腹腔鏡治療急性闌尾炎的臨床效果
林俊雙
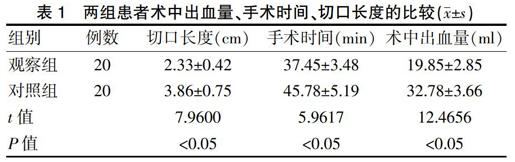
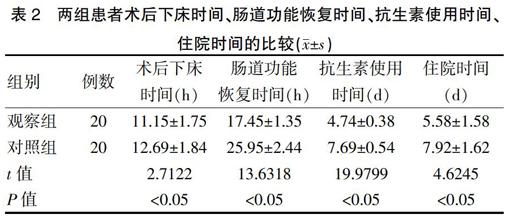
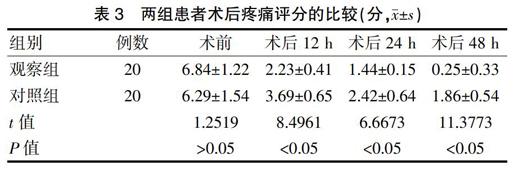
[摘要]目的 探索腹腔鏡治療急性闌尾炎的臨床效果。方法 選取2015年6月~2017年12月我院收治的40例急性闌尾炎患者,采用信封法將患者隨機分為兩組,每組各20例。對照組患者行小切口手術(shù)治療,觀察組患者行腹腔鏡手術(shù)治療,比較兩組的臨床效果。結(jié)果 觀察組患者手術(shù)時間、腸道功能恢復(fù)時間、術(shù)后下床時間、住院時間、抗生素使用時間、切口長度均短于對照組(P<0.05),術(shù)中出血量少于對照組(P<0.05),術(shù)后12、24、48 h疼痛評分、并發(fā)癥發(fā)生率均低于對照組,差異均有統(tǒng)計學(xué)意義(P<0.05)。結(jié)論 對急性闌尾炎患者行腹腔鏡手術(shù)治療效果顯著,且安全性更高。
[關(guān)鍵詞]腹腔鏡;急性闌尾炎;效果
[中圖分類號] R656.8 [文獻標(biāo)識碼] A [文章編號] 1674-4721(2018)4(c)-0036-03
Clinical efficacy of laparoscopy in the treatment of acute appendicitis
LIN Jun-shuang
Department of General Surgery,People′s Hospital of Yunan County,Guangdong Province,Yu′nan 527199,China
[Abstract]Objective To explore the clinical effect of laparoscopy in the treatment of acute appendicitis.Methods A total of 40 patients with acute appendicitis in our hospital from June 2015 to December 2017 were enrolled.They were evenly and randomly divided into two groups by the envelope method,20 cases in each group.In the control group,surgery with a small incision was used,while in the observation group,laparoscopic surgery was adopted.Results The operative time,intestinal function recovery time,postoperative bed-out time,hospital stay,antibiotic use time and incision length in the observation group were all shorter than those of the control group(P<0.05).The intraoperative blood loss was lesser than that of the control group (P<0.05).The pain scores 12,24,and 48 hour after surgery were lower than those in the control group (P<0.05).The incidence of complications was also lower than that in the control group,the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05).Conclusion Laparoscopic surgery for patients with acute appendicitis is effective in high safety.
[Key words]Laparoscope;Acute appendicitis;Effect
急性闌尾炎為臨床常見病,具有發(fā)生率高、發(fā)病急等特點,于1886年首先命名,其發(fā)病率高達6%,目前常實施手術(shù)治療[1]。由于早期手術(shù)技術(shù)和器械設(shè)備有限,常行傳統(tǒng)開腹手術(shù),雖能行病變組織切除,但具有較大的創(chuàng)傷性,且不利于術(shù)后恢復(fù),近年來廣泛推廣腹腔鏡手術(shù)和小切口手術(shù),且均具有微創(chuàng)性,但相比之下,腹腔鏡手術(shù)能夠在影像技術(shù)引導(dǎo)下,完成手術(shù)治療,保證了手術(shù)的安全性,減輕對周圍組織的損傷,且能夠避免腸梗阻、腸粘連、切口感染的發(fā)生[2]。本文旨在探索不同手術(shù)方式在急性闌尾炎患者中的價值,現(xiàn)報道如下。
1資料與方法
1.1一般資料
選取我院2015年6月~2017年12月收治的40例闌尾炎患者,采用信封法將其隨機分為兩組,每組各20例。入選標(biāo)準(zhǔn):①患者臨床資料均齊全;②患者均有手術(shù)適應(yīng)證;③經(jīng)CT、MRI、X線檢查,均確診為急性闌尾炎;④患者均無嚴重心功能不全;⑤患者均未合并心力衰竭;⑥患者均無相關(guān)手術(shù)史。觀察組男11例,女9例;平均年齡(42.85±3.19)歲;……

