Chondrosarcoma of temporal bone: Imaging finding in a rare case report
竇鑫 劉小燕 張利華
[Abstract]:Chondrosarcoma of temporal bone is a primary malignant bone tumor composed of chondrocytes and cartilage matrix. It is common for middle-aged and old people around 50 years old. We report CT and MRI appearances of a 64 year old man with chondrosarcoma of temporal bone that was proven by postoperative pathological examination. This article describes the imaging features of the tumor, which may help to know its characteristic of T2WI high signal, DWI low signal, ADC high signal.We further discuss disease characteristics, pathological characteristics, types, imaging features, differential diagnosis, treatment and prognosis, conclusion .
[Key words] Temporal bone Chondrosarcoma Pathology Imaging Prognosis
【中圖分類號(hào)】R4 【文獻(xiàn)標(biāo)識(shí)碼】A 【文章編號(hào)】1673-9026(2021)11-02
1.Introduction
Chondrosarcomas are malignant tumors that occur in chondrocytes. Most of them were found in long bones, pelvis and scapula, and in the head and neck, accounting for 5% ~ 12%[1]. The primary chondrosarcomas of the skull base account for about 1.5‰[2] of all skull base tumors. However, the primary chondrosarcomas of the temporal bone are very rare.It has been suggested that chondrosarcomas arise from fetal cartilage remains or multipotent mesenchymal cells are involved in tumorigenesis[3]. This article reports the imaging features of a case of well-differentiated chondrosarcoma of the temporal bone, and literature review, in order to deepen the understanding of this disease.
2. Case presentation
A 64-year-old man, right ear intermittent discharge, deafness, tinnitus history 10 years, no special treatment, the main cause of intermittent headache, dizziness 20 days in hospital. Physical examination: old abscess in the right external auditory canal, occasionally a small amount of purulent leakage.
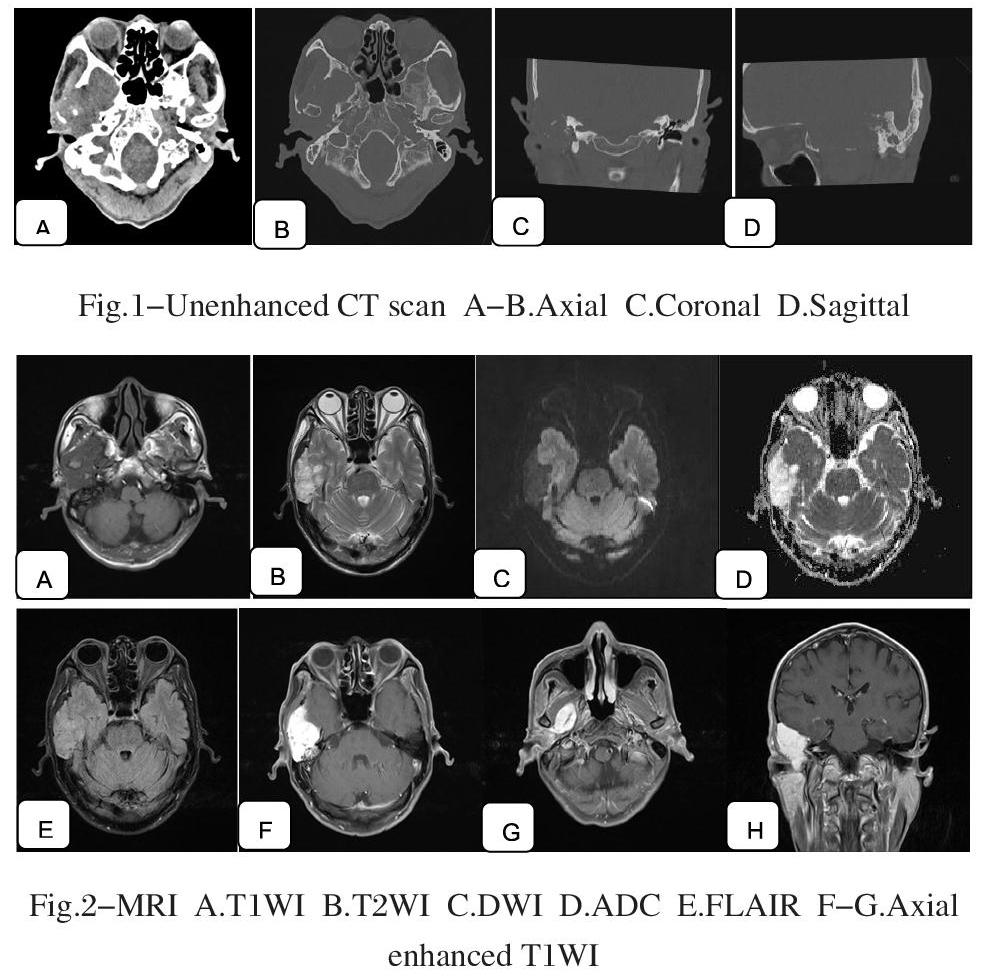
After the hospital examination,the CT findings of the temporal bone showed that the right temporal bone and the large wing of the sphenoid bone were corroded like worms. The lesion is adjacent to the temporal lobe and extends downward to the medial pterygoid muscle.The lesion involved the right inner ear, middle ear, external auditory meatus and temporomandibular joint (Fig. 1). The MRI findings of the right temporal brain were 3.4 * 6.1 * 6.1 cm in size, T1WI low signal intensity, T2WI mixed high signal intensity, FLAIR equal/slightly high signal intensity, DWI low signal intensity, ADC high signal intensity, and enhanced scan shows significant enhancement. The lesion grew to the right infratemporal fossa and penetrated deep into the medial pterygoid muscle with destruction of bone (Fig. 2). The final diagnosis was eosinophilic granuloma of the right temporal region. Surgical findings: part of the right temporal bone was completely eroded by the lesion, part of the lesion was exposed and yellow in color. The lesion was excised in several parts, showing that the blood supply of the lesion was abundant, the petrous bone is partly eroded and a small portion of the lesion penetrates the dura and grows into the subdural space. It was found that the anterior part of the lesion was located in the infratemporal fossa, and the posterior part grew into the extradural part of the middle fossa. Postoperative follow-up: no recurrence or metastasis was observed for two years. Pathological findings: it appears as grey-red nodular broken tissue with grey-white cut surface and total volume of 7cm* 4cm * 3cm. Microscopically, a large number of chondrocytes with slightly heterogeneous nuclei are seen. Immunohistochemical: S-100(+), D2-40(+), R132H(+). Pathological diagnosis: well-differentiated chondrosarcoma of right temporal bone.
3.Discussion
3.1 General characteristics
Chondrosarcomas are most common in the 40 to 70 years old[4], and some literature reports have reported that they often occur in the 50 years old or so[5], and usually occur in sphenoid fissure, occipital fissure, sphenoid scale fissure, pore fissure near oblique fissure and so on[6], the temporal bone is rare. Chondrosarcomas of the temporal bone generally grow slowly, and may not show any symptoms when the tumor mass is small in the early stage. When the tumor mass increases to a certain extent, it presents local mass swelling and corresponding structural and functional disorders [7-8], the length and wide range of lesions usually make it difficult to determine the exact primary site of the tumor. It is easy to grow into adjacent tissues, so it is easy to recur, but with less metastasis. There are no reports of distant metastasis from chondrosarcoma of the temporal bone.
3.2 Pathological characteristics
Chondrosarcomas were pale translucent rotten cartilage-like, light yellow fish flesh-like, gray-red nodules, lobulated masses, medium soft texture, the cut surface was mostly gray-white. Microscopically, the tumor is lobulated, with sheets of chondroid cells varying in size and shape, with mild atypia, and calcification and ossification of the stroma. Immunohistochemistry showed that both cytoplasm and nucleus of tumor cells expressed S-100, cytoplasm expressed D2-40 and Isocitrate dehydrogenase 1.
3.3 Types
Histologically, it can be divided into three subtypes: well-differentiated chondrosarcoma, myxoid chondrosarcoma and mesenchymal chondrosarcoma, of which the most common is well-differentiated chondrosarcoma.
Well-differentiated chondrosarcoma consists mainly of a large number of chondrocytes, common calcification and ossification. Myxoid chondrosarcoma: because the tumor cell stroma is mainly for maid named. Mesenchymal chondrosarcoma: because the tumor is composed of short fusiform mesenchymal cells and highly differentiated chondrocytes [9] .
3.4 Image characteristics
CT findings: slightly low or isodensity irregular soft tissue mass with clear margin. Some of them showed calcification. Some of them were considered to be the important pathologic and imaging features of chondrosarcoma. Most of the lesions involved the skull base sutures or bone fracture joint. The surrounding bone had no sclerotic edge, and the edge was irregular. Non-uniform enhancement on the enhanced scan. The DSA examination showed no obvious blood supply artery.
MRI findings: compared with the adjacent gray matter, T1WI showed low signal intensity, T2WI showed uneven high signal intensity, FLAIR showed equal or slightly high signal intensity, DWI showed low signal intensity, ADC showed high signal intensity, the average ADC value was about 2.1 x 10-3 mm2/ s, enhanced and delayed enhancement, TIC curve increased obviously.Some of the tumors showed rosette-like or separate enhancement due to the rich blood vessels in the periphery and septa. MRS: NAA peak was absent/very low, and the ratio of Cho peak to Cr peak is less than 1[10]
Histopathologic basis: high signal intensity of T2 indicates that the tumor is composed of chondrocytes and cartilage matrix with long T2 relaxation time[11]. The high ADC values were presumed to be related to the presence of a large amount of mucus and cartilage matrix in the tumor, and the low density of tumor cells and the unrestricted movement of water molecules[10]. Delayed enhancement may be related to the presence of a large amount of mucin matrix within the tumor and the role of mucin in the absorption of contrast media [12].
3.5 Differential diagnosis of eosinophilic granuloma
Eosinophilic granuloma is a benign bone tumor-like lesion with reticuloendothelial cell proliferation. It accounts for about 60% of Langerhans histiocytes [13]. From the board, frontal bone is more common, temporal bone is rare. Eosinophilic granuloma of the temporal bone occurs at the age of 1~4 years. The ratio of males to females is approximately 2:1[14]. It is composed mainly of Langerhans cells and is infiltrated with numerous eosinophils, lymphocytes, plasma cells, and neurophils. Immunohistochemistry CD1a (+), S-100 (+)
CT findings: the appearance of irregular perforation-like bone destruction, complete destruction of the inner and outer plates leading to oblique sign or bilateral sign [15] , the destruction scope of the outer plate is larger than that of the inner plate, the edge of the destruction area is clear and not smooth, and slightly higher soft tissue filling can be seen, the soft tissue shadow was more than skull destruction when the lesion broke through skull inner and outer plate, and it was dumbbell shape when protruded to both sides.
MRI findings: isointense on T1WI, moderately hyperintense on T2WI, high/slightly hyperintense on Flair, medium/slightly hyperintense on DWI, mild to moderate inhomogeneous enhancement on enhanced scan, intracranial growth of the lesion, invasion and compression of the dura mater and brain tissue, meningeal tail sign seen on enhanced scan [16]. Eosinophilic granulomas are very different from chondrosarcomas by their general features and imaging findings.
3.6 Treatment and prognosis
As with other chondrosarcomas of the temporal bone, chondrosarcomas are not sensitive to radiotherapy and chemotherapy [4] . Therefore, surgical resection of the tumor is the main treatment. Because of its invasive growth to adjacent tissues, it is difficult to remove completely and has a high recurrence rate. In recent years, some foreign literature suggests that postoperative radiotherapy and chemotherapy can improve the local control rate [17-18] . The prognosis of the patients was related to the degree of differentiation of the tumor, and the prognosis was better in those with high differentiation; 15% of the chondrosarcomas had distant metastasis, but no distant metastasis of the chondrosarcomas of the temporal bone was reported[6]. For the first two years, physical examination, chest x-ray and pathological changes were carried out every 6-12 months, then annually. Local recurrences occur and extensive excision may be continued if resectable[19].
4.Conclusion
If HRCT showed multi-bone worm erosion in skull base, dot-like and flake calcification were found in different areas, and heterogeneous hyperintense lesions were found on T2WI, and the enhancement was obviously enhanced. The ADC value was about (1.96 ± 0.1) x 10-3mm2/ s [10], the ratio of Cho Peak to CR peak is less than 1, so the possibility of highly differentiated chondrosarcoma should be considered.
REFERENCES
[1]張伶,王振常,趙鵬飛.顳骨巖乳交界區(qū)軟骨肉瘤影像表現(xiàn)1例[J].中國(guó)醫(yī)學(xué)影像技術(shù),2017,33(04):642.
[2]F. Cianfriglia and A. Pompili and E. Occhipinti. Intracranial malignant cartilaginous tumours. Report of two cases and review of literature[J]. Acta Neurochirurgica, 1978, 45(1-2) : 163-175.
[3]Arthur G G C Korten,Hans J W ter Berg,Geert H Spincemaille,Ronald T van der Laan,Antoinet M Van de Wel. Intracranial chondrosarcoma: review of the literature and report of 15 cases[J]. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry,1998,65(1):88-92.
[4]陳澤宇,王正敏.顳骨軟骨肉瘤1例[J].臨床耳鼻咽喉科雜志,2006(10):443.
[5]韓朝,陳兵,遲放魯,王紓宜.顳骨軟骨肉瘤1例[J].中國(guó)耳鼻咽喉頭頸外科,2007(05):310.
[6]Brian Neff,Robert Thayer Sataloff,Leslie Storey,Mary Hawkshaw,Joseph R. Spiegel. Chondrosarcoma of the Skull Base[J]. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd,2002,112(1):134-139.
[7]Andrés Coca-Pelaz,Juan P. Rodrigo,Asterios Triantafyllou,Jennifer L. Hunt,Juan C. Fernández-Miranda,Primo? Strojan,Remco Bree,Alessandra Rinaldo,Robert P. Takes,Alfio Ferlito. Chondrosarcomas of the head and neck[J]. European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology,2014,271(10):2601-2609.
[8]Phillip K. Pellitteri,Alfio Ferlito,Johannes J. Fagan,Carlos Suárez,Kenneth O. Devaney,Alessandra Rinaldo. Mesenchymal chondrosarcoma of the head and neck[J]. Oral Oncology,2007,43(10):970-975.
[9]彭澤峰,夏宇,陳風(fēng)華,蔣星軍,李學(xué)軍,楊治權(quán),張明宇.顱底軟骨肉瘤CT、MRI與病理表現(xiàn)[J].中國(guó)醫(yī)學(xué)影像技術(shù),2006(03):398-400.
[10]姜夢(mèng)達(dá),劉玉,陶曉峰,李開成.高分辨率CT、常規(guī)及功能MRI對(duì)顱底低級(jí)別軟骨肉瘤的診斷價(jià)值[J].分子影像學(xué)雜志,2021,44(02):213-218.
[11]盧紅,王健,蔡萍,黎海濤,陳偉.顱底高分化軟骨肉瘤的CT及MRI診斷價(jià)值[J].中國(guó)醫(yī)學(xué)影像學(xué)雜志,2017,25(07):501-504.
[12]Yeom K W,Lober R M,Mobley B C,Harsh G,Vogel H,Allagio R,Pearson M,Edwards M S B,F(xiàn)ischbein N J. Diffusion-weighted MRI: distinction of skull base chordoma from chondrosarcoma.[J]. AJNR. American journal of neuroradiology,2013,34(5):1056-1061.
[13]侯文忠,王琳琳,程敬亮,盧善明,于昭,鄧君良.骨嗜酸性肉芽腫影像學(xué)表現(xiàn)與病理學(xué)的對(duì)比研究[J].現(xiàn)代醫(yī)用影像學(xué),2017,26(02):311-314.
[14]Irving R M,Broadbent V,Jones N S. Langerhans' cell histiocytosis in childhood: management of head and neck manifestations.[J]. The Laryngoscope,1994,104(1 Pt 1):64-70.
[15]馮德勇,劉丹琳,秦勇,翟軒.兒童顱骨嗜酸性肉芽腫的影像學(xué)表現(xiàn)及分型探討[J].局解手術(shù)學(xué)雜志,2014,23(01):14-17.
[16]劉宗才,鄧奇平.單發(fā)性顱骨嗜酸性肉芽腫11例CT和MRI影像分析[J].貴州醫(yī)藥,2013,37(09):837-839.
[17]Chowhan Amit K,Rukmangadha Nandyala,Patnayak Rashmi,Bodapati Chandra Mouliswara Prasad,Bodagala Vijaya Laxmi,Reddy Mandyam Kumaraswamy. Myxoid chondrosarcoma of sphenoid bone.[J]. Journal of neurosciences in rural practice,2012,3(3):395-398.
[18]Nomura Tsutomu,Kobayashi Tadaharu,Shingaki Susumu,Saito Chikara. A case of chondrosarcoma arising in the temporomandibular joint.[J]. Case reports in otolaryngology,2015,2015:832532.
[19]郭衛(wèi),邵增務(wù),張偉濱,葉招明.軟骨肉瘤臨床循證診療指南[J].中華骨與關(guān)節(jié)外科雜志,2018,11(04):302-311.
作者簡(jiǎn)介: First author: 竇鑫 E-mail: 2223169080@qq.com
Corresponding author: 張利華 副主任醫(yī)師 E-mail: hpzlhfsk@126.com

