吞咽石蠟油置胃管法的臨床有效性研究
夏秋燕

[摘要] 目的 探討吞咽石蠟油置胃管法的臨床有效性研究。 方法 選擇2019年1~11月進行治療的患者90例作為對象,隨機數字表分為對照組(n=45)和觀察組(n=45)。對照組給予常規經鼻置胃管,觀察組采用吞咽石蠟油置胃管法,比較兩組患者的置管效果以及置管后不良并發癥。 結果 觀察組患者一次成功置管的例數顯著高于對照組(P<0.05)。觀察組患者置管過程中惡心、置管過程中嘔吐的情況顯著低于對照組(P<0.05)。觀察組患者出現咽喉不適癥狀、聲帶沙啞癥狀、食道出血癥狀及鼻腔出血癥狀的情況顯著低于對照組(P<0.05)。 結論 使用吞咽石蠟油置胃管法,有助于提高患者的置管成功率并減少了并發癥,值得推廣應用。
[關鍵詞] 吞咽石蠟油置胃管法;常規經鼻置胃管;置管成功率;不良癥狀;臨床應用
[中圖分類號] R473? ? ? ? ? [文獻標識碼] B? ? ? ? ? [文章編號] 1673-9701(2020)16-0176-03
Research on clinical efficacy of setting gastric tube after swallowing paraffin oil
XIA Qiuyan
First Department of General Surgery, Jiujiang First People's Hospital in Jiangxi Province, Jiujiang? ?332000, China
[Abstract] Objective To explore the clinical efficacy of setting gastric tube after swallowing paraffin oil. Methods Ninety patients treated from January 2019 to November 2019 were selected as research subjects and were divided into the control group(n=45) and the observation group(n=45) by the random number table. Routine transnasal gastric catheterization was given to the control group, and the observation group adopted the method of setting gastric tube after swallowing paraffin oil. The catheterization effect and adverse complications after catheterization in the two groups were compared. Results The number of successful catheterization in one time in the observation group was significantly higher than that in the control group(P<0.05). The incidences of nausea and vomiting during the catheterization in the observation group were significantly lower than those in the control group(P<0.05). The incidences of laryngeal discomfort, hoarseness, esophageal bleeding and nasal bleeding in the observation group were significantly lower than those in the control group(P<0.05). Conclusion The method of setting gastric tube after swallowing paraffin oil can improve the success rate of catheterization and reduce complications, which is worthy of popularization and application.
[Key words] Method of setting gastric tube after swallowing paraffin oil; Routine transnasal gastric catheterization; Success rate of catheterization; Adverse symptoms; Clinical application
胃置管是目前臨床醫學較為常用的一種醫療技術,對于患者來說屬于一種侵入式的操作。當前較為常見的胃置管方式以經鼻胃置管為主,這種方式難以一次性成功置管,患者在置管后還容易出現咽喉不適等不良癥狀[1-2]。而吞咽石蠟油置胃管法在常規置管方式上進行良好的改善,有效降低常規置管方式的弊端,且臨床應用越發廣泛[3]。但是當前對于此方面的研究較少,因此,本文采用隨機對照方法進行研究,探討吞咽石蠟油置胃管法的臨床有效性研究,現報道如下。
1 資料與方法
1.1 臨床資料
選擇2019年1~11月進行治療的患者90例作為對象,隨機數字表分為對照組(n=45)和觀察組(n=45)。對照組45例,男20例,女25例,年齡10~80歲,平均(45.22±6.01)歲。病理類型:創傷性蛛網膜下腔出血5例,頸脊髓損傷并截癱5例,基底節出血4例,頸脊髓損傷6例,腦外傷術后3例,腦外傷后遺癥2例,腦外傷、器質性精神障礙4例,腦出血4例,丘腦出血2例,染料中毒性腦病2例,一氧化碳中毒遲發性腦病7例,腦梗死1例。觀察組45例,男19例,女26例,年齡12~66歲,平均(39.15±5.97)歲。病理類型:病毒性腦炎后遺癥5例,腦梗死、血管性癡呆4例,腦出血后遺癥1例,脫髓鞘性腦病4例,抑郁障礙3例,視網膜病變3例,一氧化碳中毒6例,腦出血4例,一氧化碳中毒遲發性腦病8例,腦梗死7例。兩組患者的臨床資料比較均無統計學意義(P>0.05)。
1.2 納入、排除標準
納入標準:(1)患者均第一次進行經鼻置管治療[4]。(2)患者均同意本次研究且配合醫護人員對其進行相關數據調查統計[5]。排除標準:(1)患有其他呼吸系統、神經類疾病[6]。(2)不能積極認真配合醫護人員治療的患者[7-8]。
1.3 實驗方法
對照組患者給予常規經鼻置胃管的方式,首先要求醫護人員進行手部清潔并帶好手套、口罩,準備相關器具并對患者進行步驟說明與置管過程中可能出現的現象,幫助患者減輕心理壓力。指導患者采取半坐臥位并鋪好治療巾,對患者可正常順利呼吸的一側鼻孔進行清潔,為置管措施做好準備。在取出胃管并消毒處理后測量其長度,并根據患者鼻尖到耳垂再到胸骨劍的長度確定插入的長度,進行插管。在成功插管后應使用紗布幫助患者清理口角異物并使用膠布以及紗布進行固定。此外要定期詢問患者感受,并幫助患者采用較為舒適的臥位進行修養。觀察組患者采用吞咽石蠟油置胃管法,首先要求與對照組實施相同的操作手段,但是,在對患者清潔好某一側鼻孔后,讓患者在醫護人員的指導下吞咽10~15 mL的石蠟油后,醫護人員快速將胃管插入,在插入胃管的長度達到14~16 cm時讓患者做吞咽的動作并順勢將胃管送入胃內。如果在連接氬氣后可以馬上看到部分的胃液與石蠟油已經順著胃管流出,證明插管成功。
1.4 觀察指標
(1)兩組患者置管效果比較。要求醫護人員觀察并記錄一次成功置管的患者例數、置管過程中出現惡心的患者例數以及置管過程中嘔吐的患者例數,并分別計算三種情況的百分比[9]。(2)兩組患者置管后不良并發癥比較。觀察并記錄兩組患者在置管成功后出現咽喉不適、聲帶沙啞、食道出血、鼻腔出血的患者例數并計算發生率[10]。
1.5統計學分析
采用SPSS22.0軟件處理,計數資料行χ2檢驗,采用[n(%)]表示,計量資料行t檢驗,采用(x±s)表示,P<0.05為差異有統計學意義。
2 結果
2.1 兩組患者的置管效果比較
觀察組患者一次成功置管的例數顯著高于對照組(P<0.05)。觀察組患者置管過程中惡心、置管過程中嘔吐的情況顯著低于對照組(P<0.05),見表1。
2.2 兩組患者置管后不良并發癥比較
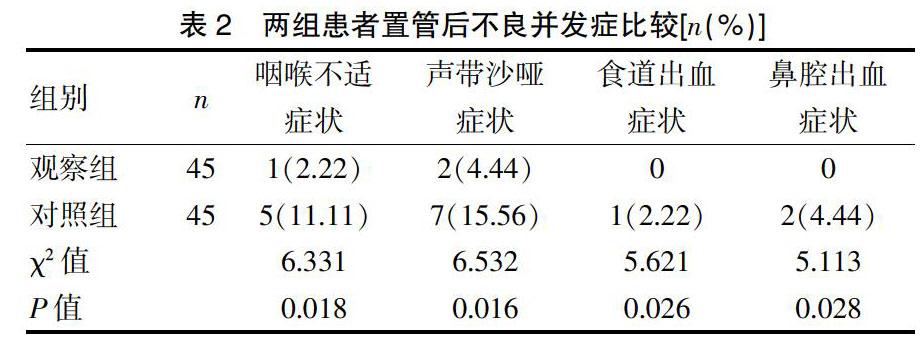
觀察組患者置管后不良并發癥顯著低于對照組(P<0.05),見表2。
3 討論
近些年,隨著社會經濟水平與人們生活質量的提高,患者及家屬對于醫療手段的要求已經不僅僅局限于治療好疾病,提高痊愈的可能性,也更加希望可以通過更為先進的科學技術,減輕在治療過程中產生的疼痛,提高治療的安全性等[11-13]。胃置管是目前經常使用的一種治療措施。尤其是對于創傷性蛛網膜下腔出血、基底節出血、腦梗死、一氧化碳中毒遲發性腦病等重大疾病的患者來說,進行胃置管是必不可少的步驟。胃置管作為臨床醫學中經常用來觀測患者病情狀態、治療相關疾病的一種醫療技術,由于在操作過程中需要在醫護人員的專業操作下將胃管插入患者胃內并進行留置,導致很多患者不僅在心理上難以接受,還為患者帶來了很多生理上的痛苦[14-15]。這要求對于該類患者,在進行置管之前,不僅要進行心理上的疏通指導、提高主動配合性,還要不斷加強醫護人員的置管專業性,爭取提高置管成功率,避免二次置管給患者造成的疼痛[16]。相關資料顯示,如果想要成功置管,不僅與以上因素密切相關,更需要患者的吞咽配合。但是,由于患者在進行胃置管操作前是禁止食用任何食物的,且不能飲水,此時患者的咽喉部極為干燥,這致使常規的經鼻置管方法在胃管經過患者的咽喉處時造成的摩擦加大,極易出現惡心嘔吐的狀況,無法到達配合吞咽[17]。這在很大程度上影響了置管的成功率。而吞咽石蠟油置胃管法,在常規操作的基礎上讓患者吞咽了石蠟油,這有效提高了咽喉處的潤滑性,加上醫護人員快速的插管技術,提高一次性置管成功的幾率,與此同時也讓患者減少在置管過程中出現惡心、嘔吐的狀況。在本研究中,觀察組患者一次成功置管的例數顯著高于對照組(P<0.05)。觀察組患者置管過程中惡心、置管過程中嘔吐的情況顯著低于對照組(P<0.05),由此可見,與常規的經鼻胃置管的方式相比較,使用吞咽石蠟油置胃管法,能夠極大的提高置管成功率。置管成功率的提高為降低患者因置管帶來的痛苦提供保障。
石蠟油屬于一種礦物油,無毒無害。醫用的石蠟油在患者的腸內不易被吸收消化,在臨床醫學中主要發揮潤滑的作用,在經鼻胃置管操作中的應用主要是幫助增加患者咽喉處、食道等部位的潤滑度,以此達到順利置管并減輕留置后患者身體痛苦的作用[18-19]。對于患者來說,在進行成功置管后,患者時常出現咽喉不適、聲帶沙啞的癥狀,甚至會導致食道出血、鼻腔出血等不良癥狀的出現,嚴重影響著患者的身體康復[20]。而吞咽石蠟油置胃管法在常規置管方式的基礎配以吞咽石蠟油的方式,為患者增加一層無形的保護膜,降低了不良癥狀的產生[21-22]。在本研究中,觀察組患者一次成功置管的例數顯著高于對照組(P<0.05)。觀察組患者置管過程中惡心、置管過程中嘔吐的情況顯著低于對照組(P<0.05),說明對于患者來說,與常規經鼻胃置管的方式相比較,吞咽石蠟油置胃管法的應用成功降低了患者在留置管期間出現咽喉不適、聲帶沙啞、食道出血以及鼻腔出血的不良癥狀,這不僅有助于患者的康復治療,還可以減輕對患者在生活中產生的不便。
綜上所述,吞咽石蠟油置胃管法的應用有效提高了置管的成功率,幫助減輕了患者的置管痛苦,同時降低了置管過程中以及置管后等不良癥狀的產生,屬于較為理想的置管方式,值得推廣應用。
[參考文獻]
[1] Chrystoja Caitlin C,Darling Gail E,Diamant Nicholas E,et al. Achalasia-Specific Quality of Life After Pneumatic Dilation or Laparoscopic Heller Myotomy With Partial Fundoplication:A Multicenter,Randomized Clinical Trial[J].American Journal of Gastroenterology,2016,111(10):44-46.
[2] Lin Z,Sarosiek I,Forster J,et al. Is chronic high-frequency gastric electrical stimulation effective in patients with chronic functional nausea and vomiting and a normal gastric emptying?[J]. Journal of Investigative Medicine,2016,54(1):S269.
[3] Chen Du,Ning-Li Chai,En-Qiang Ling-Hu,et al. Submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection:An effective and safe therapy for upper gastrointestinal submucosal tumors originating from the muscularis propria layer[J]. World Journal of Gastroenterology,2019,25(2):245-257.
[4] 樊曉靜. 胃腸手術患者胃管不同處理策略對術后并發癥風險及胃腸恢復的影響[J]. 實用醫學雜志,2016,32(18):3060-3063.
[5] Jong Chi Oh. Effect of partial head extension swallowing exercise on the strength of the suprahyoid and tongue muscles in healthy subjects:A feasibility study[J]. Journal of Oral Rehabilitation,2018,46(3):900-914.
[6] Aggarwal Rajesh,Brown Kimberly M,de Groen Piet C,et al. Simulation Research in Gastrointestinal and Urologic Care—Challenges and Opportunities:Summary of a National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases and National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering Workshop[J]. Annals of Surgery,2018, 267(2):20-23.
[7] Karoline Freeman,Hema Mistry,Alexander Tsertsvadze,et al. Multiplex tests to identify gastrointestinal bacteria,viruses and parasites in people with suspected infectious gastroenteritis:A systematic review and economic analysis[J]. Health Technology Assessment,2017,21(23):188.
[8] Nicolas Kerckhove,Julien Scanzi,Bruno Pereira,et al. Assessment of the effectiveness and safety of ethosuximide in the treatment of abdominal pain related to irritable bowel syndrome-IBSET:protocol of a randomised,parallel,controlled,double-blind and multicentre trial[J]. Bmj Open,2017,7(7):34-38.
[9] Anne-Marie A Verenna,Kim A Noble,Helen E Pearson,et al. Role of comprehension on performance at higher levels of Bloom's taxonomy:Findings from assessments of healthcare professional students[J]. Anatomical Sciences Education,2018,11(1):102-107.
[10] 肖鑫,欒思源,楊玉賞,等. 錐形管狀胃聯合頸部端端分層吻合在胸腹腔鏡食管癌切除術中的應用價值[J]. 中華消化外科雜志,2019,18(6):542-548.
[11] 楊昆,胡建昆. 胃腫瘤圍手術期胃管放置所致并發癥[J].中華胃腸外科雜志,2017,20(2):173-174.
[12] Nicola Pusterla,Samantha Barnum,Kirsten Kenelty. Comparison of flocked and rayon swabs for the molecular detection of selected equine viruses and bacteria from nasal secretions of healthy horses[J]. Veterinary Record,2017,181(8):197-199.
[13] Adam Bobkiewicz,Adam Studniarek,Lukasz Krokowicz,et al. Gastrointestinal tract anastomoses with the biofragmentable anastomosis ring:is it still a valid technique for bowel anastomosis? Analysis of 203 cases and review of the literature[J]. International Journal of Colorectal Disease,2016,32(1):107-111.
[14] 代小探,李子海,張百江,等. 胃管內引流在治療食管癌術后胸內局限性縱隔瘺中的應用[J]. 實用醫學雜志,2016,32(20):3458-3459.
[15] Yigang Xu,Xiaolin Zong,Bing Han,et al. Lactobacillus pentosus expressing porcine lactoferrin elevates antibacterial activity and improves the efficacy of vaccination against Aujeszky's disease[J]. Acta Veterinaria Hungarica,2016,64(3):289-300.
[16] Avinash Mishra,Justine J Sheppard,Cagla Kantarcigil,et al. Novel Mealtime Duration Measures:Reliability and Preliminary Associations With Clinical Feeding and Swallowing Performance in Self-Feeding Children With Cerebral Palsy[J]. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology,2017,27(1):1-8.
[17] 張群,吳洪磊. 改進固定胃管的方法與應用研究[J]. 中國全科醫學,2016,19(12):1482-1484.
[18] 王翠娥,陳祥榮,朱蓉蓉,等. 鼻腸管與鼻胃管腸內營養對重型顱腦損傷患者預后和并發癥、炎癥反應和腸黏膜屏障功能的影響[J]. 中華神經醫學雜志,2017,16(6):599-603.
[19] 李娜,趙春光,張桂香. 急性胰腺炎患者應用三腔營養管與螺旋胃管給予腸內營養的效果觀察[J]. 中國內鏡雜志,2016,22(5):30-34.
[20] 任晉瑞,甄自剛,任少華,等. 鼻腸管聯合鼻胃管的腸內營養方式治療重型顱腦損傷患者的療效分析[J]. 中華神經外科雜志,2018,34(11):1143.
[21] Roganie Govender. Patient Experiences of Swallowing Exercises After Head and Neck Cancer:A Qualitative Study Examining Barriers and Facilitators Using Behaviour Change Theory[J]. Dysphagia,2017,3(10):2-8.
[22] Sahm F,Ochs K,Bunse L,et al. OS2.4 Expression and relevance of tumoral and stromal MHC class II in gliomas[J]. Neuro-Oncology,2016,18(4):1-3.
(收稿日期:2019-12-26)

