兩種麻醉方法在支氣管鏡檢查中的麻醉效果比較
王瑩瑩 李瑞銳
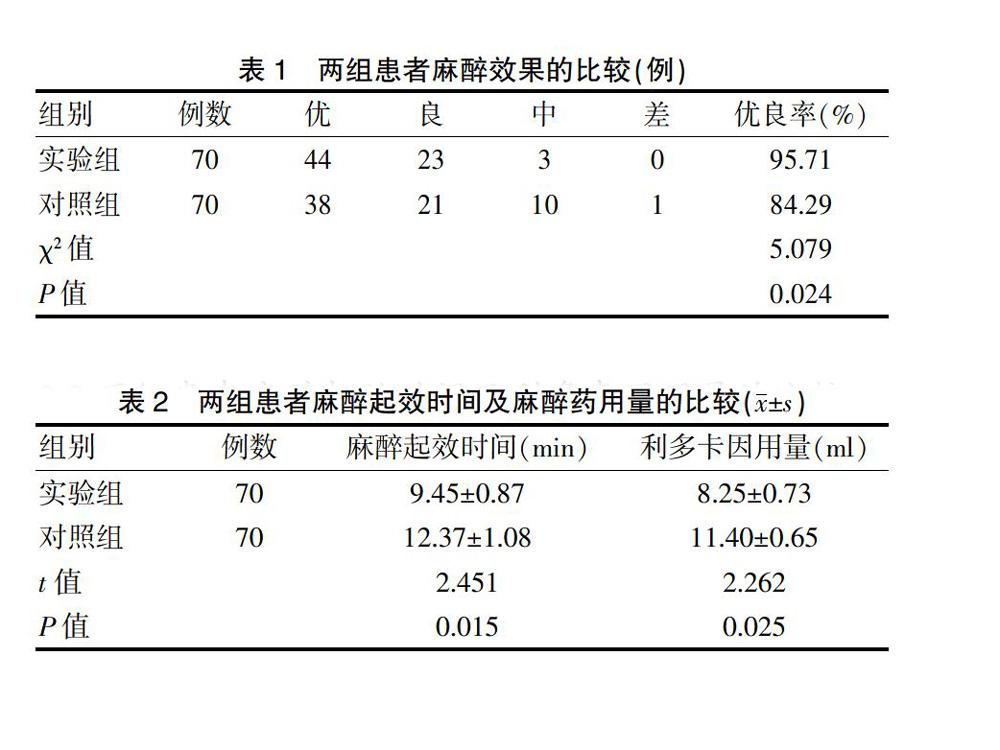
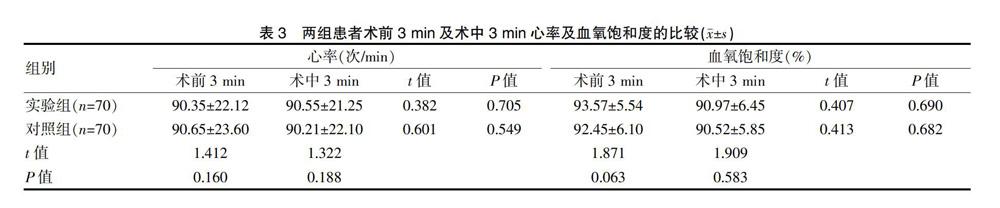
[摘要]目的 探討兩種不同麻醉方法在支氣管鏡檢查中的麻醉效果。方法 選取2017年6月~2018年6月在我院進行支氣管鏡檢查的140例患者作為研究對象,隨機分為實驗組和對照組,每組各70例。實驗組采用氧驅動利多卡因霧化吸入加利多卡因喉頭噴霧法,對照組采用氧驅動利多卡因霧化吸入加利多卡因鼻腔黏膜滴注法,比較兩組的麻醉效果優良率、麻醉起效時間和利多卡因用量的差異。結果 實驗組的麻醉效果優良率(95.71%)高于對照組(84.29%),差異有統計學意義(P<0.05);實驗組的麻醉起效時間短于對照組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05);實驗組利多卡因用量少于對照組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。兩組患者術前3 min及術中3 min的心率、血氧飽和度比較,差異均無統計學意義(P>0.05)。結論 氧驅動利多卡因霧化吸入加利多卡因喉頭噴霧法的效果優于利多卡因鼻腔黏膜滴注法。
[關鍵詞]支氣管鏡檢查;麻醉方法;利多卡因;喉頭噴霧
[中圖分類號] R614? ? ? ? ? [文獻標識碼] A? ? ? ? ? [文章編號] 1674-4721(2019)8(c)-0108-03
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the anesthetic effect of two different anesthesia methods in bronchoscopy. Methods A total of 140 patients who underwent bronchoscopy in our hospital from June 2017 to June 2018 were selected as the subjects. They were randomly divided into the experimental group and the control group, with 70 cases in each group. In the experimental group, patients were given oxygen-driven Lidocaine inhalation plus Lidocaine throat spray, and in the control group, patients were given oxygen-driven Lidocaine inhalation plus Lidocaine nasal mucosa dripping. The excellent and good rate, onset time of anesthesia, and dose of Lidocaine difference were compared in the two groups. Results The excellent and good rate of anesthesia in the experimental group was 95.71%, higher than that in the control group accounting for 84.29% (P<0.05). The onset time of the anesthesia in the experimental group was shorter than that in the control group with statistical significance (P<0.05). The dose of Lidocaine in the experimental group was less than that in the control group with a significant difference (P<0.05). There were no significant differences in heart rate and blood oxygen saturation between the two groups 3 min before surgery and 3 min after surgery (P>0.05). Conclusion Oxygen-driven Lidocaine aerosol inhalation plus Lidocaine throat spray is superior to Lidocaine nasal mucosal dripping.
[Key words] Bronchoscopy; Anesthesia methods; Lidocaine; Throat spray
隨著技術的快速發展,支氣管鏡成為臨床醫生診斷及治療呼吸系統疾病不可或缺的設備工具[1]。支氣管鏡檢查及治療操作由患者口鼻經喉進入呼吸道,在檢查過程中會出現惡心、咳嗽、憋氣等不良反應[2],因此,在做支氣管鏡檢查前,良好的麻醉效果是支氣管鏡檢查及治療能否順利進行的關鍵[3]。目前支氣管鏡檢查前的麻醉方法有很多,但不同麻醉方法的麻醉效果也存在較大差異。本研究為探尋一種較好的支氣管鏡檢查前麻醉方法,選取在我院進行支氣管鏡檢查的140例患者作為研究對象,對目前醫院常規開展的兩種支氣管檢查前麻醉方法的麻醉效果進行分析比較,現報道如下。
1資料與方法

