after corrective surgeries
. For example, spherical aberration is a fourthorder aberration that causes a decrease in contrast sensitivity and also causes halos around light sources. Trefoil is a thirdorder aberration that has an effect on image quality, but less so than coma aberration which severely affects vision quality
.The preexisting HOAs increased 6mo after surgery. The increase was significant for spherical aberration and aberration coefficient; while an increase of trefoil aberration was not statistically significant. Several studies have previously confirmed a rise in HOA following t-PRK
. Newer versions of equipment and software for the t-PRK need to address these issues to improve vision and contrast and glare sensitivity complaints of patients after refractive surgeries.Serrao
also noted that in high myopic eyes, the rise of HOAs was more compared to eyes with moderate myopia managed by t-PRK. Perhaps the difference in pupillary diameter in high myopic compared to mild and moderate myopia could have influenced HOAs induced by t-PRK
.
Ablation machine settings for the correction of HOAs need to be based on the grades of myopia, central corneal thickness, as well as pupillary diameter before surgery
.
RESULTS
Our cohort comprised of 154 eyes of 77 myopic patients (mean age, 25.4±5.2y; females,
=47, 61%). Mild, moderate, and severe grades of myopia were in 59 (38.3%), 83 (53.9%), and 12 (7.8%) eyes, respectively.
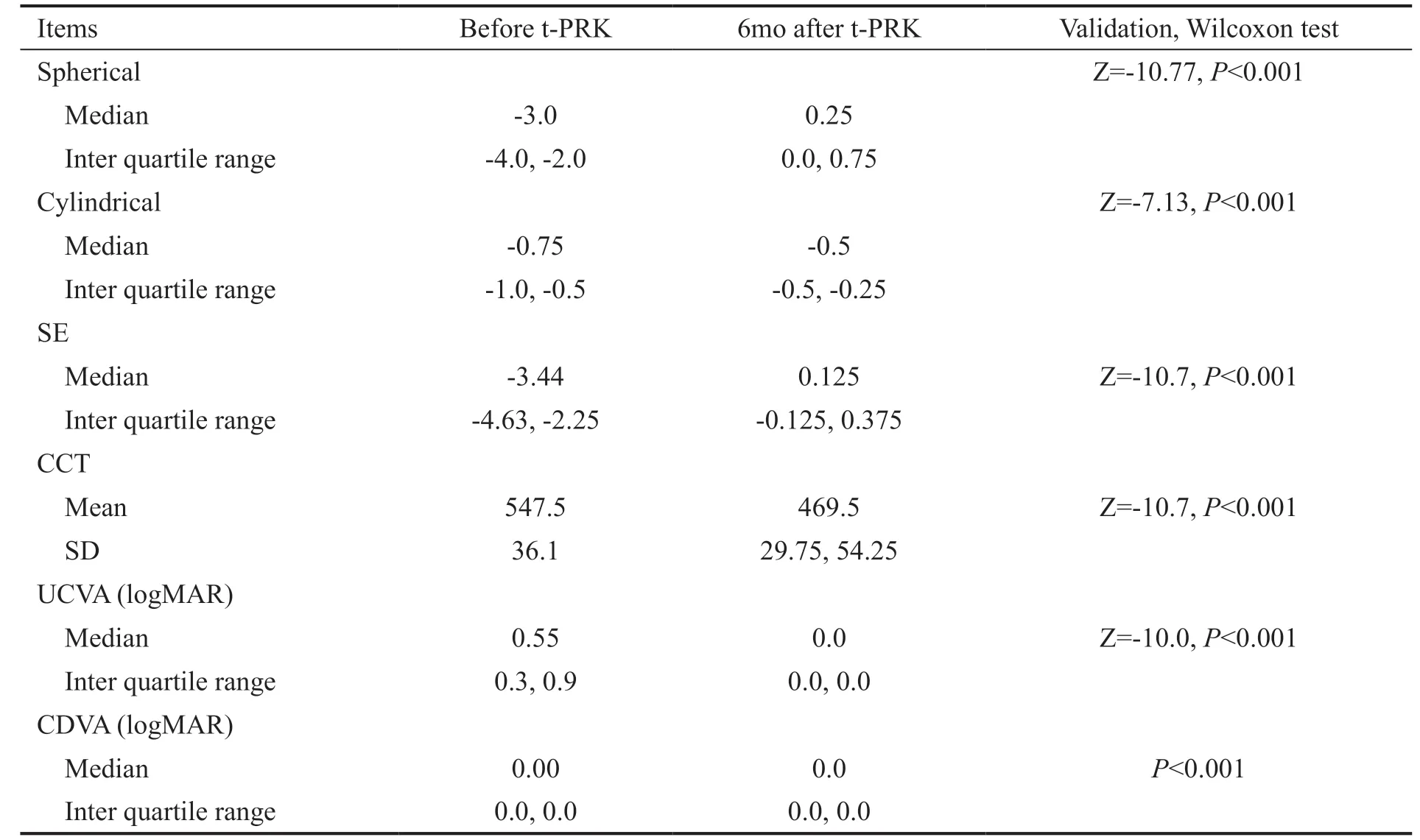
The refractive status, central corneal thickness, and visual acuity before and 6mo after single-step t-PRK are given in Table 1. All eyes had significant improvement in vision and refractive status 6mo after t-PRK compared to before surgery.The median of K1 was 42.9 (IQR 42.0, 43.8) and K2 was 44.0 (IQR 42.9, 44.9) before surgery. The efficiency index of t-PRK in achieving targeted UCVA was 98% and the safety index was 100%. The success in achieving targeted refractive status in eyes 6mo after t-PRK was in 151 eyes (98%; 95%CI 95.9, 100). The efficiency of reaching targeted SE correction is shown in Figure 1.



The median of the S.IOS was 1.18 (IQR 1.0, 1.4). Determinants of S.IOS and correction of SE 6mo after t-PRK to treat myopia are given in Tables 2, 3. S.IOS was positively correlated to age (
=0.007), 6.5 mm ablation zone (
<0.01), and mild and moderate grade of myopia (
<0.001). The SE correction was significantly associated with increase in myopia grade and ablation zone size.
The HOAs before and 6mo after t-PRK using 6 mm diameter of analysis were compared (Table 4, Figure 2). Trefoil aberration, spherical aberration, and aberration coefficient types of HOAs increased significantly after surgery (
<0.001).The change in HOAs at 6mo after t-PRK compared to before surgery in eyes of three different grades of myopia is given in Table 5. With increase in grade of myopia, there was a significant decrease in fourth-order spherical aberration and coefficient of spherical aberration (
<0.05).
學(xué)完“消費(fèi)和消費(fèi)觀”后,筆者給學(xué)生布置的作業(yè)是:(1)了解家里一個(gè)月的收支情況,做一份家庭消費(fèi)觀的調(diào)查,分析家庭開支是否符合正確消費(fèi)原則。(2)設(shè)計(jì)并制作一份關(guān)于勤儉節(jié)約的海報(bào)或倡議書。……
 International Journal of Ophthalmology
2022年5期
International Journal of Ophthalmology
2022年5期
- International Journal of Ophthalmology的其它文章
- Multimodal imaging in immunogammopathy maculopathy secondary to Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia: a case report
- Periorbital necrotizing fasciitis accompanied by sinusitis and intracranial epidural abscess in an immunocompetent patient
- Multimodal imaging in Purtscher-like retinopathy associated with sarcoidosis: a case report
- Can a sneeze after phacoemulsification cause endophthalmitis? A case report
- Persistent macular oedema following Best vitelliform macular dystrophy undergoing anti-VEGF treatment
- Genetic, environmental and other risk factors for progression of retinitis pigmentosa
