探討血管外科下肢深靜脈血栓患者實施人性化護理的臨床價值
張廣蘊
【摘要】 目的 探討血管外科下肢深靜脈血栓(DVT)患者實施人性化護理的臨床價值。方法 248例采用同一種溶栓方法治療的血管外科下肢深靜脈血栓患者, 隨機分為觀察組和對照組, 各124例。對照組患者給予血管外科下肢深靜脈血栓常規護理, 觀察組患者在對照組基礎上增加人性化護理。比較兩組患者的護理質量評分、護理操作評分、護理行為評分, 下肢股動脈的血流速度、血流峰速, 不良事件發生率、護理投訴率、滿意度。結果 護理前, 兩組患者的護理質量評分、護理操作評分、護理行為評分比較, 差異均無統計學意義(P>0.05);護理后, 觀察組患者的護理質量評分(86.86±5.49)分、護理操作評分(88.16±4.98)分、護理行為評分(87.72±11.23)分均高于對照組的(72.65±5.31)、(76.93±3.23)、(68.48±9.77)分, 差異均具有統計學意義(P<0.05)。對照組患者的下肢股動脈血流速度為(57.67±7.21)cm/s、血流峰速為(61.15±5.91)cm/s;觀察組患者的下肢股動脈血流速度為(83.45±7.43)cm/s、血流峰速為(92.72±6.56)cm/s。觀察組患者的下肢股動脈血流速度、血流峰速均大于對照組, 差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05)。觀察組患者的不良事件發生率4.84%、護理投訴率8.87%均低于對照組的17.74%、37.10%, 滿意度90.32%高于對照組的55.65%, 差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05)。結論 血管外科下肢深靜脈血栓患者實施人性化護理有著良好的應用效果, 可以明顯提高護理質量, 對患者的恢復有著良性的作用, 值得在臨床中推廣。
【關鍵詞】 血管外科;下肢深靜脈血栓;人性化護理
DOI:10.14163/j.cnki.11-5547/r.2020.31.080
Clinical value of humanized nursing for patients with lower extremity deep venous thrombosis in vascular surgery? ?ZHANG Guang-yun. Department of Surgery, Peoples Hospital of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, Hohhot 010017, China
【Abstract】 Objective? ?To discuss the clinical value of humanized nursing for patients with lower extremity deep venous thrombosis (DVT) in vascular surgery. Methods? ?A total of 248 patients with deep venous thrombosis of lower extremity in vascular surgery treated by the same thrombolytic method were randomly divided into observation group and control group, with 124 cases in each group. The control group received routine nursing of lower extremity deep venous thrombosis in vascular surgery, and the observation group received humanized nursing on the basis of the control group. The nursing quality score, nursing operation score, nursing behavior score, blood flow velocity and peak velocity of lower extremity femoral artery, incidence of adverse events, nursing complaint rate and satisfaction were compared between the two groups. Results? ?Before nursing, there was no statistically significant difference in nursing quality score, nursing operation score, nursing behavior score between the two groups (P>0.05). After nursing, the nursing quality score (86.86±5.49) points, nursing operation score (88.16±4.98) points, nursing behavior score (87.72±11.23) points of the observation group were higher than (72.65±5.31), (76.93±3.23) and (68.48±9.77) points of the control group, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). The blood flow velocity and peak velocity of lower extremity femoral artery of the control group were (57.67±7.21) and (61.15±5.91) cm/s, which were (83.45±7.43) and (92.72±6.56) cm/s of the observation group. The blood flow velocity and peak velocity of lower extremity femoral artery of the observation group was faster than those of the control group, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). The incidence of adverse events 4.84%, nursing complaint rate 8.87% of the observation group were lower than 17.74% and 37.10% of the control group, and satisfaction rate 90.32% was higher than 55.65% of the control group, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Conclusion? ?The implementation of humanized nursing has a good practical effect for patients with lower extremity deep venous thrombosis in vascular surgery, which can significantly improve the quality of nursing, has a benign role in the recovery of patients, and is worthy of clinical promotion.
【Key words】 Vascular surgery; Lower extremity deep venous thrombosis; Humanized nursing
隨著社會生活的發展、飲食習慣的改變, 下肢深靜脈血栓患者的數量在不斷增加[1, 2]。因此如何增強下肢深靜脈血栓患者的護理也成為了現階段的一個問題[3, 4]。為了探討血管外科下肢深靜脈血栓患者實施人性化護理的臨床價值, 作者選取本院2018年3月~2020年3月在本院血管外科收治的血管外科下肢深靜脈血栓患者248例, 將患者隨機分為觀察組和對照組, 分別進行護理觀察, 現將結果報告如下。
1 資料與方法
1. 1 一般資料 選取本院2018年3月~2020年3月收治的均采用同一種溶栓方法治療的血管外科下肢深靜脈血栓患者248例, 隨機分為觀察組和對照組, 各124例。觀察組患者中男63例, 女61例, 平均年齡(53.67±14.78)歲;對照組患者中男64例, 女60例, 平均年齡(55.01±14.65)歲。兩組患者的一般資料比較, 差異無統計學意義(P>0.05), 具有可比性。所有患者及家屬均同意參加本次研究且經倫理委員會批準。
1. 2 方法 對照組患者給予血管外科下肢深靜脈血栓常規護理。觀察組患者在對照組基礎上增加人性化護理。人性化護理包括:①情緒安撫:下肢深靜脈血栓患者常有下肢疼痛的表現, 使患者產生較重的心理負擔。護理時, 應積極與患者交流, 為患者提供有針對性的疏導。②飲食指導:不宜食用辛辣刺激性食物, 指導其多食用富含蛋白質、維生素以及低脂肪類食物, 多進食新鮮果蔬。③健康教育:采取適當的語言向患者普及有關 DVT 的形成原因、臨床表現、治療方法及護理要點等知識, 以增強患者的配合。④指導患者用藥:經患肢足背靜脈給藥時, 需稍微上抬患肢呈 30°;經腘靜脈給藥者, 則需妥善固定導管, 并定期檢查等。
1. 3 觀察指標及判定標準 ①比較兩組患者的護理質量評分、護理操作評分、護理行為評分, 評分越高, 護理質量越好。②比較兩組患者的下肢股動脈血流速度、血流峰速, 均采用超聲多普勒法檢測。③比較兩組患者的不良事件發生率、護理投訴率、滿意度。
1. 4 統計學方法 采用SPSS22.0統計學軟件進行統計分析。計量資料以均數±標準差( x-±s)表示, 采用t檢驗;計數資料以率(%)表示, 采用χ2檢驗。P<0.05表示差異具有統計學意義。
2 結果
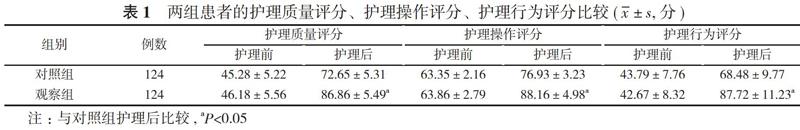
2. 1 兩組患者的護理質量評分、護理操作評分、護理行為評分比較 對照組患者護理前的護理質量評分為(45.28±5.22)分、護理操作評分為(63.35±2.16)分、護理行為評分為(43.79±7.76)分;護理后的護理質量評分為(72.65±5.31)分、護理操作評分為(76.93±3.23)分、護理行為評分為(68.48±9.77)分。觀察組患者護理前的護理質量評分為(46.18±5.56)分、護理操作評分為(63.86±2.79)分、護理行為評分為(42.67±8.32)分;護理后的護理質量評分為(86.86±5.49)分、護理操作評分為(88.16±4.98)分、護理行為評分為(87.72±11.23)分。護理前, 兩組患者的護理質量評分、護理操作評分、護理行為評分比較, 差異均無統計學意義(P>0.05);護理后, 觀察組患者的護理質量評分、護理操作評分、護理行為評分均高于對照組, 差異均具有統計學意義(P<0.05)。見表1。
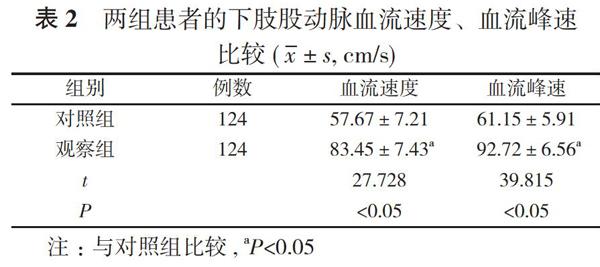
2. 2 兩組患者的下肢股動脈血流速度、血流峰速比較 對照組患者的下肢股動脈血流速度為(57.67±7.21)cm/s、血流峰速為(61.15±5.91)cm/s;觀察組患者的下肢股動脈血流速度為(83.45±7.43)cm/s、血流峰速為(92.72±6.56)cm/s。觀察組患者的下肢股動脈血流速度、血流峰速均大于對照組, 差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05)。見表2。
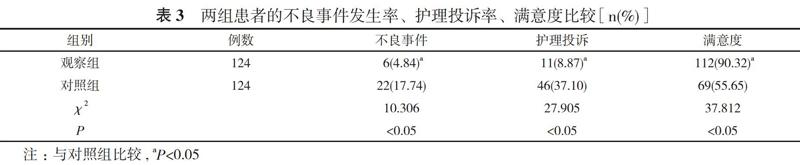
2. 3 兩組患者的不良事件發生率、護理投訴率、滿意度比較 觀察組患者的不良事件發生率4.84%、護理投訴率8.87%均低于對照組的17.74%、37.10%, 滿意度90.32%高于對照組的55.65%, 差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05)。見表3。
3 討論
人性化護理是近年來新興的護理方式, 是一種有效的護理手段[5, 6]。為了探討血管外科下肢深靜脈血栓患者實施人性化護理的臨床價值, 作者選取本院2018年3月~2020年3月血管外科收治的下肢深靜脈血栓患者248例, 將患者隨機分為觀察組和對照組, 進行護理觀察。結果顯示, 護理前, 兩組患者的護理質量評分、護理操作評分、護理行為評分比較, 差異均無統計學意義(P>0.05);護理后, 觀察組患者的護理質量評分(86.86±5.49)分、護理操作評分(88.16±4.98)分、護理行為評分(87.72±11.23)分均高于對照組的(72.65±5.31)、(76.93±3.23)、(68.48±9.77)分, 差異均具有統計學意義(P<0.05)。對照組患者的下肢股動脈血流速度為(57.67±7.21)cm/s、血流峰速為(61.15±5.91)cm/s;觀察組患者的下肢股動脈血流速度為(83.45±7.43)cm/s、血流峰速為(92.72±6.56)cm/s。觀察組患者的下肢股動脈血流速度、血流峰速均大于對照組, 差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05)。觀察組患者的不良事件發生率4.84%、護理投訴率8.87%均低于對照組的17.74%、37.10%, 滿意度90.32%高于對照組的55.65%, 差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05)。說明血管外科下肢深靜脈血栓患者實施人性化護理有著良好的應用效果, 可以明顯改善護理人員的護理質量情況, 減少護理人員失誤情況, 同時對患者的恢復有著良性的作用, 明顯改善護患關系。
許芳[7]研究發現, 血管外科下肢深靜脈血栓患者實施人性化護理有著良好的應用效果, 與本研究的結果相似, 說明了血管外科下肢深靜脈血栓患者實施人性化護理有著良好的應用效果, 可以明顯的改善患者的臨床癥狀, 對患者的康復有著良性的影響。
綜上所述, 血管外科下肢深靜脈血栓患者實施人性化護理有著良好的應用效果, 可以明顯護理質量情況, 減少護理人員失誤情況, 對患者的恢復有著良性的作用, 值得在臨床中推廣。
參考文獻
[1] Rinde FB, Fronas SG, Ghanima W, et al. D-dimer as a stand-alone test to rule out deep vein thrombosis. Thromb Res, 2020(191):134-139.
[2] Liu XC, Chen XW, Li ZL, et al. Anatomical distribution of lower-extremity deep venous thrombosis in patients with acute stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis, 2020, 29(7):104866.
[3] 王秀英, 張玉希, 閻寧. 人性化護理在直腸癌術后下肢深靜脈血栓形成預防中的應用. 血栓與止血學, 2020, 26(3):537-538.
[4] Rabinovich A, Gu CS, Vedantham S, et al. External validation of the SOX-PTS score in a prospective multicenter trial of patients with proximal deep vein thrombosis. J Thromb Haemost, 2020, 18(6):1381-1389.
[5] Mioc ML, Prejbeanu R, Vermesan D, et al. Deep vein thrombosis following the treatment of lower limb pathologic bone fractures-a comparative study. Bmc Musculoskeletal Disorders, 2018, 19(1):213.
[6] Theerakulpisut D, Wongsurawat N, Somboonporn C. Detection of Lower Limb Deep Vein Thrombosis: Comparison between Radionuclide Venography and Venous Ultrasonography.World Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 2018, 17(1):27-33.
[7] 許芳. 探討血管外科下肢深靜脈血栓(DVT)患者實施人性化護理的臨床價值. 臨床醫藥文獻電子雜志, 2020, 7(25):14-15.
[收稿日期:2020-06-19]

