Characterization and validation of a chronic retinal neovascularization rabbit model by evaluating the efficacy of anti-angiogenic and anti-inflammatory drugs
INTRODUCTION
Animals with no ocular anomalies, as examined and confirmed by slit-lamp biomicroscopy and indirect ophthalmoscopy, were enrolled onto the study. Ocular discharge and hyperemia was observed after IVT administration of DL-AAA, anti-VEGF and TAA on dosing day but resolved in most animals by the next day,confirming that they were related to ⅠVT injection procedure.Occasional recurrences of ocular discharge were observed in a subset of animals, along with, more rarely, instances of ocular swelling. These symptoms of ocular irritation were likely due to underlying ocular inflammation. Post 12wk of DL-AAA administration, all the animals were presented with moderate to severe retinal/choroidal inflammation and were accompanied by faint to intense vitreous flare and sparse to numerous cells in the vitreous humor (VH). These findings likely reflect infiltration of inflammatory cells into the VH subsequent to persistent posterior inflammation and retinal hemorrhage. A subset of eyes also exhibited posterior lens opacities, likely due to cells from the vitreous space precipitating onto the posterior lens capsule. Sluggish pupillary response was noted in a subset of eyes, was likely also a result of persistent ocular inflammation.Eyes treated with 1 μg/eye of bevacizumab, ranibizumab,aflibercept and TAA had mild inflammation accompanied by very mild vitreous flare and low number of inflammatory cells into the VH, however, controls eyes treated with BSS had moderate to severe retinal/choroidal inflammation with intense vitreous flare and presence of significant number of cells in the VH, suggesting suppression of inflammation and vascular leakage post bevacizumab, ranibizumab, aflibercept and TAA administration. Ocular anomalies were significantly low by day 30 in the eyes treated with bevacizumab, ranibizumab, and aflibercept. However, TAA treated eyes had lowest level on day 7.
Endeavors in ocular medicine has encouraged the ocular research community to not only focus on the development of novel anti-VEGF agents, but to also develop novel sustained drug delivery systems that increase the duration of action for currently available therapies. This is applicable to IVT administration as well as other routes like topical,trans-conjunctival, trans-scleral or suprachoroidal. This approach helps to reduce the frequency, and consequently the risks related to multiple IVT injections and post injection complications like endophthalmitis. The bigger obstacle however to the discovery and development of improved therapies for retinal vascular diseases is the lack of animal models with larger eyes that can mimic the chronic phenotype of human ocular vascular diseases.
Currently available animal models that can be used to test the duration of action of newly developed therapies have some limitations such as a short efficacy window or retinal ocular vascular pathologies which heal rapidly over time. It has been shown that post laser treatment in the laser induced choroidal neovascularization (CNV) model, that VEGF levels reach a peak on day 5 but decline quickly thereafter causing the CNV lesion to completely heal by day 14. The VEGF induced retinopathy model has retinal vascular leakage which peaks on day 3 but returns to baseline levels on day 7 post VEGF IVT injection, resulting in the requirement for repeat IVT injections of active VEGF which in turn may cause post IVT injection related complications. In the current study,we have developed and characterized a DL-2-aminoadipic acid(DL-AAA) (retinal glial cell toxin)induced retinopathy model in pigmented Dutch Belted rabbits and evaluated the duration of action of currently available anti-VEGF and antiinflammatory drugs over a period of 2mo. The DL-AAA rabbits were tested for sustained vascular leakage over 36mo with fluorescein angiography (FA). Additionally, a novel FA grading system was developed to enable accurate and consistent comparison between the drug’s efficacy and it’s duration of action. In summary, we demonstrated that the DLAAA rabbit model represents the most ideal chronic model of retinal vascular leakage that can be utilized to test and develop novel therapies for ocular vascular diseases over an extended period of time.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
All animal experiments adhered to the Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology(ARVO) Statement for the Use of Animals in Ophthalmic and Vision Research. The project was supervised by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) at Absorption Systems, a Pharmaron company, San Diego (CA, USA).
關于公司,鄭斌董事長又一次強調“精益求精”四個字,恰如精密達一直專注于印后。智能化是公司發展的方向,鄭斌董事長對此也有自己的理解:于精密達而言,智能化是一個“在路上”的過程,企業要一直進步和創新。精密達成立的24年里,正是在不斷調整中順應趨勢,經歷必然的發展過程。印刷設備要實現智能化,前提是機械化和自動化。如今,機械化已經實現,自動化正在實現,具有選擇性能的智能化正在努力實現,而在智能化的基礎上還要再實現“互聯網+”,遠程控制等。
Thirty-eight na?ve (19 male and 19 female) Dutch Belted () rabbits, approximately 1.5 to 2.5 kg, were purchased from Western Oregon Rabbit Company(OR, USA). Animals were acclimated for 10d before the enrollment on the study. All animals were maintained with a room temperature between 18℃ and 26℃, a relative humidity between 30% and 70%, and a 12-hour light-dark cycle inhouse under pathogen-free conditions.
Statistical analysis was performed by using the GraphPad Prism 5.0 (GraphPad Software, Inc.,San Diego, CA, USA). Percent of FA scores was compared and plotted among treatments groups. Data was presented as mean±standard error of the mean (SEM).
Animals were anesthetized with an intramuscular injection of ketamine hydrochloride (20 mg/kg) and xylazine (5 mg/kg) prior to surgical procedures. Prior to test/control articles IVT administration, pupils were dilated with topical application of one drop each of 10% phenylephrine and 1% tropicamide on each cornea. A 5% Betadine solution was used to clean the eye and surrounding area. Betadine was applied for 5min,after which the eye was rinsed with balanced salt solution(BSS). After the area was surgically prepared, one to two drops of topical 0.5% proparacaine hydrochloride anesthetic were applied to the animal’s eyes. After surgical procedure,atipamezole hydrochloride (1 mg/kg via intramuscular injection) was used as a reversal agent and after full anesthesia recovery animal received one injection of buprenorphine(0.02 mg/kg via subcutaneous injection). Allimaging procedures were performed without anesthesia.
樁身完整性是檢驗基礎樁是否滿足承載要求的重要指標。通常采用低應變反射法進行測試,這種測試方法的依據是:在激振錘敲擊基礎樁樁頂時,其質點的震動會產生應力波,在應力波從樁頂傳至樁底并反彈回時,樁身的阻抗變化會對應力波形成反射,使得反射信號傳感器接收到的信號在進行計算機分析時,造成曲線的波形、相位、振幅等因素的改變。工作人員會根據這些變化,分析出樁內是否存在縮徑、擴徑、離析、夾泥等情況,進而了解基礎樁的樁長、質量是否達標,并采取必要的措施進行改進。
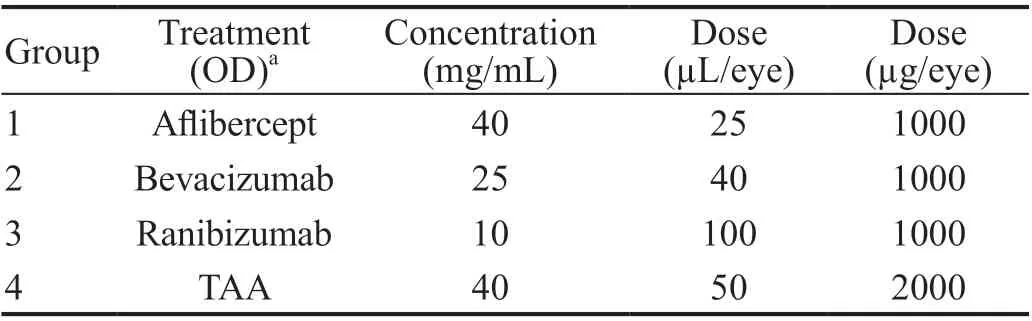
Once stable retinal leakage (12wk post DL-AAA induction) was established in rabbits, following the IVT injection procedure described in the previous section,the right eye was injected with either 40 μL of bevacizumab(solution 25 mg/mL, Genentech), 100 μL of ranibizumab(10 mg/mL, Genentech ), 25 μL of aflibercept (solution 40 mg/mL, Regeneron) at a dose of 1 mg/eye or triamcinolone(TAA; 40 mg/mL, Bristol-Meyers Squibb) at a dose of 2 mg/eye (Table 1). The contralateral eye of each animal received equal volume of BSS. All drugs were delivered into the mid vitreous cavity.
Prior to placement on study,each animal underwent clinical ophthalmic examinations (slitlamp biomicroscopy and indirect ophthalmoscopy) and ocular findings were scored according to a modified McDonald-Shadduck Scoring System. The acceptance criteria for placement on study was scores of “0” for all ocular variables.All animals were assigned to one experimental groups based on body weight for DL-AAA induction for retinal leakage.Post 12wk of DL-AAA induction, 20 animals were assigned a numeric rank from 1 to 20 according their FA scores in a decreasing order (animal with highest FA score was assigned rank =1) into four groups (Table 1).
A 31G beveled needle attached to 0.3 mL insulin syringe was inserted (right eye approximately 11 o’clock position and left eye approximately 1 o’clock)3-4 mm away from the limbus into the vitreous body and 80 μL of the 80 mmol/L DL-AAA solution was administered into the mid vitreous. The needle was removed slowly to reduce risk of back flow from the injection track, and the eye was rinsed with BSS. Triple antibiotic ophthalmic ointment was administered to all eyes after dosing.
The 80 mmol/L DL-AAA solution(Sigma-Aldrich Corp.) was freshly prepared based on published procedures. IVT injections were performed in 2 staggers (Stagger 1:10 males and 9 females; stagger 2:9 males and 10 females). In brief, 120 mg of DL-AAA was dissolved in 1 mL 1 mol/L hydrochloric acid (HCl) to create a stock solution. The components were gently swirled for 5min until a clear solution formed. For IVT administration, DL-AAA stock solution was diluted by adding 4 mL of 0.9% sterile normal saline solution, followed by sufficient 1 mol/L sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to adjust the pH of the solution to 7.4.Sufficient volume of saline was then added to bring the DL‐AAA concentration to 80 mmol/L, the pH was re-tested, and a minimal volume of NaOH (4-5 μL) was added to bring the pH back to 7.4. The solution was then sterile filtered through a disposable 0.2 μm syringe filter to remove any potential particulates. DL-AAA solution was administrated within 15min of formulation preparation. Solutions were kept at room temperature until injection.
FA was performed using Heidelberg Retina Angiograph (HRA) device from Heidelberg Engineering (Heidelberg, Germany), the Spectralis ophthalmic imaging system on both eyes of all animals at baseline (prior to DL-AAA administration) and on weeks 2, 4, 6, 8, and 12 post DL-AAA administration. Additional FA was performed on days 7, 30, and 60 post IVT administration of bevacizumab,ranibizumab, aflibercept and TAA. Ⅰn brief, sodium fluorescein was injected intravenously (IV) and FA time-course images were captured on both eyes between 30s to at least 10min post fluorescein injection. Laser intensity was kept at constant(55%) to avoid any overexposure of FA images. FA images were captured in three areas for retinal vascular leakage: optic nerve head, nasal optic streak, and temporal optic streak. In addition to leakage, any other associated pathology that was secondary to the retinal leakage (such as hemorrhage and retinal detachment) was also imaged. A novel grid based FA grading system was developed based on the published FA scoring system on monkey and rabbits and used for retinal vascular leakage grading.
Infrared (IR) and color fundus imaging were performed at baseline and 2wk post DL-AAA administration.Spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT)imaging was performed using HRA-OCT device from Heidelberg Engineering (Heidelberg, Germany), the Spectralis ophthalmic imaging system on both eyes of all animals at baseline (prior to DL-AAA administration) and on weeks 2, 4, 6,8, and 12 post DL-AAA administration. In brief, OCT sessions were taken on superior/inferior/nasal/temporal and center retinal at 55° field of view using the high-resolution mode(signal quality ≥24 dB) with scan speed of 40 000 A‐scans per second. The image scalingandwere 1.10 μm per pixel and 3.87 μm per pixel, respectively. The optimal focus depth was approximately 3 diopters. Axial resolution was 7 μm optical and 3.5 μm digital. SD‐OCT data were exported as 8‐bit grayscale image.
從公司到我住的地方走20分鐘的路就到了,不用坐公車倒省了我一大麻煩。出公司大門,直走,過紅綠燈,再直走右拐,經過一條巷子,就是我住的小區。那條巷子,快走需要5分鐘,雖然有路燈,但是昏暗的路燈沒有給我多少安全感。今天走到巷子口的時候發現,路燈壞了,眼前的這條路漆黑漆黑,有些不想走,可是這是回家唯一的路,又不得不走,只能硬著頭皮往前走。……
 International Journal of Ophthalmology
2022年1期
International Journal of Ophthalmology
2022年1期
- International Journal of Ophthalmology的其它文章
- lnstructions for Authors
- Comment on: Trends in research related to high myopia from 2010 to 2019: a bibliometric and knowledge mapping analysis
- Progress of clinical therapies for dry age-related macular degeneration
- Observation seasonal variation of intraocular pressure in young healthy volunteers
- Effectiveness of oral probiotics supplementation in the treatment of adult small chalazion
- lmpact of systemic steroids combined with immunosuppressive treatment on glaucomatous features in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus
