基于網絡藥理學的黨參干預腸易激綜合征作用機制研究
蒙潔 陳冬梅 劉佳佳 李丹丹 王晶
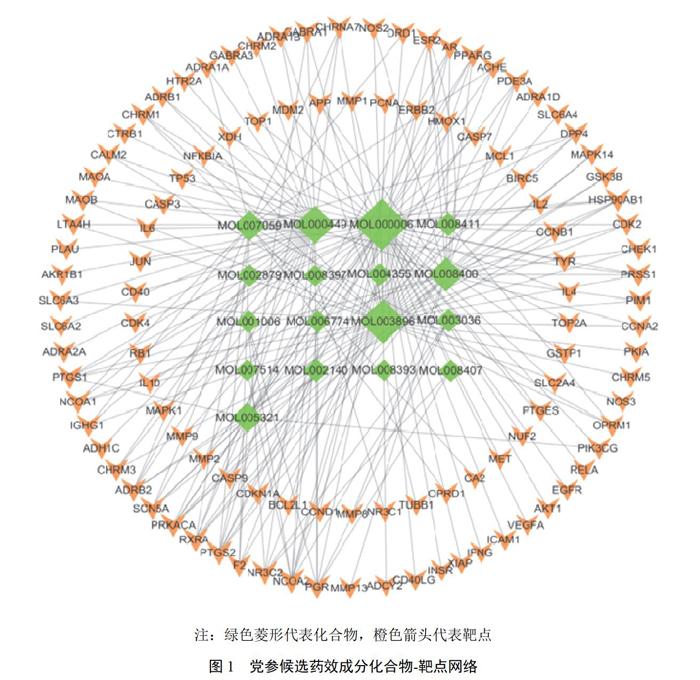


摘要:目的? 基于網絡藥理學探討黨參治療腸易激綜合征的作用靶點和作用機制。方法? 通過中藥系統藥理學數據庫與分析平臺(TCMSP)篩選出黨參口服生物利用度≥30%和類藥性≥0.18的化合物作為候選藥效成分,利用HTDocking平臺預測與候選藥效成分匹配的靶蛋白,采用Cytoscape3.7.0軟件構建化合物-靶點網絡。通過GeneCards、NCBI和OMIM數據庫查找腸易激綜合征相關基因,利用Cytoscape3.7.0繪制疾病基因蛋白相互作用網絡,并與黨參化合物-靶點網絡進行映射,發現黨參治療腸易激綜合征的關鍵化合物和潛在作用靶點。使用Funrich3.1.3軟件對潛在作用靶點進行GO功能注釋和KEGG通路富集,對黨參治療腸易激綜合征的作用機制做出合理推測。結果? 共得到黨參候選藥效成分17個,預測作用靶點111個,腸易激綜合征相關基因1368個,黨參治療腸易激綜合征的關鍵化合物15個,潛在作用靶點55個(包括IL6、PTGS2、AKT1、EGFR、IL2、IL10、IL4等),靶點參與的功能主要有免疫應答、炎癥反應等,主要富集通路有TRAILA信號通路、TNF信號通路等448條。結論? 黨參可能通過調節PTGS2等炎癥因子,參與TRAIL信號通路、TNF信號通路等途徑,調節免疫反應,從而達到治療腸易激綜合征的目的。
關鍵詞:黨參;腸易激綜合征;免疫反應;炎癥因子;網絡藥理學
中圖分類號:R259.744;R2-05? ? 文獻標識碼:A? ? 文章編號:1005-5304(2020)01-0080-06
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-5304.201903174
Study on Mechanism of Codonopsis Radix in Treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Based on Network Pharmacology
MENG Jie, CHEN Dongmei, LIU Jiajia, LI Dandan, WANG Jing
Gansu University of Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730000, China
Abstract: Objective To explore the targets and mechanism of Codonopsis Radix in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) based on network pharmacology. Methods Compounds with oral bioavailability of 30% or more and drug-like ratio of 0.18 or higher in Codonopsis Radix were screened as candidate drug-effect components by TCMSP database, and then the biomacromolecules matched with candidate drug-effect components were extracted by HTDocking platform. The compound-target interaction network was constructed by Cytoscape 3.7.0. The genes for IBS was searched by GeneCards, NCBI and OMIM, and the protein interaction (PPI) network was mapped using cytoscape 3.7.0, and mapping with the compound-target network of Codonopsis Radix revealed the key compounds and potential targets of Codonopsis Radix in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome. Funrich 3.1.3 software was used to perform GO function annotation and KEGG pathway enrichment on potential targets, and made a reasonable speculation on the mechanism of Codonopsis Radix in the treatment of IBS. Results Totally 17 candidate pharmacodynamic components, 111 predicted targets, and 1368 genes related to IBS were identified. 15 key components of irritable bowel syndrome. There were 55 potential targets, including IL6, PTGS2, AKT1, EGFR, IL2, IL10, IL4, etc.; the main functions involved in the targets were immune response, inflammatory response, etc., and the main enrichment pathways included TRAILA signaling pathway and TNF signaling
pathway. Conclusion Codonopsis Radix participates in the TRAIL signaling pathway, TNF signaling pathway, etc., and regulates the immune response through the regulation of inflammatory factors such as PTGS2, so as to achieve the purpose of treating IBS.
Keywords: Codonopsis Radix; irritable bowel syndrome; immune reaction; inflammatory factor; network pharmacology
黨參味甘,性平,有補中益氣、止渴、健脾益肺、養血生津功效。研究表明,黨參及其成方制劑可調理胃腸運動功能[1],但其整體作用機制尚不清楚。腸易激綜合征是一種臨床常見的胃腸功能性疾病,其發生與精神緊張、內臟高敏感性、胃腸激素和神經遞質分泌異常、腸道感染有關[2-5],而腸道高敏感性可能與腸道免疫狀態改變有關[6]。……

