手衛(wèi)生干預(yù)在提高醫(yī)務(wù)人員手衛(wèi)生依從率中的效果觀察
李冷媚 宋小梅 朱鳳婉
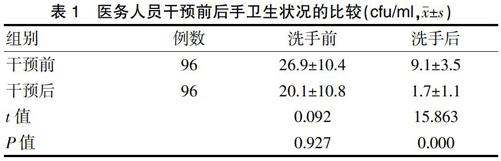
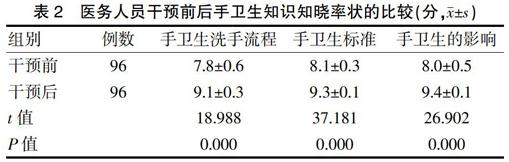
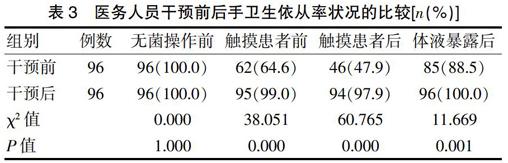
[摘要]目的 探討手衛(wèi)生干預(yù)在提高醫(yī)務(wù)人員手衛(wèi)生依從率中的應(yīng)用效果。方法 選取本院2017年1~11月多科室的96例醫(yī)務(wù)人員作為研究對象,對所有醫(yī)務(wù)人員手衛(wèi)生知識知曉率、手衛(wèi)生依從率、手衛(wèi)生實踐準確性狀況實施調(diào)查,調(diào)查后根據(jù)醫(yī)務(wù)人員實際手衛(wèi)生狀況實施干預(yù),分析實施干預(yù)后對醫(yī)務(wù)人員手衛(wèi)生狀況、知識知曉率、手衛(wèi)生依從率、手衛(wèi)生實踐準確性的影響。結(jié)果 干預(yù)后醫(yī)務(wù)人員洗手后菌落數(shù)[(1.7±1.1)cfu/ml]明顯低于干預(yù)前(9.1±3.5)cfu/ml],差異有統(tǒng)計學意義(P<0.05)。醫(yī)務(wù)人員干預(yù)后手衛(wèi)生知識知曉率評分、手衛(wèi)生依從率高于干預(yù)前,差異有統(tǒng)計學意義(P<0.05)。醫(yī)務(wù)人員干預(yù)后手衛(wèi)生實踐準確性(95.8%)高于干預(yù)前(41.7%),差異有統(tǒng)計學意義(P<0.05)。結(jié)論 實施手衛(wèi)生干預(yù)可改善醫(yī)務(wù)人員的手衛(wèi)生依從率狀況。
[關(guān)鍵詞]醫(yī)務(wù)人員;手衛(wèi)生;依從率;干預(yù);效果
[中圖分類號] R197.324 [文獻標識碼] A [文章編號] 1674-4721(2018)4(c)-0161-03
Effect observation of hand hygiene intervention in improvement of the hand hygiene compliance rate for medical staff
LI Leng-mei SONG Xiao-mei ZHU Feng-wan
Department of Laboratory,Hengli Hospital of Dongguan City in Guangdong Province,Dongguan 523460,China
[Abstract]Objective To explore the effect of hand hygiene intervention in improvement of hand hygiene compliance rate for medical staff.Methods Altogether 96 cases of medical personnel who worked in our hospital from January to November in 2017 were selected as the subjects.An investigation on medical personnel′s awareness of hand hygiene knowledge,hand hygiene compliance rate and practice accuracy was conducted.After investigation,intervention was given according to the actual situation of medical personnel′s hand hygiene.After implementation of the intervention,its effectiveness in actual hand hygiene situation,hand hygiene knowledge awareness rate,compliance rate and practice accuracy was analyzed for medical staff.Results The post-interventional number of colonies ([1.7±1.1] cfu/ml) after hand washing was significantly lower than that before the intervention ([9.1±3.5] cfu/ml),the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05).The post-interventional hand hygiene knowledge awareness rate score and hand hygiene compliance rate were significantly higher than those before intervention,the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05).The post-interventional hand hygiene practice accuracy of medical staff was 95.8%,significantly higher than that before the intervention (41.7%),the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05).Conclusion Hand hygiene intervention can improve the hand hygiene compliance rate of medical staff.
[Key words]Medical staff;Hand hygiene;Compliance rate;Intervention;Effect
醫(yī)院感染是目前患者院內(nèi)治療階段最為常見的并發(fā)癥,醫(yī)院感染的發(fā)生不僅增加患者治療的經(jīng)濟負擔及治療痛苦,還會影響患者疾病的治療效果,嚴重時將威脅患者的生命安全,影響患者的疾病預(yù)后[1]。積極預(yù)防醫(yī)院感染的發(fā)生是當前醫(yī)院管理中的重點問題。研究發(fā)現(xiàn)醫(yī)務(wù)人員手衛(wèi)生狀況是當前引起院內(nèi)感染的重要因素,因此不斷加強醫(yī)務(wù)人員手衛(wèi)生管理效果是當前醫(yī)院預(yù)防院內(nèi)感染的重要方式[2]。醫(yī)務(wù)人員手衛(wèi)生管理已經(jīng)逐漸成為目前醫(yī)院管理的重點內(nèi)容。但本院在醫(yī)院管理實踐中發(fā)現(xiàn)醫(yī)務(wù)人員手衛(wèi)生依從率狀況較差,直接影響了手衛(wèi)生管理效果。尋求有效的干預(yù)手段,不斷提高醫(yī)務(wù)人員手衛(wèi)生依從率是當前手衛(wèi)生管理中的重點關(guān)注問題。本院在臨床實踐中總結(jié)出手衛(wèi)生干預(yù)方案,在臨床實踐過程中取得了良好效果,現(xiàn)報道如下。……

