支氣管擴張癥狀與纖維支氣管鏡治療的關系
潘振雷
【摘要】 目的:研究支氣管擴張合并感染經纖維支氣管鏡注藥治療的效果。方法:選擇2015年7月-2016年6月本院收治的支氣管擴張伴感染的患者120例,隨機分成研究組與對照組,每組各60例。對照組采用常規抗感染治療,研究組在對照組的基礎上經纖維支氣管鏡注入敏感抗生素進行治療。使用酶聯免疫吸附法(ELISA法)測定及比較兩組患者hs-CRP的濃度,比較兩組患者體溫恢復正常的時間、治療前及治療第13天的PaO2與PaCO2血氣水平,觀察兩組臨床療效及不良反應。結果:研究組體溫恢復時間為(3.5±1.3)d,顯著低于對照組的(6.1±1.7)d,兩組比較差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。治療13 d后,研究組hs-CRP水平低于對照組,兩組比較差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。研究組患者PaO2水平高于對照組, PaCO2水平低于對照組,兩組比較差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。研究組治療總有效率為98.3%,高于對照組的81.7%,兩組比較差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。研究組不良反應發生率為3.3%低于對照組的11.7%,兩組比較差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。結論:經纖維支氣管鏡注藥治療支氣管擴張合并感染效果顯著,能有效促進體溫恢復,降低炎癥水平,改善血氣水平,不良反應少,值得應用及推廣。
【關鍵詞】 支氣管擴張; 感染; 纖維支氣管鏡; 注藥治療
The Relationship between the Symptoms of Bronchial Dilation and the Treatment of Fibrous Bronchoscopy/PAN Zhen-lei.//Medical Innovation of China,2016,13(31):035-038
【Abstract】 Objective:To analyze the effect of fiberoptic bronchoscopy alveolar lavage on the treatment of bronchiectasis with infection.Method:120 patients with bronchiectasis combined infection in our hospital were chosen as research objects,they were randomly divided into control group with conventional treatment and study group with fiberoptic bronchoscopy alveolar lavage,60 cases in each group.The clinical symptoms time,serum hs-CRP levels,blood gas levels,the patients body temperature returned to normal,clinical efficacy and adverse reactions of two groups were compared.Result:The relieved time of fever symptom in study group was (3.5±1.3)d significantly shorter than that of control group with (6.1±1.7)d,the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05).After 13 days treatment,the patients serum hs-CRP levels in study group was significantly lower than that of control group,the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05).In study group,the patients PaO2 level was higher than control group, while PaCO2 level was lower than control group,the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05).The total effective rate of the study group was 98.3% higher than that of control group with 81.7%,the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05).The incidence of adverse reaction in study group was 3.3% lower than that of control group with 11.7%,the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05).Conclusion:The effect of injecting medicine through the fiber bronchoscopy in the treatment of bronchial dilatation and infection is significant,can effectively promote the recovery of body temperature, reduce the level of inflammation, improve blood gas levels and less adverse reactions,it is worthy of application and promotion.endprint
【Key words】 Bronchial dilation; Infection; Bronchoscopy; Drug injection therapy
First-authors address:The Third Peoples Hospital of Hechi City,Hechi 547000,China
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-4985.2016.31.010
支氣管擴張癥屬于臨床一種較為常見的慢性支氣管化膿性疾病,此類疾病往往是呼吸道感染與支氣管阻塞的繼發病[1]。合并感染則是支氣管擴張比較常見的一種并發癥。隨著疾病病程的快速進展,患者支氣管中的纖毛運動能力難免會受到損傷,且肺部功能減弱,自主排痰能力逐漸降低,致使分泌物在患者肺部不斷積聚,進而誘發局部或者全身性感染,產生嚴重的通氣換氣方面的功能障礙[2-4]。對于支氣管擴張合并感染患者使用全身廣譜抗生素治療,往往收效甚微[5-6]。近年來,經纖維支氣管鏡注入敏感抗生素治療此類患者日益受到人們的關注。本文則系統評價經纖維支氣管鏡注入敏感抗生素在支氣管擴張伴感染中的應用效果,現總結報告如下。
1 資料與方法
1.1 一般資料 選擇2015年7月-2016年6月本院收治的支氣管擴張伴感染的患者120例,其中年齡33~76歲,平均(58.4±2.3)歲;痰量30~200 mL,平均(143.5±21.3)mL;病程2~21年,平均(12.3±2.4)年。入選病例經CT檢查證實為支氣管擴張癥,均為意識清醒者,排除存在嚴重的心與腦等重大器官疾病者。隨機分成研究組與對照組,每組各60例,兩組的一般資料比較差異均無統計學意義(P>0.05)。
1.2 方法 對照組采用常規抗感染治療,即祛痰、止血、營養支持及體外抗生素控制感染等。研究組在對照組的基礎上經纖維支氣管鏡注入敏感抗生素進行治療,即采用奧林巴斯BF-260電子支氣管鏡(西安明克斯檢測設備有限公司,中國,西安)及其配套附件對患者的病變部位進行檢查、支氣管沖洗、吸痰,選取標本行細菌培養及藥敏性試驗,結合細菌培養結果,合理選擇敏感抗生素,通過纖維支氣管鏡慢慢地滴入患者的病灶,敏感抗生素使用劑量為5 mL/次,每4天給予1次治療。
1.3 觀察指標 (1)兩組患者體溫恢復正常的時間。(2)比較兩組治療前、治療后第1、5、9、13天的血清hs-CRP水平變化,在上述不同時間點抽取患者空腹靜脈血2 mL,離線分離血清置于冰箱備用。采用酶聯免疫吸附法(ELISA法)測定患者hs-CRP的濃度,操作步驟分別按照人hs-CRP ELISA檢測試劑盒(上海基免實業有限公司,中國,上海)說明書實施操作。(3)兩組治療前、治療第9天的PaO2、PaCO2血氣水平。(4)兩組臨床療效:①治愈:患者臨床癥狀消失,經肺部CT復查顯示為全部吸收或者只遺留少許纖維化索條陰影;②好轉:患者臨床癥狀消失,經肺部CT復查顯示吸收小于50%;③無效:患者臨床癥狀沒有改善、肺部CT顯示也沒有變化或者惡化。總有效=治愈+好轉。(5)比較兩組的不良反應。
1.4 統計學處理 使用SPSS 20.0統計軟件進行分析,計量資料采用(x±s)表示,比較采用t檢驗,計數資料采用 字2檢驗,以P<0.05為差異有統計學意義。
2 結果
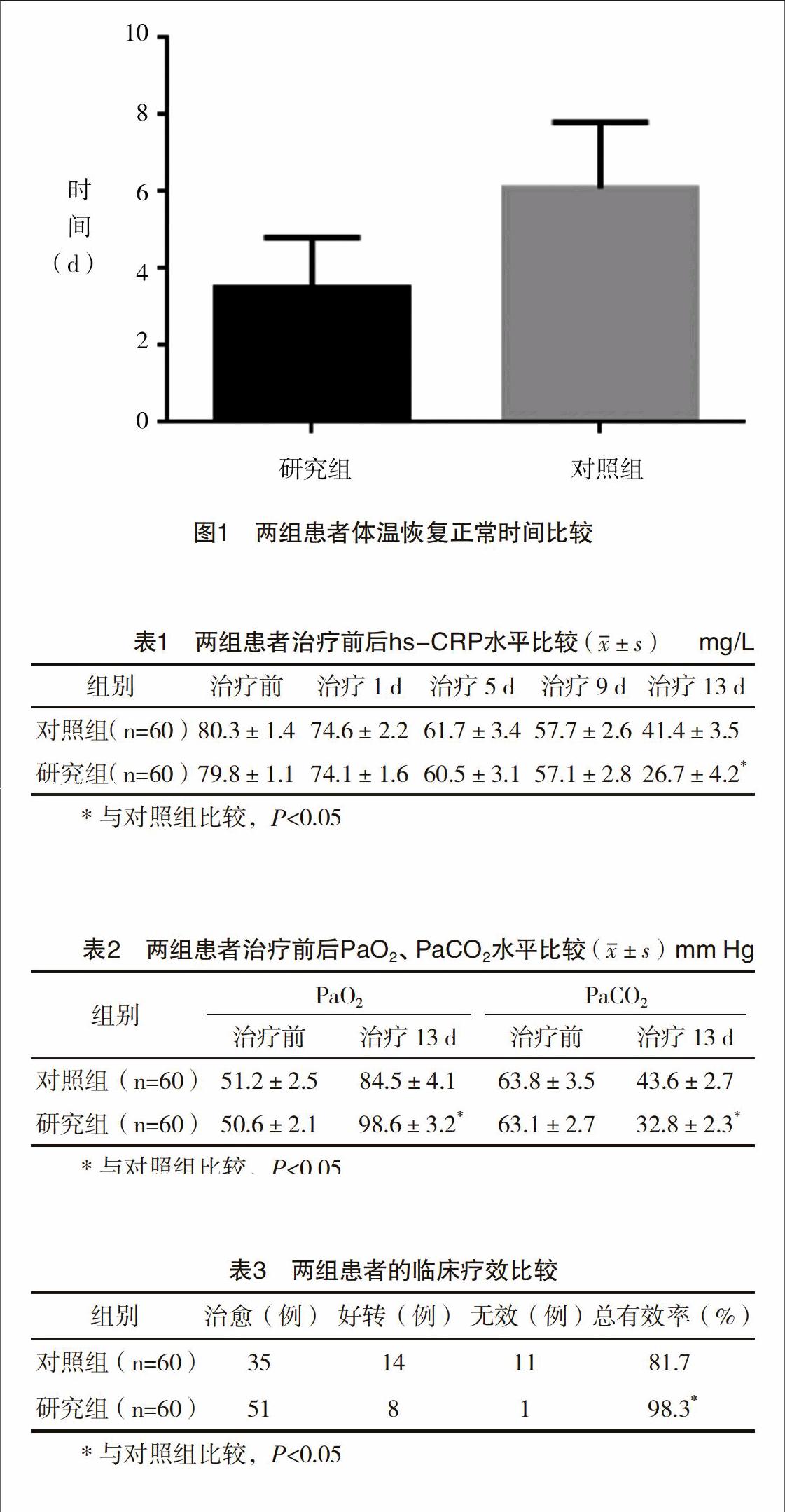
2.1 兩組患者體溫恢復正常時間比較 研究組體溫恢復時間為(3.5±1.3)d,顯著低于對照組體溫恢復時間(6.1±1.7)d,兩組比較差異有統計學意義(P<0.05),見圖1。
2.2 兩組患者治療前后hs-CRP水平比較 治療過程中,研究組與對照組hs-CRP 水平呈逐漸下降的趨勢;治療13 d后,研究組hs-CRP水平低于對照組,兩組比較差異有統計學意義(P<0.05),見表1。
2.3 兩組患者的血氣指標比較 治療前兩組PaO2、PaCO2血氣指標比較差異無統計學意義(P>0.05);治療13 d后,研究組患者PaO2水平高于對照組,PaCO2水平低于對照組,兩組比較差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05),見表2。
2.4 兩組患者的臨床療效比較 治療13 d后,研究組治療總有效率為98.3%,高于對照組的81.7%,兩組比較差異有統計學意義(P<0.05),見表3。
2.5 兩組患者的不良反應比較 研究組胸悶、呼吸困難等不良反應發生率低于對照組,兩組比較差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。兩組均未出現嚴重的呼吸衰竭、感染加重、猝死與大出血等并發癥,見表4。
3 討論
支氣管擴張癥屬于比較常見的氣道破壞性疾病,人體氣道管壁結構遭到破壞及纖毛功能受到損傷,則肺炎桿菌、銅綠假單胞菌與腸桿菌等致病菌比較容易定植于氣道[7-9],引發反復性呼吸道感染,甚至發生咯血[10-12]。本研究顯示,研究組中的60份標本,查出銅綠假單胞菌,肺炎克雷伯菌、鮑氏不動桿菌、大腸埃希菌、白色念珠菌54株,并以混合感染為主。
因為支氣管擴張大部分發生于下葉,特別是左下葉的支氣管受到心臟及血管的壓迫,導致支氣管中的分泌物引流受阻,不易排出,易致病原菌定植在患者的下呼吸道中,進而繼發肺部感染。支氣管擴張合并感染常出現全身性的炎癥反應,如果只憑借經驗對患者實施全身用藥,則很難獲得藥物有效的濃度,與此同時人體支氣管黏膜出現充血及水腫,又會進一步使得感染很難得到控制[13-16]。單純進行全身用藥在臨床中也出現療程長及治療成本比較高等弊端,所以臨床應用受到一定的限制[17]。
纖維支氣管鏡是近年來新興起來的一種治療呼吸系統疾病的手段,經纖維支氣管鏡注藥治療是通過灌洗方式將支氣管腔中的分泌物沖洗掉,然后根據樣本篩選出來的病原菌特性,局部注入對應的敏感抗生素,這樣藥物能夠直接到達人體病變部位,且有效藥物濃度比較高,故可以將病原菌直接殺死[18-20]。本研究顯示,研究組體溫恢復時間為(3.5±1.3)d,顯著低于對照組體溫恢復時間(6.1±1.7)d,兩組比較差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。研究組治療總有效率為98.3%,高于對照組的81.7%,兩組比較差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。研究組不良反應發生率3.3%低于對照組11.7%,兩組比較差異有統計學意義(P<0.05),且兩組均未出現嚴重的呼吸衰竭、感染加重、猝死與大出血等并發癥。說明經纖維支氣管鏡注藥治療可以促進支氣管擴張合并感染患者體溫盡快恢復正常,不良反應少,安全可靠。endprint
hs-CRP則可以比較好地反應患者全身狀態變化,其含量高低跟患者病情的炎癥程度呈正相關,其濃度越高,則病情炎癥程度越厲害。本研究表明,經治療后,研究組hs-CRP水平低于對照組,兩組比較差異有統計學意義(P<0.05),說明經纖維支氣管鏡注藥治療能夠降低局部與全身性炎癥反應,可有效緩解患者臨床癥狀。本研究發現,經治療后研究組患者PaO2水平高于對照組,PaCO2水平低于對照組,兩組比較差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05)。由此可見,經纖維支氣管鏡注藥治療能夠在直視條件下有效引流氣道中的痰液,通暢氣道,緩解呼吸困難、低氧與二氧化碳潴留等臨床癥狀,有效改善患者血氣水平。
綜上所述,經纖維支氣管鏡注藥治療支氣管擴張合并感染效果顯著,能有效促進體溫恢復,降低炎癥水平,改善血氣水平,不良反應少,值得應用及推廣。
參考文獻
[1] Sly P D,Gangell C L,Chen L,et al.Risk factors for bronchiectasis in children with cystic fibrosis[J].New England Journal of Medicine,2013,368(21):1963-1970.
[2] Gould C M,Freeman A F,Olivier K N.Genetic causes of bronchiectasis [J].Clinics in Chest Medicine,2012,33(2):249-263.
[3] Shoemark A,Ozerovitch L,Wilson R.Aetiology in adult patients with bronchiectasis[J].Respiratory Medicine,2007,101(6):1163-1170.
[4] Wills P,Greenstone M.Inhaled hyperosmolar agents for bronchiectasis[J].Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews,2014,5(5):367-371.
[5] Feldman C.Bronchiectasis: new approaches to diagnosis and management[J].Clinics in Chest Medicine,2011,32(3):535-546.
[6] Hill S L,Morrison H M,Burnett D,et al.Short term response of patients with bronchiectasis to treatment with amoxycillin given in standard or high doses orally or by inhalation[J].Thorax,2012,41(7):559-565.
[7] Menzies D,Holmes L,Mccumesky G,et al.Aspergillus sensitization is associated with airflow limitation and bronchiectasis in severe asthma[J].Allergy,2011,66(5):679-685.
[8] Griffith D E,Aksamit T R.Bronchiectasis and nontuberculous mycobacterial disease[J].Clinics in Chest Medicine,2012,33(33):283-295.
[9] Nicolson C H,Stirling R G,Borg B M,et al.The long term effect of inhaled hypertonic saline 6% in non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis[J].Respiratory Medicine,2012,106(5):661-667.
[10] Geraci G,Pisello F,Sciumè C,et al.Complication of flexible fiberoptic bronchoscopy literature review[J].Annali Italiani Di Chirurgia,2007,78(3):183-192.
[11] Umutoglu T,Gedik A H,Bakan M,et al.The influence of airway supporting maneuvers on glottis view in pediatric fiberoptic bronchoscopy[J].Brazilian Journal of Anesthesiology,2015,23(5):313-318.
[12] Hadique S,Jain P.Safety of bronchoscopy in elderly[J].Current Geriatrics Reports,2015,4(2):154-165.
[13] Chalumeaulemoine L,Stoclin A,Billard V,et al.Flexible fiberoptic bronchoscopy and remifentanil target-controlled infusion in icu:a preliminary study[J].Intensive Care Medicine,2013,39(1):53-58.endprint
[14] ?pi?ek M,Jasna.Flexible fiberoptic bronchoscopy[J].Clinical Privilege White Paper,2012,56(20):1-14.
[15] Taha A S.Diagnosis of ruptured pulmonary hydatid cyst by means of flexible fiberoptic bronchoscopy: a report of three cases[J].Journal of Thoracic & Cardiovascular Surgery,2005,130(4):1196-1197.
[16] Campos J H.Update on tracheobronchial anatomy and flexible fiberoptic bronchoscopy in thoracic anesthesia[J].Current Opinion in Anaesthesiology,2009,22(1):4-10.
[17] Shin J A,Chang Y S,Kim T H,et al.Fiberoptic bronchoscopy for the rapid diagnosis of smear-negative pulmonary tuberculosis[J].Bmc Infectious Diseases,2012,12(26):141.
[18] Khan M H.Role of flexible fiberoptic bronchoscopy in suspected sputum smear negative pulmonary tuberculosis cases at microscopy centre under rntcp[J].International Journal of Medical Science & Public Health,2014,3(1):31-34.
[19] Mark Z,Bajzik G,Nagy A,et al.Comparison of virtual and fiberoptic bronchoscopy in the management of airway stenosis[J].Pathology & Oncology Research,2008,14(14):313-319.
[20] Elizondo E,Navarro F,Pérez-Romo A,et al.Endotracheal intubation with flexible fiberoptic bronchoscopy in patients with abnormal anatomic conditions of the head and neck[J].Ear Nose & Throat Journal,2007,86(11):682-684.
(收稿日期:2016-07-18) (本文編輯:周亞杰)endprint

